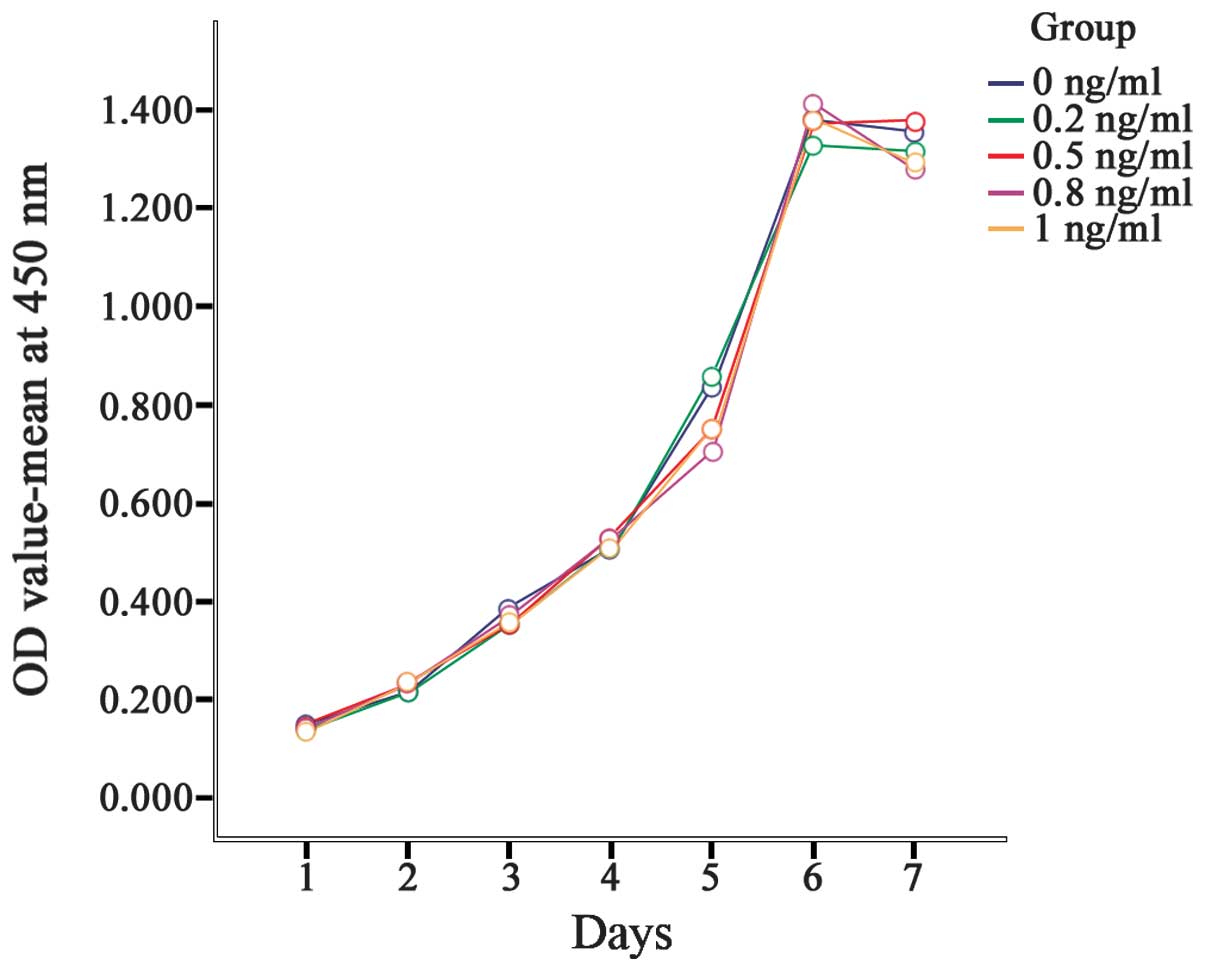
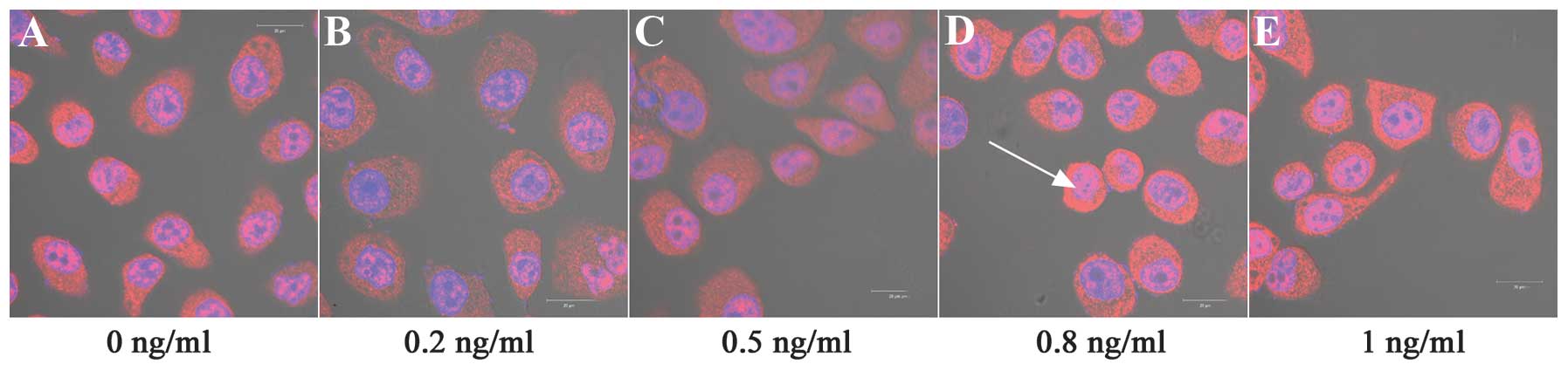
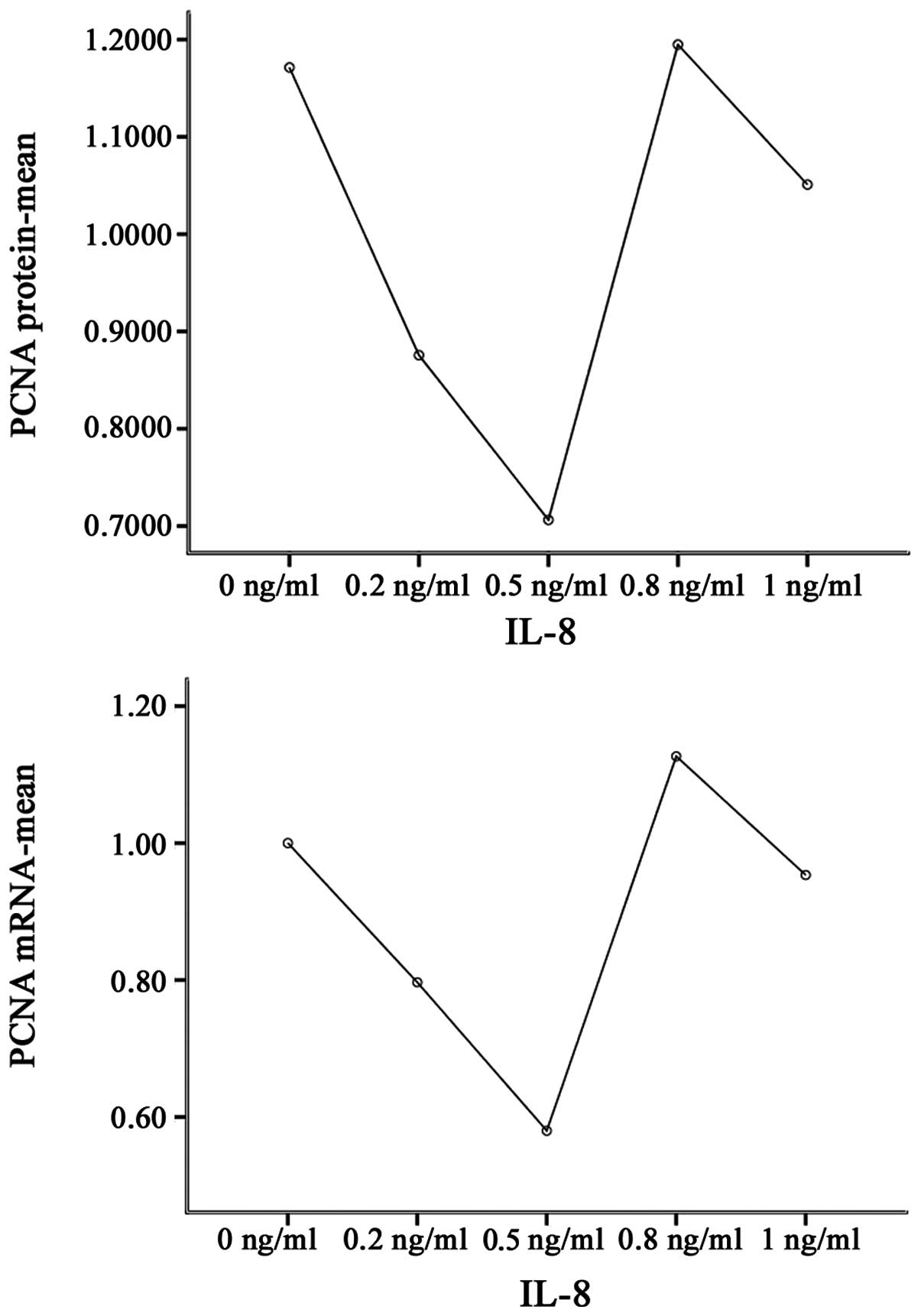
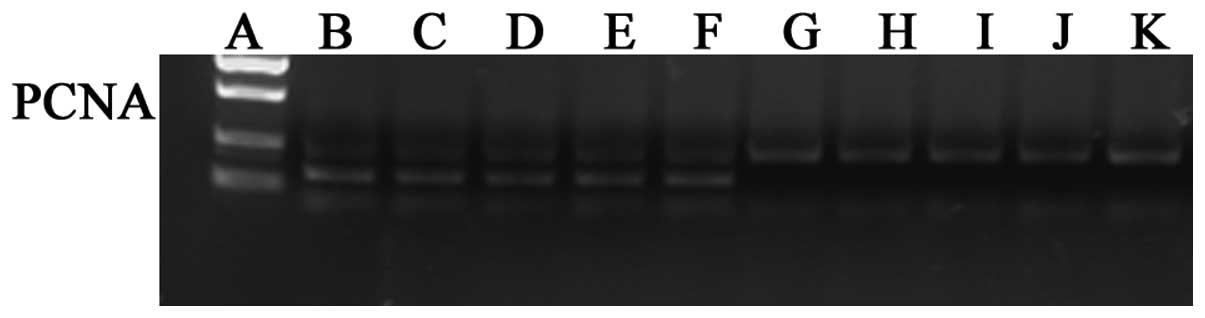
|
1
|
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, et al:
Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with
predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer.
50:1330–1344. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Forman
D, Bray F, Dikshit R, Elser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M and Parkin DM:
GLOBOCAN 2012 v10, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide. IARC
CancerBase No. 11 Lyon, France: International Agency for Research
on Cancer; 2013, Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr.
accessed on August 30, 2014
|
|
3
|
Harada A, Sekido N, Akahoshi T, et al:
Essential involvement of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in acute
inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 56:559–564. 1994.
|
|
4
|
Raman D, Baugher PJ, Thu YM and Richmond
A: Role of chemokines in tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 256:137–165.
2007.
|
|
5
|
Xie K: Interleukin-8 and human cancer
biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 12:375–391. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Xu L and Fidler IJ: Interleukin-8: an
autocrine growth factor for human ovarian cancer. Oncol Res.
12:97–106. 2000.
|
|
7
|
Huang S, Mills L, Mian B, et al: Fully
humanized neutralizing antibodies to interleukin-8 (ABX-IL8)
inhibit angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis of human
melanoma. Am J Pathol. 161:125–134. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Mukaida N, et al:
Regulation of disease-progression genes in human gastric carcinoma
cells by interleukin-8. Clin Cancer Res. 6:2735–2740. 2000.
|
|
9
|
Kuai WX, Wang Q, Yang XZ, et al:
Interleukin-8 associates with adhesion, migration, invasion and
chemosensitivity of human gastric cancer cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:979–985. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Peek RM Jr and Blaser MJ: Helicobacter
pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:28–37. 2002.
|
|
11
|
Ren Z, Pang G, Clancy R, et al: Shift of
the gastric T-cell response in gastric carcinoma. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:142–148. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Sheh A, Chaturvedi R, Merrell DS, et al:
Phylogeographic origin of Helicobacter pylori determines
host-adaptive responses upon coculture with gastric epithelial
cells. Infect Immun. 81:2468–2477. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Wang YC and Huang KM: In vitro
anti-inflammatory effect of apigenin in the Helicobacter
pylori-infected gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 53:376–383. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, et al:
Induction of various cytokines and development of severe mucosal
inflammation by cagA gene positive Helicobacter pylori
strains. Gut. 41:442–451. 1997.
|
|
15
|
D’Elios MM and Andersen LP:
Helicobacter pylori inflammation, immunity, and vaccines.
Helicobacter. 12(Suppl 1): 15–19. 2007.
|
|
16
|
D’Elios MM and Andersen LP: Inflammation,
immunity, and vaccines for Helicobacter pylori.
Helicobacter. 14(Suppl 1): 21–28. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Montecucco C and Rappuoli R: Living
dangerously; How Helicobacter pylori survives in the human
stomach. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:457–466. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Naito Y and Yoshikawa T: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced
inflammation and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:323–336.
2002.
|
|
19
|
Peek RM Jr, Fiske C and Wilson KT: Role of
innate immunity in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric
malignancy. Physiol Rev. 90:831–858. 2010.
|
|
20
|
Chiba T, Marusawa H, Seno H and Watanabe
N: Mechanism for gastric cancer development by Helicobacter
pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1175–1181.
2008.
|
|
21
|
Nozawa Y, Nishihara K, Peek RM, et al:
Identification of a signaling cascade for interleukin-8 production
by Helicobacter pylori in human gastric epithelial cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 64:21–30. 2002.
|
|
22
|
Sharma SA, Tummuru MK, Blaser MJ and Kerr
LD: Activation of IL-8 gene expression by Helicobacter
pylori is regulated by transcription factor nuclear
factor-kappa B in gastric epithelial cells. J Immunol.
160:2401–2407. 1998.
|
|
23
|
Keates S, Keates AC, Warny M, et al:
Differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in AGS
gastric epithelial cells by cag+ and cag− Helicobacter
pylori. J Immunol. 163:5552–5559. 1999.
|
|
24
|
Eftang LL, Esbensen Y, Tannæs TM, Bukholm
IR and Bukholm G: Interleukin-8 is the single most up-regulated
gene in whole genome profiling of H. Pylori exposed gastric
epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 12:92012.
|
|
25
|
Crabtree JE, Farmery SM, Lindley IJ, et
al: CagA/cytotoxic strains of Helicobacter pylori and
interleukin-8 in gastric epithelial cell lines. J Clin Pathol.
47:945–950. 1994.
|
|
26
|
Sharma SA, Tummuru MK, Miller GG and
Blaser MJ: Interleukin-8 response of gastric epithelial cell lines
to Helicobacter pylori stimulation in vitro. Infect Immun.
63:1681–1687. 1995.
|
|
27
|
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, et al:
Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric
cancer. N Engl J Med. 345:784–789. 2001.
|
|
28
|
Correa P and Houghton J: Carcinogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 133:659–672.
2007.
|
|
29
|
World Health Organization; International
Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC monographs on the
evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. 61. World Health
Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: pp. 177–240. 1994
|
|
30
|
Waugh DJ and Wilson C: The interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008.
|
|
31
|
Takagi A, Kamiya S, Koga Y, et al:
Analysis of interleukin-8 secretion induced by Helicobacter
pylori from the gastric epithelial cell line MKN45: a mechanism
independent of the intensity of cytotoxicity. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 12:368–372. 1997.
|
|
32
|
Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Sumii K, et al:
Expression of interleukin-8 correlates with vascularity in human
gastric carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 152:93–100. 1998.
|
|
33
|
Kido S, Kitadai Y, Hattori N, et al:
Interleukin-8 and vascular endothelial growth factor - prognostic
factors in human gastric carcinomas? Eur J Cancer. 37:1482–1487.
2001.
|
|
34
|
Ju D, Sun D, Xiu L, et al: Interleukin-8
is associated with adhesion, migration and invasion in human
gastric cancer SCG-7901 cells. Med Oncol. 29:91–99. 2012.
|
|
35
|
Zhu YM and Woll PJ: Mitogenic effects of
interleukin-8/CXCL8 on cancer cells. Future Oncol. 1:699–704.
2005.
|
|
36
|
Gabellini C, Trisciuoglio D, Desideri M,
et al: Functional activity of CXCL8 receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, on
human malignant melanoma progression. Eur J Cancer. 45:2618–2627.
2009.
|
|
37
|
Christofakis EP, Miyazaki H, Rubink DS and
Yeudall WA: Roles of CXCL8 in squamous cell carcinoma proliferation
and migration. Oral Oncol. 44:920–926. 2008.
|
|
38
|
Wu S, Shang H, Cui L, et al: Targeted
blockade of interleukin-8 abrogates its promotion of cervical
cancer growth and metastasis. Mol Cell Biochem. 375:69–79.
2013.
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Xu RC, Zhang XL, et al:
Interleukin-8 secretion by ovarian cancer cells increases
anchorage-independent growth, proliferation, angiogenic potential,
adhesion and invasion. Cytokine. 59:145–155. 2012.
|
|
40
|
Luppi F, Longo AM, de Boer WI, Rabe KF and
Hiemstra PS: Interleukin-8 stimulates cell proliferation in
non-small cell lung cancer through epidermal growth factor receptor
transactivation. Lung Cancer. 56:25–33. 2007.
|
|
41
|
Ning Y, Manegold PC, Hong YK, et al:
Interleukin-8 is associated with proliferation, migration,
angiogenesis and chemosensitivity in vitro and in vivo in colon
cancer cell line models. Int J Cancer. 128:2038–2049. 2011.
|
|
42
|
Shao N, Chen LH, Ye RY, Lin Y and Wang SM:
The depletion of interleukin-8 causes cell cycle arrest and
increases the efficacy of docetaxel in breast cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 431:535–541. 2013.
|
|
43
|
Iwai M, Matsuda M and Iwai Y: Cloning of a
cancer cell-producing hepatocyte growth factor, vascular
endothelial growth factor, and interleukin-8 from gastric cancer
cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 39:288–290. 2003.
|
|
44
|
Kubo F, Ueno S, Hiwatashi K, et al:
Interleukin-8 in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with
cancer cell invasion of vessels but not with tumor angiogenesis.
Ann Surg Oncol. 12:800–807. 2005.
|
|
45
|
Lin Y, Wang SM, Lü WM and Huang RP: Effect
of interleukin-8 in cell invasion and proliferation of human breast
cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 43:1541–1544. 2005.(In
Chinese).
|
|
46
|
Jain S, Filipe MI, Hall PA, et al:
Prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in gastric
carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 44:655–659. 1991.
|
|
47
|
Li N: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
(PCNA/cyclin) in gastric carcinoma in relation to its prognosis.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 15:34–36. 1993.(In Chinese).
|
|
48
|
Shibata W and Maeda S: Mechanism of H.
pylori-induced gastric inflammation and carcinogenesis. Nihon
Rinsho. 71:1346–1351. 2013.(In Japanese).
|
|
49
|
Song H, Michel A, Nyrén O, Ekström AM,
Pawlita M and Ye W: A CagA-independent cluster of antigens related
to the risk of noncardia gastric cancer: associations between
Helicobacter pylori antibodies and gastric adenocarcinoma explored
by multiplex serology. Int J Cancer. 134:2942–2950. 2014.
|
|
50
|
Yoshida T, Kato J, Inoue I, Yoshimura N,
Deguchi H, Mukoubayashi C, Oka M, Watanabe M, Enomoto S, Niwa T, et
al: Cancer development based on chronic active gastritis and
resulting gastric atrophy as assessed by serum levels of pepsinogen
and Helicobacter pylori antibody titer. Int J Cancer.
134:1445–1457. 2014.
|
|
51
|
Berber U, Yılmaz I, Erkul BE and Kaplan M:
Peptic ulcer and intestinal metaplasia associated with Helicobacter
pylori colonization in gastric heterotopia of the tongue. Turk J
Gastroenterol. 25:224–225. 2014.
|
|
52
|
Kara N, Urganci N, Kalyoncu D and Yilmaz
B: The association between Helicobacter pylori gastritis and
lymphoid aggregates, lymphoid follicles and intestinal metaplasia
in gastric mucosa of children. J Paediatr Child Health. 50:605–609.
2014.
|