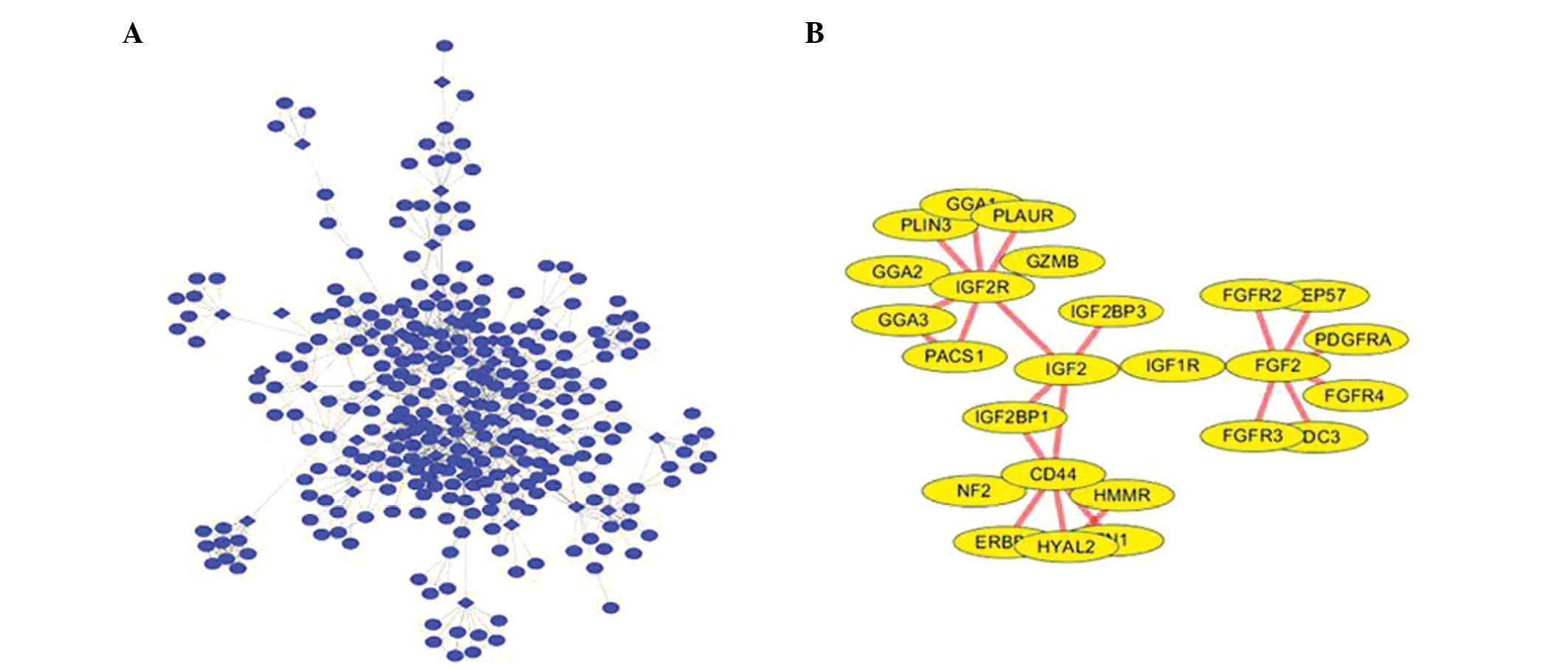
|
1
|
Zygogianni AG, Kyrgias G, Karakitsos P, et
al: Oral squamous cell cancer: early detection and the role of
alcohol and smoking. Head Neck Oncol. 3:22011.
|
|
2
|
Zini A, Czerninski R and Sgan-Cohen HD:
Oral cancer over four decades: epidemiology, trends, histology, and
survival by anatomical sites. J Oral Pathol Med. 39:299–305.
2010.
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L, Primrose
JN and Packham G: MicroRNAs: key players in carcinogenesis and
novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:339–347. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Ruan K, Fang X and Ouyang G: MicroRNAs:
novel regulators in the hallmarks of human cancer. Cancer Lett.
285:116–126. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Cicatiello L, Mutarelli M, Grober OM, et
al: Estrogen receptor alpha controls a gene network in luminal-like
breast cancer cells comprising multiple transcription factors and
microRNAs. Am J Pathol. 176:2113–2130. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Siow M, Karen Ng L, Vincent Chong V, et
al: Dysregulation of miR-31 and miR-375 expression is associated
with clinical outcomes in oral carcinoma. Oral Dis. Apr
17–2013.(Epub ahead of print). DOI: 10.1111/odi.12118
|
|
8
|
Jung HM, Phillips BL, Patel RS, et al:
Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor
suppressor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal
motifs (RECK) in oral cancer. J Biol Chem. 287:29261–29272.
2012.
|
|
9
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
et al: STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, et al:
miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005.
|
|
11
|
Calin GA, Cimmino A, Fabbri M, et al:
MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:5166–5171. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Urbich C, Kuehbacher A and Dimmeler S:
Role of microRNAs in vascular diseases, inflammation, and
angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 79:581–588. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, et al: The
miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting
multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277. 2008.
|
|
14
|
Bandi N, Zbinden S, Gugger M, et al:
miR-15a and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a
Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5553–5559. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Xin C, Buhe B, Hongting L, et al:
MicroRNA-15a promotes neuroblastoma migration by targeting
reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK)
and regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. FEBS J.
280:855–866. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Ricieri Brito JA, Gomes CC, Santos Pimenta
FJ, et al: Reduced expression of mir15a in the blood of patients
with oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with tumor staging.
Exp Ther Med. 1:217–221. 2010.
|
|
17
|
Okada-Ban M, Thiery JP and Jouanneau J:
Fibroblast growth factor-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 32:263–267.
2000.
|
|
18
|
Dow JK and deVere White RW: Fibroblast
growth factor 2: its structure and property, paracrine function,
tumor angiogenesis, and prostate-related mitogenic and oncogenic
functions. Urology. 55:800–806. 2000.
|
|
19
|
Chalkiadaki G, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, et
al: Fibroblast growth factor-2 modulates melanoma adhesion and
migration through a syndecan-4-dependent mechanism. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 41:1323–1331. 2009.
|
|
20
|
Giri D, Ropiquet F and Ittmann M:
Alterations in expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 2
and its receptor FGFR-1 in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
5:1063–1071. 1999.
|
|
21
|
Cross MJ and Claesson-Welsh L: FGF and
VEGF function in angiogenesis: signalling pathways, biological
responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
22:201–207. 2001.
|
|
22
|
Lau MT, So WK and Leung PC: Fibroblast
growth factor 2 induces E-cadherin down-regulation via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK/ERK signaling in ovarian cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e590832013.
|
|
23
|
Kelleher FC, O’Sullivan H, Smyth E,
McDermott R and Viterbo A: Fibroblast growth factor receptors,
developmental corruption and malignant disease. Carcinogenesis.
34:2198–2205. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Liang G, Chen G, Wei X, Zhao Y and Li X:
Small molecule inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptors in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:467–475. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Weiss J, Sos ML, Seidel D, et al: Frequent
and focal FGFR1 amplification associates with therapeutically
tractable FGFR1 dependency in squamous cell lung cancer. Sci Transl
Med. 2:62ra932010.
|
|
26
|
Dutt A, Salvesen HB, Chen TH, et al:
Drug-sensitive FGFR2 mutations in endometrial carcinoma. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:8713–8717. 2008.
|
|
27
|
Kunii K, Davis L, Gorenstein J, et al:
FGFR2-amplified gastric cancer cell lines require FGFR2 and Erbb3
signaling for growth and survival. Cancer Res. 68:2340–2348.
2008.
|