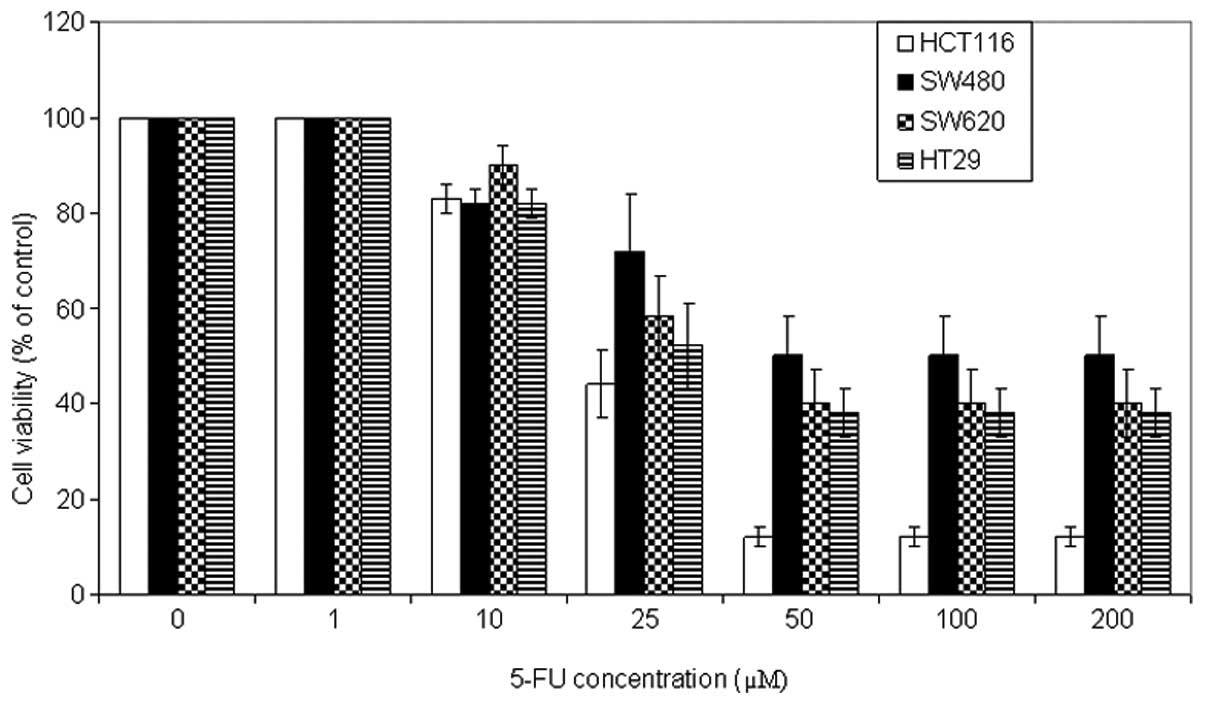
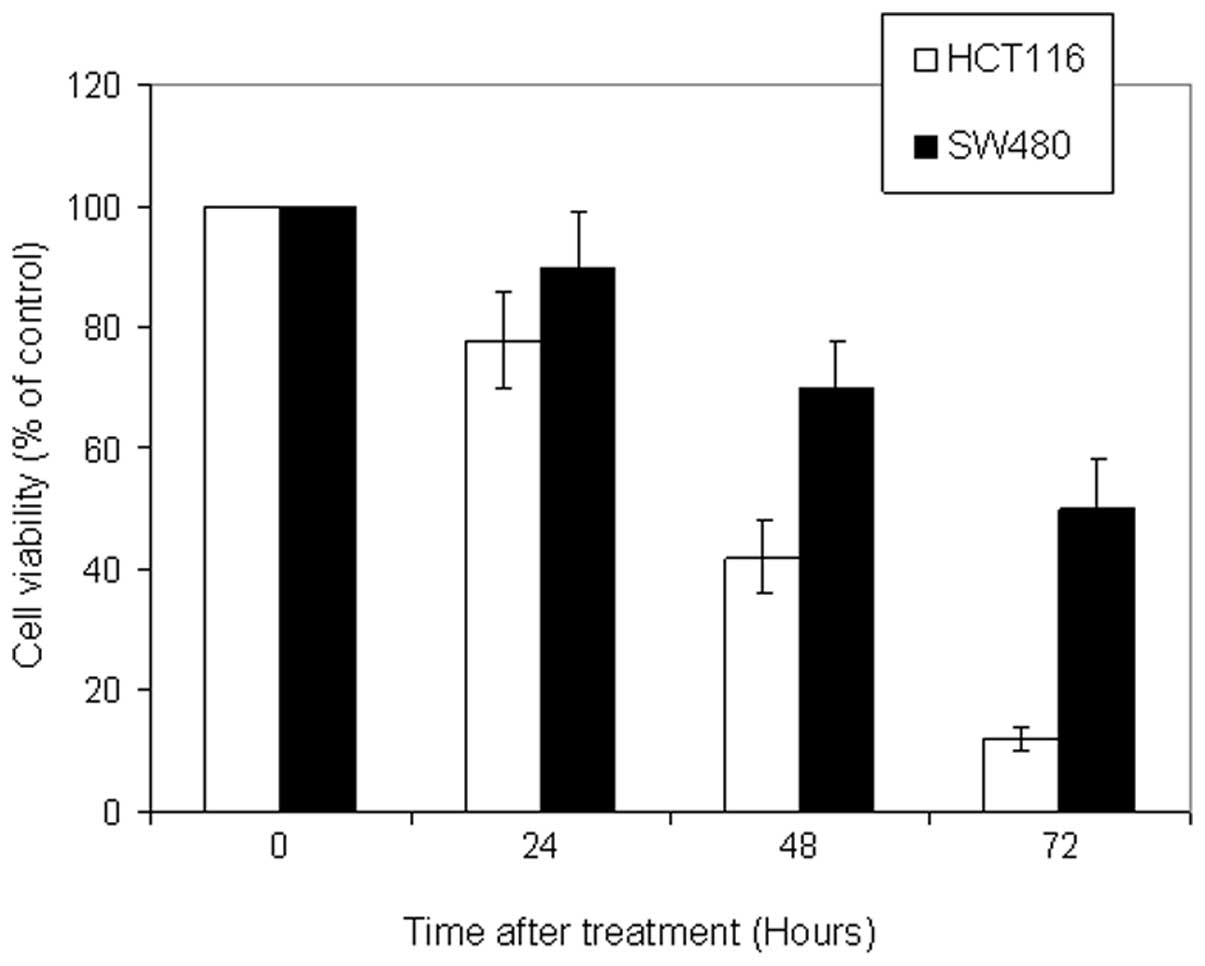
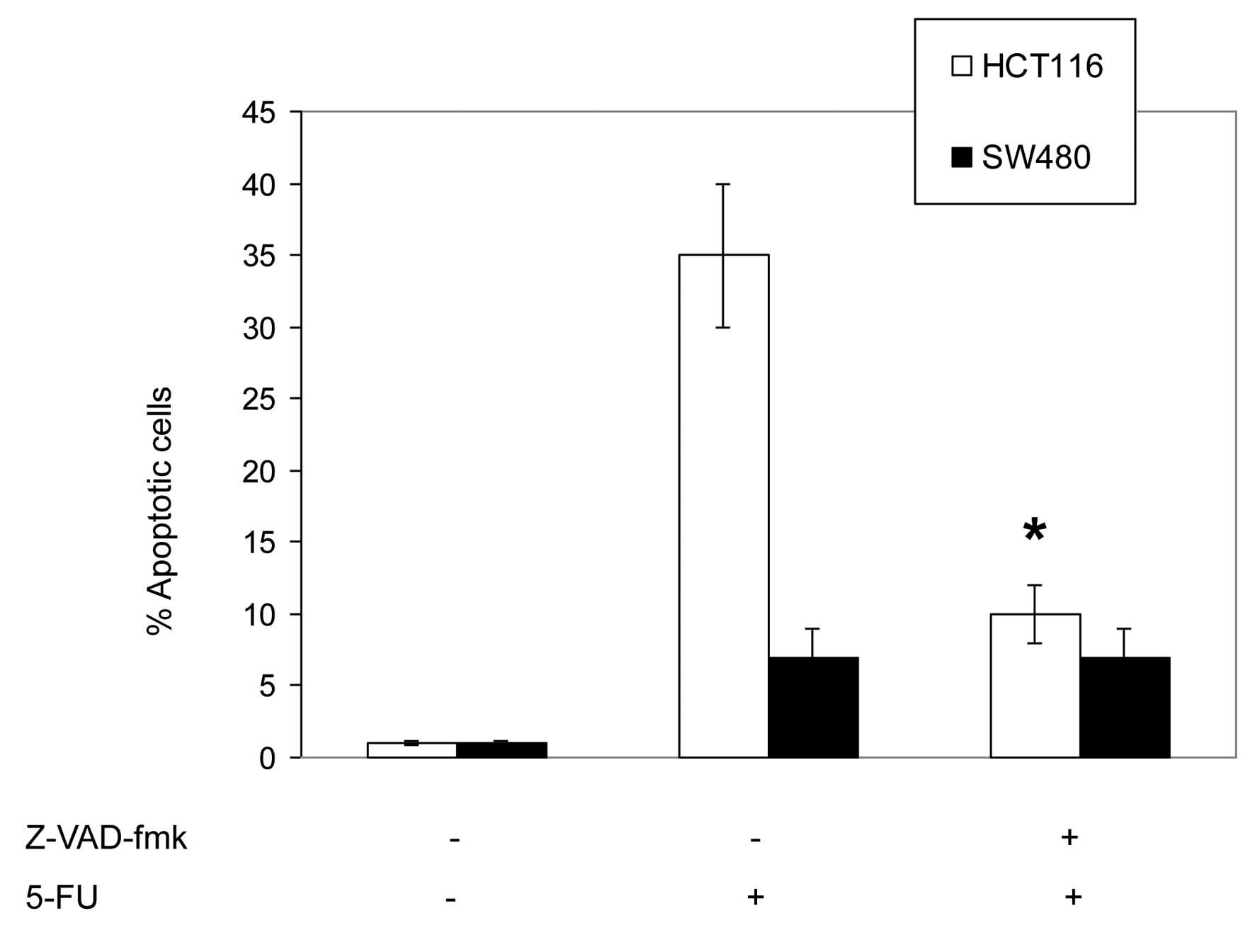
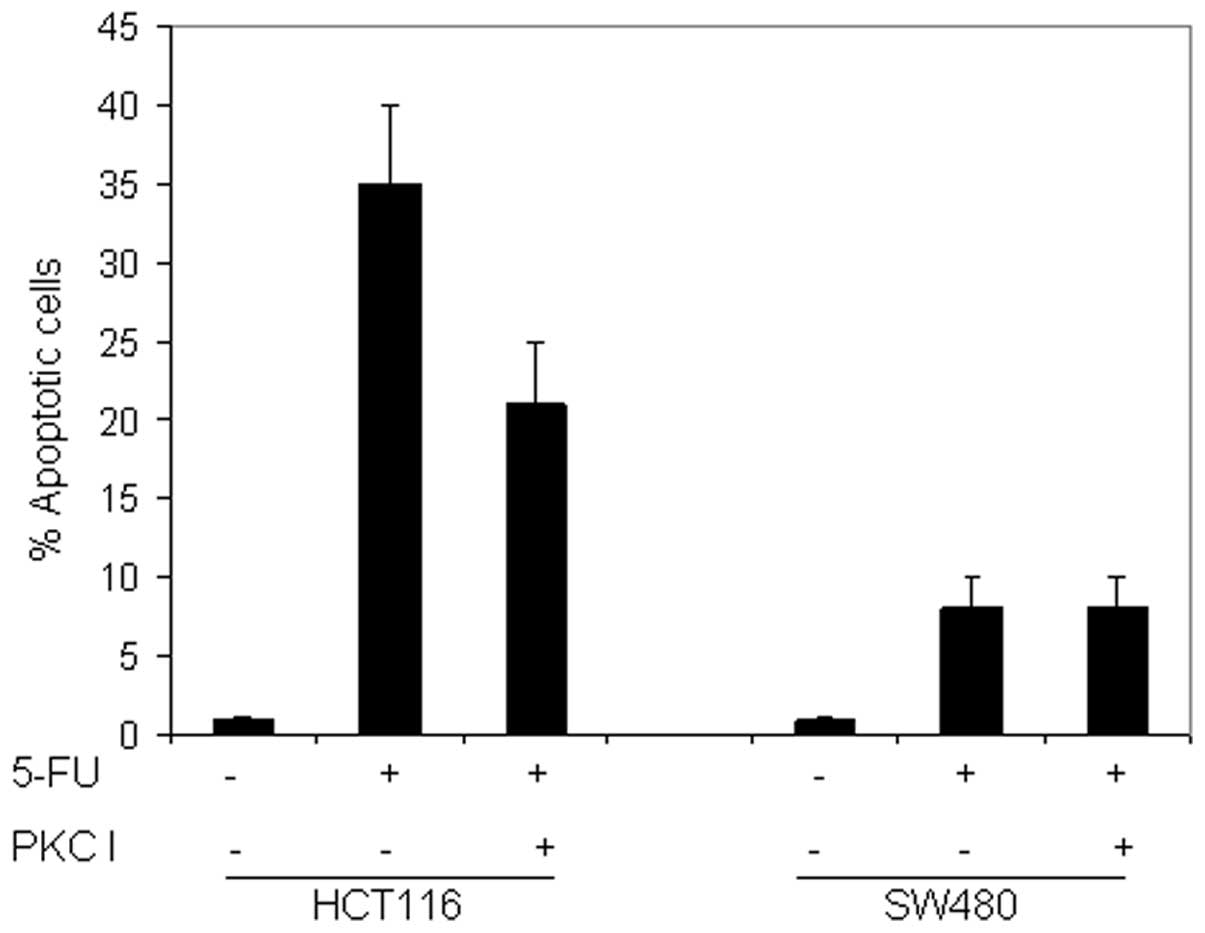
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Al-Tarawneh M, Khatib S and Arqub K:
Cancer incidence in Jordan, 1996–2005. East Mediterr Health J.
16:837–845. 2010.
|
|
3
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003.
|
|
4
|
Willett CG, Czito BG and Bendell JC:
Radiation therapy in stage II and III rectal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:6903–6908. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Goldberg RM, Rothenberg ML, Van Cutsem E,
et al: The continuum of care: a paradigm for the management of
metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 12:38–50. 2007.
|
|
6
|
Loehrer PJ Sr, Turner S, Kubilis P, et al:
A prospective randomized trial of fluorouracil versus fluorouracil
plus cisplatin in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a
Hoosier Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol. 6:642–648. 1988.
|
|
7
|
Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, et
al: Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with
fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic
colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet.
355:1041–1047. 2000.
|
|
8
|
Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R, et al:
Phase III multicenter randomized trial of oxaliplatin added to
chronomodulated fluorouracil-leucovorin as first-line treatment of
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 18:136–147. 2000.
|
|
9
|
Newton AC: Protein kinase C: structural
and spatial regulation by phosphorylation, cofactors, and
macromolecular interactions. Chem Rev. 101:2353–2364. 2001.
|
|
10
|
Nishizuka Y: Protein kinase C and lipid
signaling for sustained cellular responses. FASEB J. 9:484–496.
1995.
|
|
11
|
Basu A, Lu D, Sun B, et al: Proteolytic
activation of protein kinase C-epsilon by caspase-mediated
processing and transduction of antiapoptotic signals. J Biol Chem.
277:41850–41856. 2002.
|
|
12
|
Akita Y: Protein kinase C-epsilon
(PKC-epsilon): its unique structure and function. J Biochem.
132:847–52. 2002.
|
|
13
|
Reyland ME, Anderson SM, Matassa AA,
Barzen KA and Quissell DO: Protein kinase C delta is essential for
etoposide-induced apoptosis in salivary gland acinar cells. J Biol
Chem. 274:19115–19123. 1999.
|
|
14
|
Mhaidat NM, Zhang XD, Allen J, et al:
Temozolomide induces senescence but not apoptosis in human melanoma
cells. Br J Cancer. 97:1225–1233. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Mhaidat NM, Wang Y, Kiejda KA, Zhang XD
and Hersey P: Docetaxel-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells is
dependent on activation of caspase-2. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:752–761.
2007.
|
|
16
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998.
|
|
17
|
Jaattela M: Escaping cell death: survival
proteins in cancer. Exp Cell Res. 248:30–43. 1999.
|
|
18
|
Tinel A and Tschopp J: The PIDDosome, a
protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response
to genotoxic stress. Science. 304:843–846. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Lin CF, Chen CL, Chang WT, et al:
Sequential caspase-2 and caspase-8 activation upstream of
mitochondria during ceramideand etoposide-induced apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 279:40755–40761. 2004.
|
|
20
|
Baliga BC, Read SH and Kumar S: The
biochemical mechanism of caspase-2 activation. Cell Death Differ.
11:1234–1241. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M, Orrenius S and
Zhivotovsky B: Functional connection between p53 and caspase-2 is
essential for apoptosis induced by DNA damage. Oncogene.
25:5683–5692. 2006.
|
|
22
|
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A,
Fernandes-Alnemri T and Alnemri ES: Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by
releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria. J Biol Chem.
277:13430–13437. 2002.
|
|
23
|
Basu A, Woolard MD and Johnson CL:
Involvement of protein kinase C-delta in DNA damage-induced
apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 8:899–908. 2001.
|
|
24
|
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, et al:
Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade: hierarchical
activation of caspases-2, -3, -6, -7, -8, and -10 in a
caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 144:281–292. 1999.
|
|
25
|
Ding L, Wang H, Lang W and Xiao L: Protein
kinase C-epsilon promotes survival of lung cancer cells by
suppressing apoptosis through dysregulation of the mitochondrial
caspase pathway. J Biol Chem. 277:35305–35313. 2002.
|
|
26
|
McJilton MA, Van Sikes C, Wescott GG, et
al: Protein kinase Cepsilon interacts with Bax and promotes
survival of human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 22:7958–7968.
2003.
|
|
27
|
Gillespie S, Zhang XD and Hersey P:
Variable expression of protein kinase C epsilon in human melanoma
cells regulates sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:668–676. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Matassa AA, Carpenter L, Biden TJ,
Humphries MJ and Reyland ME: PKCdelta is required for
mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in salivary epithelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 276:29719–29728. 2001.
|
|
29
|
Stempka L, Girod A, Müller HJ, et al:
Phosphorylation of protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta) at threonine
505 is not a prerequisite for enzymatic activity. Expression of rat
PKCdelta and an alanine 505 mutant in bacteria in a functional
form. J Biol Chem. 272:6805–6811. 1997.
|
|
30
|
Emoto Y, Kisaki H, Manome Y, Kharbanda S
and Kufe D: Activation of protein kinase Cdelta in human myeloid
leukemia cells treated with 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine.
Blood. 87:1990–1996. 1996.
|
|
31
|
Gomel R, Xiang C, Finniss S, et al: The
localization of protein kinase Cdelta in different subcellular
sites affects its proapoptotic and antiapoptotic functions and the
activation of distinct downstream signaling pathways. Mol Cancer
Res. 5:627–639. 2007.
|
|
32
|
Basu A and Tu H: Activation of ERK during
DNA damage-induced apoptosis involves protein kinase Cdelta.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:1068–1073. 2005.
|
|
33
|
Owens TW, Valentijn AJ, Upton JP, et al:
Apoptosis commitment and activation of mitochondrial Bax during
anoikis is regulated by p38MAPK. Cell Death Differ. 16:1551–1562.
2009.
|
|
34
|
Choi SY, Kim MJ, Kang CM, et al:
Activation of Bak and Bax through c-abl-protein kinase Cdelta-p38
MAPK signaling in response to ionizing radiation in human non-small
cell lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 281:7049–7059. 2006.
|
|
35
|
Vucic D, Dixit VM and Wertz IE:
Ubiquitylation in apoptosis: a post-translational modification at
the edge of life and death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:439–452.
2011.
|