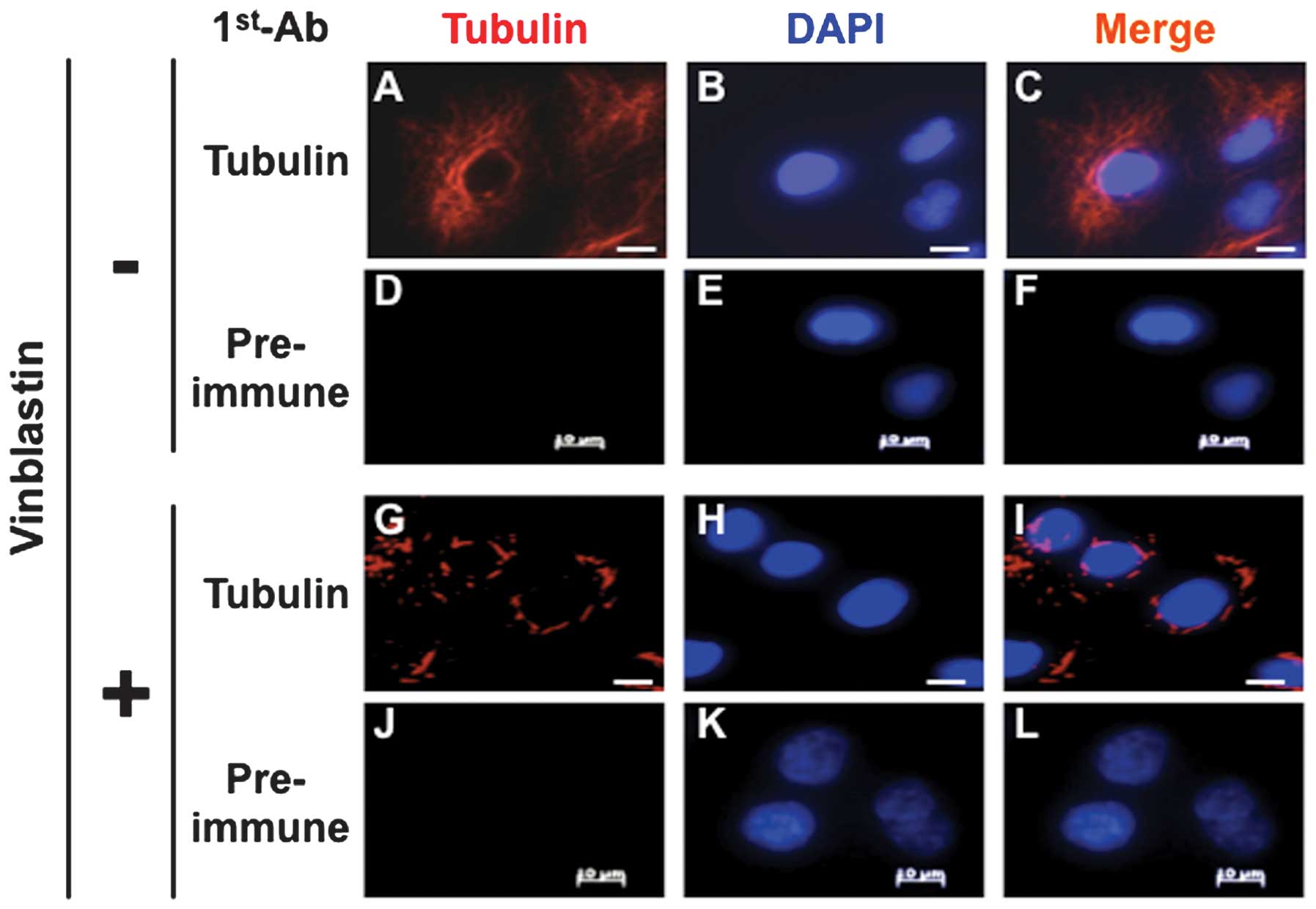
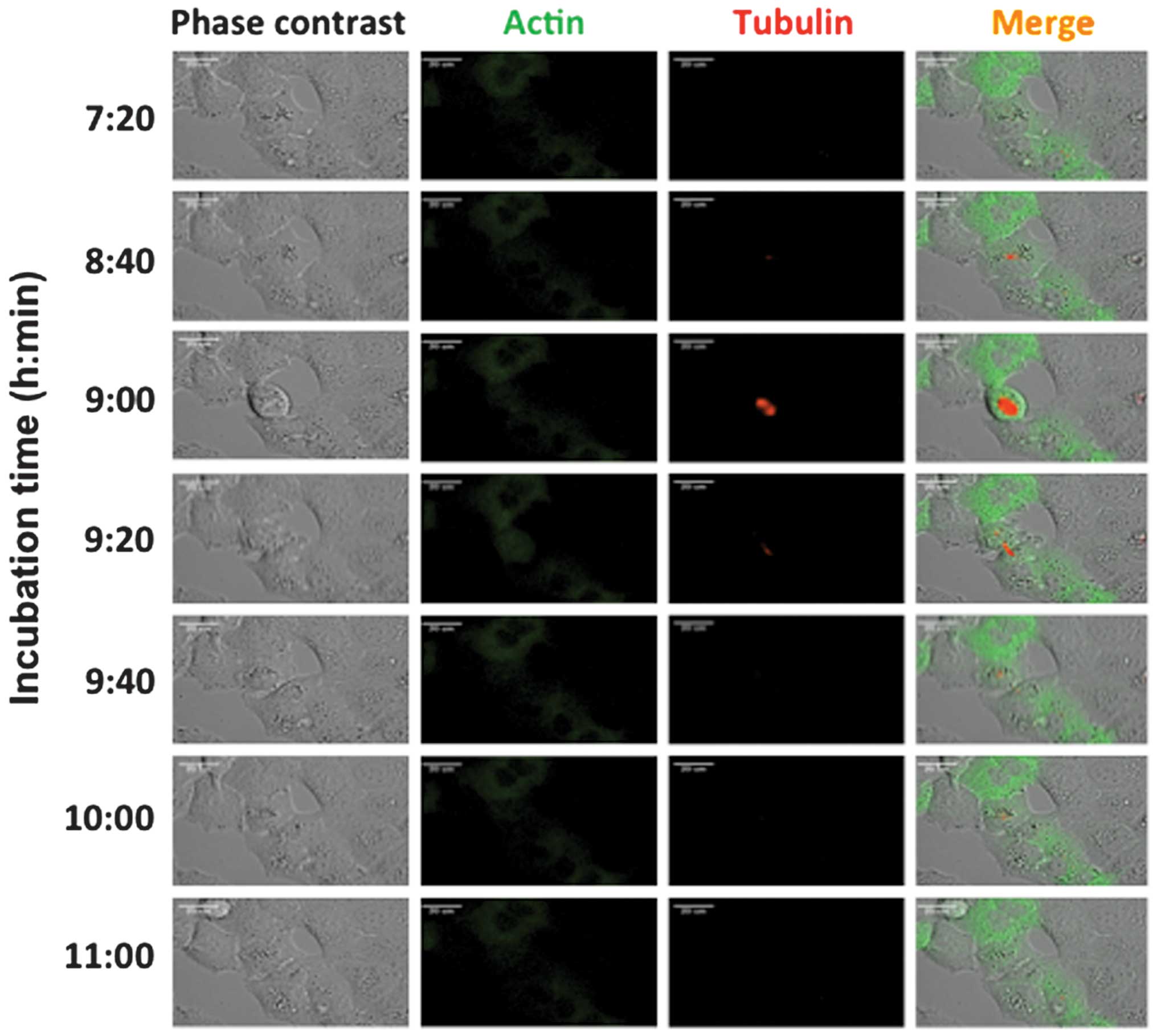
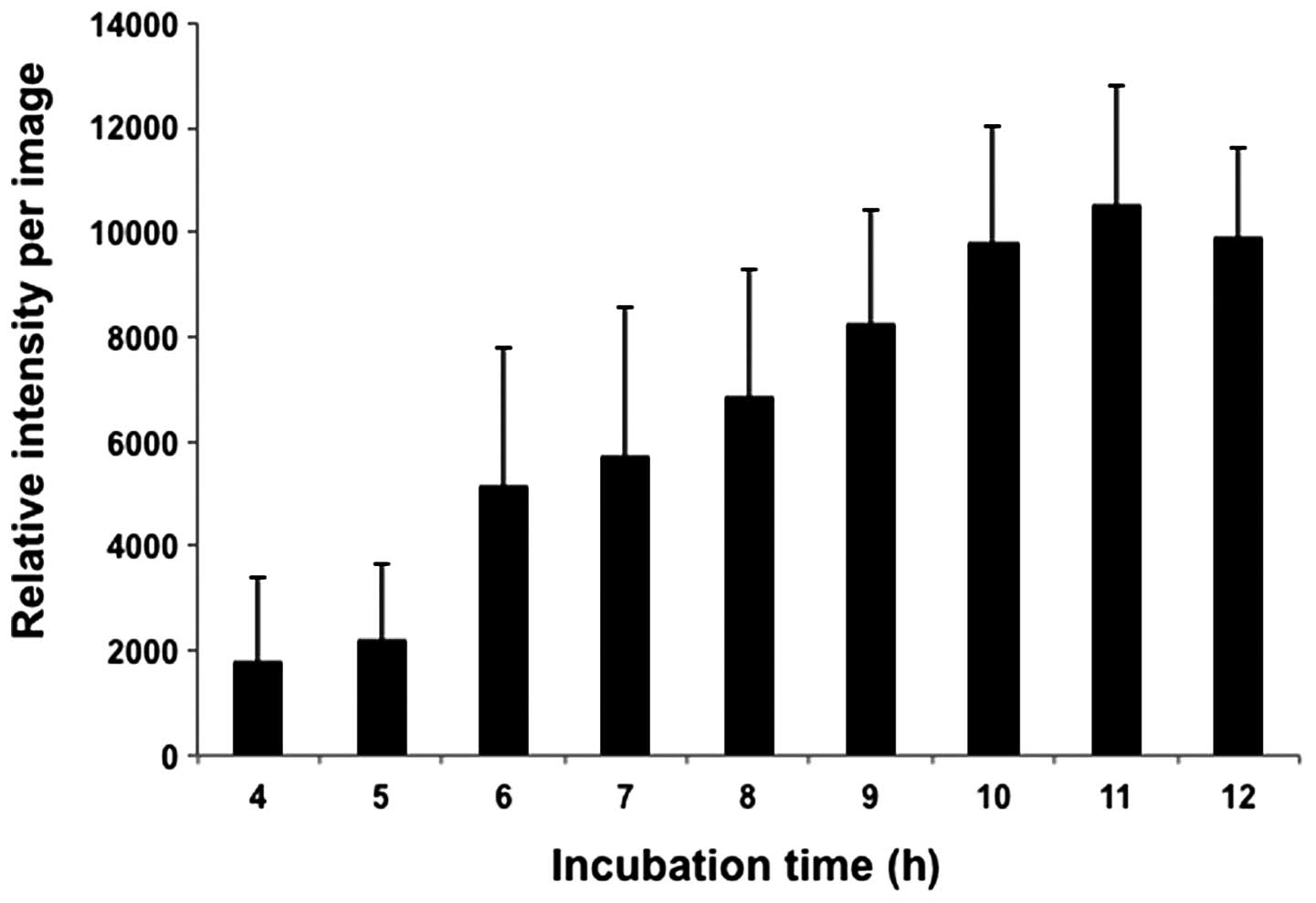
|
1
|
Moudi M, Go R, Yien CY and Nazre M: Vinca
alkaloids. Int J Prev Med. 4:1231–1235. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Nelson RL: The comparative clinical
pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of vindesine, vincristine, and
vinblastine in human patients with cancer. Med Pediatr Oncol.
10:115–127. 1982.
|
|
3
|
Duggan DB, Petroni GR, Johnson JL, et al:
Randomized comparison of ABVD and MOPP/ABV hybrid for the treatment
of advanced Hodgkin’s disease: report of an intergroup trial. J
Clin Oncol. 21:607–614. 2003.
|
|
4
|
Ladisch S, Gadner H, Aricò M, et al:
LCH-I: a randomized trial of etoposide vs. vinblastine in
disseminated Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Med Pediatr Oncol.
23:107–110. 1994.
|
|
5
|
Epstein JB: Treatment of oral Kaposi
sarcoma with intralesional vinblastine. Cancer. 71:1722–1725.
1993.
|
|
6
|
Einhorn LH: Curing metastatic testicular
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:4592–4595. 2002.
|
|
7
|
Woodcock TM, Blumenreich MS, Richman SP,
Kubota TT, Gentile PS and Allegra JC: Combination chemotherapy with
cis-diamminedichloroplatinum and vinblastine in advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1:247–250. 1983.
|
|
8
|
Kovacs K and Horvath E:
Vinblastine-induced ultrastructural changes in perisinusoidal cells
of the rat liver. Res Exp Med (Berl). 165:245–249. 1975.
|
|
9
|
Shiino M: Ultrastructural observation of
paracrystalline aggregates of microtubules in anterior pituitary
cells of the chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger). Cell Tissue
Res. 213:433–440. 1980.
|
|
10
|
De Brabander M, De May J, Joniau M and
Geuens G: Ultrastructural immunocytochemical distribution of
tubulin in cultured cells treated with microtubule inhibitors. Cell
Biol Int Rep. 1:177–183. 1977.
|
|
11
|
Shiino M and Rennels EG:
Vinblastine-induced microtubular paracrystals in prolactin cells of
anterior pituitary gland of lactating rats. Am J Anat. 144:399–405.
1975.
|
|
12
|
Nogales E, Medrano FJ, Diakun GP, Mant GR,
Towns-Andrews E and Bordas J: The effect of temperature on the
structure of vinblastine-induced polymers of purified tubulin:
detection of a reversible conformational change. J Mol Biol.
254:416–430. 1995.
|
|
13
|
Brockstedt U, Dobra K, Nurminen M and
Hjerpe A: Immunoreactivity to cell surface syndecans in cytoplasm
and nucleus: tubulin-dependent rearrangements. Exp Cell Res.
274:235–245. 2002.
|
|
14
|
Salicioni AM, Xi M, Vanderveer LA, et al:
Identification and structural analysis of human RBM8A and RBM8B:
two highly conserved RNA-binding motif proteins that interact with
OVCA1, a candidate tumor suppressor. Genomics. 69:54–62. 2000.
|
|
15
|
Lau CK, Diem MD, Dreyfuss G and Van Duyne
GD: Structure of the Y14-Magoh core of the exon junction complex.
Curr Biol. 13:933–941. 2003.
|
|
16
|
Chuang TW, Chang WL, Lee KM and Tarn WY:
The RNA-binding protein Y14 inhibits mRNA decapping and modulates
processing body formation. Mol Biol Cell. 24:1–13. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Le Hir H, Gatfield D, Braun IC, Forler D
and Izaurralde E: The protein Mago provides a link between splicing
and mRNA localization. EMBO Rep. 2:1119–1124. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Sudo H, Tsuji AB, Sugyo A, et al:
Knockdown of COPA, identified by loss-of-function screen, induces
apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in mesothelioma mouse model.
Genomics. 95:210–216. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Ishigaki Y, Nakamura Y, Tatsuno T, et al:
Depletion of RNA-binding protein RBM8A (Y14) causes cell cycle
deficiency and apoptosis in human cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
238:889–897. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Ishigaki Y, Nakamura Y, Tatsuno T,
Hashimoto M, Iwabuchi K and Tomosugi N: RNA-binding protein RBM8A
(Y14) and MAGOH localize to centrosome in human A549 cells.
Histochem Cell Biol. 141:101–109. 2014.
|
|
21
|
Kost TA, Condreay JP and Jarvis DL:
Baculovirus as versatile vectors for protein expression in insect
and mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol. 23:567–575. 2005.
|
|
22
|
Kost TA and Condreay JP: Recombinant
baculoviruses as mammalian cell gene-delivery vectors. Trends
Biotechnol. 20:173–180. 2002.
|
|
23
|
Shukla S, Schwartz C, Kapoor K, Kouanda A
and Ambudkar SV: Use of baculovirus BacMam vectors for expression
of ABC drug transporters in mammalian cells. Drug Metab Dispos.
40:304–312. 2012.
|
|
24
|
Araki R, Jincho Y, Hoki Y, et al:
Conversion of ancestral fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem
cells. Stem Cells. 28:213–220. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Sakaue-Sawano A, Kobayashi T, Ohtawa K and
Miyawaki A: Drug-induced cell cycle modulation leading to
cell-cycle arrest, nuclear mis-segregation, or endoreplication. BMC
Cell Biol. 12:22011.
|
|
26
|
Ben-Ze’ev A, Farmer SR and Penman S:
Mechanisms of regulating tubulin synthesis in cultured mammalian
cells. Cell. 17:319–325. 1979.
|
|
27
|
Wehland J, Henkart M, Klausner R and
Sandoval IV: Role of microtubules in the distribution of the Golgi
apparatus: effect of taxol and microinjected anti-alpha-tubulin
antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:4286–4290. 1983.
|
|
28
|
Sharp JA, Plant JJ, Ohsumi TK, Borowsky M
and Blower MD: Functional analysis of the microtubule-interacting
transcriptome. Mol Biol Cell. 22:4312–4323. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Sakaue-Sawano A, Ohtawa K, Hama H, Kawano
M, Ogawa M and Miyawaki A: Tracing the silhouette of individual
cells in S/G2/M phases with fluorescence. Chem Biol. 15:1243–1248.
2008.
|
|
30
|
Sakaue-Sawano A, Kurokawa H, Morimura T,
et al: Visualizing spatiotemporal dynamics of multicellular
cell-cycle progression. Cell. 132:487–498. 2008.
|