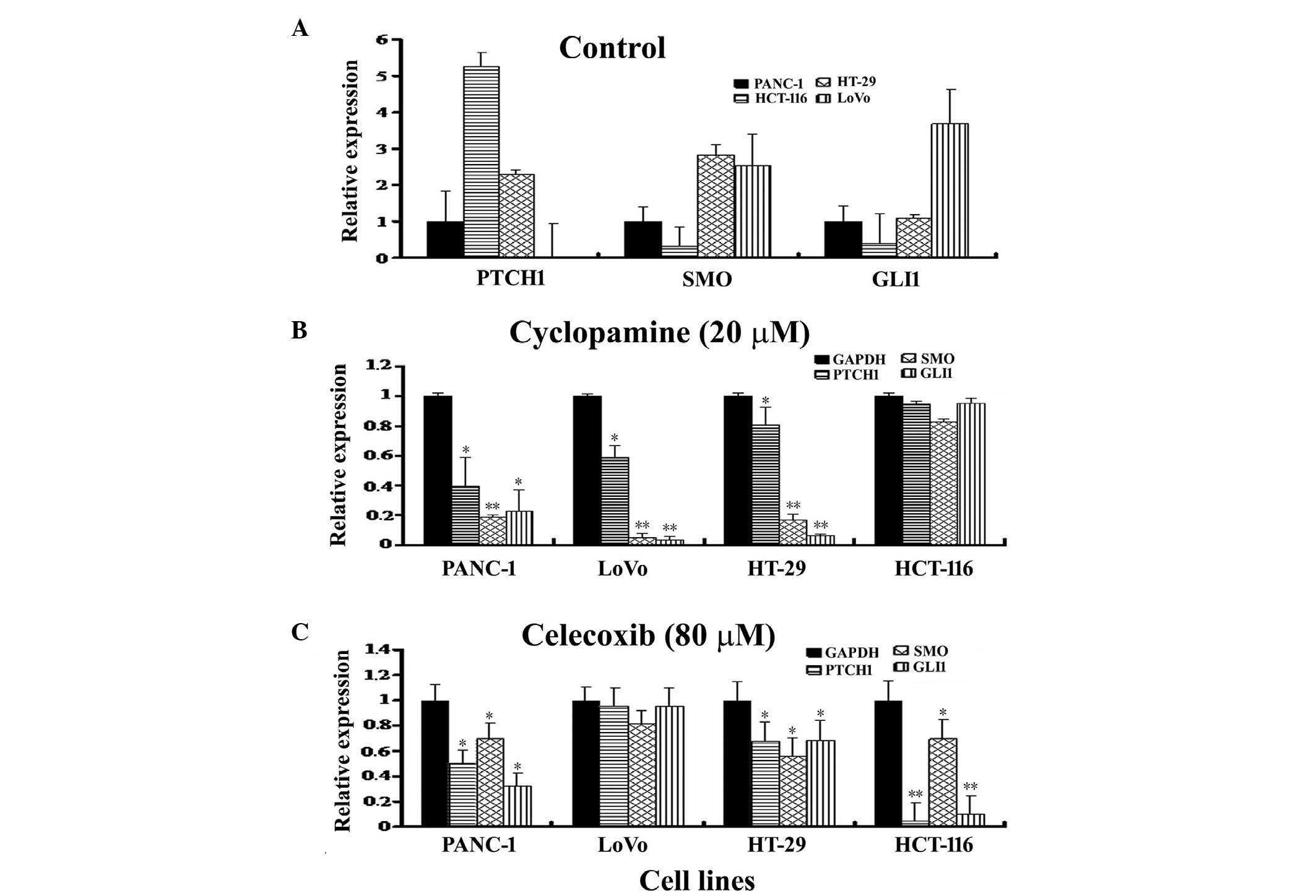
|
1
|
Globocan. 2012, Estimated Cancer
Incidence, Mortality and Prevalance Worldwide in 2012. http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_cancer.aspx.
Accessed August 7, 2014
|
|
2
|
Giles RH, van Es JH and Clevers H: Caught
up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1653:1–24. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Lampropoulos P, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A,
Rizos S, Kostakis A, Nikiteas N and Papavassiliou AG: TGF-beta
signalling in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 314:1–7. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Koduru S, Kumar R, Srinivasan S, Evers MB
and Damodaran C: Notch-1 inhibition by Withaferin-A: a therapeutic
target against colon carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:202–210.
2010.
|
|
5
|
Lièvre A, Blons H and Laurent-Puig P:
Oncogenic mutations as predictive factors in colorectal cancer.
Oncogene. 29:3033–3043. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Gulino A, Ferretti E and De Smaele E:
Hedgehog signalling in colon cancer and stem cells. EMBO Mol Med.
1:300–302. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Mazumdar T, DeVecchio J, Shi T, Jones J,
Agyeman A and Houghton JA: Hedgehog signaling drives cellular
survival in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 71:1092–1102.
2011.
|
|
8
|
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, et al:
Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of
digestive tract tumours. Nature. 425:846–851. 2003.
|
|
9
|
Chatel G, Ganeff C, Boussif N, Delacroix
L, Briquet A, Nolens G and Winkler R: Hedgehog signaling pathway is
inactive in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer.
121:2622–2627. 2007.
|
|
10
|
Fu X, Deng H, Zhao L, Li J, Zhou Y and
Zhang Y: Distinct expression patterns of hedgehog ligands between
cultured and primary colorectal cancers are associated with
aberrant methylation of their promoters. Mol Cell Biochem.
337:185–192. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Maloverjan A and Piirsoo M: Mammalian
homologues of Drosophila fused kinase. Vitam Horm. 88:91–113.
2012.
|
|
12
|
Pasca di Magliano M and Hebrok M: Hedgehog
signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:903–911. 2003.
|
|
13
|
Jenkins D: Hedgehog signalling: emerging
evidence for non-canonical pathways. Cell Signal. 21:1023–1034.
2009.
|
|
14
|
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, et
al: Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the
nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell. 85:841–851. 1996.
|
|
15
|
Teglund S and Toftgård R: Hedgehog beyond
medulloblastoma and basal cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1805:181–208. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK and Beachy
PA: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of
cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev. 16:2743–2748. 2002.
|
|
17
|
Al-Wadei HA, Al-Wadei MH, Ullah MF and
Schuller HM: Celecoxib and GABA cooperatively prevent the
progression of pancreatic cancer in vitro and in xenograft models
of stress-free and stress-exposed mice. PLoS One. 7:e433762012.
|
|
18
|
Jin CH, Wang AH, Chen JM, Li RX, Liu XM,
Wang GP and Xing Q: Observation of curative efficacy and prognosis
following combination chemotherapy with celecoxib in the treatment
of advanced colorectal cancer. J Int Med Res. 39:2129–2140.
2011.
|
|
19
|
Lum L and Beachy PA: The Hedgehog response
network: sensors, switches, and routers. Science. 304:1755–1759.
2004.
|
|
20
|
You S, Zhou J, Chen S, Zhou P, Lv J, Han X
and Sun Y: PTCH1, a receptor of Hedgehog signaling pathway, is
correlated with metastatic potential of colorectal cancer. Ups J
Med Sci. 115:169–175. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Qualtrough D, Buda A, Gaffield W, Williams
AC and Paraskeva C: Hedgehog signalling in colorectal tumour cells:
induction of apoptosis with cyclopamine treatment. Int J Cancer.
110:831–837. 2004.
|
|
22
|
Yoshimoto AN, Bernardazzi C, Carneiro AJ,
et al: Hedgehog pathway signaling regulates human colon carcinoma
HT-29 epithelial cell line apoptosis and cytokine secretion. PLoS
One. 7:e453322012.
|
|
23
|
Zhu Y, James RM, Peter A, Lomas C, Cheung
F, Harrison DJ and Bader SA: Functional Smoothened is required for
expression of GLI3 in colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
207:205–214. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Wang TP, Hsu SH, Feng HC and Huang RF:
Folate deprivation enhances invasiveness of human colon cancer
cells mediated by activation of sonic hedgehog signaling through
promoter hypomethylation and cross action with transcription
nuclear factor-kappa B pathway. Carcinogenesis. 33:1158–1168.
2012.
|
|
25
|
Lou J, Fatima N, Xiao Z, Stauffer S,
Smythers G, Greenwald P and Ali IU: Proteomic profiling identifies
cyclooxygenase-2-independent global proteomic changes by celecoxib
in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
15:1598–1606. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Takahashi-Yanaga F, Yoshihara T, Jingushi
K, Miwa Y, Morimoto S, Hirata M and Sasaguri T: Celecoxib-induced
degradation of T-cell factors-1 and −4 in human colon cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:1185–1190. 2008.
|
|
27
|
Wilson NH and Stoeckli ET: Sonic Hedgehog
regulates Wnt activity during neural circuit formation. Vitam Horm.
88:173–209. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Ilyas M, Tomlinson IP, Rowan A, Pignatelli
M and Bodmer WF: Beta-catenin mutations in cell lines established
from human colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:10330–10334. 1997.
|
|
29
|
van Erk MJ, Krul CA, Caldenhoven E,
Stierum RH, Peters WH, Woutersen RA and van Ommen B: Expression
profiling of colon cancer cell lines and colon biopsies: towards a
screening system for potential cancer-preventive compounds. Eur J
Cancer Prev. 14:439–457. 2005.
|
|
30
|
Shida D, Kitayama J, Yamaguchi H,
Yamashita H, Mori K, Watanabe T and Nagawa H: Lysophosphatidic acid
transactivates both c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor, and
induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer LoVo
cells. World J Gastroenterol. 11:5638–5643. 2005.
|