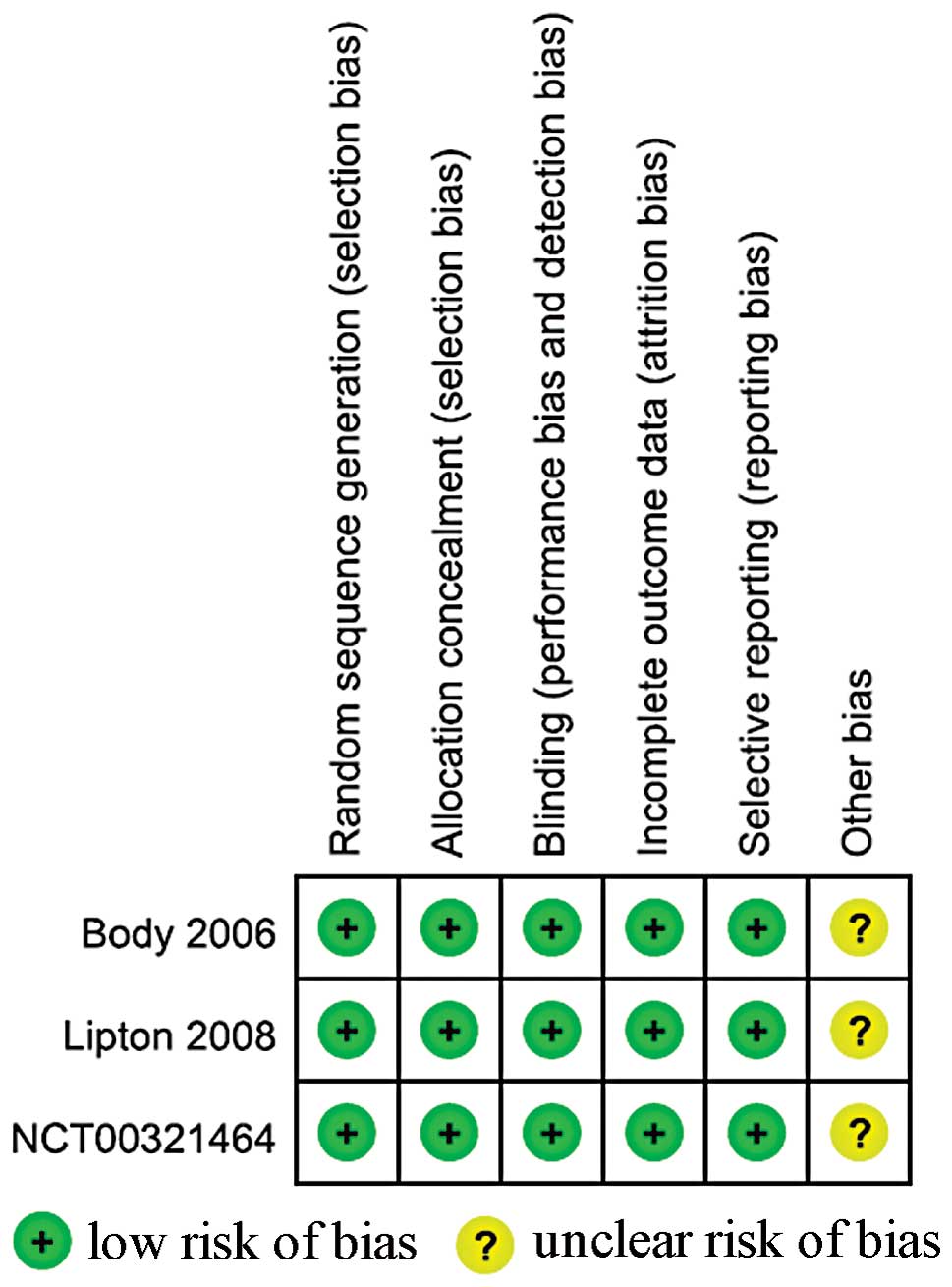
|
1
|
Bray F, Jemal A, Grey N, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global cancer transitions according to the Human
Development Index (2008–2030): a population-based study. Lancet
Oncol. 8:790–801. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coleman RE: Clinical features of
metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:S6243–S6249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coleman RE, Lipton A, Roodman GD, Guise
TA, Boyce BF, Brufsky AM, Clézardin P, Croucher PI, Gralow JR,
Hadji P, et al: Metastasis and bone loss: advancing treatment and
prevention. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:615–620. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coleman RE and Rubens RD: The clinical
course of bone metastases from breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
55:61–66. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coleman R: Potential use of
bisphosphonates in the prevention of metastases in early-stage
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 7:S29–S35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Body JJ: Effectiveness and cost of
bisphosphonate therapy in tumor bone disease. Cancer. 97:859–865.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coleman RE: Metastatic bone disease:
clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer
Treat Rev. 27:165–176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brown JE, Cook RJ, Major P, Lipton A, Saad
F, Smith M, Lee KA, Zheng M, Hei YJ and Coleman RE: Bone turnover
markers as predictors of skeletal complications in prostate cancer,
lung cancer, and other solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:59–69.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Costa L, Demers LM, Gouveia-Oliveira A,
Schaller J, Costa EB, de Moura MC and Lipton A: Prospective
evaluation of the peptide-bound collagen type I cross-links
N-telopeptide and C-telopeptide in predicting bone metastases
status. J Clin Oncol. 20:850–856. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Coleman RE, Major P, Lipton A, Brown JE,
Lee KA, Smith M, Saad F, Zheng M, Hei YJ, Seaman J and Cook R:
Predictive value of bone resorption and formation markers in cancer
patients with bone metastases receiving the bisphosphonate
zoledronic acid. J Clin Oncol. 23:4925–4935. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nørgaard M, Jensen AØ, Jacobsen JB, Cetin
K, Fryzek JP and Sørensen HT: Skeletal related events, bone
metastasis and survival of prostate cancer: a population based
cohort study in Denmark (1999 to 2007). J Urol. 184:162–167.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sathiakumar N, Delzell E, Morrisey MA,
Falkson C, Yong M, Chia V, Blackburn J, Arora T and Kilgore ML:
Mortality following bone metastasis and skeletal-related events
among men with prostate cancer: a population-based analysis of U.S.
Medicare beneficiaries, 1999–2006. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
14:177–183. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Costa L, Badia X, Chow E, Lipton A and
Wardley A: Impact of skeletal complications on patients’ quality of
life, mobility, and functional independence. Support Care Cancer.
16:879–889. 2008.
|
|
14
|
Costa L and Major PP: Effect of
bisphosphonates on pain and quality of life in patients with bone
metastases. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 6:163–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pockett RD, Castellano D, McEwan P,
Oglesby A, Barber BL and Chung K: The hospital burden of disease
associated with bone metastases and skeletal-related events in
patients with breast cancer, lung cancer, or prostate cancer in
Spain. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 19:755–760. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oefelein MG, Ricchiuti V, Conrad W and
Resnick MI: Skeletal fractures negatively correlate with overall
survival in men with prostate cancer. J Urol. 168:1005–1007. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saad F, Lipton A, Cook R, Chen YM, Smith M
and Coleman R: Pathologic fractures correlate with reduced survival
in patients with malignant bone disease. Cancer. 110:1860–1867.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weinfurt KP, Castel LD, Li Y, Timbie JW,
Glendenning GA and Schulman KA: Health-related quality of life
among patients with breast cancer receiving zoledronic acid or
pamidronate disodium for metastatic bone lesions. Med Care.
42:164–175. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wardley A, Davidson N, Barrett-Lee P, Hong
A, Mansi J, Dodwell D, Murphy R, Mason T and Cameron D: Zoledronic
acid significantly improves pain scores and quality of life in
breast cancer patients with bone metastases: a randomised,
crossover study of community vs hospital bisphosphonate
administration. Br J Cancer. 92:1869–1876. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Abrahm JL, Banffy MB and Harris MB: Spinal
cord compression in patients with advanced metastatic cancer: “all
I care about is walking and living my life. JAMA. 299:937–946.
2008.
|
|
21
|
Theriault RL, Lipton A, Hortobagyi GN,
Leff R, Glück S, Stewart JF, Costello S, Kennedy I, Simeone J,
Seaman JJ, et al: Pamidronate reduces skeletal morbidity in women
with advanced breast cancer and lytic bone lesions: a randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 17:846–854. 1999.
|
|
22
|
Rosen LS, Gordon D, Tchekmedyian S,
Yanagihara R, Hirsh V, Krzakowski M, Pawlicki M, de Souza P, Zheng
M, Urbanowitz G, Reitsma D and Seaman JJ: Zoledronic acid versus
placebo in the treatment of skeletal metastases in patients with
lung cancer and other solid tumors: a phase III, double-blind,
randomized trial - the Zoledronic Acid Lung Cancer and Other Solid
Tumors Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 21:3150–3157. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Aapro M, Abrahamsson PA, Body JJ, Coleman
RE, Colomer R, Costa L, Crinò L, Dirix L, Gnant M, Gralow J, et al:
Guidance on the use of bisphosphonates in solid tumours:
recommendations of an international expert panel. Ann Oncol.
19:420–432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hillner BE, Ingle JN, Chlebowski RT,
Gralow J, Yee GC, Janjan NA, Cauley JA, Blumenstein BA, Albain KS,
Lipton A and Brown S; American Society of Clinical Oncology.
American Society of Clinical Oncology 2003 update on the role of
bisphosphonates and bone health issues in women with breast cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 21:4042–4057. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Basch EM, Somerfield MR, Beer TM, Carducci
MA, Higano CS, Hussain MH and Scher HI; American Society of
Clinical Oncology. American Society of Clinical Oncology
endorsement of the Cancer Care Ontario Practice Guideline on
nonhormonal therapy for men with metastatic hormone-refractory
(castration-resistant) prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:5313–5318.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rosen LS, Gordon D, Kaminski M, Howell A,
Belch A, Mackey J, Apffelstaedt J, Hussein MA, Coleman RE, Reitsma
DJ, et al: Long-term efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid
compared with pamidronate disodium in the treatment of skeletal
complications in patients with advanced multiple myeloma or breast
carcinoma: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, comparative
trial. Cancer. 98:1735–1744. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Markowitz GS, Fine PL, Stack JI, Kunis CL,
Radhakrishnan J, Palecki W, Park J, Nasr SH, Hoh S, Siegel DS and
D’Agati VD: Toxic acute tubular necrosis following treatment with
zoledronate (Zometa). Kidney Int. 64:281–289. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Perazella MA and Markowitz GS:
Bisphosphonate nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 74:1385–1393. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation.
Zometa (zoledronic acid) prescribing information. East Hanover; NJ:
2011, http://www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/Zometa.pdf.
Accessed September 1, 2013
|
|
30
|
Mauri D, Valachis A, Polyzos IP, Polyzos
NP, Kamposioras K and Pesce LL: Osteonecrosis of the jaw and use of
bisphosphonates in adjuvant breast cancer treatment: a
meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 116:433–439. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thomas RJ, Guise TA, Yin JJ, Elliott J,
Horwood NJ, Martin TJ and Gillespie MT: Breast cancer cells
interact with osteoblasts to support osteoclast formation.
Endocrinology. 140:4451–4458. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
US Food and Drug Administration. Denosumab
(Xgeva, Amgen) approval for the prevention of skeletal-related
events in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors. 2010,
http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2010/125320s007ltr.pdf.
Accessed November 18, 2010
|
|
33
|
Serlin RC, Mendoza TR, Nakamura Y, Edwards
KR and Cleeland CS: When is cancer pain mild, moderate or severe?
Grading pain severity by its interference with function. Pain.
61:277–284. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Higgins JPT and Green S: Cochrane Handbook
for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. [updated
March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011, www.cochrane-handbook.orghttps://www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Accessed March 12, 2011
|
|
35
|
Lipton A, Steger GG, Figueroa J, Alvarado
C, Solal-Celigny P, Body JJ, de Boer R, Berardi R, Gascon P, Tonkin
KS, et al: Extended efficacy and safety of denosumab in breast
cancer patients with bone metastases not receiving prior
bisphosphonate therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6690–6696. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Body JJ, Facon T, Coleman RE, Lipton A,
Geurs F, Fan M, Holloway D, Peterson MC and Bekker PJ: A study of
the biological receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand
inhibitor, denosumab, in patients with multiple myeloma or bone
metastases from breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1221–1228. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Stopeck AT, Lipton A, Body JJ, Steger GG,
Tonkin K, de Boer RH, Lichinitser M, Fujiwara Y, Yardley DA,
Viniegra M, et al: Denosumab compared with zoledronic acid for the
treatment of bone metastases in patients with advanced breast
cancer: a randomized, double-blind study. J Clin Oncol.
28:5132–5139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Martin M, Bell R, Bourgeois H, Brufsky A,
Diel I, Eniu A, Fallowfield L, Fujiwara Y, Jassem J, Paterson AH,
et al: Bone-related complications and quality of life in advanced
breast cancer: results from a randomized phase III trial of
denosumab versus zoledronic acid. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4841–4849.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cleeland CS, Body JJ, Stopeck A, von Moos
R, Fallowfield L, Mathias SD, Patrick DL, Clemons M, Tonkin K,
Masuda N, et al: Pain outcomes in patients with advanced breast
cancer and bone metastases: results from a randomized, double-blind
study of denosumab and zoledronic acid. Cancer. 119:832–838. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Webster K, Cella D and Yost K: The
functional assessment of chronic illness therapy (FACIT)
measurement system: properties, applications, and interpretation.
Health Qual Life Outcomes. 1:792003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Coleman RE: Skeletal complications of
malignancy. Cancer. 80:1588–1594. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kristensen B, Ejlertsen B, Groenvold M,
Hein S, Loft H and Mouridsen HT: Oral clodronate in breast cancer
patients with bone metastases: a randomized study. J Intern Med.
246:67–74. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Body JJ, Lichinitser M, Tjulandin S,
Garnero P and Bergström B: Oral ibandronate is as active as
intravenous zoledronic acid for reducing bone turnover markers in
women with breast cancer and bone metastases. Ann Oncol.
18:1165–1171. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kohno N, Aogi K, Minami H, Nakamura S,
Asaga T, Iino Y, Watanabe T, Goessl C, Ohashi Y and Takashima S:
Zoledronic acid significantly reduces skeletal complications
compared with placebo in Japanese women with bone metastases from
breast cancer: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin
Oncol. 23:3314–3321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Olson K and Van Poznak C: Significance and
impact of bisphosphonate-induced acute phase responses. J Oncol
Pharm Pract. 13:223–229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|