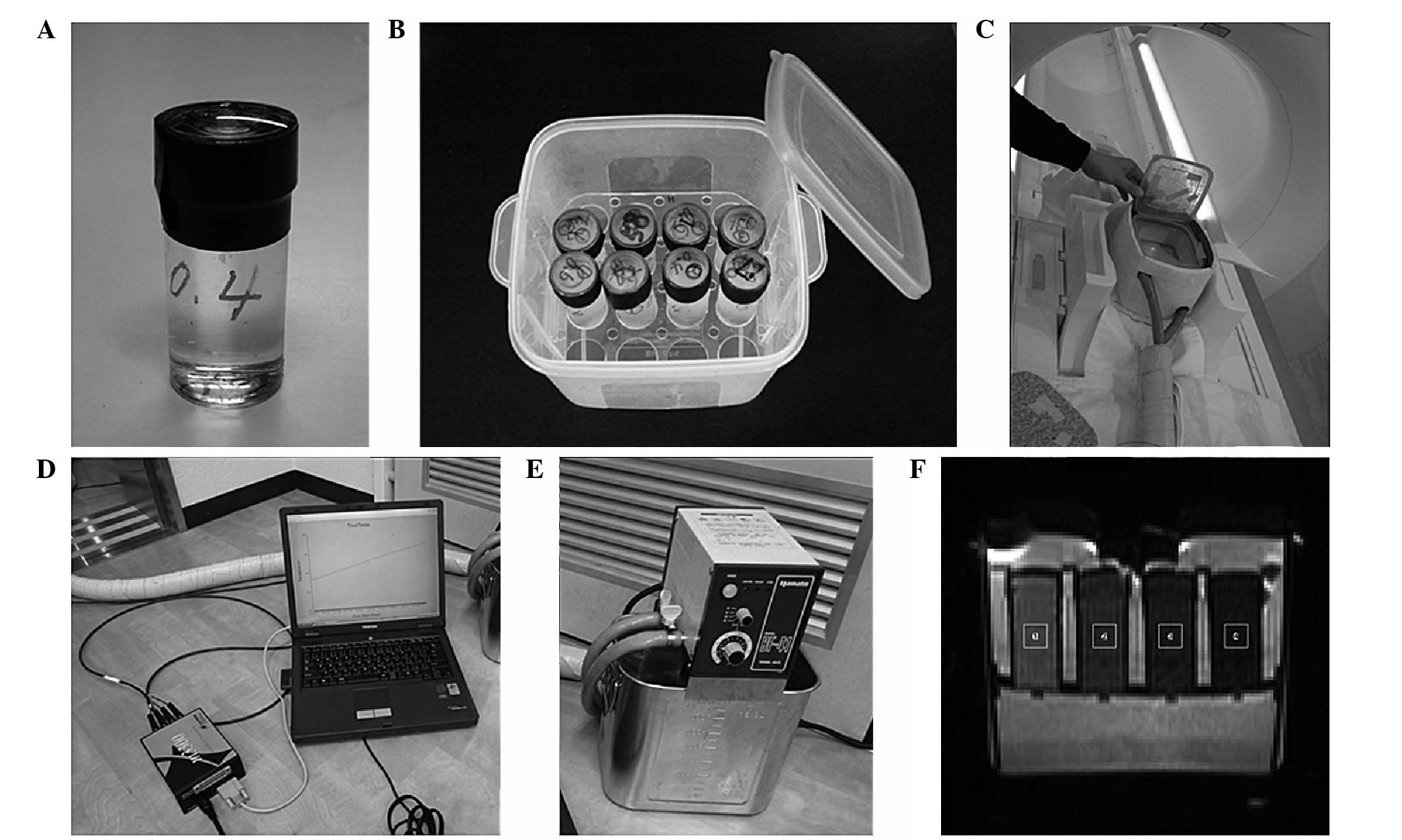
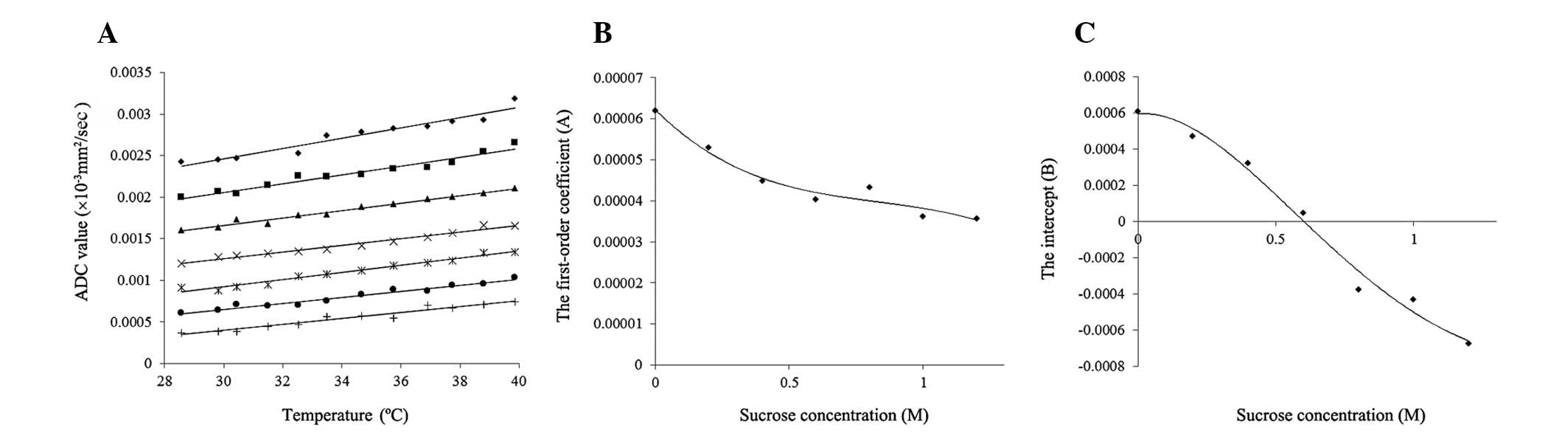
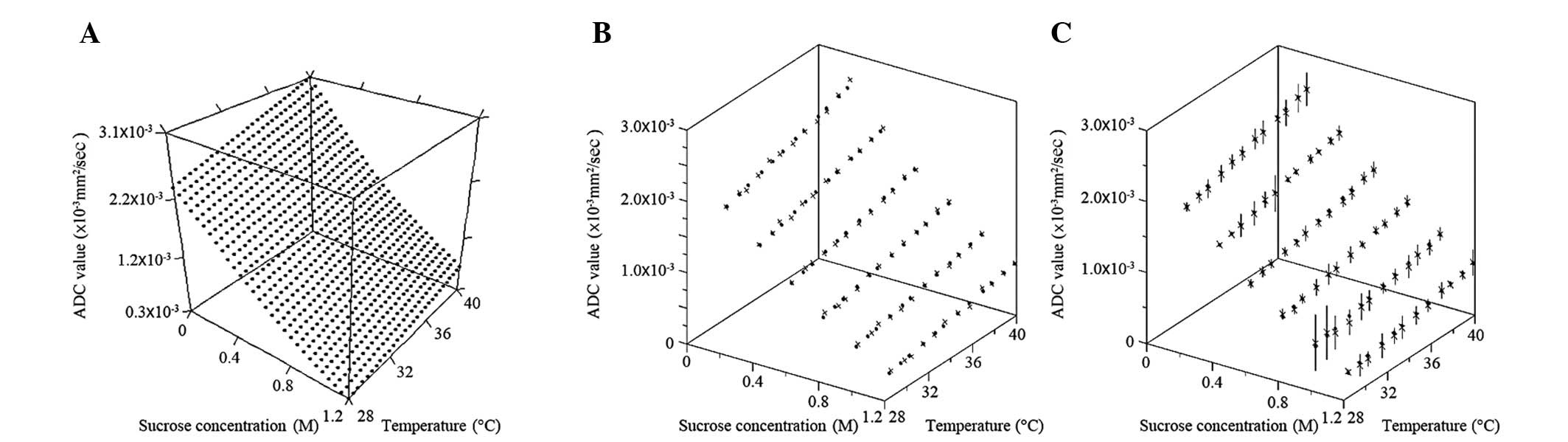
|
1
|
Srinivasan A, Dvorak R, Rohrer S and
Mukherji SK: Initial experience of 3-tesla apparent diffusion
coefficient values in characterizing squamous cell carcinomas of
the head and neck. Acta Radiol. 49:1079–1084. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Jung SH, Heo SH, Kim JW, et al: Predicting
response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced
rectal cancer: diffusion-weighted 3 Tesla MR imaging. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 35:110–116. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Kim HS, Kim CK, Park BK, Huh SJ and Kim B:
Evaluation of therapeutic response to concurrent chemoradiotherapy
in patients with cervical cancer using diffusion-weighted MR
imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 37:187–193. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Jensen LR, Garzon B, Heldahl MG, et al:
Diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in evaluation
of early treatment effects during neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
breast cancer patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 34:1099–1109.
2011.
|
|
5
|
Abdel Razek AA, Elkhamary S, Al-Mesfer S
and Alkatan HM: Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient at 3T
with prognostic parameters of retinoblastoma. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 33:944–948. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Doskaliyev A, Yamasaki F, Ohtaki M, et al:
Lymphomas and glioblastomas: Differences in the apparent diffusion
coefficient evaluated with high b-value diffusion-weighted magnetic
resonance imaging at 3T. Eur J Radiol. 81:339–344. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Mottola JC, Sahni VA, Erturk SM, et al:
Diffusion-weighted MRI of focal cystic pancreatic lesions at
3.0-Tesla: preliminary results. Abdom Imaging. 37:110–117.
2012.
|
|
8
|
Uehara T, Takahama J, Marugami N, et al:
Visualization of ovarian tumors using 3T MR imaging: diagnostic
effectiveness and difficulties. Magn Reson Med Sci. 11:171–178.
2012.
|
|
9
|
Tamura T, Usui S and Akiyama M:
Investigation of a phantom for diffusion weighted imaging that
controlled the apparent diffusion coefficient using gelatin and
sucrose. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 65:1485–1493.
2009.(In Japanese).
|
|
10
|
Matsuya R, Kuroda M, Matsumoto Y, et al: A
new phantom using polyethylene glycol as an apparent diffusion
coefficient standard for MR imaging. Int J Oncol. 35:893–900.
2009.
|
|
11
|
Einstein A: Investigations on the Theory
of the Brownian Movement. Fürth R: Dover Publications, Inc; New
York, NY: pp. p811956
|
|
12
|
Ramm LE, Whitlow MB and Mayer MM:
Transmembrane channel formation by complement: functional analysis
of the number of C5b6, C7, C8 and C9 molecules required for a
single channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:4751–4755. 1982.
|
|
13
|
Sasaki T, Kuroda M, Katashima K, et al:
In vitro assessment of factors affecting the apparent
diffusion coefficient of Ramos cells using bio-phantoms. Acta Med
Okayama. 66:263–270. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Anderson AW, Xie J, Pizzonia J, et al:
Effects of cell volume fraction changes on apparent diffusion in
human cells. Magn Reson Imaging. 18:689–695. 2000.
|
|
15
|
Roth Y, Ocherashvilli A, Daniels D, et al:
Quantification of water compartmentation in cell suspensions by
diffusion-weighted and T(2)-weighted MRI. Magn Reson Imaging.
26:88–102. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Pilatus U, Shim H, Artemov D, et al:
Intracellular volume and apparent diffusion constants of perfused
cancer cell cultures, as measured by NMR. Magn Reson Med.
37:825–832. 1997.
|
|
17
|
Kitajima K, Takahashi S, Ueno Y, et al:
Clinical utility of apparent diffusion coefficient values obtained
using high b-value when diagnosing prostate cancer using 3 tesla
MRI: comparison between ultra-high b-value (2000 s/mm2)
and standard high b-value (1000 s/mm2). J Magn Reson
Imaging. 36:198–205. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Cihangiroglu M, Ulug AM, Firat Z, et al:
High b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging of normal brain at 3T.
Eur J Radiol. 69:454–458. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Ilica AT, Artas H, Ayan A, et al: Initial
experience of 3 tesla apparent diffusion coefficient values in
differentiating benign and malignant thyroid nodules. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 37:1077–1082. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Lyng H, Haraldseth O and Rofstad EK:
Measurement of cell density and necrotic fraction in human melanoma
xenografts by diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magn
Reson Med. 43:828–836. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Kim H, Morgan DE, Buchsbaum DJ, et al:
Early therapy evaluation of combined anti-death receptor 5 antibody
and gemcitabine in orthotopic pancreatic tumor xenografts by
diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res.
68:8369–8376. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Kamel IR, Bluemke DA, Ramsey D, et al:
Role of diffusion-weighted imaging in estimating tumor necrosis
after chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 181:708–710. 2003.
|
|
23
|
Lang P, Wendland MF, Saeed M, et al:
Osteogenic sarcoma: noninvasive in vivo assessment of tumor
necrosis with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology.
206:227–235. 1998.
|
|
24
|
Gibbs P, Liney GP, Pickles MD, et al:
Correlation of ADC and T2 measurements with cell density in
prostate cancer at 3.0 Tesla. Invest Radiol. 44:572–576. 2009.
|
|
25
|
Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC and
Provenzale JM: Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of
water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology.
224:177–183. 2002.
|
|
26
|
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Chen F, et al:
Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in monitoring the effect of a
vascular targeting agent on rhabdomyosarcoma in rats. Radiology.
234:756–764. 2005.
|