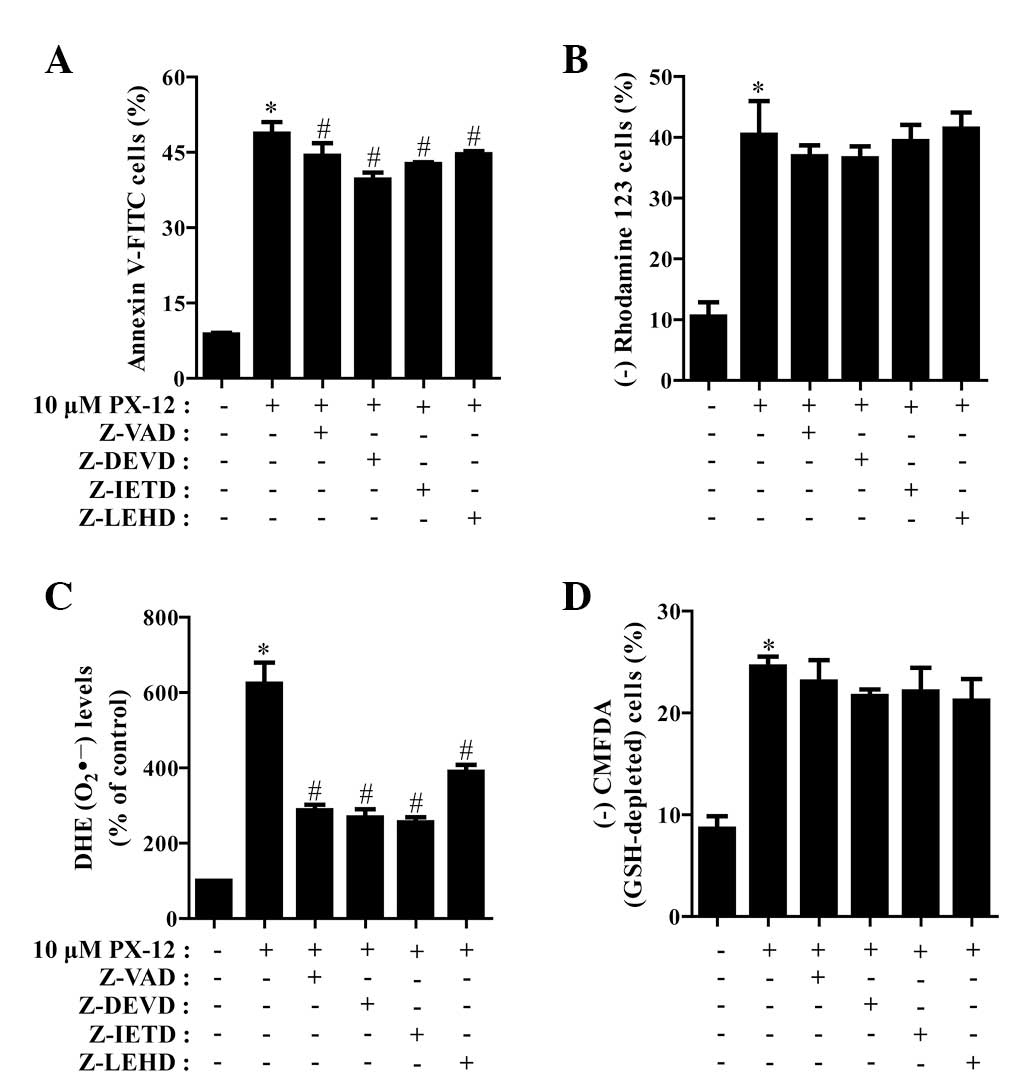
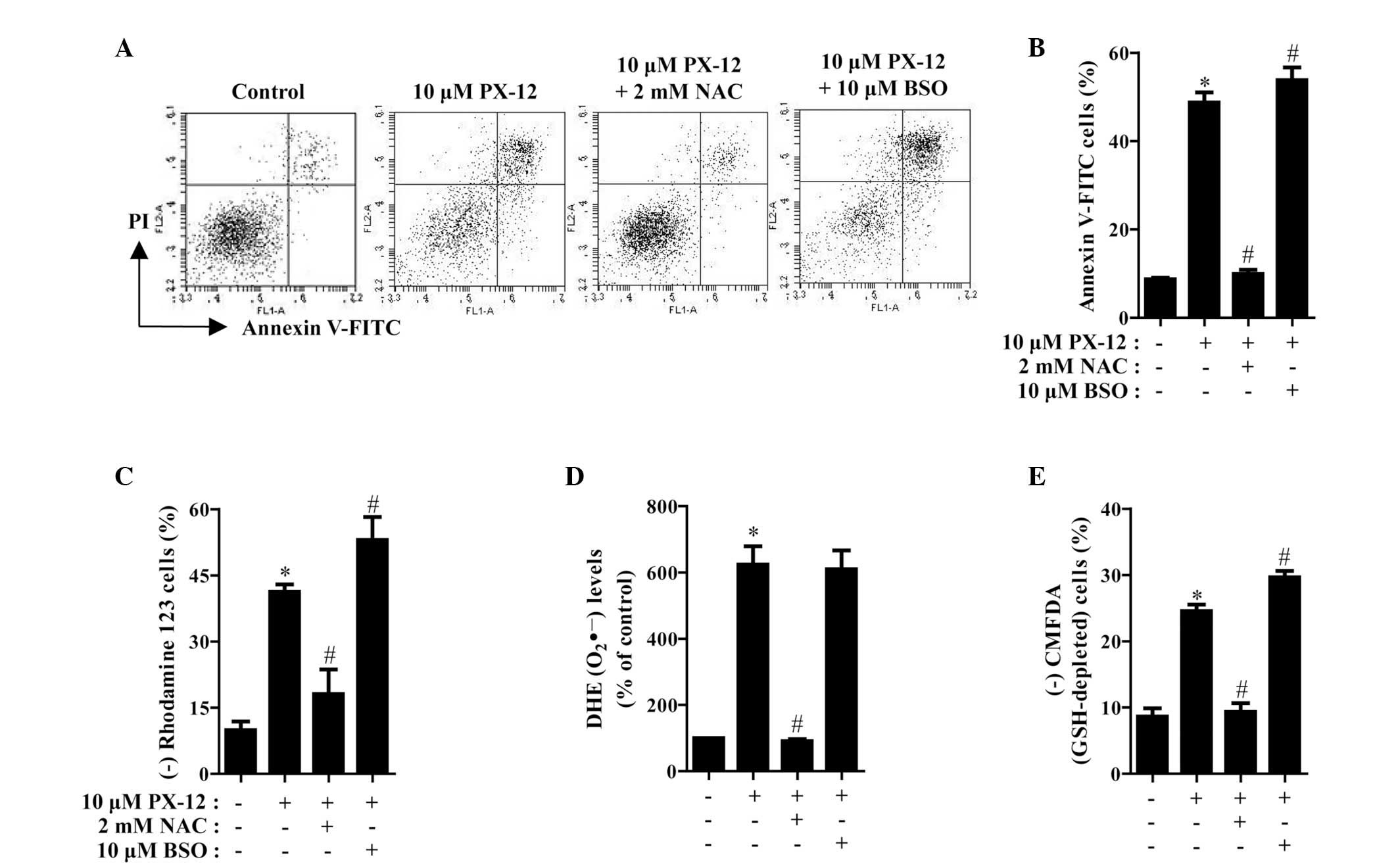
|
1
|
Shi Y, Tang B, Yu PW, Tang B, Hao YX, Lei
X, Luo HX and Zeng DZ: Autophagy protects against
oxaliplatin-induced cell death via ER stress and ROS in Caco-2
cells. PLoS One. 7:e510762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gonzalez C, Sanz-Alfayate G, Agapito MT,
Gomez-Nino A, Rocher A and Obeso A: Significance of ROS in oxygen
sensing in cell systems with sensitivity to physiological hypoxia.
Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 132:17–41. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baran CP, Zeigler MM, Tridandapani S and
Marsh CB: The role of ROS and RNS in regulating life and death of
blood monocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 10:855–866. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: an update and review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1757:509–517. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lo YL, Wang W and Ho CT:
7,3′,4′-Trihydroxyisoflavone modulates multidrug resistance
transporters and induces apoptosis via production of reactive
oxygen species. Toxicology. 302:221–232. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Bell EL, Emerling BM, Ricoult SJ and
Guarente L: SirT3 suppresses hypoxia inducible factor 1α and tumor
growth by inhibiting mitochondrial ROS production. Oncogene.
30:2986–2996. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li C, Thompson MA, Tamayo AT, Zuo Z, Lee
J, Vega F, Ford RJ and Pham LV: Over-expression of Thioredoxin-1
mediates growth, survival, and chemoresistance and is a druggable
target in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 3:314–326.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lim JY, Yoon SO, Hong SW, Kim JW, Choi SH
and Cho JY: Thioredoxin and thioredoxin-interacting protein as
prognostic markers for gastric cancer recurrence. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:5581–5588. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang J, Li C, Ding L, Guo Q, You Q and Jin
S: Gambogic acid deactivates cytosolic and mitochondrial
thioredoxins by covalent binding to the functional domain. J Nat
Prod. 75:1108–1116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chae JS, Gil Hwang S, Lim DS and Choi EJ:
Thioredoxin-1 functions as a molecular switch regulating the
oxidative stress-induced activation of MST1. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:2335–2343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ungerstedt J, Du Y, Zhang H, Nair D and
Holmgren A: In vivo redox state of human thioredoxin and redox
shift by the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide
hydroxamic acid (SAHA). Free Radic Biol Med. 53:2002–2007. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Lu H, Wang D, Li S, Sun K, Wan X,
Taylor EW and Zhang J: Inhibition of glutathione synthesis
eliminates the adaptive response of ascitic hepatoma 22 cells to
nedaplatin that targets thioredoxin reductase. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 265:342–350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Samuel SM, Thirunavukkarasu M, Penumathsa
SV, Koneru S, Zhan L, Maulik G, Sudhakaran PR and Maulik N:
Thioredoxin-1 gene therapy enhances angiogenic signaling and
reduces ventricular remodeling in infarcted myocardium of diabetic
rats. Circulation. 121:1244–1255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fath MA, Ahmad IM, Smith CJ, Spence J and
Spitz DR: Enhancement of carboplatin-mediated lung cancer cell
killing by simultaneous disruption of glutathione and thioredoxin
metabolism. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6206–6217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wondrak GT: Redox-directed cancer
therapeutics: molecular mechanisms and opportunities. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 11:3013–3069. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Welsh SJ, Williams RR, Birmingham A,
Newman DJ, Kirkpatrick DL and Powis G: The thioredoxin redox
inhibitors 1-methylpropyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide and pleurotin
inhibit hypoxia-induced factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial
growth factor formation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:235–243. 2003.
|
|
17
|
Mukherjee A and Martin SG: The thioredoxin
system: a key target in tumour and endothelial cells. Br J Radiol.
81(Spec No 1): S57–S68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baker AF, Adab KN, Raghunand N, Chow HH,
Stratton SP, Squire SW, Boice M, Pestano LA, Kirkpatrick DL and
Dragovich T: A phase IB trial of 24-hour intravenous PX-12, a
thioredoxin-1 inhibitor, in patients with advanced gastrointestinal
cancers. Invest New Drugs. 31:631–641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramanathan RK, Kirkpatrick DL, Belani CP,
Friedland D, Green SB, Chow HH, Cordova CA, Stratton SP, Sharlow
ER, Baker A and Dragovich T: A Phase I pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic study of PX-12, a novel inhibitor of thioredoxin-1,
in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
13:2109–2114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hedley D, Pintilie M, Woo J, Nicklee T,
Morrison A, Birle D, Fyles A, Milosevic M and Hill R: Up-regulation
of the redox mediators thioredoxin and apurinic/apyrimidinic
excision (APE)/Ref-1 in hypoxic microregions of invasive cervical
carcinomas, mapped using multispectral, wide-field fluorescence
image analysis. Am J Pathol. 164:557–565. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Pyrogallol inhibits the growth of lung cancer Calu-6 cells via
caspase-dependent apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact. 177:107–114. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han YH and Park WH: The effects of
N-acetyl cysteine, buthionine sulfoximine, diethyldithiocarbamate
or 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole on antimycin A-treated Calu-6 lung cells
in relation to cell growth, reactive oxygen species and
glutathione. Oncol Rep. 22:385–391. 2009.
|
|
23
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH
and Park WH: Effects of carbonyl cyanide p-(trifluoromethoxy)
phenylhydrazone on the growth inhibition in human pulmonary
adenocarcinoma Calu-6 cells. Toxicology. 265:101–107. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Pyrogallol inhibits the growth of human lung cancer Calu-6 cells
via arresting the cell cycle arrest. Toxicol In Vitro.
22:1605–1609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR and Park WH: The
effect of MG132, a proteasome inhibitor on HeLa cells in relation
to cell growth, reactive oxygen species and GSH. Oncol Rep.
22:215–221. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ and Park WH:
Carbonyl cyanide p-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP) as an
O2(*−) generator induces apoptosis via the depletion of
intracellular GSH contents in Calu-6 cells. Lung Cancer.
63:201–209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han YH and Park WH: Propyl gallate
inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via regulating intracellular GSH
level. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2531–2538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Intracellular GSH level is a factor in As4.1 juxtaglomerular cell
death by arsenic trioxide. J Cell Biochem. 104:995–1009. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Griffiths EJ: Mitochondria - potential
role in cell life and death. Cardiovasc Res. 46:24–27. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vogt A, Tamura K, Watson S and Lazo JS:
Antitumor imidazolyl disulfide IV-2 causes irreversible G(2)/M cell
cycle arrest without hyperphosphorylation of cyclin-dependent
kinase Cdk1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 294:1070–1075. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado
AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X: Prevention of apoptosis by
Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science.
275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee YJ, Kim JH, Chen J and Song JJ:
Enhancement of metabolic oxidative stress-induced cytotoxicity by
the thioredoxin inhibitor 1-methylpropyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide is
mediated through the ASK1-SEK1-JNK1 pathway. Mol Pharmacol.
62:1409–1417. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Enhancement of arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells by
diethyldithiocarbamate or buthionine sulfoximine. Int J Oncol.
33:205–213. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Estrela JM, Ortega A and Obrador E:
Glutathione in cancer biology and therapy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci.
43:143–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Suppression of arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells by
N-acetylcysteine. Mol Cells. 26:18–25. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|