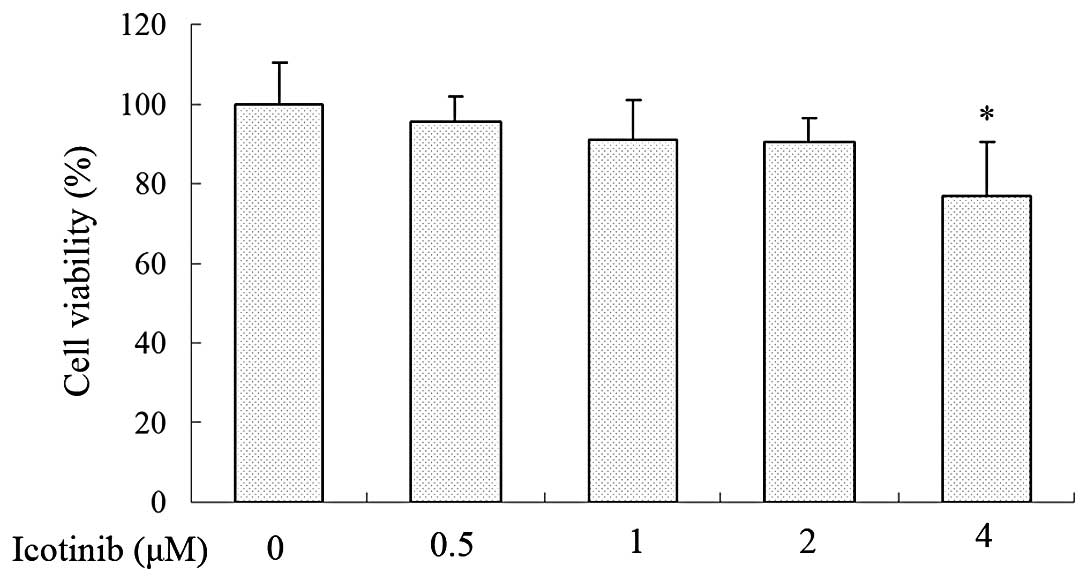
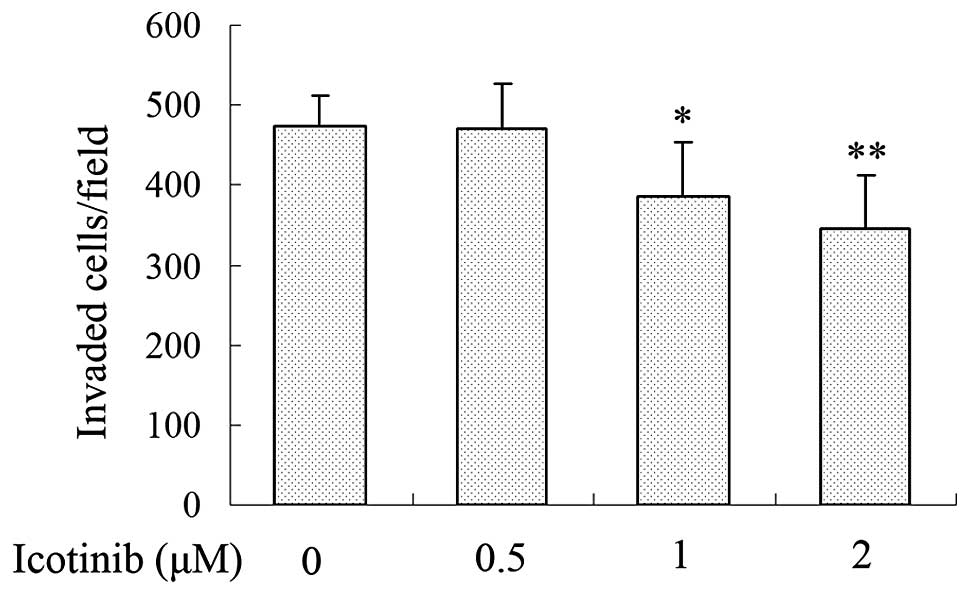
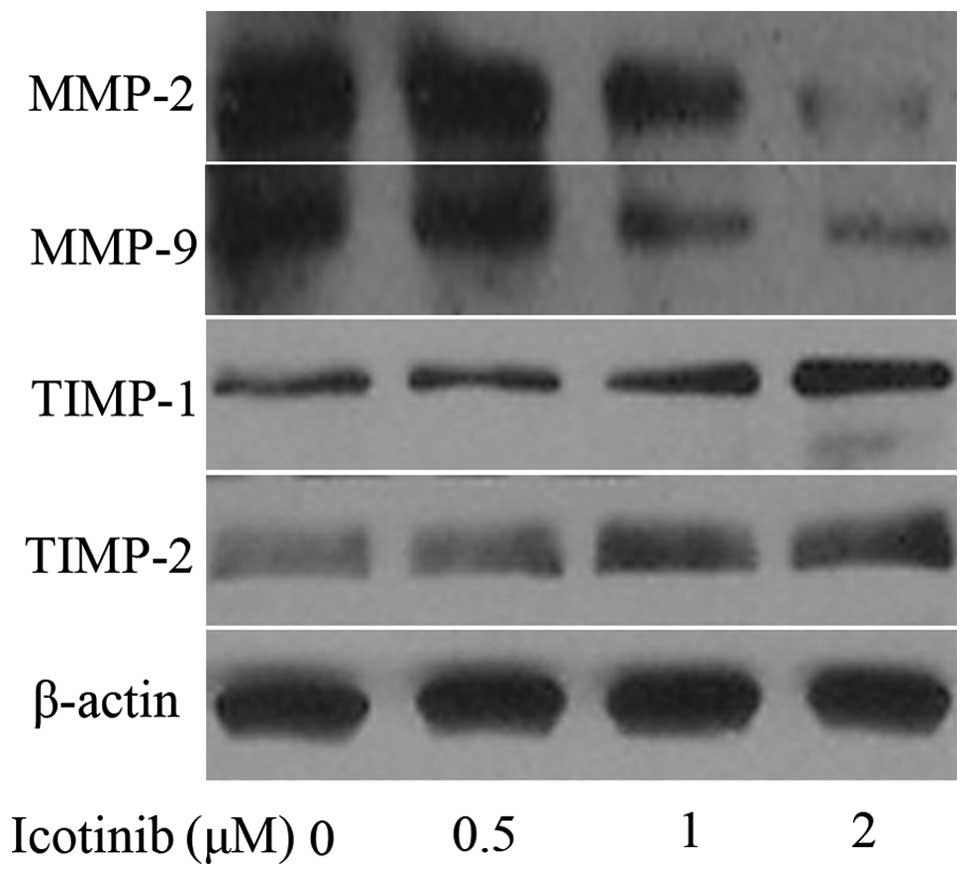
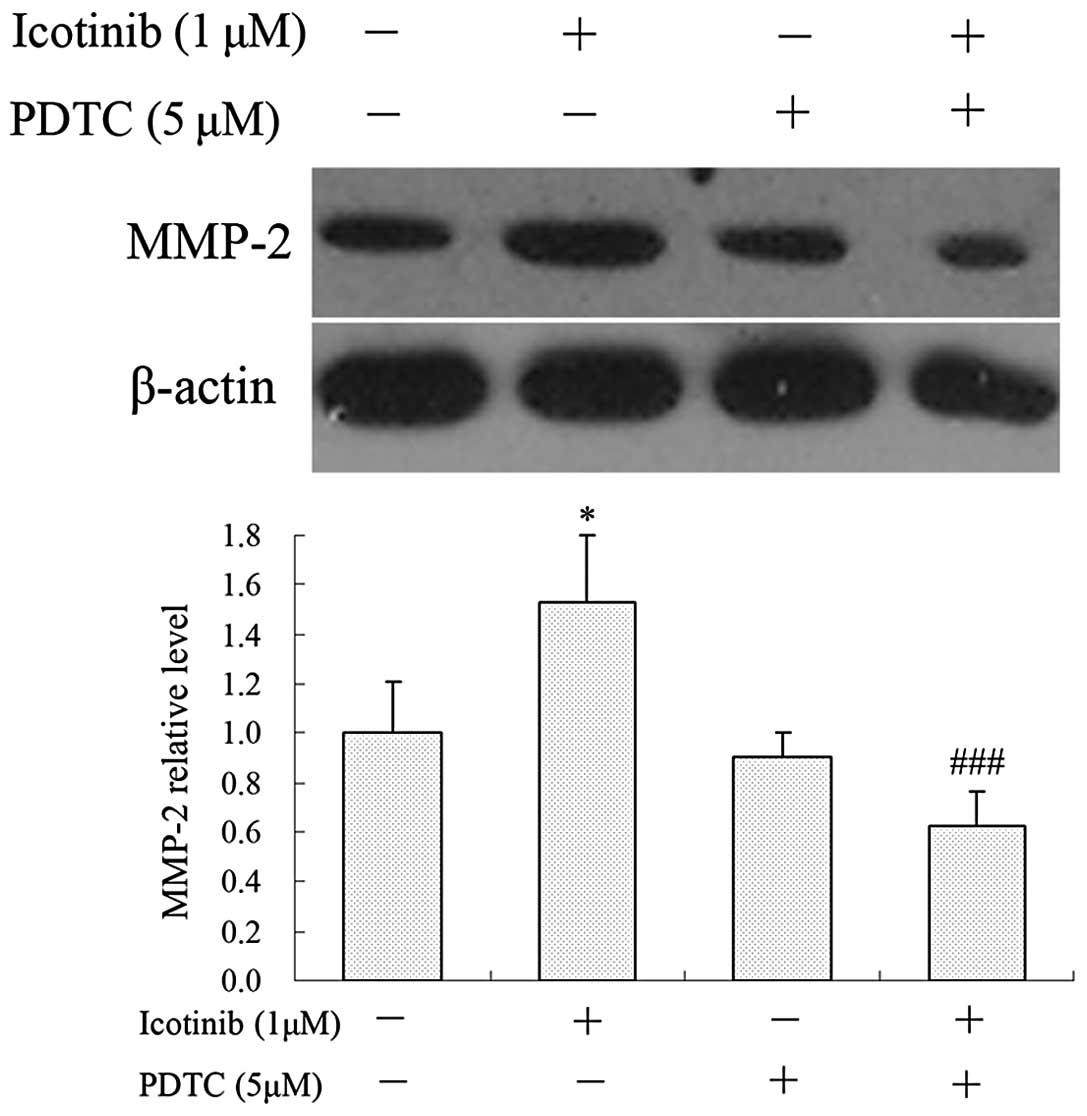
|
1
|
Chen HJ, Lin CM, Lee CY, et al: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate suppresses EGF-stimulated SAS human oral squamous
carcinoma cell invasion by targeting EGF receptor signaling. Int J
Oncol. 43:629–637. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Li F, Li C, Zhang H, et al: VI-14, a novel
flavonoid derivative, inhibits migration and invasion of human
breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 261:217–226. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Zhou H, Kimura K, Orita T, Nishida T and
Sonoda KH: Inhibition by medroxyprogesterone acetate of
interleukin-1β-induced collagen degradation by corneal fibroblasts.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:4213–4219. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Kuo PL, Shen KH, Hung SH and Hsu YL:
CXCL1/GROα increases cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer
by decreasing fibulin-1 expression through NF-κB/HDAC1 epigenetic
regulation. Carcinogenesis. 33:2477–2487. 2012.
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Sengupta R, Banerjee S, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein inhibits cell
growth and invasion in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 66:7653–7660.
2006.
|
|
6
|
Xu CL, Lu XL, Yan XN, Wang HL and Chen SQ:
Effects of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signal pathway on FSH facilitation on
cell proliferation and invasion by human epithelial ovarian cancer.
Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 47:134–138. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Ko HS, Lee HJ, Kim SH and Lee EO:
Piceatannol suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through the
inhibition of MMP-9: involvement of PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways. J
Agric Food Chem. 60:4083–4089. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Gan HK, Burgess AW, Clayton AH and Scott
AM: Targeting of a conformationally exposed, tumor-specific epitope
of EGFR as a strategy for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 72:2924–2930.
2012.
|
|
9
|
Sobhakumari A, Schickling BM, Love-Homan
L, et al: NOX4 mediates cytoprotective autophagy induced by the
EGFR inhibitor erlotinib in head and neck cancer cells. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 272:736–745. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Li P, Zhang Q, Torossian A, et al:
Simultaneous inhibition of EGFR and PI3K enhances radiosensitivity
in human breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:e391–e397.
2012.
|
|
11
|
Li D, Ji H, Zaghlul S, et al: Therapeutic
anti-EGFR antibody 806 generates responses in murine de novo EGFR
mutant-dependent lung carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 117:346–352.
2007.
|
|
12
|
Yang G, Yao Y, Zhou J and Zhao Q: Effects
of icotinib, a novel epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol
Rep. 27:2066–2072. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Gao Z, Chen W, Zhang X, et al: Icotinib, a
potent and specific EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits growth
of squamous cell carcinoma cell line A431 through negatively
regulating AKT signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:351–356.
2013.
|
|
14
|
Gu A, Shi C, Xiong L, Chu T, Pei J and Han
B: Efficacy and safety evaluation of icotinib in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:90–94.
2013.
|
|
15
|
Zhao Q, Shentu J, Xu N, et al: Phase I
study of icotinib hydrochloride (BPI-2009H), an oral EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced NSCLC and other solid
tumors. Lung Cancer. 73:195–202. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Xu Q, Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi C and Tan
Y: The impact of TGF-β1 on the mRNA expression of TβR I, TβR II,
Smad4 and the invasiveness of the JEG-3 placental choriocarcinoma
cell line. Oncol Lett. 4:1344–1348. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Bethea JR, Castro M, Keane RW, Lee TT,
Dietrich WD and Yezierski RP: Traumatic spinal cord injury induces
nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J Neurosci. 18:3251–3260.
1998.
|
|
18
|
Mu X, Zhang Y, Qu X, et al: Ubiquitin
ligase Cbl-b is involved in icotinib (BPI-2009H)-induced apoptosis
and G1 phase arrest of EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2013:7263752013.
|
|
19
|
Stark AM, Anuszkiewicz B, Mentlein R,
Yoneda T, Mehdorn HM and Held-Feindt J: Differential expression of
matrix metalloproteinases in brain- and bone-seeking clones of
metastatic MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J Neurooncol. 81:39–48.
2007.
|
|
20
|
Takino T, Miyamori H, Watanabe Y, Yoshioka
K, Seiki M and Sato H: Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase
regulates collagen-dependent mitogen-activated
protein/extracellular signal-related kinase activation and cell
migration. Cancer Res. 64:1044–1049. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Sounni NE, Rozanov DV, Remacle AG,
Golubkov VS, Noel A and Strongin AY: Timp-2 binding with cellular
MT1-MMP stimulates invasion-promoting MEK/ERK signaling in cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 126:1067–1078. 2010.
|
|
22
|
Tan BK, Adya R, Chen J, Lehnert H, Sant
Cassia LJ and Randeva HS: Metformin treatment exerts antiinvasive
and antimetastatic effects in human endometrial carcinoma cells. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:808–816. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Yan KH, Lee LM, Yan SH, et al: Tomatidine
inhibits invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma cell A549 by
reducing matrix metalloproteinases expression. Chem Biol Interact.
203:580–587. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Diosgenin
inhibits osteoclastogenesis, invasion, and proliferation through
the downregulation of Akt, I kappa B kinase activation and NF-kappa
B-regulated gene expression. Oncogene. 25:1463–1473. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Lee CH, Jeon YT, Kim SH and Song YS:
NF-kappaB as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy.
Biofactors. 29:19–35. 2007.
|