Article
Astrocyte elevated gene‑1 regulates osteosarcoma cell invasion and chemoresistance via endothelin‑1/endothelin A receptor signaling
- Authors:
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Department of Orthopaedics, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, P.R. China
-
Pages:
505-510
|
Published online on:
December 3, 2012
https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2012.1056
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
Astrocyte elevated gene‑1 (AEG‑1) and endothelin‑1 (ET‑1)/endothelin A receptor (ETAR) signaling have been demonstrated to be important in osteosarcoma (OS) progression. In the present study, we explored the interaction between AEG‑1 and ET‑1/ETAR signaling in OS cells, and investigated the mechanism(s) through which the functional interaction may impact OS cell invasion and chemoresistance. Overexpression and knockdown of AEG‑1 were performed in Saos‑2 and MG‑63 OS cells, respectively. Overexpression of AEG‑1 in Saos‑2 cells significantly increased ET‑1 expression (at both the mRNA and protein levels), cell invasion, MMP‑2 expression and cell survival against cisplatin. These effects were eradicated using a selective phosphatidylinositol 3‑kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, LY294002, or a selective ETAR inhibitor, BQ123. Knockdown of AEG‑1 in MG‑63 cells significantly decreased ET‑1 expression (at both the mRNA and protein levels), cell invasion, MMP‑2 expression and cell survival against cisplatin. Exogenous ET‑1 restored cell invasion and MMP‑2 expression levels in MG‑63 cells, in which AEG‑1 had been knocked down, in the presence of LY294002, but not in the presence of BQ123. However, exogenous ET‑1 only partially rescued cell survival against cisplatin-induced apoptosis in the presence of LY294002, in cells in which AEG‑1 had been knocked down. In conclusion, we have demonstrated that AEG‑1 regulates ET‑1 expression at the transcriptional level in a PI3K-dependent manner in OS cells. Downstream of PI3K, ET‑1/ETAR signaling primarily mediates the promoting effect of AEG‑1 on OS cell invasion, likely through the upregulation of MMP‑2 expression, thus, ET‑1/ETAR signaling partially, but significantly, mediates the AEG‑1‑induced chemoresistance in OS cells. To the best of our knowledge, this study has provided the first evidence of a functional association between AEG‑1 and ET‑1/ETAR signaling in OS cells, which adds novel insights into the molecular mechanism of OS metastasis and chemoresistance.
View Figures |
Figure 1
|
 |
Figure 2
|
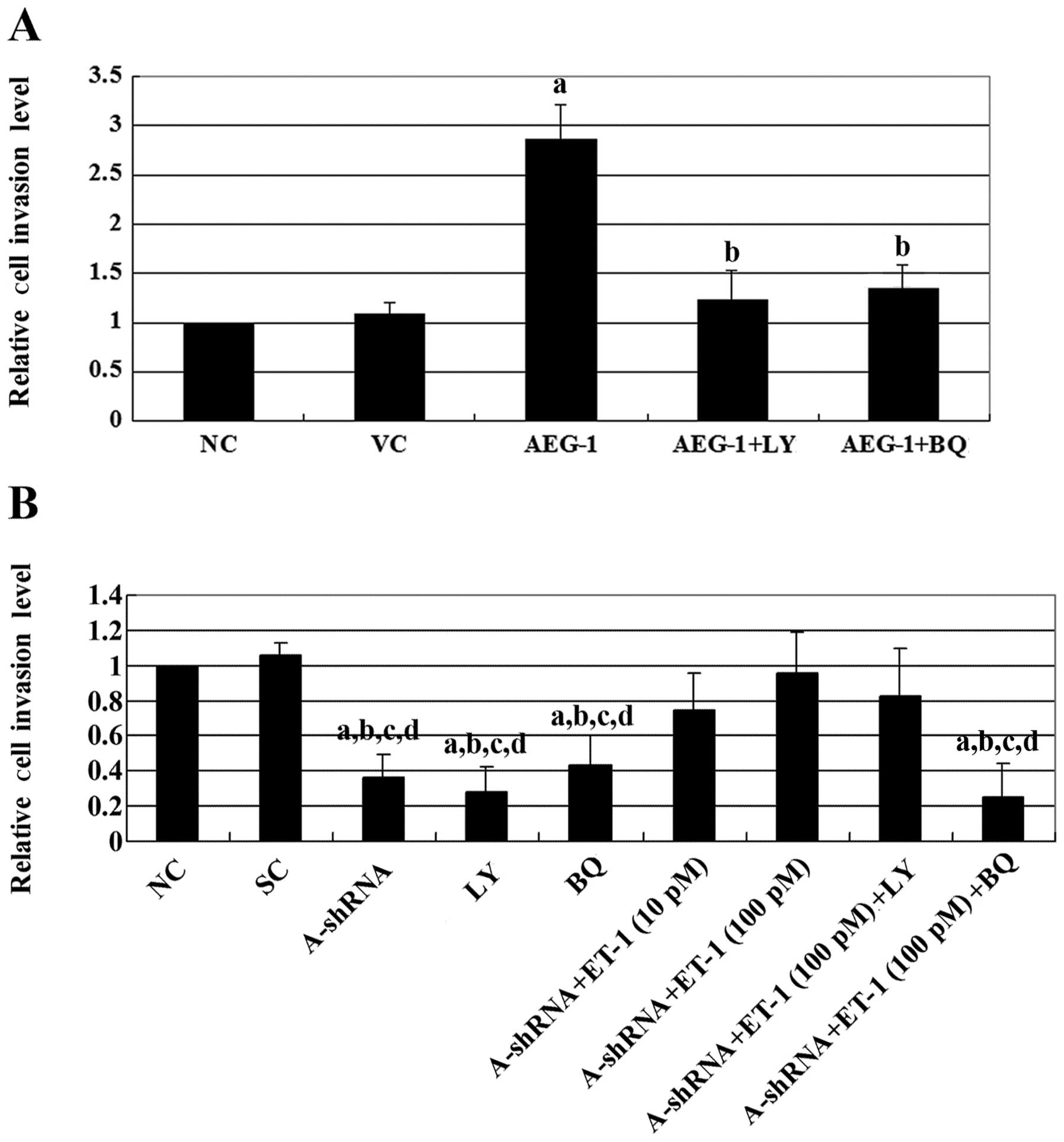 |
Figure 3
|
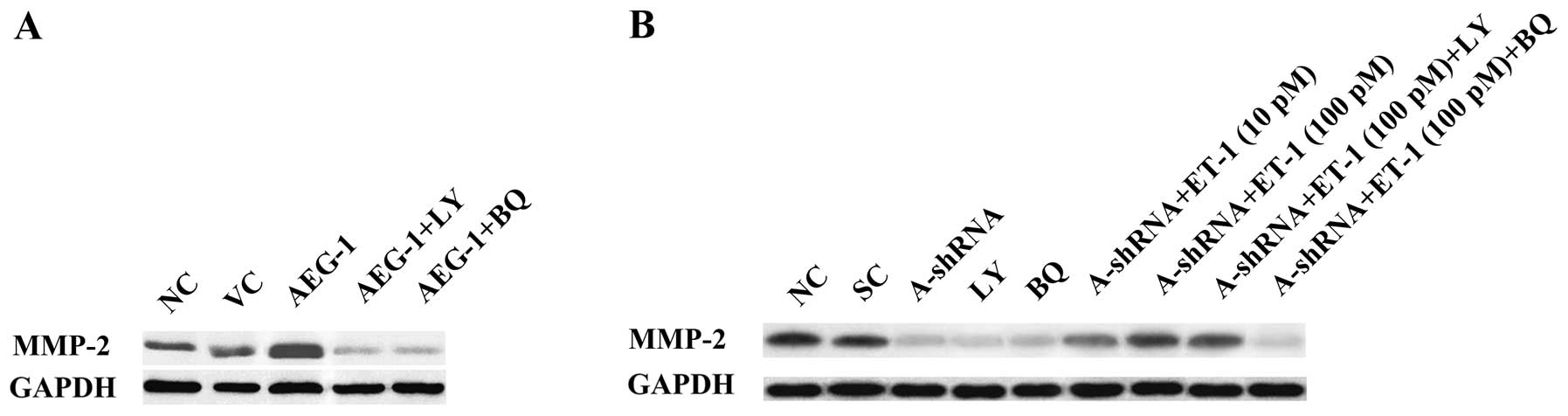 |
Figure 4
|
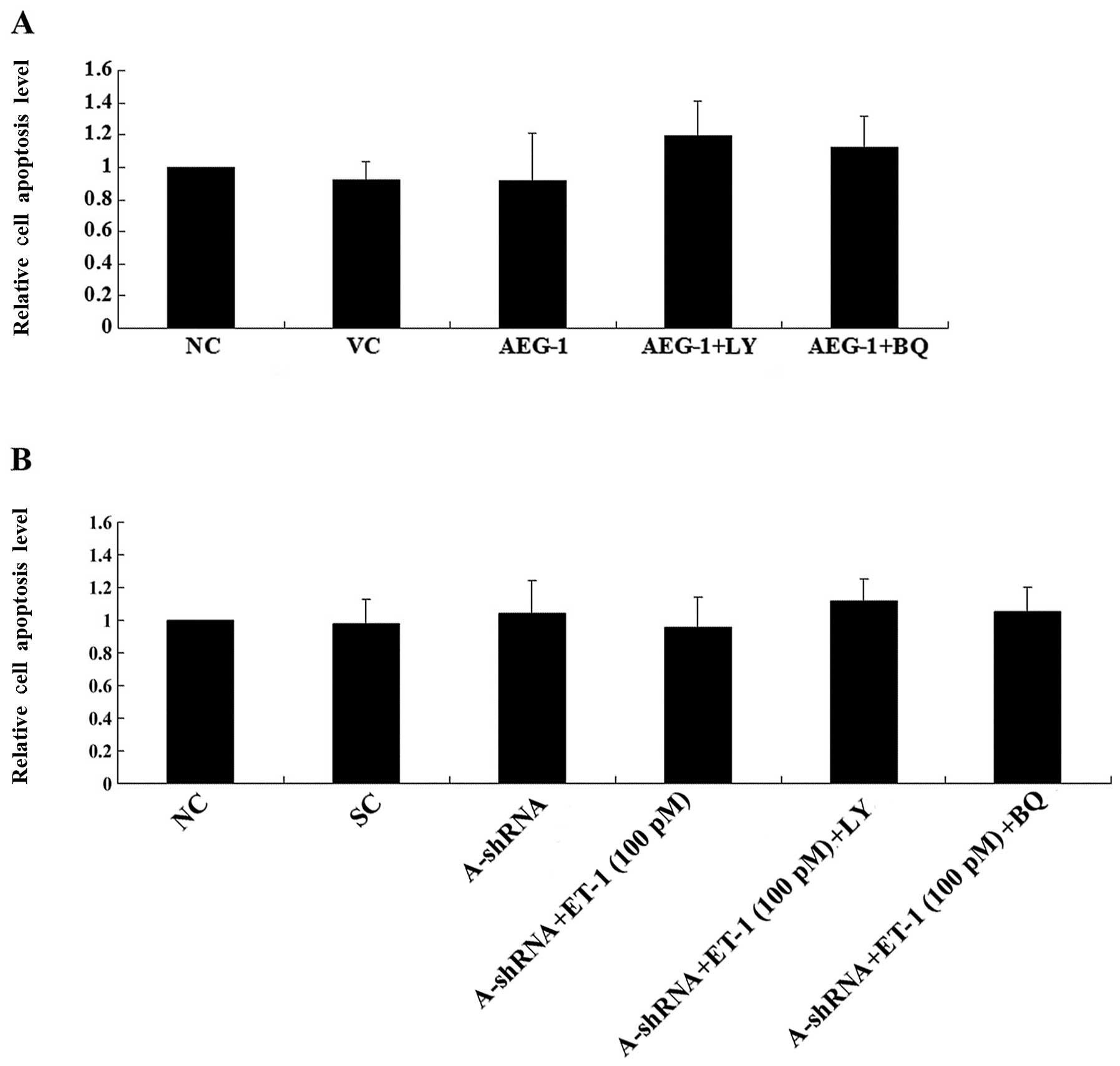 |
Figure 5
|
 |
Figure 6
|
View References
|
1.
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Gorlick R, Anderson P, Andrulis I, et al:
Biology of childhood osteogenic sarcoma and potential targets for
therapeutic development: meeting summary. Clin Cancer Res.
9:5442–5453. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Wittig JC, Bickels J, Priebat D, et al:
Osteosarcoma: a multi-disciplinary approach to diagnosis and
treatment. Am Fam Physician. 65:1123–1132. 2002.
|
|
4.
|
Su ZZ, Chen Y, Kang DC, Chao W, Simm M,
Volsky DJ and Fisher PB: Customized rapid subtraction hybridization
(RaSH) gene microarrays identify overlapping expression changes in
human fetal astrocytes resulting from human immunodeficiency
virus-1 infection or tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment. Gene.
30:67–78. 2003.
|
|
5.
|
Liao WT, Guo L, Zhong Y, Wu YH, Li J and
Song LB: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a marker for
aggressive salivary gland carcinoma. J Transl Med. 9:2052011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Sarkar D and
Fisher PB: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a target gene of
oncogenic Ha-ras requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Myc.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103:17390–17395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wang F, Ke ZF, Sun SJ, et al: Oncogenic
roles of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) in osteosarcoma
progression and prognosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:539–548. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Nelson J, Bagnato A, Battistini B and
Nisen P: The endothelin axis: emerging role in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:110–116. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Felx M, Guyot MC, Isler M, et al:
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) promotes MMP-2 and MMP-9 induction involving
the transcription factor NF-κB in human osteosarcoma. Clin Sci
(Lond). 110:645–654. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Zhao Y, Liao Q, Zhu Y and Long H:
Endothelin-1 promotes osteosarcoma cell invasion and survival
against cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
469:3190–3199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Yoo BK, Chen D, Su ZZ, et al: Molecular
mechanism of chemoresistance by astrocyte elevated gene-1. Cancer
Res. 70:3249–3258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Rosanò L, Cianfrocca R, Spinella F, et al:
Acquisition of chemoresistance and EMT phenotype is linked with
activation of the endothelin A receptor pathway in ovarian
carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2350–2360. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Ying Z, Li J and Li M: Astrocyte elevated
gene 1: biological functions and molecular mechanism in cancer and
beyond. Cell Biosci. 1:362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Yoo BK, Emdad L, Lee SG, et al: Astrocyte
elevated gene-1 (AEG-1): a multifunctional regulator of normal and
abnormal physiology. Pharmacol Ther. 130:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhang F, Yang Q, Meng F, Shi H, Li H,
Liang Y and Han A: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 interacts with
β-catenin and increases migration and invasion of colorectal
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. Mar 16–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Sun P, Xiong H, Kim TH, Ren B and Zhang Z:
Positive inter-regulation between β-catenin/T cell factor-4
signaling and endothelin-1 signaling potentiates proliferation and
survival of prostate cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 69:520–531.
2006.
|
|
17.
|
Rosenberg B, VanCamp L, Trosko JE, et al:
Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents.
Nature. 222:385–386. 1969. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|




















