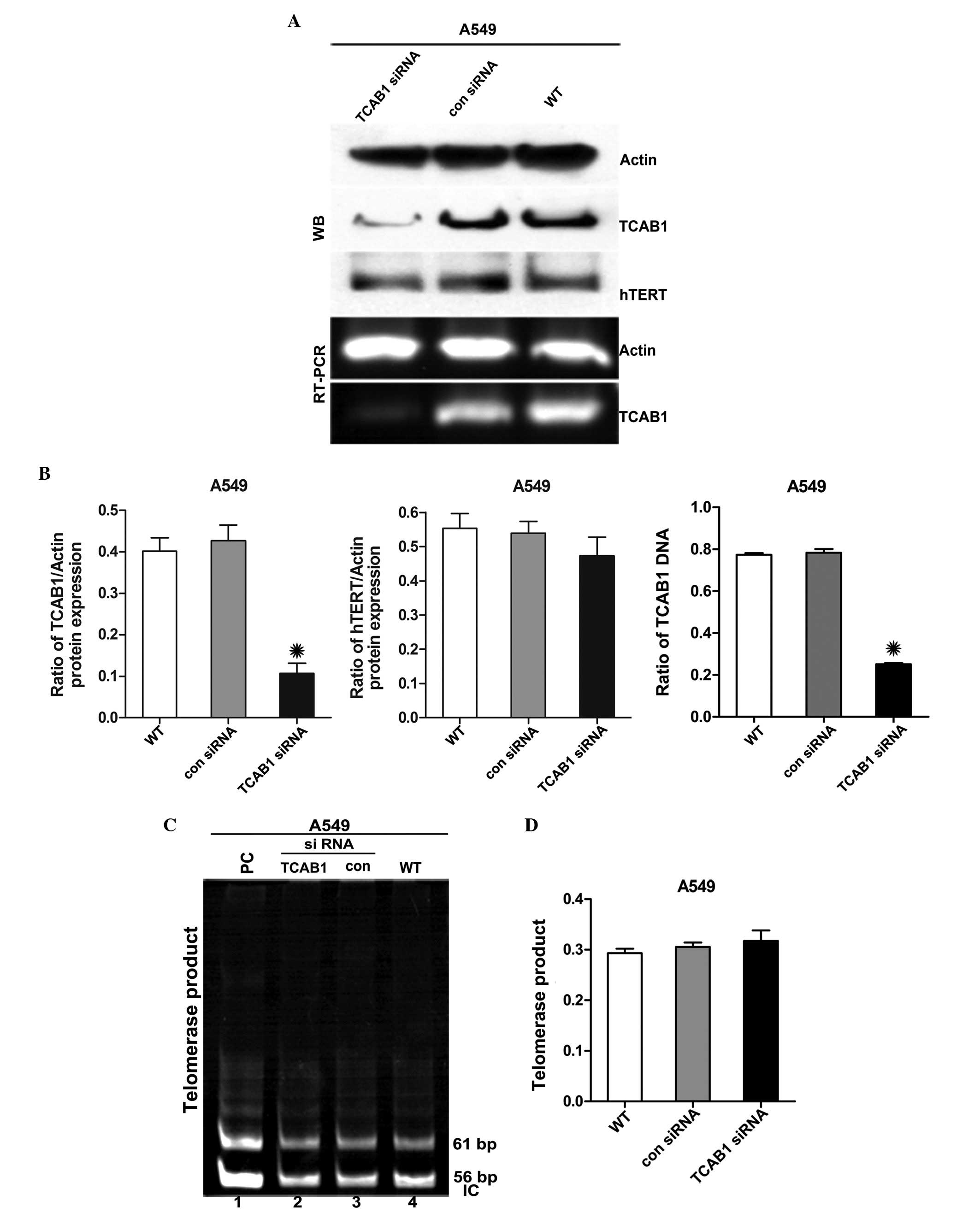
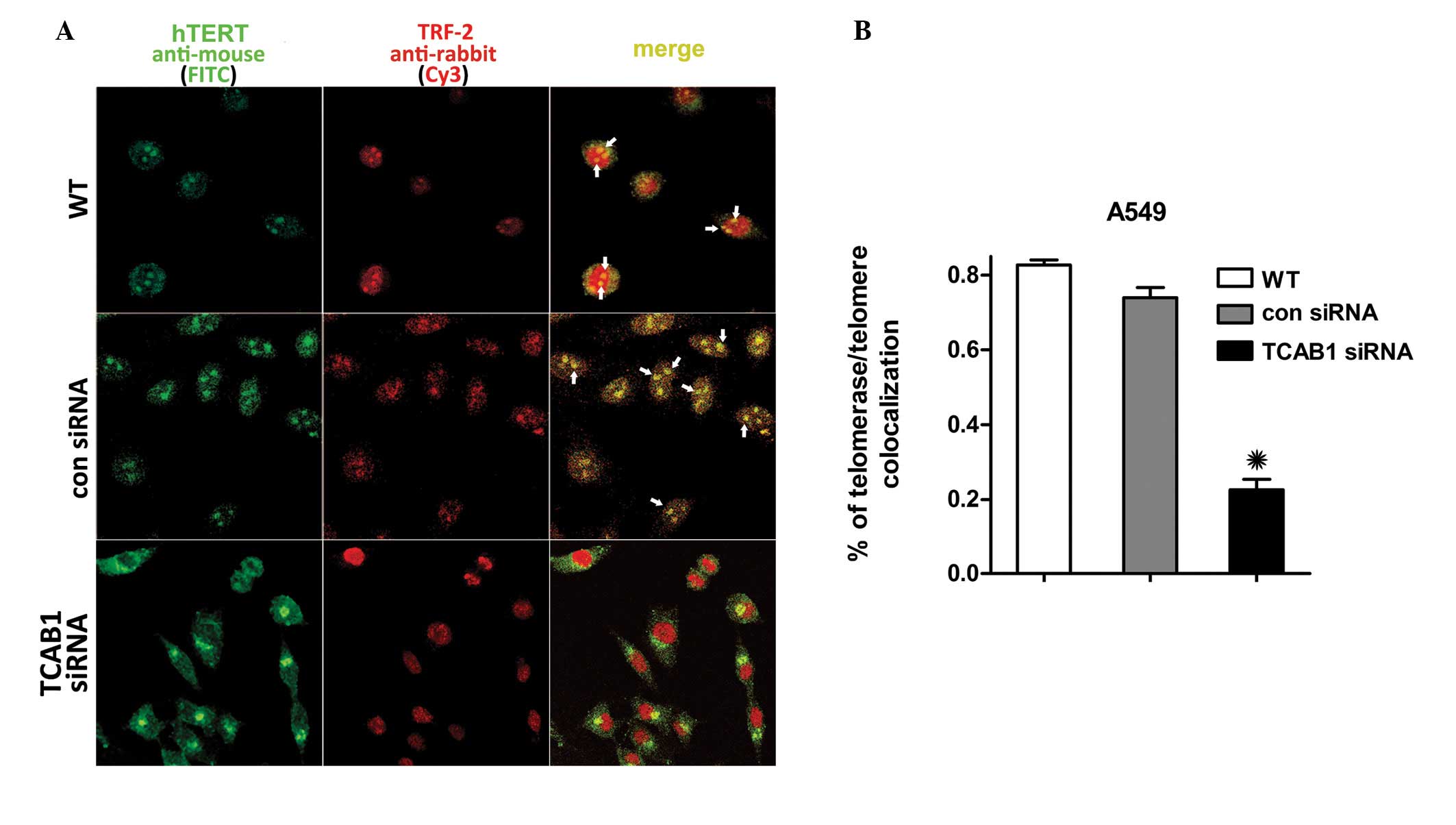
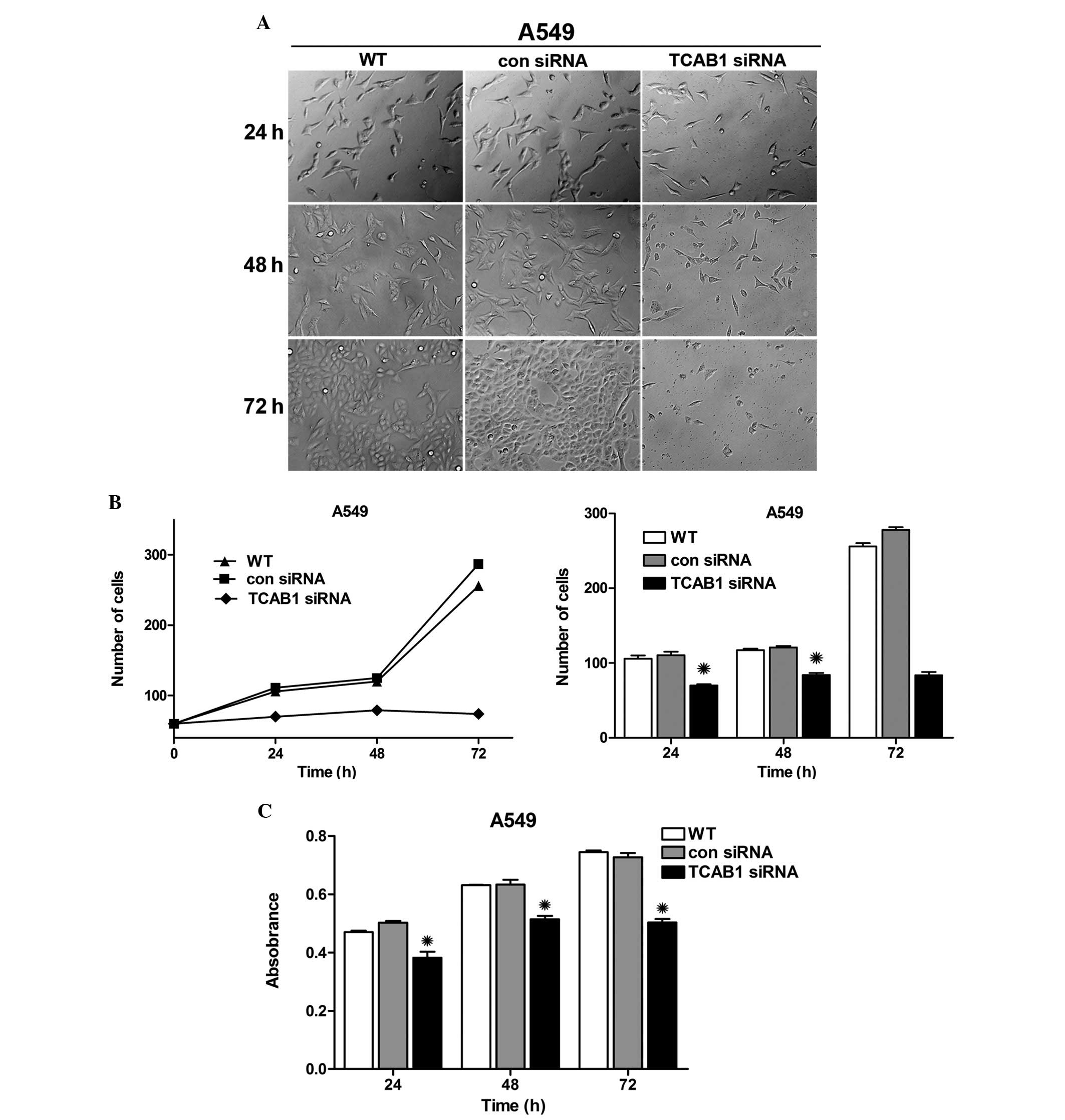
|
1
|
Greider CW and Blackburn EH:
Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity
in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 43:405–413. 1985.
|
|
2
|
Shay JW and Bacchetti S: A survey of
telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur J Cancer. 33:787–791.
1997.
|
|
3
|
Cui W, Wylie D, Aslam S, et al:
Telomerase-immortalized sheep fibroblasts can be reprogrammed by
nuclear transfer to undergo early development. Biol Reprod.
69:15–21. 2003.
|
|
4
|
Bolzán AD: Chromosomal aberrations
involving telomeres and interstitial telomeric sequences.
Mutagenesis. 27:1–15. 2012.
|
|
5
|
Granger MP, Wright WE and Shay JW:
Telomerase in cancer and aging. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 41:29–40.
2002.
|
|
6
|
Hoos A, Hepp HH, Kaul S, Ahlert T, Bastert
G and Wallwiener D: Telomerase activity correlates with tumor
aggressiveness and reflects therapy effect in breast cancer. Int J
Cancer. 79:8–12. 1998.
|
|
7
|
Yashima K, Milchgrub S, Gollahon LS, et
al: Telomerase enzyme activity and RNA expression during the
multistage pathogenesis of breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
4:229–234. 1998.
|
|
8
|
Mokbel K and Williams NJ: Telomerase and
breast cancer: from diagnosis to therapy. Int J Surg Investig.
2:85–88. 2000.
|
|
9
|
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS, et al: The RNA
component of human telomerase. Science. 269:1236–1241. 1995.
|
|
10
|
Cech TR, Nakamura TM and Lingner J:
Telomerase is a true reverse transcriptase. A review. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 62:1202–1205. 1997.
|
|
11
|
Avilion AA, Piatyszek MA, Gupta J, Shay
JW, Bacchetti S and Greider CW: Human telomerase RNA and telomerase
activity in immortal cell lines and tumor tissues. Cancer Res.
56:645–650. 1996.
|
|
12
|
Ito H, Kyo S, Kanaya T, Takakura M, Inoue
M and Namiki M: Expression of human telomerase subunits and
correlation with telomerase activity in urothelial cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 4:1603–1608. 1998.
|
|
13
|
Kyo S, Kanaya T, Takakura M, Tanaka M and
Inoue M: Human telomerase reverse transcriptase as a critical
determinant of telomerase activity in normal and malignant
endometrial tissues. Int J Cancer. 80:60–63. 1999.
|
|
14
|
Cristofari G, Adolf E, Reichenbach P, et
al: Human telomerase RNA accumulation in Cajal bodies facilitates
telomerase recruitment to telomeres and telomere elongation. Mol
Cell. 27:882–889. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Zhu Y, Tomlinson RL, Lukowiak AA, Terns RM
and Terns MP: Telomerase RNA accumulates in Cajal bodies in human
cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 15:81–90. 2004.
|
|
16
|
Tomlinson RL, Abreu EB, Ziegler T, et al:
Telomerase reverse transcriptase is required for the localization
of telomerase RNA to cajal bodies and telomeres in human cancer
cells. Mol Biol Cell. 19:3793–3800. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Arnoult N, Schluth-Bolard C, Letessier A,
et al: Replication timing of human telomeres is chromosome
arm-specific, influenced by subtelomeric structures and connected
to nuclear localization. PLoS Genet. 6:e10009202010.
|
|
18
|
Mahmoudi S, Henriksson S, Weibrecht I, et
al: WRAP53 is essential for Cajal body formation and for targeting
the survival of motor neuron complex to Cajal bodies. PLoS Biol.
8:e10005212010.
|
|
19
|
Tycowski KT, Shu MD, Kukoyi A and Steitz
JA: A conserved WD40 protein binds the Cajal body localization
signal of scaRNP particles. Mol Cell. 34:47–57. 2009.
|
|
20
|
Venteicher AS, Abreu EB, Meng Z, et al: A
human telomerase holoenzyme protein required for Cajal body
localization and telomere synthesis. Science. 323:644–648.
2009.
|
|
21
|
Egan ED and Collins K: An enhanced H/ACA
RNP assembly mechanism for human telomerase RNA. Mol Cell Biol.
32:2428–2439. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Smogorzewska A, van Steensel B, Bianchi A,
et al: Control of human telomere length by TRF1 and TRF2. Mol Cell
Biol. 20:1659–1668. 2000.
|
|
23
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008.
|
|
24
|
Helmstetter CE: DNA synthesis during the
division cycle of rapidly growing Escherichia coli B/r. J
Mol Biol. 31:507–518. 1968.
|
|
25
|
Hu J, Hwang SS, Liesa M, et al:
Antitelomerase therapy provokes ALT and mitochondrial adaptive
mechanisms in cancer. Cell. 148:651–663. 2012.
|
|
26
|
Henson JD, Neumann AA, Yeager TR and
Reddel RR: Alternative lengthening of telomeres in mammalian cells.
Oncogene. 21:598–610. 2002.
|
|
27
|
Slatter TL, Tan X, Yuen YC, et al: The
alternative lengthening of telomeres pathway may operate in
non-neoplastic human cells. J Pathol. 226:509–518. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Lundblad V and Blackburn EH: An
alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues
est1-senescence. Cell. 73:347–360. 1993.
|
|
29
|
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Dalla-Pozza L,
Dunham MA and Reddel RR: Evidence for an alternative mechanism for
maintaining telomere length in human tumors and tumor-derived cell
lines. Nat Med. 3:1271–1274. 1997.
|
|
30
|
Pajalunga D, Mazzola A, Franchitto A,
Puggioni E and Crescenzi M: The logic and regulation of cell cycle
exit and reentry. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:8–15. 2008.
|
|
31
|
Cesare AJ and Karlseder J: A three-state
model of telomere control over human proliferative boundaries. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 24:731–738. 2012.
|
|
32
|
Verdun RE and Karlseder J: The DNA damage
machinery and homologous recombination pathway act consecutively to
protect human telomeres. Cell. 127:709–720. 2006.
|
|
33
|
Stern JL, Zyner KG, Pickett HA, Cohen SB
and Bryan TM: Telomerase recruitment requires both TCAB1 and Cajal
bodies independently. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2384–2395. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Zhong FL, Batista LF, Freund A, Pech MF,
Venteicher AS and Artandi SE: TPP1 OB-fold domain controls telomere
maintenance by recruiting telomerase to chromosome ends. Cell.
150:481–494. 2012.
|
|
35
|
Schildkraut JM, Goode EL, Clyde MA, et al:
Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Group: Single nucleotide
polymorphisms in the TP53 region and susceptibility to invasive
epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 69:2349–2357. 2009.
|