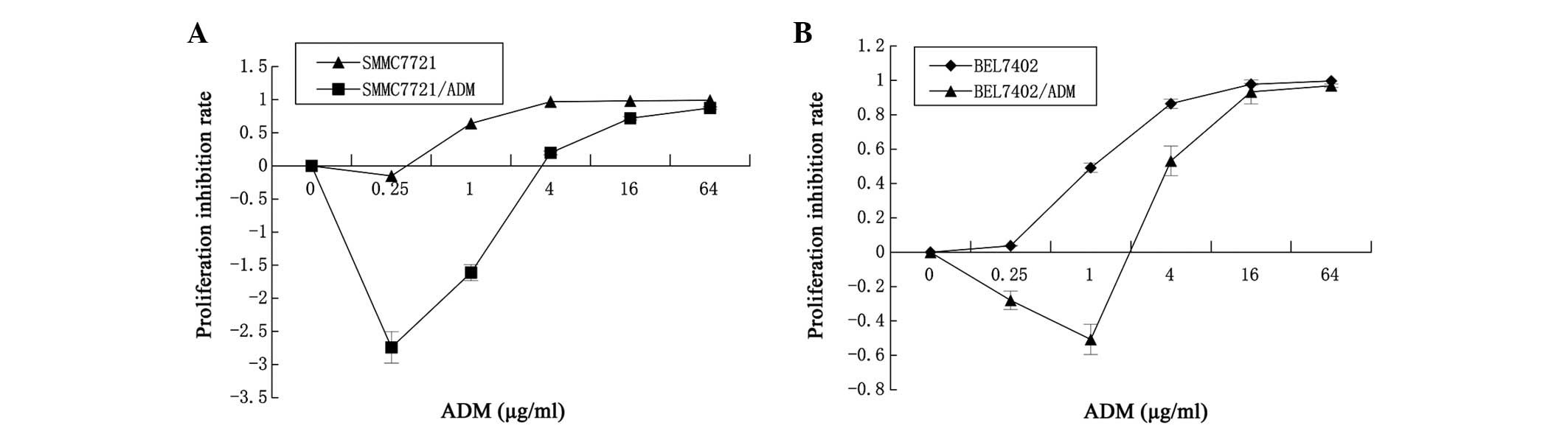
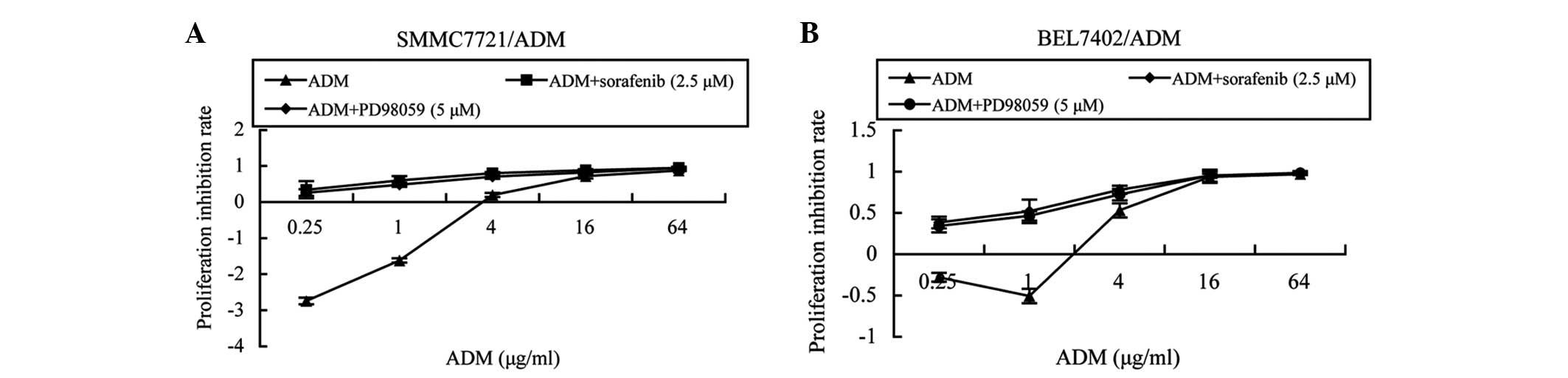
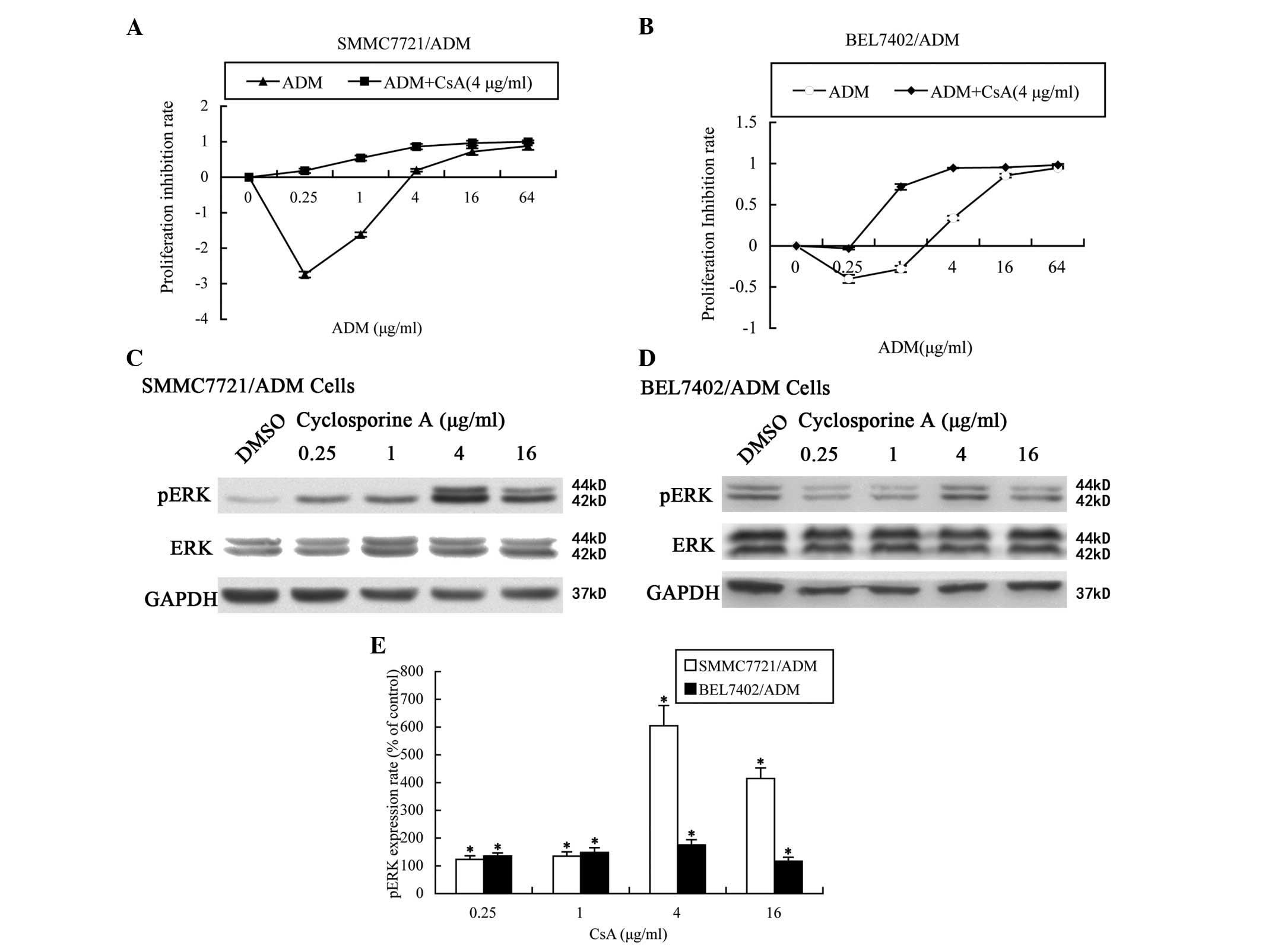
|
1
|
Tang S, Bao H, Zhang Y, et al:
14-3-3epsilon mediates the cell fate decision-making pathways in
response of hepatocellular carcinoma to Bleomycin-induced DNA
damage. PLoS One. 8:e552682013.
|
|
2
|
Zhong X, Xiong M, Meng X and Gong R:
Comparison of the multi-drug resistant human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell line Bel-7402/ADM model established by three
methods. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1152010.
|
|
3
|
Zhang Z, Zhou X, Shen H, Wang D and Wang
Y: Phosphorylated ERK is a potential predictor of sensitivity to
sorafenib when treating hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence from an
in vitro study. BMC Med. 7:412009.
|
|
4
|
Zhu AX: Systemic therapy of advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: how hopeful should we be? Oncologist.
11:790–800. 2006.
|
|
5
|
Wakamatsu T, Nakahashi Y, Hachimine D,
Seki T and Okazaki K: The combination of glycyrrhizin and
lamivudine can reverse the cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through inhibition of multidrug
resistance-associated proteins. Int J Oncol. 31:1465–1472.
2007.
|
|
6
|
Gottesman MM, Fojo T and Bates SE:
Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:48–58. 2002.
|
|
7
|
List AF, Kopecky KJ, Willman CL, et al:
Benefit of cyclosporine modulation of drug resistance in patients
with poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia: a Southwest Oncology Group
study. Blood. 98:3212–3220. 2001.
|
|
8
|
Yamamoto K, Kikuchi Y, Kudoh K and Nagata
I: Modulation of cisplatin sensitivity by taxol in
cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant human ovarian carcinoma cell
lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 126:168–172. 2000.
|
|
9
|
Holmström TH, Tran SE, Johnson VL, et al:
Inhibition of mitogen-activated kinase signaling sensitizes HeLa
cells to Fas receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
19:5991–6002. 1999.
|
|
10
|
Cowley GP and Smith ME: Modulation of
E-cadherin expression and morphological phenotype in the
intravascular component of adenocarcinomas. Int J Cancer.
60:325–329. 1995.
|
|
11
|
Huang C, Jacobson K and Schaller MD: MAP
kinases and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 117:4619–4628. 2004.
|
|
12
|
Mansour SJ, Matten WT, Hermann AS, et al:
Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP
kinase kinase. Science. 265:966–970. 1994.
|
|
13
|
Mansour SJ, Resing KA, Candi JM, et al:
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase phosphorylation of MAP
kinase kinase: determination of phosphorylation sites by mass
spectrometry and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 116:304–314.
1994.
|
|
14
|
Sturgill TW, Ray LB, Erikson E and Maller
JL: Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates
ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 334:715–718. 1988.
|
|
15
|
Boulton TG, Nye SH, Robbins DJ, et al:
ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are
activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and
NGF. Cell. 65:663–675. 1991.
|
|
16
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995.
|
|
17
|
Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A and Karin
M: Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein
kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain.
Genes Dev. 7:2135–2148. 1993.
|
|
18
|
Kyriakis JM, Banerjee P, Nikolakaki E, et
al: The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases.
Nature. 369:156–160. 1994.
|
|
19
|
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L and Ulevitch RJ: A
MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian
cells. Science. 265:808–811. 1994.
|
|
20
|
Freshney NW, Rawlinson L, Guesdon F, et
al: Interleukin-1 activates a novel protein kinase cascade that
results in the phosphorylation of Hsp27. Cell. 78:1039–1049.
1994.
|
|
21
|
Rouse J, Cohen P, Trigon S, et al: A novel
kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates
MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock
proteins. Cell. 78:1027–1037. 1994.
|
|
22
|
Lee JC, Laydon JT, McDonnell PC, et al: A
protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine
biosynthesis. Nature. 372:739–746. 1994.
|
|
23
|
Zhou G, Bao ZQ and Dixon JE: Components of
a new human protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol
Chem. 270:12665–12669. 1995.
|
|
24
|
Lee JD, Ulevitch RJ and Han J: Primary
structure of BMK1: a new mammalian map kinase. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 213:715–724. 1995.
|
|
25
|
Kohno M, Tanimura S and Ozaki K: Targeting
the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in cancer
therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1781–1784. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Yan X, Ruan W, Wang X, et al: The effects
of multidrug resistance on cell proliferation, apoptosis and
invasion activity and the expression of mitogen-activated protein
kinase in human hepatocellular cancer cells. Zhong Liu. 32:507–515.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Philip PA, Mahoney MR, Allmer C, et al:
Phase II study of Erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced
hepatocellular cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:6657–6663. 2005.
|
|
28
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007.
|
|
29
|
Geng W, Ng KT, Sun CK, et al: The role of
proline rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) on cisplatin resistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e273622011.
|
|
30
|
Long Sheng and Maoming Xiong: Progress in
primary liver cancer resistant MDR reversal of Hepatobiliary
Surgery. 20:236–238. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Dai CL and Fu LW: The development of the
reversal of the tumor multidrug resistance. Chin Pharm Bulletin.
21:513–8. 2005.
|
|
32
|
Pétriz J, Sánchez J, Bertrán J and
García-López J: Comparative effect of verapamil, cyclosporin A and
SDZ PSC 833 on rhodamine 123 transport and cycle in
vinblastine-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells overexpressing
P-glycoprotion. Anticancer Drugs. 8:869–875. 1997.
|
|
33
|
Dreuw A, Hermanns HM, Heise R, et al:
Interleukin-6-type cytokines upregulate expression of multidrug
resistance-associated proteins in NHEK and dermal fibroblasts. J
Invest Dermatol. 124:28–37. 2005.
|
|
34
|
Imai Y, Ohmori K, Yasuda S, et al: Breast
cancer resistance protein/ABCG2 is differentially regulated
downstream of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Cancer Sci.
100:1118–1127. 2009.
|
|
35
|
Gómez-Martínez A, García-Morales P,
Carrato A, et al: Post-transcriptional regulation of P-glycoprotein
expression in cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Res. 5:641–653.
2007.
|
|
36
|
Guan J, Chen XP, Zhu H, et al: Involvement
of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway in multidrug resistance induced by HBx in hepatoma
cell line. World J Gastroenterol. 10:3522–3527. 2004.
|
|
37
|
Zhu H, Chen XP, Luo SF, et al: The role of
extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway in multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 45:917–920. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Kisucká J, Barancík M, Bohácová V and
Breier A: Reversal effect of specific inhibitors of
extracellular-signal regulated protein kinase pathway on
P-glycoprotein mediated vincristine resistance of L1210 cells. Gen
Physiol Biophys. 20:439–444. 2001.
|
|
39
|
Chen B, Jin F, Lu P, et al: Effect of
mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway on
multidrug resistance induced by vincristine in gastric cancer cell
line MGC803. World J Gastroenterol. 10:795–799. 2004.
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Li S, Han Y, et al: Calebin-A
induces apoptosis and modulates MAPK family activity in drug
resistant human gastric cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 591:252–258.
2008.
|
|
41
|
Hu Y, Bally M, Dragowska WH and Mayer L:
Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase kinase enhances chemotherapeutic effects on
H460 human non-small cell lung cancer cells through activation of
apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:641–649. 2003.
|
|
42
|
Anglicheau D, Pallet N, Rabant M, et al:
Role of P-glycoprotein in cyclosporine cytotoxicity in the
cyclosporine-sirolimus interaction. Kidney Int. 70:1019–1025.
2006.
|
|
43
|
Tanaka S, Hirano T, Saito T, Wakata N and
Oka K: P-glycoprotein function in peripheral blood mononuclear
cells of myasthenia gravis patients treated with tacrolimus. Biol
Pharm Bull. 30:291–296. 2007.
|
|
44
|
Alvarez-Arroyo MV, Yagüe S, Wenger RM, et
al: Cyclophilin-mediated pathways in the effect of cyclosporin A on
endothelial cells: role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Circ
Res. 91:202–209. 2002.
|
|
45
|
Robida AM, Xu K, Ellington ML and Murphy
TJ: Cyclosporin A selectively inhibits mitogen-induced
cyclooxygenase-2 gene transcription in vascular smooth muscle
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 58:701–708. 2000.
|
|
46
|
Chen HW, Chien CT, Yu SL, Lee YT and Chen
WJ: Cyclosporine A regulate oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes: mechanisms via ROS generation, iNOS and Hsp70. Br J
Pharmacol. 137:771–781. 2002.
|
|
47
|
Kiely B, Feldman G and Ryan MP: Modulation
of renal epithelial barrier function by mitogen-activated protein
kinases (MAPKs): mechanism of cyclosporine A-induced increase in
transepithelial resistance. Kidney Int. 63:908–916. 2003.
|
|
48
|
Hojo M, Morimoto T, Maluccio M, et al:
Cyclosporine induces cancer progression by a cell-autonomous
mechanism. Nature. 397:530–534. 1999.
|
|
49
|
Paslaru L, Trigon S, Kuhlmann M and
Morange M: MAP kinase activation by cyclosporine A. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 236:599–603. 1997.
|
|
50
|
Du MR, Zhou WH, Yan FT, et al:
Cyclosporine A induces titin expression via MAPK/ERK signalling and
improves proliferative and invasive potential of human trophoblast
cells. Hum Reprod. 22:2528–2537. 2007.
|
|
51
|
Zhou WH, Du MR, Dong L, et al: Cyclosporin
A increases expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and 2 and
invasiveness in vitro of the first-trimester human trophoblast
cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Hum Reprod.
22:2743–2750. 2007.
|
|
52
|
Cen J and Li YM: Combination therapy on
multidrug-resistance tumor. World Notes Antibiotics. 5:224–228.
2009.
|