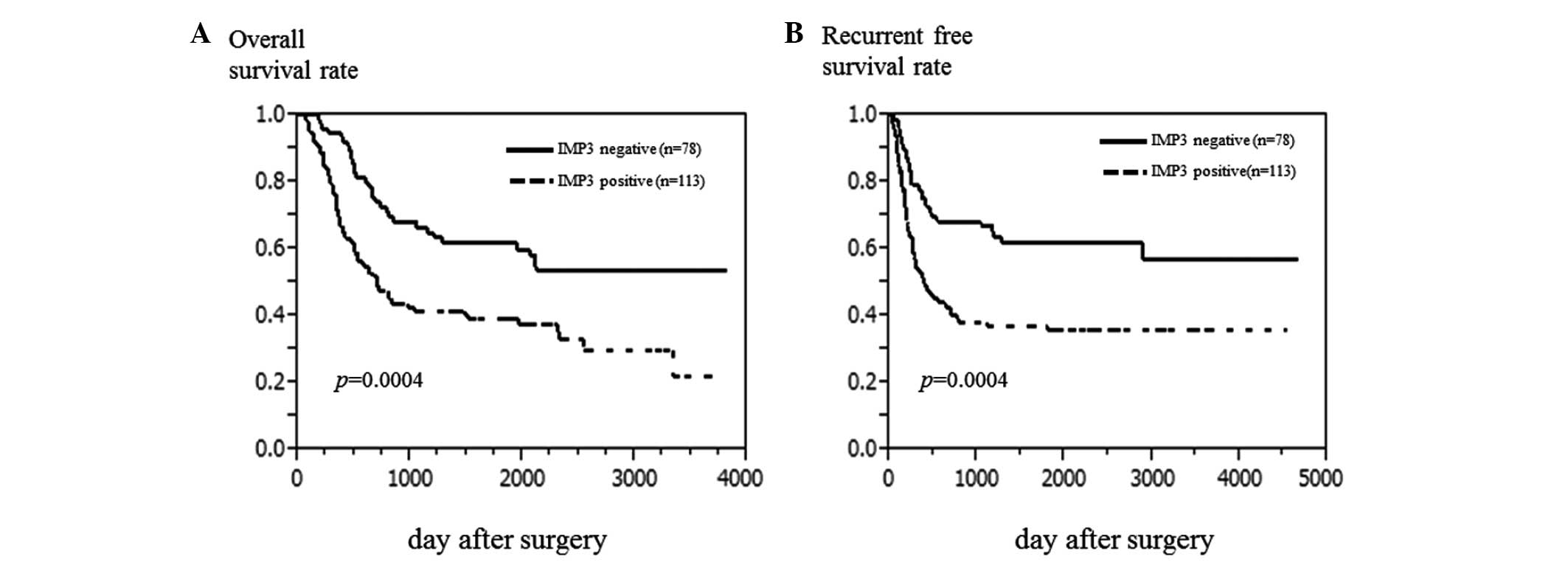
|
1
|
Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, et al:
Prediction of survival with squamous cell carcinoma antigen in
patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Surgery. 133:486–494. 2003.
|
|
2
|
Tamoto E, Tada M, Murakawa K, et al:
Gene-expression profile changes correlated with tumor progression
and lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:3629–3638. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Nielsen J, Christiansen J, Lykke-Andersen
J, et al: A family of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding
proteins represses translation in late development. Mol Cell Biol.
19:1262–1270. 1999.
|
|
4
|
Mueller-Pillasch F, Pohl B, Wilda M, et
al: Expression of the highly conserved RNA binding protein KOC in
embryogenesis. Mech Dev. 88:95–99. 1999.
|
|
5
|
Yaniv K and Yisraeli JK: The involvement
of a conserved family of RNA binding proteins in embryonic
development and carcinogenesis. Gene. 287:49–54. 2002.
|
|
6
|
Gu L, Shigemasa K and Ohama K: Increased
expression of IGF II mRNA-binding protein 1 mRNA is associated with
an advanced clinical stage and poor prognosis in patients with
ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 24:671–678. 2004.
|
|
7
|
Hammer NA, Hansen T, Byskov AG, et al:
Expression of IGF-II mRNA-binding proteins (IMPs) in gonads and
testicular cancer. Reproduction. 130:203–212. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Hoffmann NE, Sheinin Y, Lohse CM, et al:
External validation of IMP3 expression as an independent prognostic
marker for metastatic progression and death for patients with clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 112:1471–1479. 2008.
|
|
9
|
Jiang Z, Chu PG, Woda BA, et al: Analysis
of RNA-binding protein IMP3 to predict metastasis and prognosis of
renal-cell carcinoma: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol.
7:556–564. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Li D, Yan D, Tang H, et al: IMP3 is a
novel prognostic marker that correlates with colon cancer
progression and pathogenesis. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:3499–3506.
2009.
|
|
11
|
Okada K, Fujiwara Y, Nakamura Y, et al:
Oncofetal protein, IMP3, a potential marker for prediction of
postoperative peritoneal dissemination in gastric adenocarcinoma. J
Surg Oncol. 105:780–785. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Simon R, Bourne PA, Yang Q, et al:
Extrapulmonary small cell carcinomas express K homology domain
containing protein overexpressed in cancer, but carcinoid tumors do
not. Hum Pathol. 38:1178–1183. 2007.
|
|
13
|
Xu H, Bourne PA, Spaulding BO and Wang HL:
High-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung express K homology
domain containing protein overexpressed in cancer but carcinoid
tumors do not. Hum Pathol. 38:555–563. 2007.
|
|
14
|
Yantiss RK, Woda BA, Fanger GR, et al: KOC
(K homology domain containing protein overexpressed in cancer): a
novel molecular marker that distinguishes between benign and
malignant lesions of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:188–195.
2005.
|
|
15
|
Zheng W, Yi X, Fadare O, et al: The
oncofetal protein IMP3: a novel biomarker for endometrial serous
carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 32:304–315. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Doyle GA, Betz NA, Leeds PF, et al: The
c-myc coding region determinant-binding protein: a member of a
family of KH domain RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res.
26:5036–5044. 1998.
|
|
17
|
Gress TM, Müller-Pillasch F, Geng M, et
al: A pancreatic cancer-specific expression profile. Oncogene.
13:1819–1830. 1996.
|
|
18
|
Liao B, Hu Y, Herrick DJ and Brewer G: The
RNA-binding protein IMP3 is a translational activator of
insulin-like growth factor II leader-3 mRNA during proliferation of
human K562 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 280:18517–18524. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Runge S, Nielsen FC, Nielsen J, et al: H19
RNA binds four molecules of insulin-like growth factor II
mRNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 275:29562–29569. 2000.
|
|
20
|
Mueller F, Bommer M, Lacher U, et al: KOC
is a novel molecular indicator of malignancy. Br J Cancer.
88:699–701. 2003.
|
|
21
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: Oesophagus including oesophagogastric junction. International
Union Against Cancer (UICC) TNM classification of Malignant Tumors.
7th edition. Wiley-Blackwell; New York, NY: pp. 66–72. 2009
|
|
22
|
Hansen TV, Hammer NA, Nielsen J, et al:
Dwarfism and impaired gut development in insulin-like growth factor
II mRNA-binding protein 1-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol.
24:4448–4464. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Chao W and D’Amore PA: IGF2: epigenetic
regulation and role in development and disease. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 19:111–120. 2008.
|
|
24
|
Foulstone E, Prince S, Zaccheo O, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor ligands, receptors, and binding proteins
in cancer. J Pathol. 205:145–153. 2005.
|
|
25
|
Vikesaa J, Hansen TV, Jønson L, et al:
RNA-binding IMPs promote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation.
EMBO J. 25:1456–1468. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Jeng YM, Wang TH, Lu SH, Yuan RH and Hsu
HC: Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor II
mRNA-binding protein 3 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. Br J
Surg. 96:66–73. 2009.
|
|
27
|
Pryor JG, Bourne PA, Yang Q, et al: IMP3
is a novel progression marker in malignant melanoma. Mod Pathol.
21:431–437. 2008.
|
|
28
|
Yoshino K, Motoyama S, Koyota S, et al:
Identification of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein
3 as a radioresistance factor in squamous esophageal cancer cells.
Dis Esophagus. Sep 18–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
29
|
Nischalke HD, Schmitz V, Luda C, et al:
Detection of IGF2BP3, HOXB7, and NEK2 mRNA expression in brush
cytology specimens as a new diagnostic tool in patients with
biliary strictures. PLoS One. 7:e421412012.
|
|
30
|
Kono K, Iinuma H, Akutsu Y, et al:
Multicenter, phase II clinical trial of cancer vaccination for
advanced esophageal cancer with three peptides derived from novel
cancer-testis antigens. J Transl Med. 10:1412012.
|