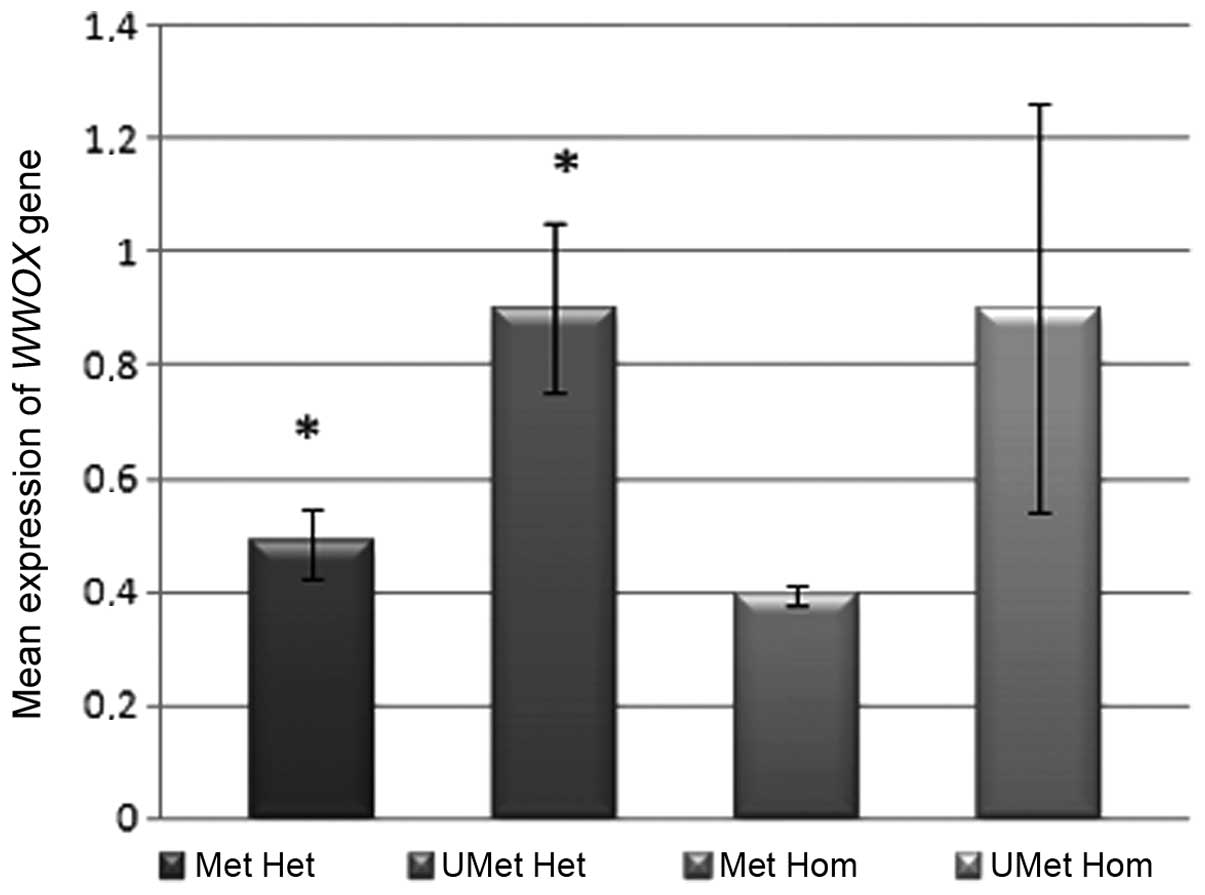
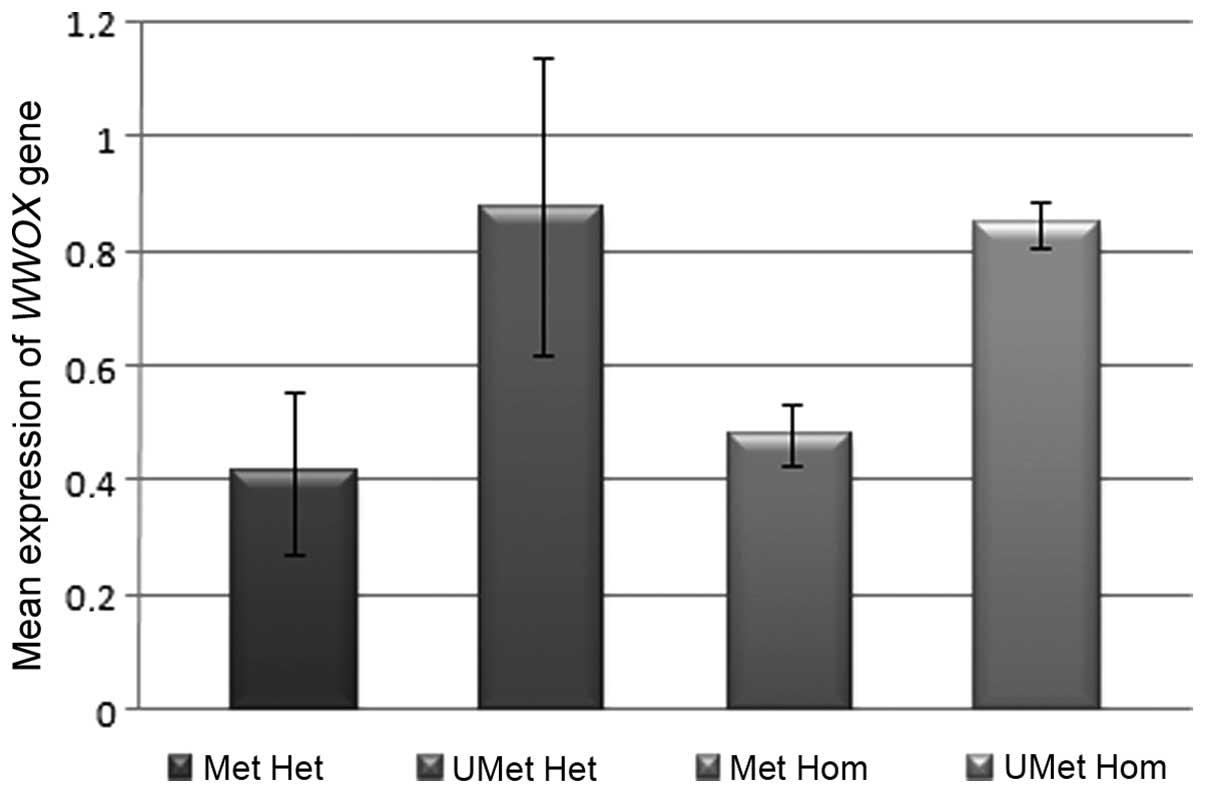
|
1
|
Ministry of Health, Poland. National
Cancer Registry. http://epid.coi.waw.pl/krn/.
Accessed June 30, 2010
|
|
2
|
Luis NM, López-Knowles E and Real FX:
Molecular biology of bladder cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:5–12.
2007.
|
|
3
|
Kim WJ and Bae SC: Molecular biomarkers in
urothelial bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:646–652. 2008.
|
|
4
|
Jung I and Messing E: Molecular mechanisms
and pathways in bladder cancer development and progression. Cancer
Control. 7:325–334. 2000.
|
|
5
|
Mitra AP, Datar RH and Cote RJ: Molecular
pathways in invasive bladder cancer: new insights into mechanisms,
progression, and target identification. J Clin Oncol. 24:5552–5564.
2006.
|
|
6
|
Yoon DS, Li L, Zhang RD, Kram A, et al:
Genetic mapping and DNA sequence-based analysis of deleted regions
on chromosome 16 involved in progression of bladder cancer from
occult preneoplastic conditions to invasive disease. Oncogene.
20:5005–5014. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Bednarek AK, Laflin KJ, Daniel RL, et al:
WWOX, a novel WW domain-containing protein mapping to human
chromosome 16q23.3–24.1, a region frequently affected in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 60:2140–2145. 2000.
|
|
8
|
Qin HR, Iliopoulos D, Semba S, et al: A
role for the WWOX gene in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
66:6477–6481. 2006.
|
|
9
|
Lan C, Chenggang W, Yulan B, et al:
Aberrant expression of WWOX protein in epithelial ovarian cancer: a
clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study. Int J Gynecol
Pathol. 31:125–132. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Yang W, Cui S, Ma J, et al: Cigarette
smoking extract causes hypermethylation and inactivation of WWOX
gene in T-24 human bladder cancer cells. Neoplasma. 59:216–223.
2012.
|
|
11
|
Ramos D, Abba M, Lopez-Guerrero JA, et al:
Low levels of WWOX protein immunoexpression correlate with tumour
grade and a less favourable outcome in patients with urinary
bladder tumours. Histopathology. 52:831–839. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Iliopoulos D, Guler G, Han SY, et al:
Fragile genes as biomarkers: epigenetic control of WWOX and FHIT in
lung, breast and bladder cancer. Oncogene. 24:1625–1633. 2005.
|
|
13
|
Knudson AG Jr: Hereditary cancer,
oncogenes, and antioncogenes. Cancer Res. 45:1437–1443. 1985.
|
|
14
|
Kuroki T, Yendamuri S, Trapasso F, et al:
The tumor suppressor gene WWOX at FRA16D is involved in pancreatic
carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2459–2465. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Kuroki T, Trapasso F, Shiraishi T, et al:
Genetic alterations of the tumor suppressor gene WWOX in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:2258–2260. 2002.
|
|
16
|
Aqeilan RI, Donati V, Palamarchuk A, et
al: WW domain-containing proteins, WWOX and YAP, compete for
interaction with ErbB-4 and modulate its transcriptional function.
Cancer Res. 65:6764–6772. 2005.
|
|
17
|
Aqeilan RI, Donati V, Gaudio E, et al:
Association of Wwox with ErbB4 in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
67:9330–9336. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Gaudio E, Palamarchuk A, Palumbo T, et al:
Physical association with WWOX suppresses c-Jun transcriptional
activity. Cancer Res. 66:11585–11589. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Aqeilan RI, Pekarsky Y, Herrero JJ, et al:
Functional association between Wwox tumor suppressor protein and
p73, a p53 homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4401–4406.
2004.
|
|
20
|
Aqeilan RI, Hassan MQ, de Bruin A, et al:
The WWOX tumor suppressor is essential for postnatal survival and
normal bone metabolism. J Biol Chem. 283:21629–21639. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Jin C, Ge L, Ding X, et al: PKA-mediated
protein phosphorylation regulates ezrin-WWOX interaction. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 341:784–791. 2006.
|
|
22
|
Nunez MI, Ludes-Meyers J and Aldaz CM:
WWOX protein expression in normal human tissues. J Mol Histol.
37:115–125. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Aqeilan RI, Hagan JP, de Bruin A, et al:
Targeted ablation of the WW domain-containing oxidoreductase tumor
suppressor leads to impaired steroidogenesis. Endocrinology.
150:1530–1535. 2009.
|
|
24
|
World Health Organization Classification
of Tumours. World Health Organization, IARC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
25
|
Kosla K, Pluciennik E, Kurzyk A,
Jesionek-Kupnicka D, et al: Molecular analysis of WWOX expression
correlation with proliferation and apoptosis in glioblastoma
multiforme. J Neurooncol. 101:207–213. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Płuciennik E, Nowakowska M, Wujcicka WI,
et al: Genetic alterations of WWOX in Wilms’ tumor are involved in
its carcinogenesis. Oncol Rep. 28:1417–1422. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002.
|
|
28
|
Maeda N, Semba S, Nakayama S, et al: Loss
of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase expression in the
progression and development of gastric carcinoma: clinical and
histopathologic correlations. Virchows Arch. 457:423–432. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Aqeilan RI, Kuroki T, Pekarsky Y, et al:
Loss of WWOX expression in gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:3053–3058. 2004.
|
|
30
|
Yendamuri S, Kuroki T, Trapasso F, et al:
WW domain containing oxidoreductase gene expression is altered in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 63:878–881. 2003.
|
|
31
|
Chen T, Sahin A and Aldaz CM: Deletion map
of chromosome 16q in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast:
refining a putative tumor suppressor gene region. Cancer Res.
56:5605–5609. 1996.
|
|
32
|
Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Sagalowsky AI and
Lotan Y: Correlation of cyclin D1 and E1 expression with bladder
cancer presence, invasion, progression, and metastasis. Hum Pathol.
37:1568–1576. 2006.
|
|
33
|
Shiina H, Igawa M, Urakami S, et al:
Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2 expression in transitional
cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Clin Pathol. 49:395–399. 1996.
|
|
34
|
Bilim VN, Tomita Y, Kawasaki T, et al:
Variable Bcl-2 phenotype in benign and malignant lesions of
urothelium. Cancer Lett. 128:87–92. 1998.
|
|
35
|
Wang H, Xi X, Kong X, et al: The
expression and significance of survivin mRNA in urinary bladder
carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 130:487–490. 2004.
|
|
36
|
Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Karakiewicz PI, et
al: Survivin expression is associated with bladder cancer presence,
stage, progression, and mortality. Cancer. 109:1106–1113. 2007.
|
|
37
|
Kitamur H, Torigoe T, Honma I, et al:
Expression and antigenicity of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis
family member, in bladder cancer: Implications for specific
immunotherapy. Urology. 67:955–959. 2006.
|
|
38
|
Gonzalez-Campora R, Davalos-Casanova G,
Beato-Moreno A, et al: Apoptotic and proliferation indexes in
primary superficial bladder tumors. Cancer Lett. 242:266–272.
2006.
|
|
39
|
Yang CC, Chu KC and Yeh WM: The expression
of vascular endothelial growth factor in transitional cell
carcinoma of urinary bladder is correlated with cancer progression.
Urol Oncol. 22:1–6. 2004.
|
|
40
|
Crew JP, O’Brien T, Bradburn M, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor is a predictor of relapse and
stage progression in superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Res.
57:5281–5285. 1997.
|
|
41
|
Pfister C, Moore L, Allard P, Larue H,
Lacombe L, Têtu B, Meyer F and Fradet Y: Predictive value of cell
cycle markers p53, MDM2, p21, and Ki-67 in superficial bladder
tumor recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 5:4079–4084. 1999.
|
|
42
|
Behnsawy HM, Miyake H, Abdalla MA, Sayed
MA, Ahmed Ael-F and Fujisawa M: Expression of cell cycle-associated
proteins in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: correlation with
intravesical recurrence following transurethral resection. Urol
Oncol. 29:495–501. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Chen L, Wang X, Mei H and Chen W:
Apoptosis and expression of PCNA in superficial transitional cell
bladder cancer as related to recurrence. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.
36:484–486. 1998.(In Chinese).
|
|
44
|
Gazzaniga P, Gradilone A, Giuliani L,
Gandini O, Silvestri I, Nofroni I, Saccani G, Frati L and Aglianò
AM: Expression and prognostic significance of LIVIN, SURVIVIN and
other apoptosis-related genes in the progression of superficial
bladder cancer. Ann Oncol. 14:85–90. 2003.
|
|
45
|
Jeong IG, Kim SH, Jeon HG, Kim BH, Moon
KC, Lee SE and Lee E: Prognostic value of apoptosis-related markers
in urothelial cancer of the upper urinary tract. Hum Pathol.
40:668–677. 2009.
|
|
46
|
Chow NH, Liu HS, Lee EI, Chang CJ, Chan
SH, Cheng HL, Tzai TS and Lin JS: Significance of urinary epidermal
growth factor and its receptor expression in human bladder cancer.
Anticancer Res. 17:1293–1296. 1997.
|
|
47
|
Neal DE, Marsh C, Bennett MK, et al:
Epidermal-growth-factor receptors in human bladder cancer:
comparison of invasive and superficial tumours. Lancet. 1:366–368.
1985.
|