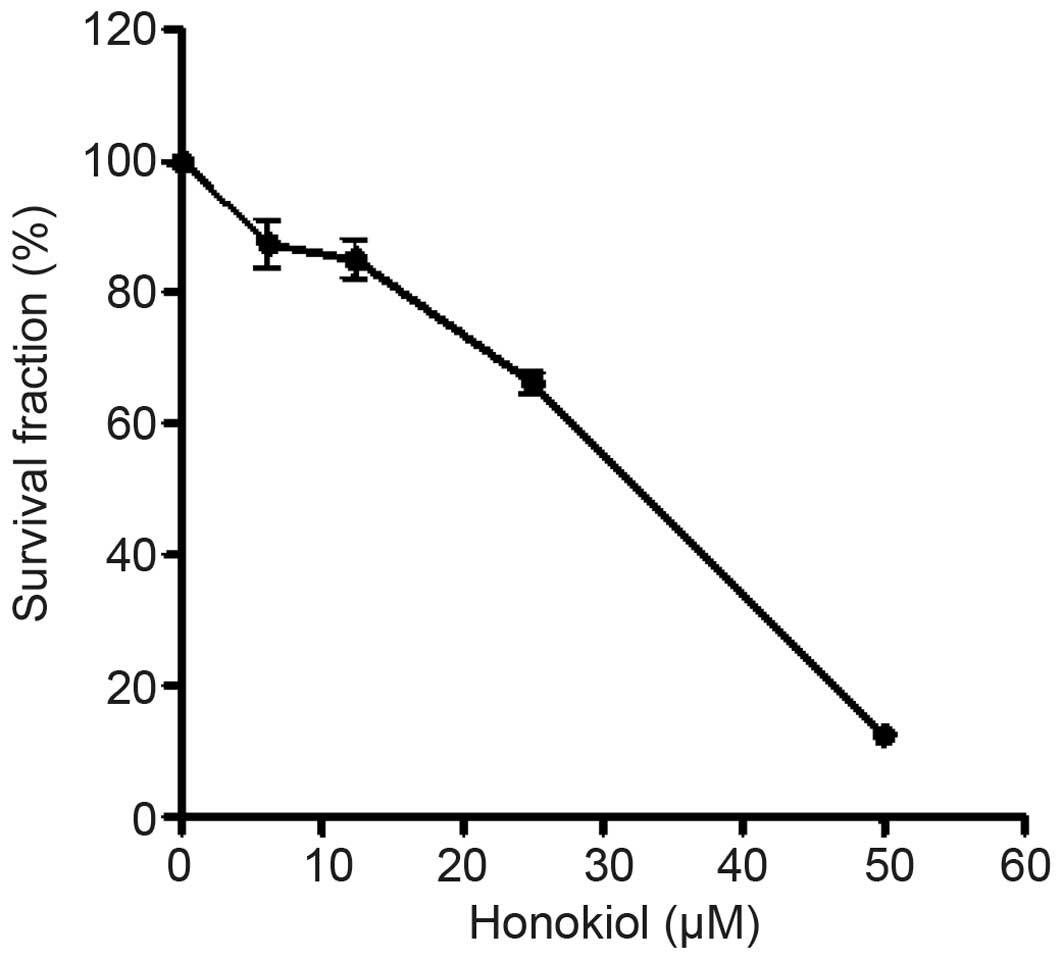
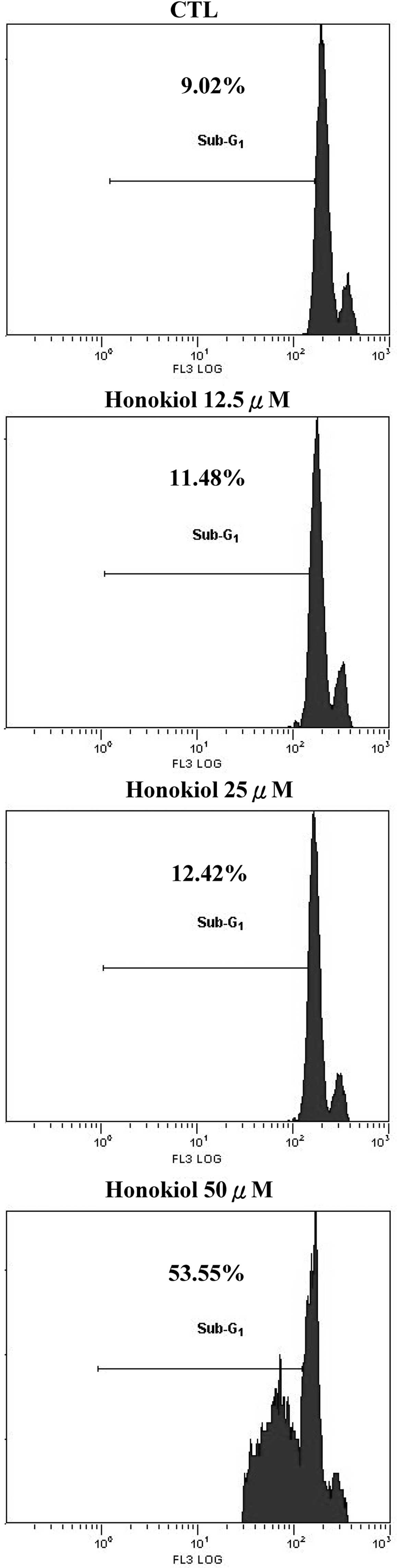
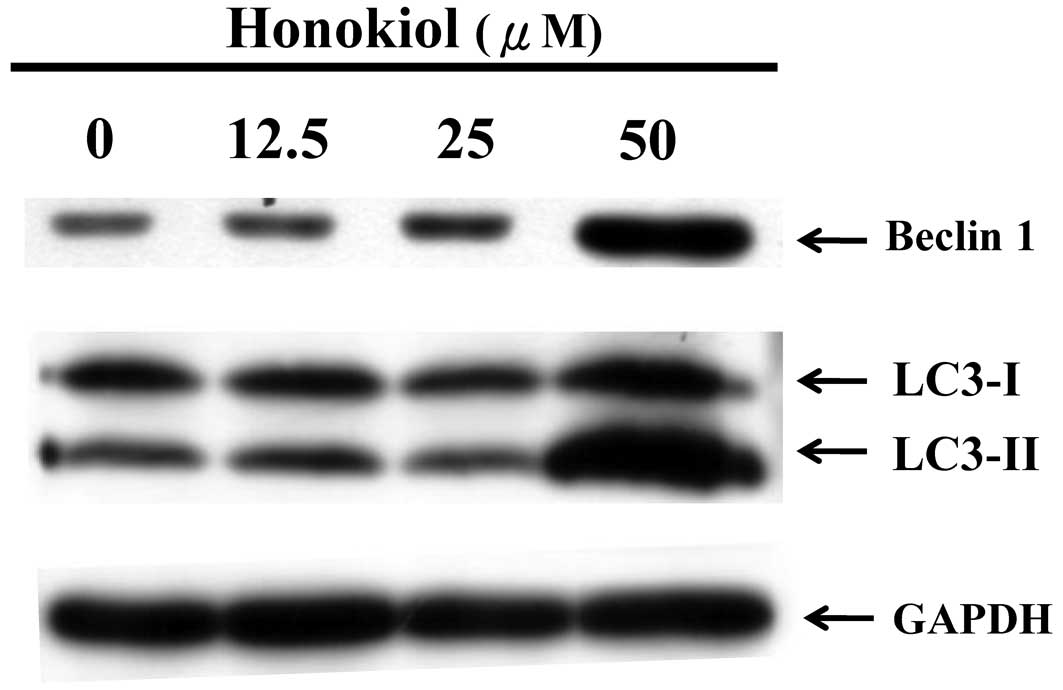
|
1
|
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch
DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK and DePinho RA: Malignant glioma: genetics
and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 15:1311–1333. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morandi E, Severini C, Quercioli D, D’Ario
G, Perdichizzi S, Capri M, Farruggia G, Mascolo MG, Horn W, Vaccari
M, Serra R, Colacci A and Silingardi P: Gene expression time-series
analysis of camptothecin effects in U87-MG and DBTRG-05
glioblastoma cell lines. Mol Cancer. 7:662008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang LF, Lin PC, Ho LI, Liu PY, Wu WC,
Chiang IP, Chang HW, Lin SZ, Harn YC, Harn HJ and Chiou TW:
Overexpression of the orphan receptor Nur77 and its translocation
induced by PCH4 may inhibit malignant glioma cell growth and induce
cell apoptosis. J Surg Oncol. 103:442–450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Long JS and Ryan KM: New frontiers in
promoting tumour cell death: targeting apoptosis, necroptosis and
autophagy. Oncogene. 31:5045–5060. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Torres S, Lorente M, Rodríguez-Fornés F,
Hernández-Tiedra S, Salazar M, García-Taboada E, Barcia J, Guzmán M
and Velasco G: A combined preclinical therapy of cannabinoids and
temozolomide against glioma. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:90–103. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hahm ER, Arlotti JA, Marynowski SW and
Singh SV: Honokiol, a constituent of oriental medicinal herb
magnolia officinalis, inhibits growth of PC-3 xenografts in
vivo in association with apoptosis induction. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1248–1257. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bai X, Cerimele F, Ushio-Fukai M, Waqas M,
Campbell PM, Govindarajan B, Der CJ, Battle T, Frank DA, Ye K,
Murad E, Dubiel W, Soff G and Arbiser JL: Honokiol, a small
molecular weight natural product, inhibits angiogenesis in vitro
and tumor growth in vivo. J Biol Chem. 278:35501–35507. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Munroe ME, Arbiser JL and Bishop GA:
Honokiol, a natural plant product, inhibits inflammatory signals
and alleviates inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol. 179:753–763.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park J, Lee J, Jung E, Park Y, Kim K, Park
B, Jung K, Park E, Kim J and Park D: In vitro antibacterial and
anti-inflammatory effects of honokiol and magnolol against
Propionibacterium sp. Eur J Pharmacol. 496:189–195. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen F, Wang T, Wu YF, Gu Y, Xu XL, Zheng
S and Hu X: Honokiol: a potent chemotherapy candidate for human
colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 10:3459–3463.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang T, Chen F, Chen Z, Wu YF, Xu XL,
Zheng S and Hu X: Honokiol induces apoptosis through
p53-independent pathway in human colorectal cell line RKO. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:2205–2208. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Konoshima T, Kozuka M, Tokuda H, Nishino
H, Iwashima A, Haruna M, Ito K and Tanabe M: Studies on inhibitors
of skin tumor promotion, IX. Neolignans from Magnolia
officinalis. J Nat Prod. 54:816–822. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu D, Lu Q and Hu X: Down-regulation of
P-glycoprotein expression in MDR breast cancer cell MCF-7/ADR by
honokiol. Cancer Lett. 243:274–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Duan X, Yang G, Zhang X, Deng L,
Zheng H, Deng C, Wen J, Wang N, Peng C, Zhao X, Wei Y and Chen L:
Honokiol crosses BBB and BCSFB, and inhibits brain tumor growth in
rat 9L intracerebral gliosarcoma model and human U251 xenograft
glioma model. PLoS One. 6:e184902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chilampalli S, Zhang X, Fahmy H, Kaushik
RS, Zeman D, Hildreth MB and Dwivedi C: Chemopreventive effects of
honokiol on UVB-induced skin cancer development. Anticancer Res.
30:777–783. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Liu Y, Zhao X, Pan X, Yin R, Huang
C, Chen L and Wei Y: Honokiol, a natural therapeutic candidate,
induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis of ovarian tumor cells.
Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 140:95–102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Battle TE, Arbiser J and Frank DA: The
natural product honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. Blood.
106:690–697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chau BN and Wang JY: Coordinated
regulation of life and death by RB. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:130–138.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fujita N, Nagahashi A, Nagashima K,
Rokudai S and Tsuruo T: Acceleration of apoptotic cell death after
the cleavage of Bcl-XL protein by caspase-3-like proteases.
Oncogene. 17:1295–1304. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itoh M, Chiba H, Noutomi T, Takada E and
Mizuguchi J: Cleavage of Bax-alpha and Bcl-x(L) during
carboplatin-mediated apoptosis in squamous cell carcinoma cell
line. Oral Oncol. 36:277–285. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lefranc F, Facchini V and Kiss R:
Proautophagic drugs: a novel means to combat apoptosis-resistant
cancers, with a special emphasis on glioblastomas. Oncologist.
12:1395–1403. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eimer S, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Airiau K,
Jeanneteau M, Laharanne E, Véron N, Vital A, Loiseau H, Merlio JP
and Belloc F: Autophagy inhibition cooperates with erlotinib to
induce glioblastoma cell death. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:1017–1027.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu WK, Coffelt SB, Cho CH, Wang XJ, Lee
CW, Chan FK, Yu J and Sung JJ: The autophagic paradox in cancer
therapy. Oncogene. 31:939–953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen N and Karantza V: Autophagy as a
therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:157–168. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|