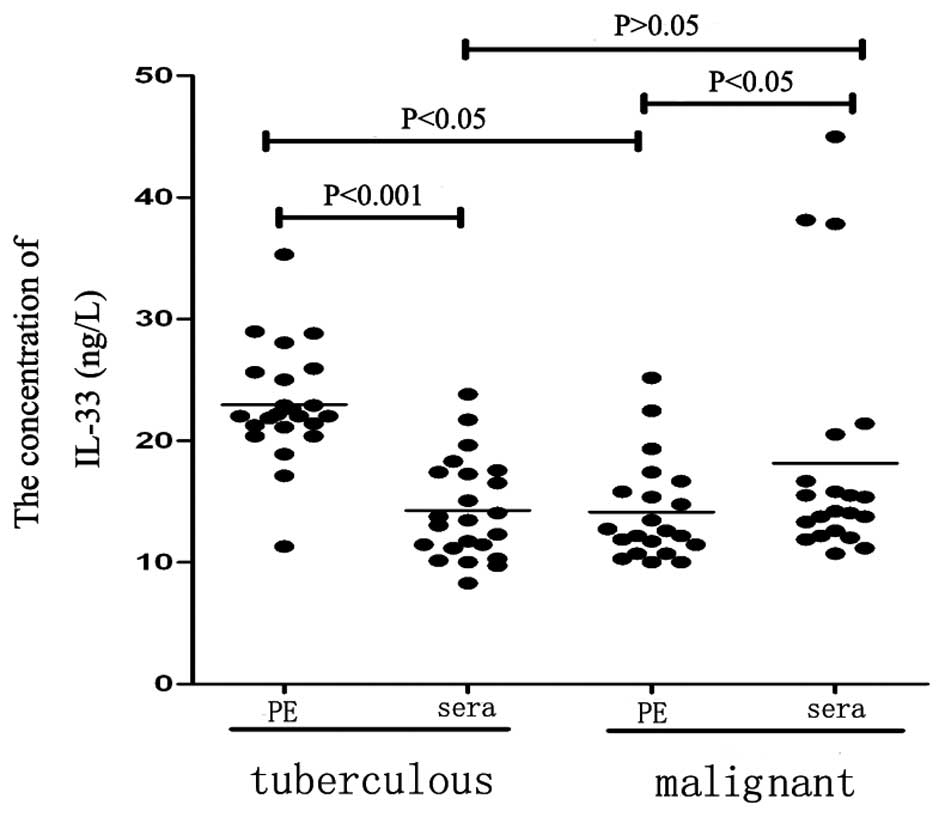
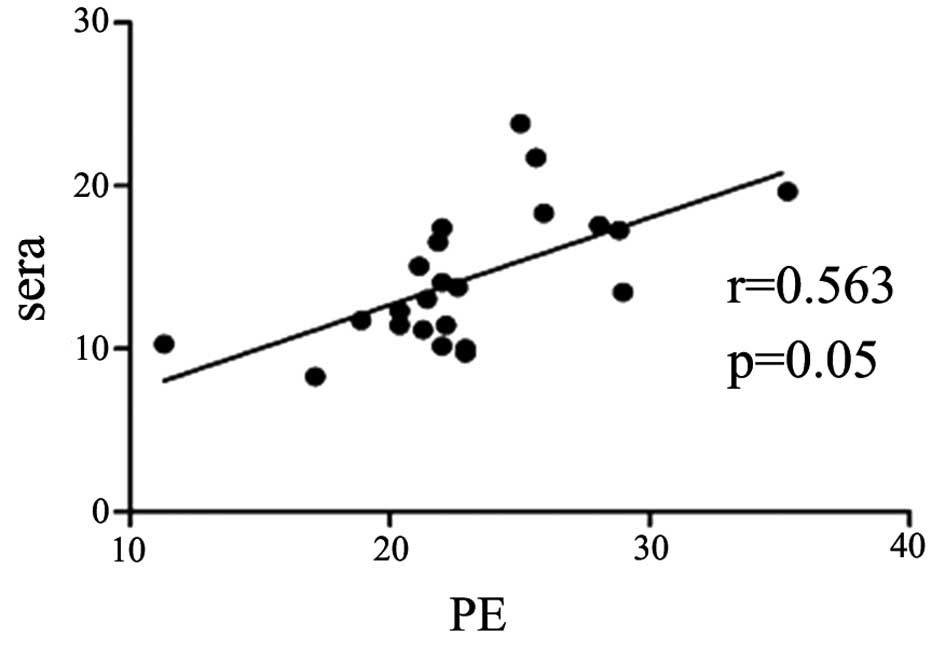
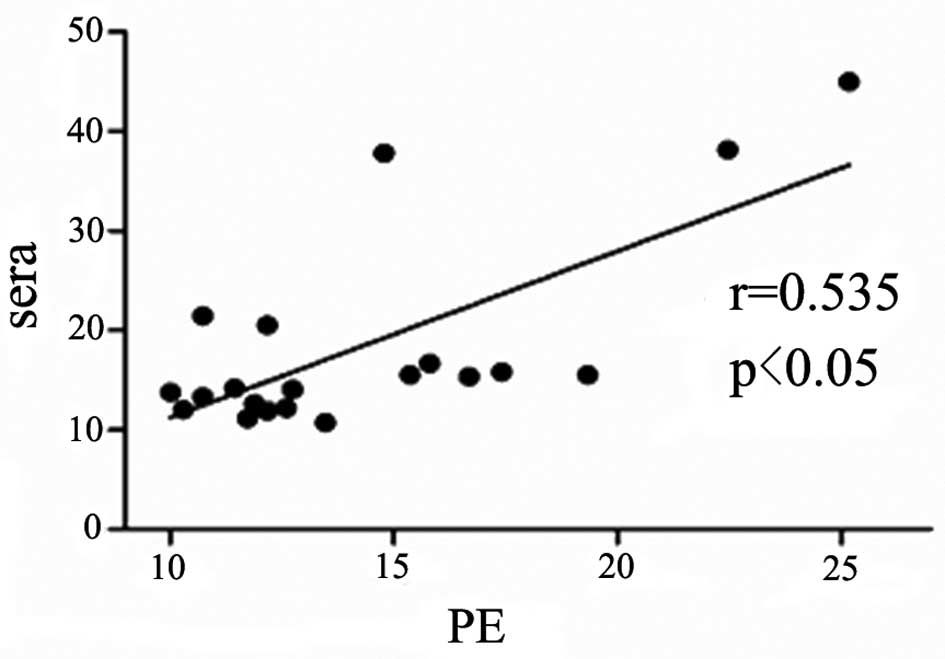
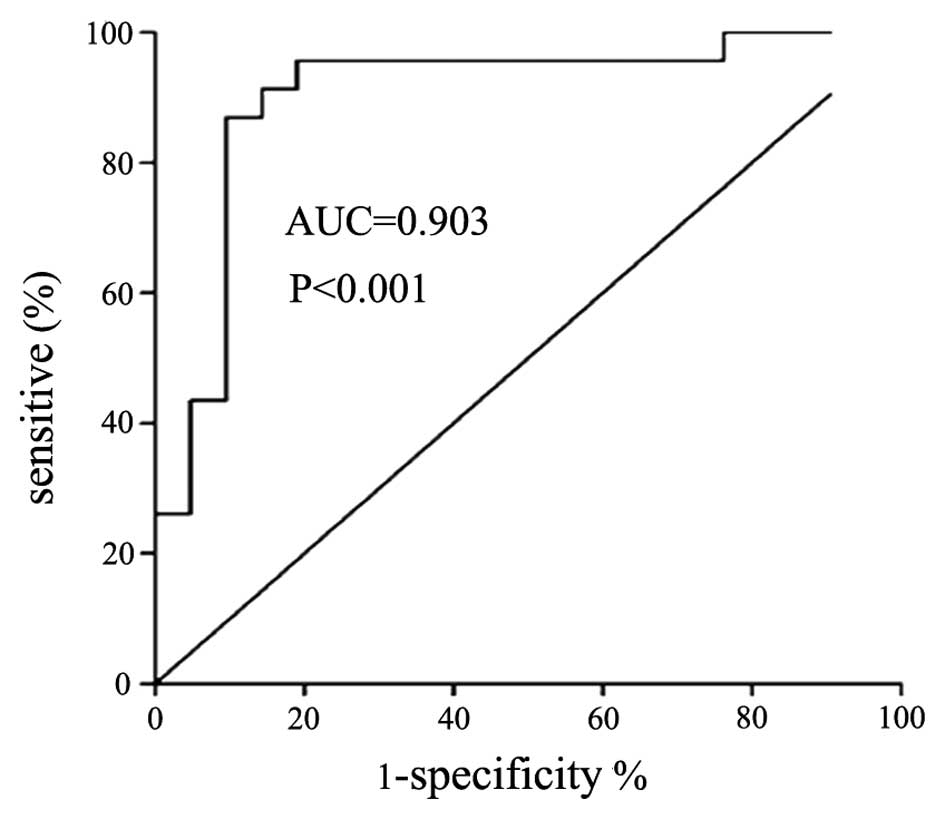
|
1
|
Hua CC, Chang LC, Chen YC and Chang SC:
Proinflammatory cytokines and fibrinolytic enzymes in tuberculous
and malignant pleural effusions. Chest. 116:1292–1296. 1999.
|
|
2
|
Wong CF, Yew WW, Leung SK, Chan CY, Hui M,
Yeang C and Cheng AF: Assay of pleural fluid interleukin-6, tumour
necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in the diagnosis and
outcome correlation of tuberculous effusion. Respir Med.
97:1289–1295. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Qin XJ, Shi HZ, Huang ZX, Kang LF, Mo WN
and Wu C: Interleukin-16 in tuberculous and malignant pleural
effusions. Eur Respir J. 25:605–611. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, et al:
IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a
chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:282–287. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, et al:
IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type2-associated
cytokines. Immunity. 23:479–490. 2005.
|
|
6
|
Yasuda K, Muto T, Kawagoe T, et al:
Contribution of IL-33-activated type II innate lymphoid cells to
pulmonary eosinophilia in intestinal nematode-infected mice. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:3451–3456. 2012.
|
|
7
|
van der Veerdonk FL and Netea MG: New
insights in the immunobiology of IL-1 family members. Front
Immunol. 4:1672013.
|
|
8
|
Milovanovic M, Volarevic V, Radosavljevic
G, Jovanovic I, Pejnovic N, Arsenijevic N and Lukic ML: IL-33/ST2
axis in inflammation and immunopathology. Immunol Res. 52:89–99.
2012.
|
|
9
|
Tjota MY, Williams JW, Lu T, et al:
IL-33-dependent induction of allergic lung inflammation by FcγRIII
signaling. J Clin Invest. 123:2287–2297. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Bonilla WV, Fröhlich A, Senn K, et al: The
alarmin interleukin-33 drives protective antiviral CD8+
T cell responses. Science. 335:984–989. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Cohen I, Rider P, Carmi Y, et al:
Differential release of chromatin-bound IL-1alpha discriminates
between necrotic and apoptotic cell death by the ability to induce
sterile inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:2574–2579.
2010.
|
|
12
|
Ali S, Mohs A, Thomas M, et al: The dual
function cytokine IL-33 interacts with the transcription factor
NF-κB to dampen NF-κB-stimulated gene transcription. J Immunol.
187:1609–1616. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Light RW, Macgregor MI, Luchsinger PC and
Ball WC Jr: Pleural effusions: the diagnostic separation of
transudates and exudates. Ann Intern Med. 77:507–513. 1972.
|
|
14
|
Lee KS, Kim HR, Kwak S, et al: Association
between elevated pleural interleukin-33 levels and tuberculous
pleurisy. Ann Lab Med. 33:45–51. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Lefrançais E, Roga S, Gautier V,
Gonzalez-de-Peredo A, Monsarrat B, Girard JP and Cayrol C: IL-33 is
processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and
cathepsin G. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:1673–1678. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Barnes PF, Fong SJ, Brennan PJ, Twomey PE,
Mazumder A and Modlin RL: Local production of tumor necrosis factor
and IFN-gamma in tuberculous pleuritis. J Immunol. 145:149–154.
1990.
|
|
17
|
Oboki K, Ohno T, Kajiwara N, Saito H and
Nakae S: IL-33 and IL-33 receptors in host defense and diseases.
Allergol Int. 59:143–160. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Okamoto M, Hasegawa Y, Hara T, Hashimoto
N, Imaizumi K, Shimokata K and Kawabe T: T-helper type 1/T-helper
type 2 balance in malignant pleural effusions compared to
tuberculous pleural effusions. Chest. 128:4030–4035. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Smithgall MD, Comeau MR, Yoon BR, Kaufman
D, Armitage R and Smith DE: IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type
responses through its activity on human basophils,
allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int Immunol.
20:1019–1030. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Bourgeois E, Van LP, Samson M, et al: The
pro-Th2 cytokine IL-33 directly interacts with invariant NKT and NK
cells to induce IFN-gamma production. Eur J Immunol. 39:1046–1055.
2009.
|
|
21
|
Espinassous Q, Garcia-de-Paco E,
Garcia-Verdugo I, et al: IL-33 enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory cytokine production from mouse macrophages by
regulating lipopolysaccharide receptor complex. J Immunol.
183:1446–1455. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Feng CG, Kaviratne M, Rothfuchs AG, et al:
NK cell-derived IFN-gamma differentially regulates innate
resistance and neutrophil response in T cell-deficient hosts
infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol.
177:7086–7093. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Schierloh P, Yokobori N, Alemán M, et al:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced gamma interferon
production by natural killer cells requires cross talk with
antigen-presenting cells involving Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and
the mannose receptor in tuberculous pleurisy. Infect Immun.
75:5325–5337. 2007.
|
|
24
|
Caramori G, Lasagna L, Casalini AG, et al:
Immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in
the parietal pleura of patients with tuberculous pleurisy. PLoS
One. 6:e226372011.
|
|
25
|
Miller AM: Role of IL-33 in inflammation
and disease. J Inflamm (Lond). 8:222011.
|
|
26
|
Joshi AD, Oak SR, Hartigan AJ, et al:
Interleukin-33 contributes to both M1 and M2 chemokine marker
expression in human macrophages. BMC Immunol. 11:522010.
|
|
27
|
Choi YS, Choi HJ, Min JK, et al:
Interleukin-33 induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability
through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production.
Blood. 114:3117–3126. 2009.
|
|
28
|
Jovanovic I, Radosavljevic G, Mitrovic M,
et al: ST2 deletion enhances innate and acquired immunity to murine
mammary carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 41:1902–1912. 2011.
|