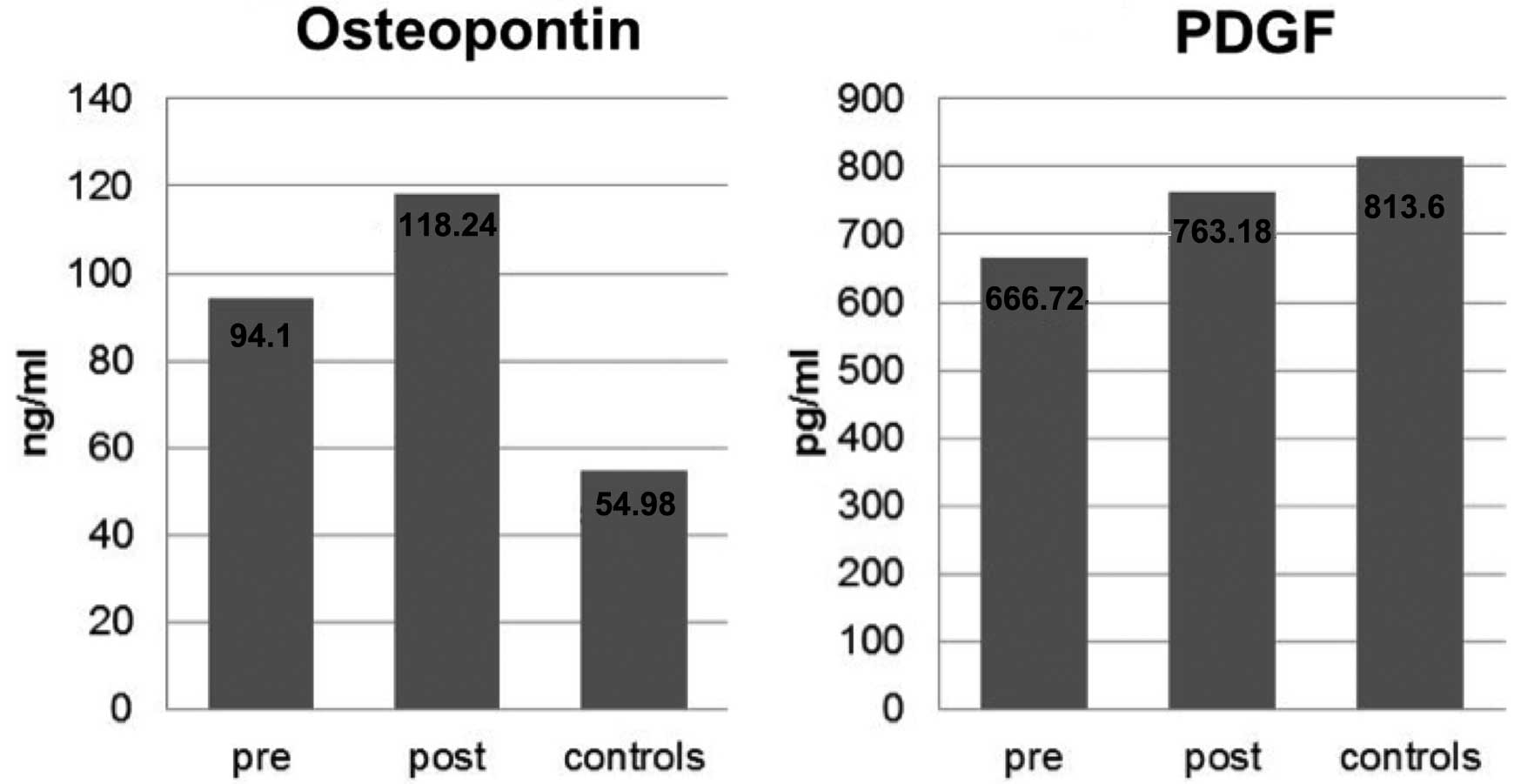
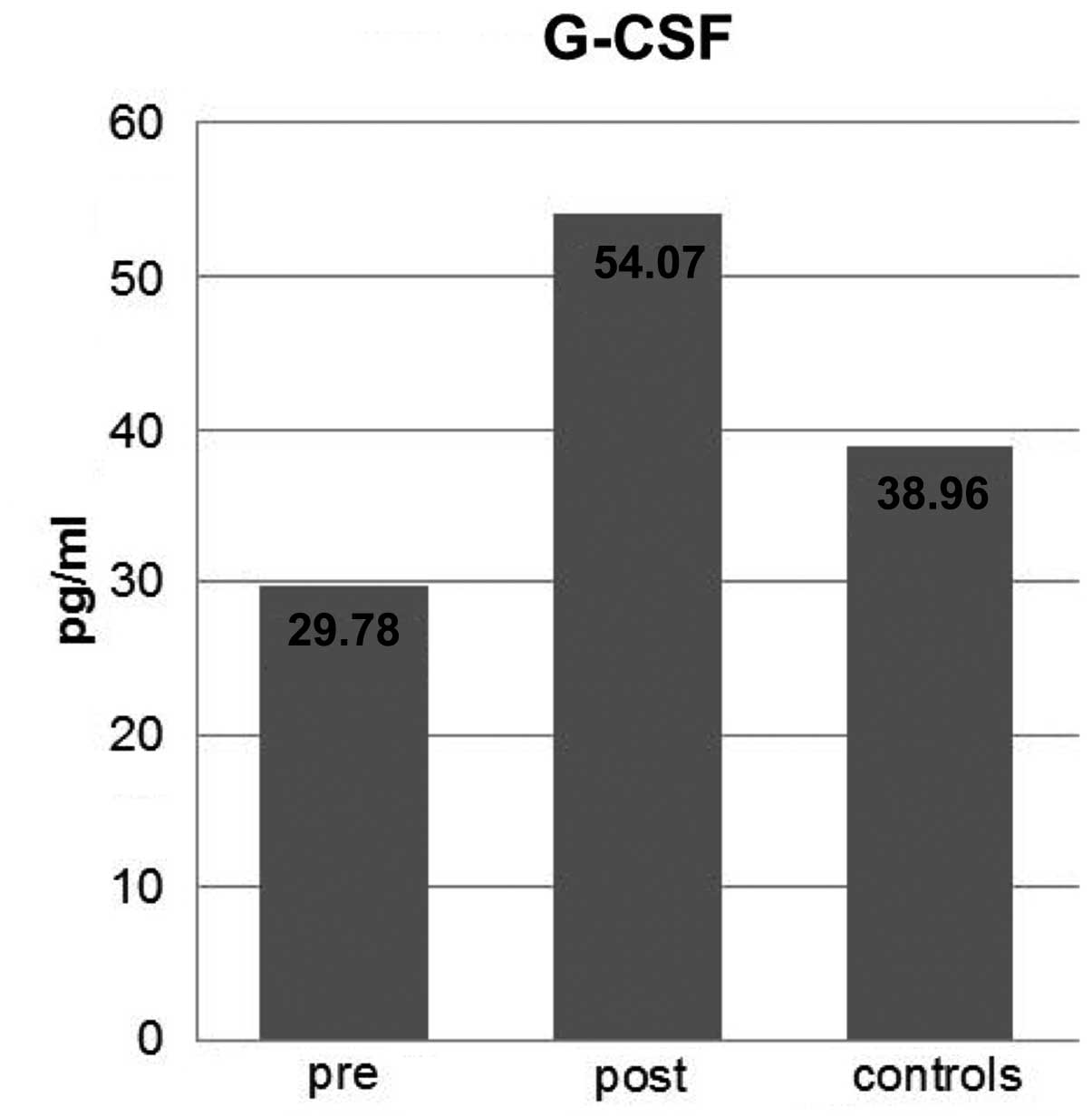
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Winn DM, et al:
Smoking and drinking in relation to oral and pharyngeal cancer.
Cancer Res. 48:3282–3287. 1988.
|
|
3
|
Riedel F and Hörmann K: Alcohol related
diseases of the head and neck. HNO. 52:590–598. 2004.(In
German).
|
|
4
|
Petti S: Lifestyle risk factors for oral
cancer. Oral Oncol. 45:340–350. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Brugere J, Guenel P, Leclerc A and
Rodriguez J: Differential effects of tobacco and alcohol in cancer
of the larynx, pharynx, and mouth. Cancer. 57:391–395. 1986.
|
|
6
|
Dietz A and Wichmann G: Translational
research in head and neck cancer. Biological characteristics and
general aspects. HNO. 59:874–884. 2011.(In German).
|
|
7
|
Sugiura T, Inoue Y, Matsuki R, et al:
VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression is correlated with lymphatic vessel
density and lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma:
Implications for use as a prognostic marker. Int J Oncol.
34:673–680. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Ninck S, Reisser C, Dyckhoff G, Helmke B,
Bauer H and Herold-Mende C: Expression profiles of angiogenic
growth factors in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck.
Int J Cancer. 106:34–44. 2003.
|
|
9
|
Boonkitticharoen V, Kulapaditharom B,
Leopairut J, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor a and
proliferation marker in prediction of lymph node metastasis in oral
and pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 134:1305–1311. 2008.
|
|
10
|
Brieger J, Schroeder P and Mann WJ:
Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth
factor are secreted by squamous cell carcinoma cell lines after
radiotherapy and induce resistance to radiation in vitro. GMS Curr
Posters Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1:932005.(In German).
|
|
11
|
Riedel F: Expression of VEGF and
inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by abrogation of VEGF in head and
neack cancer. Laryngorhinootologie. 82:436–437. 2003.(In
German).
|
|
12
|
Montag M, Dyckhoff G, Lohr J, et al:
Angiogenic growth factors in tissue homogenates of HNSCC:
expression pattern, prognostic relevance, and interrelationships.
Cancer Sci. 100:1210–1218. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Palmer B, Bran GM, Hörmann K and Riedel F:
Analysis of the serum concentration of PDGF (-AB) in patients with
HNSCC. Presented at 78. German Society for Otorhinolaryngology,
Head and Neck Surgery Congress; 2007; http://www.egms.de/stat-ic/de/meetings/hnod2007/07hnod458.shtml.
(In German).
|
|
14
|
Hofmann TK: Immunotherapy of head and neck
cancer. Identification of a novel mechanism for anti-EGFR mAb
anti-tumor effects. HNO. 59:224–229. 2011.(In German).
|
|
15
|
de Oliveira MV, Fraga CA, Gomez RS and
Paula AM: Immunohistochemical expression of interleukin-4, -6, -8
and -12 in inflammatory cells in surrounding invasive front of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 31:1439–1446. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Myers JN, Yasumura S, Suminami Y, et al:
Growth stimulation of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
cell lines by interleukin 4. Clin Cancer Res. 2:127–135. 1996.
|
|
17
|
Mojtahedi Z, Khademi B, Yehya A, et al:
Serum levels of interleukins 4 and 10 in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. J Laryngol Otol. 126:175–179. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Obiri NI, Hillman GG, Haas GP, et al:
Expression of high affinity interleukin-4 receptors on human renal
cell carcinoma cells and inhibition of tumor cell growth in vitro
by interleukin-4. J Clin Invest. 91:88–93. 1993.
|
|
19
|
Obiri NI, Siegel JP, Varricchio F and Puri
RK: Expression of high-affinity IL-4 receptors on human melanoma,
ovarian and breast carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 95:148–155.
1994.
|
|
20
|
Morisaki T, Yuzuki DH, Lin RT, et al:
Interleukin 4 receptor expression and growth inhibition of gastric
carcinoma cells by interleukin 4. Cancer Res. 52:6059–6065.
1992.
|
|
21
|
Volpert OV, Fong T, Koch AE, et al:
Inhibition of angiogenesis by interleukin 4. J Exp Med.
188:1039–1046. 1998.
|
|
22
|
Yamaji H, Iizasa T, Koh E, et al:
Correlation between interleukin 6 production and tumor
proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 53:786–792. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Riedel F, Zaiss I, Herzog D, et al: Serum
levels of interleukin-6 in patients with primary head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 25:2761–2765. 2005.
|
|
24
|
Wang YF, Chang SY, Tai SK, et al: Clinical
significance of interleukin-6 and interleukin-6 receptor
expressions in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 24:850–858.
2002.
|
|
25
|
Lu JG, Li Y and Kan X: Overexpression of
osteopontin and integrin αv in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal
carcinomas associated with differentiation and metastasis. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 137:1613–1618. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Weber GF, Lett GS and Haubein NC:
Osteopontin is a marker for cancer aggressiveness and patient
survival. Br J Cancer. 103:861–869. 2010.
|
|
27
|
Lim AM, Rischin D, Fisher R, et al:
Prognostic significance of osteopontin in patients with
locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
treated on TROG 02.02 phase III trial. Clin Cancer Res. 18:301–307.
2012.
|
|
28
|
Wang HH, Wang XW and Tang CE: Osteopontin
expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: its relevance to the
clinical stage of the disease. J Cancer Res Ther. 7:138–142.
2011.
|
|
29
|
Tlsty TD: Stromal cells can contribute
oncogenic signals. Semin Cancer Biol. 11:97–104. 2001.
|
|
30
|
Mroczko B and Szmitkowski M: Hematopoietic
cytokines as tumor markers. Clin Chem Lab Med. 42:1347–1354.
2004.
|
|
31
|
Gutschalk CM, Herold-Mende CC, Fusenig NE
and Mueller MM: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promote malignant
growth of cells from head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in
vivo. Cancer Res. 66:8026–8036. 2006.
|
|
32
|
van Warmerdam LJ, Rodenhuis S, ten Bokkel
Huinink WW, et al: The use of the Calvert formula to determine the
optimal carboplatin dosage. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 121:478–486.
1995.
|
|
33
|
Wittekind C: 2010 TNM system: on the 7th
edition of TNM classification of malignant tumors. Pathologe.
31:331–332. 2010.(In German).
|
|
34
|
Zhou XH, Obuchowski NA and McClish DK:
Measures of diagnostic accuracy. Statistical Methods in Diagnostic
Medicine. Wiley J; Hoboken, NJ: pp. 23–26. 2011
|
|
35
|
Klein F: Interleukins give poor evidence.
J Laryngol Otol. 126:175–179. 2012.(In German).
|
|
36
|
Sato J, Ohuchi M, Abe K, et al:
Correlation between salivary interleukin-6 levels and early
locoregional recurrence in patients with oral squamous cell
carcinoma: preliminary study. Head Neck. 35:889–894. 2013.
|
|
37
|
Snitcovsky I, Leitão GM, Pasini FS, et al:
Plasma osteopontin levels in patients with head and neck cancer
undergoing chemoradiotherapy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
135:807–811. 2009.
|
|
38
|
Thariat J, Yildirim G, Mason KA, et al:
Combination of radiotherapy with EGFR antagonists for head and neck
carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 12:99–110. 2007.
|
|
39
|
Bergler W and Bier H: Cisplatin reduces
epidermal growth factor receptors in squamous-cell carcinoma in
vitro. Preliminary results. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec.
52:297–302. 1990.
|
|
40
|
Riedel F, Götte K, Li M, et al: EGFR
antisense treatment of human HNSCC cell lines down-regulates VEGF
expression and endothelial cell migration. Int J Oncol. 21:11–16.
2002.
|
|
41
|
Pei XH, Nakanishi Y, Takayama K, et al:
Granulocyte, granulocyte-macrophage, and macrophage
colony-stimulating factors can stimulate the invasive capacity of
human lung cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 79:40–46. 1999.
|
|
42
|
Nasu K, Inoue C, Takai N, et al: Squamous
cell carcinoma of the cervix producing granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor. Obstet Gynecol. 104:1086–1088. 2004.
|
|
43
|
Snyder RA, Liu E and Merchant NB:
Granulocyte colony stimulating factor secreting hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am Surg. 78:821–822. 2012.
|