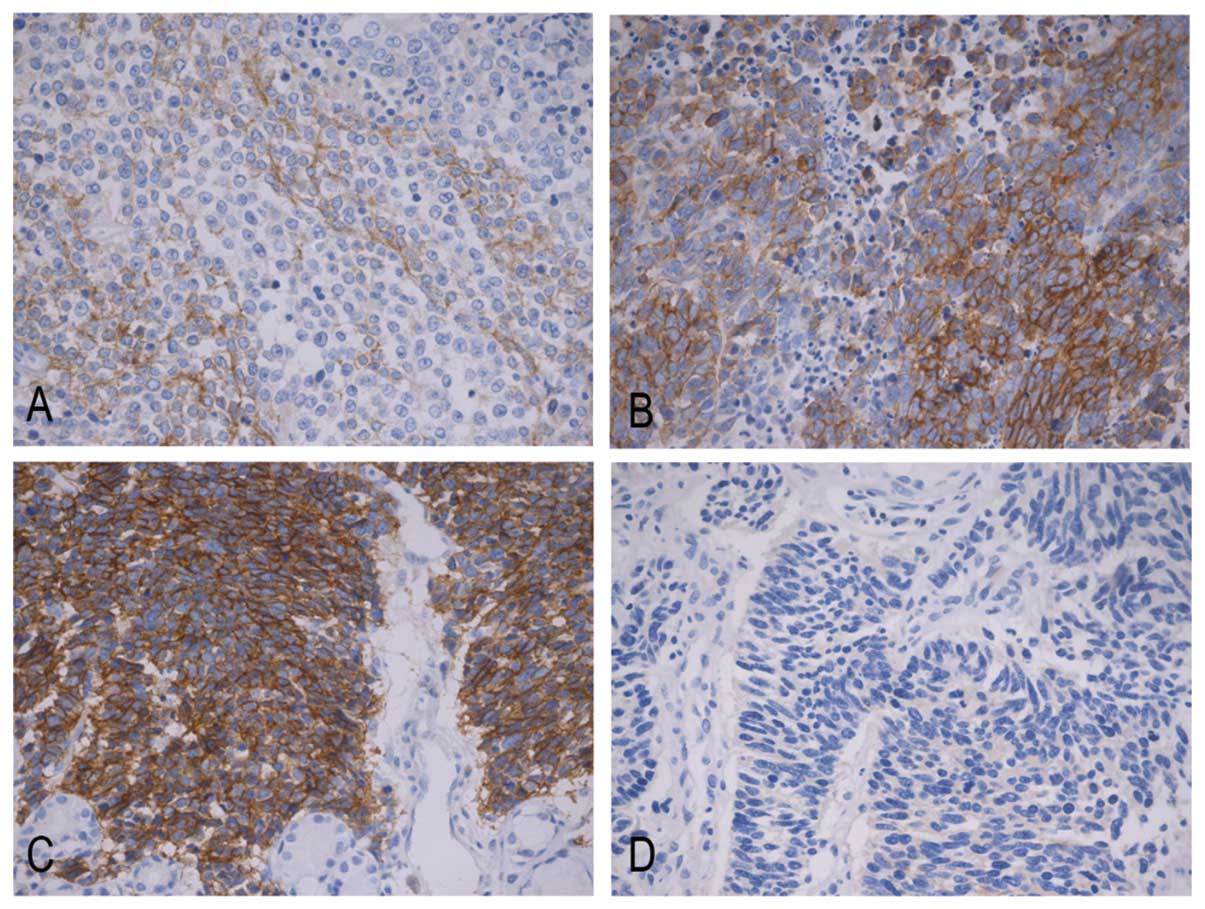
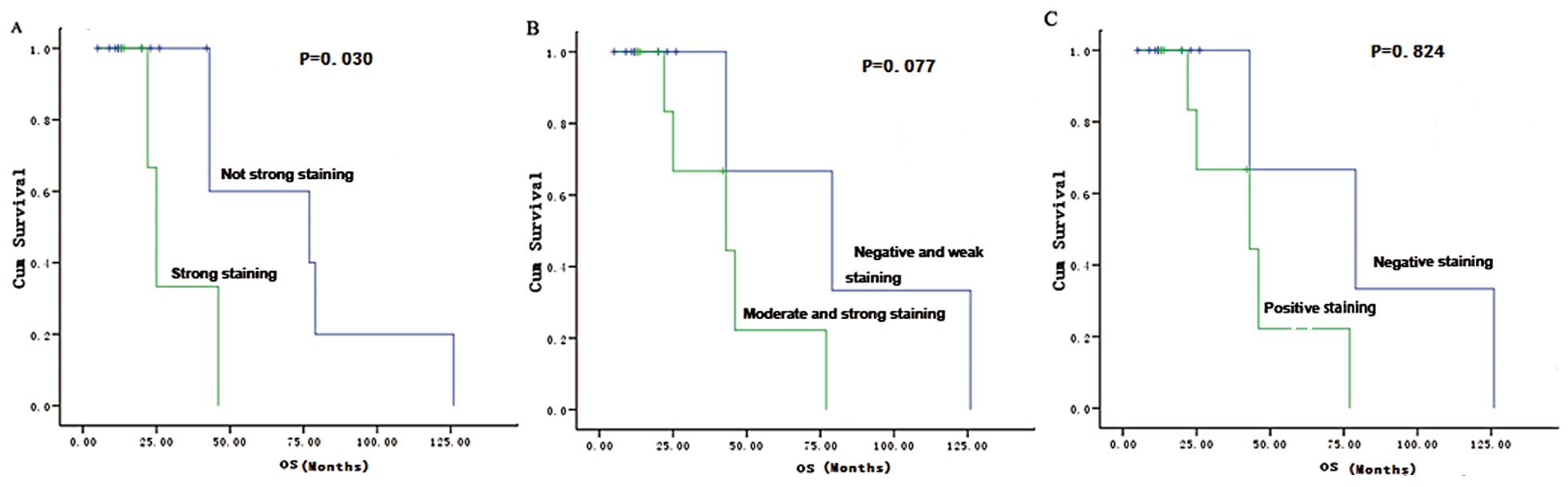
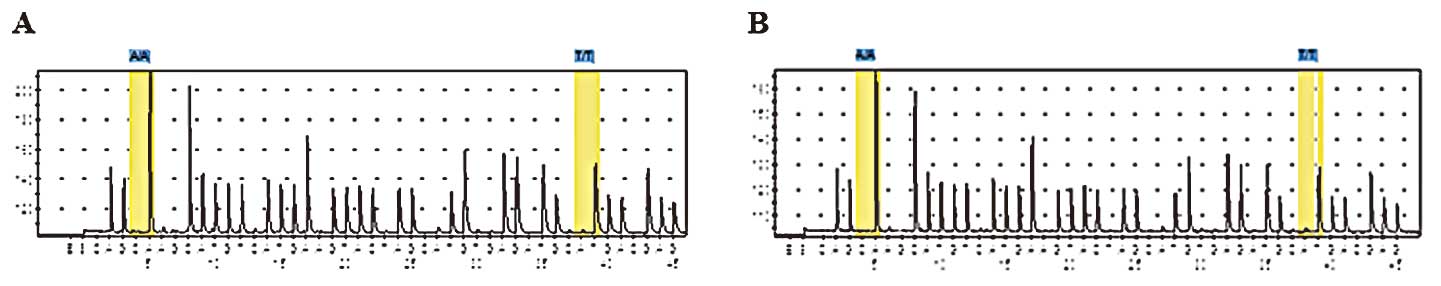
|
1
|
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al:
Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United
States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance,
epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol.
24:4539–4544. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rygaard K, Nakamura T and Spang-Thomsen M:
Expression of the proto-oncogenes c-met and c-kit and their
ligands, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and stem cell
factor, in SCLC cell lines and xenografts. Br J Cancer. 67:37–46.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cirocchi R, Farinella E, La Mura F, et al:
Efficacy of surgery and imatinib mesylate in the treatment of
advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a systematic review.
Tumori. 96:392–399. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reichardt P: Optimal use of targeted
agents for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Oncology.
78:130–40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnson BE, Fischer T, Fischer B, et al:
Phase II study of imatinib in patients with small cell lung cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:5880–5887. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schneider BJ, Kalemkerian GP, Ramnath N,
et al: Phase II trial of imatinib maintenance therapy after
irinotecan and cisplatin in patients with c-Kit-positive,
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer.
11:223–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dy GK, Miller AA, Mandrekar SJ, et al: A
phase II trial of imatinib (ST1571) in patients with c-kit
expressing relapsed small-cell lung cancer: a CALGB and NCCTG
study. Ann Oncol. 16:1811–1816. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boldrini L, Ursino S, Gisfredi S, et al:
Expression and mutational status of c-kit in small-cell lung
cancer: prognostic relevance. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4101–4108. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Douillard JY, Shepherd FA, Hirsh V, et al:
Molecular predictors of outcome with gefitinib and docetaxel in
previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer: data from the
randomized phase III INTEREST trial. J Clin Oncol. 28:744–752.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al:
Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with
mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al:
Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 361:947–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al:
Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal
growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase
3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 11:121–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al: Erlotinib
versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase
3 study. Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moore AM, Einhorn LH, Estes D, et al:
Gefitinib in patients with chemo-sensitive and chemo-refractory
relapsed small cell cancers: A Hoosier Oncology Group phase II
trial. Lung Cancer. 52:93–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T, et al:
Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth
factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:339–346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu YL, Zhong WZ, Li LY, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor mutations and their correlation with
gefitinib therapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a
meta-analysis based on updated individual patient data from six
medical centers in mainland China. J Thorac Oncol. 2:430–439. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Micke P, Basrai M, Faldum A, et al:
Characterization of c-kit expression in small cell lung cancer:
prognostic and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res.
9:188–194. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blackhall FH, Pintilie M, Michael M, et
al: Expression and prognostic significance of kit, protein kinase
B, and mitogen-activated protein kinase in patients with small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:2241–2247. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mangum MD, Greco FA, Hainsworth JD, et al:
Combined small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
7:607–612. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fraire AE, Johnson EH, Yesner R, et al:
Prognostic significance of histopathologic subtype and stage in
small cell lung cancer. Hum Pathol. 23:520–528. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nicholson SA, Beasley MB, Brambilla E, et
al: Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC): a clinicopathologic study of
100 cases with surgical specimens. Am J Surg Pathol. 26:1184–1197.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu HY, Sun WY, Chen B, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor mutations in small cell lung cancer patients
who received surgical resection in China. Neoplasma. 59:100–104.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tatematsu A, Shimizu J, Murakami Y, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6092–6096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shiao TH, Chang YL, Yu CJ, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in small cell lung
cancer: a brief report. J Thorac Oncol. 5:195–198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|