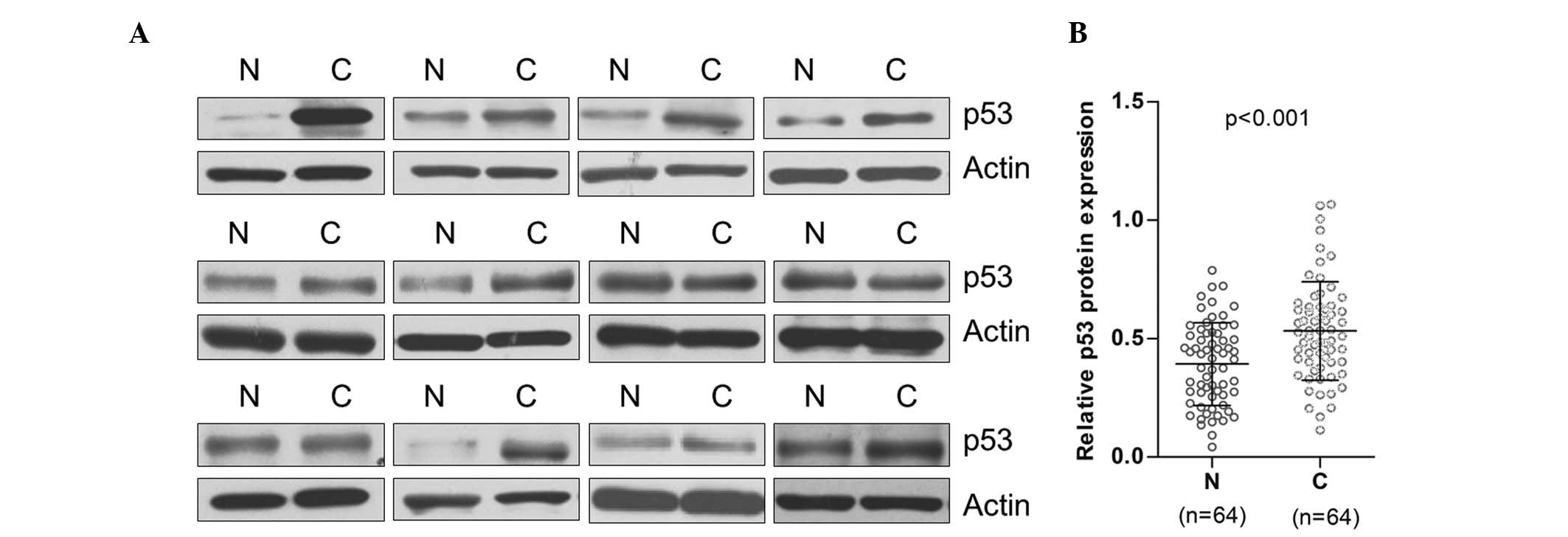
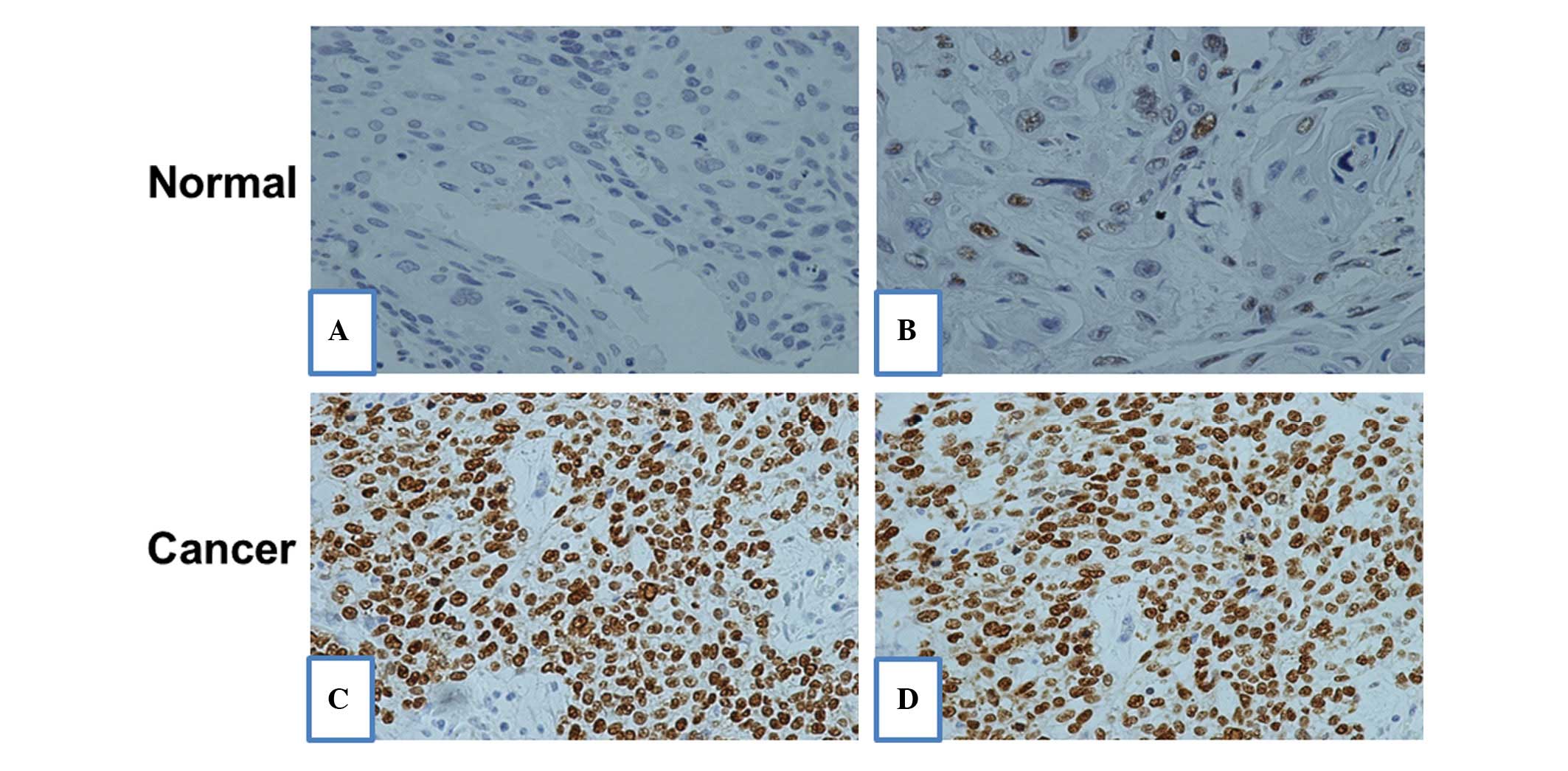
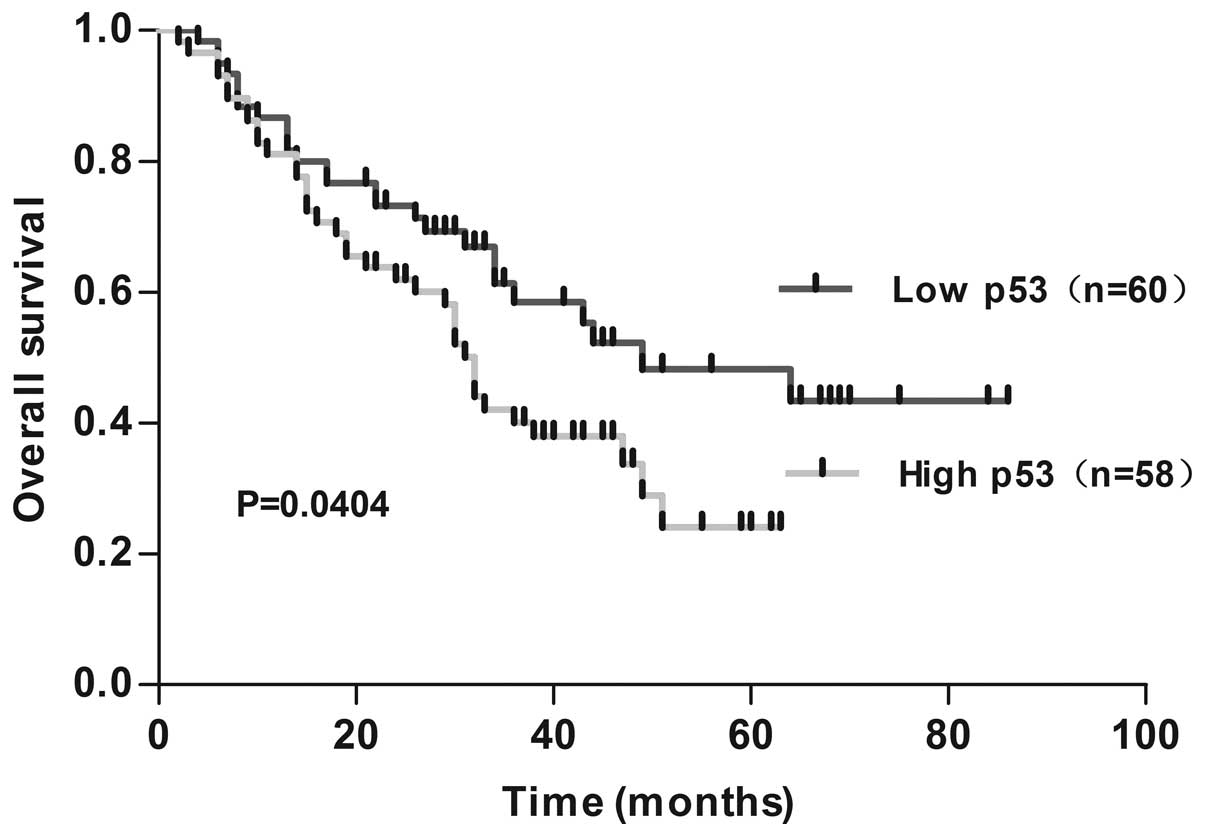
|
1
|
Song QK, Li J, Jiang HD, He YM, Zhou XQ
and Huang CY: Esophageal cancer mortality during 2004–2009 in
Yanting County, China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5003–5006.
2012.
|
|
2
|
Blot WJ: Esophageal cancer trends and risk
factors. Semin Oncol. 21:403–410. 1994.
|
|
3
|
Brooks-Brunn JA: Esophageal cancer: an
overview. Medsurg Nurs. 9:248–254. 2000.
|
|
4
|
Cho H, Ha SY, Park SH, Park K and Chae YS:
Role of p53 gene mutation in tumor aggressiveness of intracranial
meningiomas. J Korean Med Sci. 14:199–205. 1999.
|
|
5
|
Murata A, Baba Y, Watanabe M, et al: p53
immunohistochemical expression and patient prognosis in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:7282013.
|
|
6
|
Cardin R, Piciocchi M, Tieppo C, et al:
Oxidative DNA damage in Barrett mucosa: correlation with telomeric
dysfunction and p53 mutation. Ann Surg Oncol. 20(Suppl 3):
S583–S589. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Di Agostino S, Strano S and Blandino G:
Gender, mutant p53 and PML: a growing ‘affaire’ in tumor
suppression and oncogenesis. Cell Cycle. 12:1824–1825. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Guinan P, Sobin LH, Algaba F, et al: TNM
staging of renal cell carcinoma: Workgroup No 3. Union
International Contre le Cancer (UICC) and the American Joint
Committee on Cancer (AJCC). Cancer. 80:992–993. 1997.
|
|
9
|
Sobin LH and Fleming ID: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors, fifth edition (1997). Union
Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on
Cancer. Cancer. 80:1803–1804. 1997.
|
|
10
|
Nocito A, Bubendorf L, Tinner EM, et al:
Microarrays of bladder cancer tissue are highly representative of
proliferation index and histological grade. J Pathol. 194:349–357.
2001.
|
|
11
|
Nie X, Li M, Lu B, et al: Down-regulating
overexpressed human Lon in cervical cancer suppresses cell
proliferation and bioenergetics. PloS One. 8:e810842013.
|
|
12
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German).
|
|
13
|
Cheng AN, Jiang SS, Fan CC, et al:
Increased Cdc7 expression is a marker of oral squamous cell
carcinoma and overexpression of Cdc7 contributes to the resistance
to DNA-damaging agents. Cancer Lett. 337:218–225. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Bolander A, Agnarsdóttir M, Strömberg S,
et al: The protein expression of TRP-1 and galectin-1 in cutaneous
malignant melanomas. Cancer genomics Proteomics. 5:293–300.
2008.
|
|
15
|
Grelewski PG and Bar JK: The role of p53
protein and MMP-2 tumor/stromal cells expression on progressive
growth of ovarian neoplasms. Cancer Invest. 31:472–479. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Lee JY, Kim HJ, Yoon NA, et al: Tumor
suppressor p53 plays a key role in induction of both
tristetraprolin and let-7 in human cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:5614–5625. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Krell J, Frampton AE, Colombo T, et al:
The p53 miRNA interactome and its potential role in the cancer
clinic. Epigenomics. 5:417–428. 2013.
|
|
18
|
Gu Z, Jiang J, Tan W, et al: p53/p21
Pathway involved in mediating cellular senescence of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus
erythematosus patients. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:1342432013.
|
|
19
|
Zhou Y and Ho WS: Combination of
liquiritin, isoliquiritin and isoliquirigenin induce apoptotic cell
death through upregulating p53 and p21 in the A549 non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 31:298–304. 2014.
|
|
20
|
Formigari A, Gregianin E and Irato P: The
effect of zinc and the role of p53 in copper-induced cellular
stress responses. J Appl Toxicol. 33:527–536. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Biramijamal F, Allameh A, Mirbod P, Groene
HJ, Koomagi R and Hollstein M: Unusual profile and high prevalence
of p53 mutations in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas from
northern Iran. Cancer Res. 61:3119–3123. 2001.
|
|
22
|
Guimaraes DP and Hainaut P: TP53: a key
gene in human cancer. Biochimie. 84:83–93. 2002.
|
|
23
|
Taghavi N, Biramijamal F, Sotoudeh M, et
al: Association of p53/p21 expression with cigarette smoking and
prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:4958–4967. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Chiarugi V and Ruggiero M: Role of three
cancer ‘master genes’ p53, bcl2 and c-myc on the apoptotic process.
Tumori. 82:205–209. 1996.
|
|
25
|
Huerta S, Gao X, Dineen S, Kapur P, Saha D
and Meyer J: Role of p53, Bax, p21, and DNA-PKcs in radiation
sensitivity of HCT-116 cells and xenografts. Surgery. 154:143–151.
2013.
|
|
26
|
Jung SY, Jeong J, Shin SH, et al:
Accumulation of p53 determined by immunohistochemistry as a
prognostic marker in node negative breast cancer; analysis
according to St Gallen consensus and intrinsic subtypes. J Surg
Oncol. 103:207–211. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Koshiyama M, Konishi I, Wang DP, et al:
Immunohistochemical analysis of p53 protein over-expression in
endometrial carcinomas: inverse correlation with sex steroid
receptor status. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol.
423:265–271. 1993.
|
|
28
|
Zhu HB, Yang K, Xie YQ, Lin YW, Mao QQ and
Xie LP: Silencing of mutant p53 by siRNA induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. World J Surg Oncol.
11:222013.
|
|
29
|
Chava S, Mohan V, Shetty PJ, et al:
Immunohistochemical evaluation of p53, FHIT, and IGF2 gene
expression in esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 25:81–87. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Launoy G, Milan C, Day NE, Pienkowski MP,
Gignoux M and Faivre J: Diet and squamous-cell cancer of the
oesophagus: a French multicentre case-control study. Int J Cancer.
76:7–12. 1998.
|
|
31
|
Sammon AM and Alderson D: Diet, reflux and
the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus in
Africa. Br J Surg. 85:891–896. 1998.
|
|
32
|
Morse DE, Pendrys DG, Katz RV, et al: Food
group intake and the risk of oral epithelial dysplasia in a United
States population. Cancer Causes Control. 11:713–720. 2000.
|
|
33
|
Mizobuchi S, Furihata M, Sonobe H, et al:
Association between p53 immunostaining and cigarette smoking in
squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
30:423–428. 2000.
|