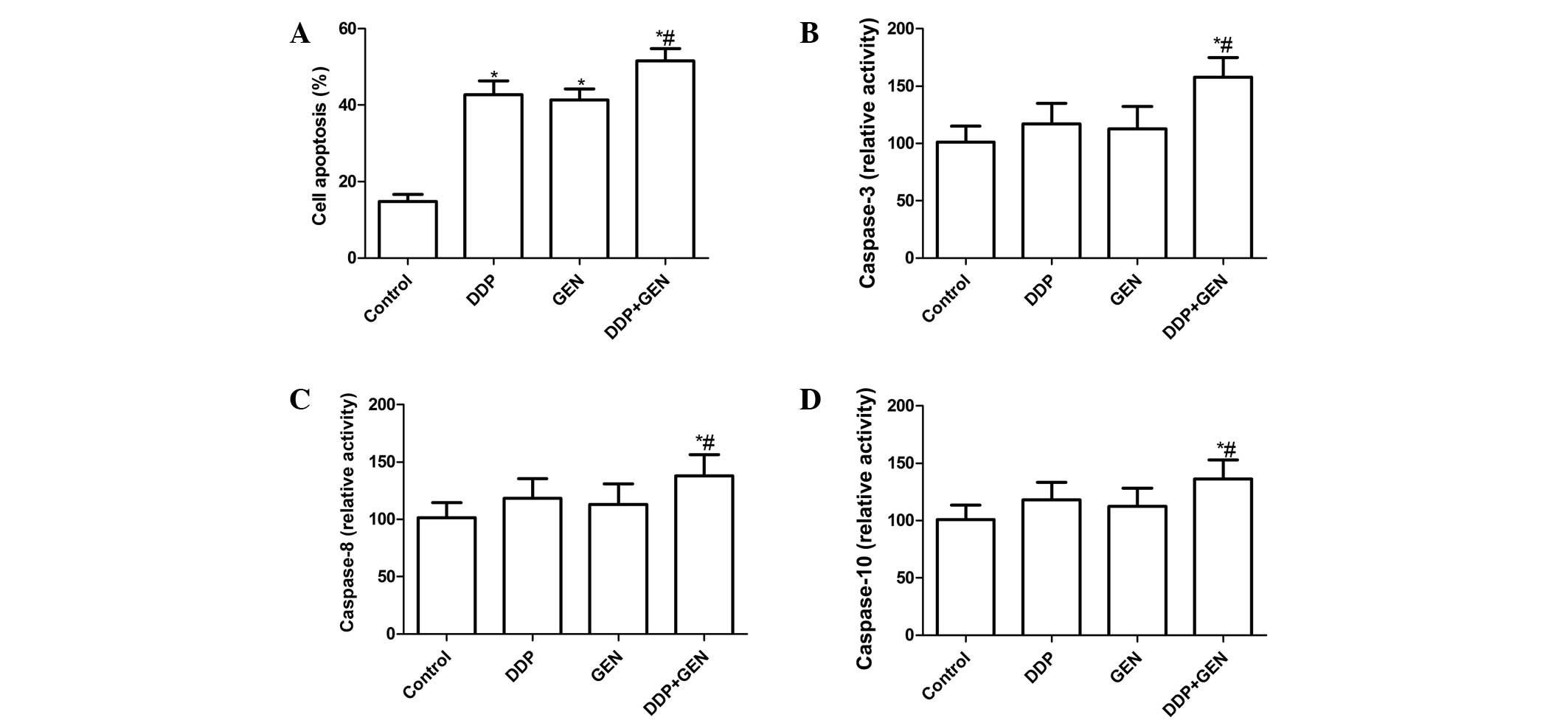
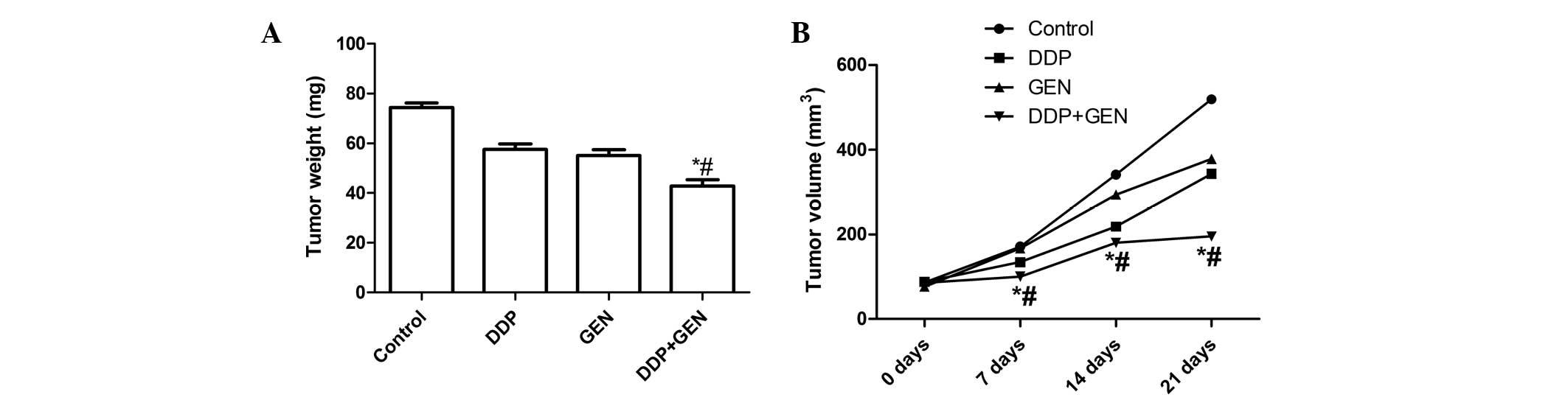
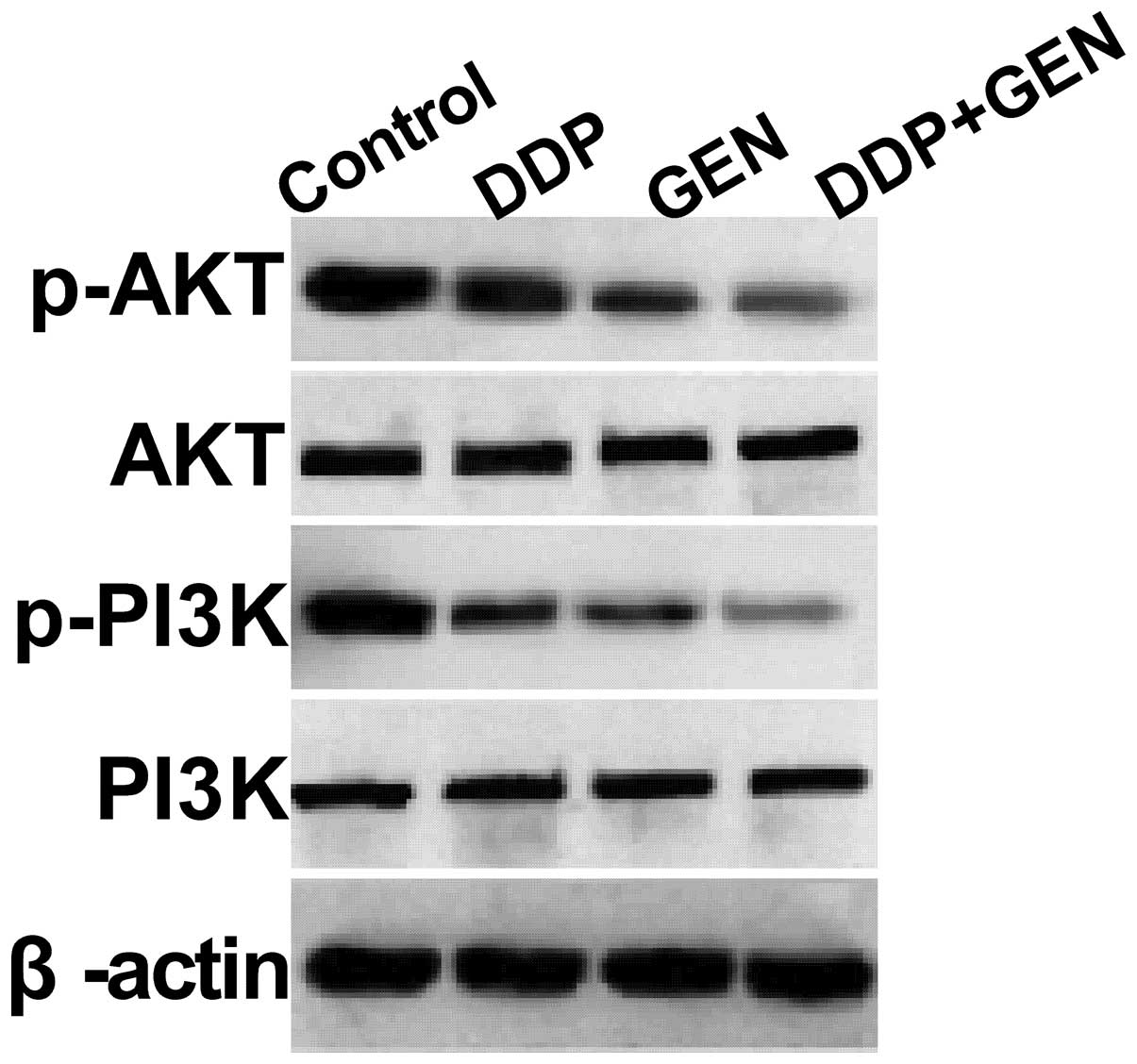
|
1
|
Méndez M, Custodio A and Provencio M: New
molecular targeted therapies for advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Dis. 3:30–56. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Roy M, Luo YH, Ye M and Liu J: Nonsmall
cell lung cancer therapy: insight into multitargeted small-molecule
growth factor receptor inhibitors. Biomed Res Int.
2013:9647432013.
|
|
4
|
Raez LE and Lilenbaum R: Chemotherapy for
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol.
2:173–178. 2004.
|
|
5
|
Rinaldi M, Belvedere O, Cauchi C, et al:
Maintenance chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol.
17(Suppl 2): ii67–ii70. 2006.
|
|
6
|
Chang A: Chemotherapy, chemoresistance and
the changing treatment landscape for NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 71:3–10.
2011.
|
|
7
|
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA,
Booth-Genthe C and Gottesman MM: Targeting multidrug resistance in
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:219–234. 2006.
|
|
8
|
Gadgeel SM, Ali S, Philip PA, Wozniak A
and Sarkar FH: Genistein enhances the effect of epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and inhibits nuclear
factor kappa B in nonsmall cell lung cancer cell lines. Cancer.
115:2165–2176. 2009.
|
|
9
|
Li Q and Chen H: Epigenetic modifications
of metastasis suppressor genes in colon cancer metastasis.
Epigenetics. 6:849–852. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Nagata Y, Sonoda T, Mori M, et al: Dietary
isoflavones may protect against prostate cancer in Japanese men. J
Nutr. 137:1974–1979. 2007.
|
|
11
|
Ali S, Varghese L, Pereira L, et al:
Sensitization of squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin induced
killing by natural agents. Cancer Lett. 278:201–209. 2009.
|
|
12
|
Lattrich C, Lubig J, Springwald A, et al:
Additive effects of trastuzumab and genistein on human breast
cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 22:253–261. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Schabath MB, Hernandez LM, Wu X, Pillow PC
and Spitz MR: Dietary phytoestrogens and lung cancer risk. JAMA.
294:1493–1504. 2005.
|
|
14
|
Mai Z, Blackburn GL and Zhou JR: Genistein
sensitizes inhibitory effect of tamoxifen on the growth of estrogen
receptor-positive and HER2-overexpressing human breast cancer
cells. Mol Carcinog. 46:534–542. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Mohammad RM, Banerjee S, Li Y, et al:
Cisplatin-induced antitumor activity is potentiated by the soy
isoflavone genistein in BxPC-3 pancreatic tumor xenografts. Cancer.
106:1260–1268. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.
|
|
17
|
Petty RD, Nicolson MC, Skaria S, et al:
Aberdeen Pancreatic Cancer Focus Group: A phase II study of
mitomycin C, cisplatin and protracted infusional 5-fluorouracil in
advanced pancreatic carcinoma: efficacy and low toxicity. Ann
Oncol. 14:1100–1105. 2003.
|
|
18
|
Rajeswaran A, Trojan A, Burnand B and
Giannelli M: Efficacy and side effects of cisplatin- and
carboplatin-based doublet chemotherapeutic regimens versus
non-platinum-based doublet chemotherapeutic regimens as first line
treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung carcinoma: a systematic
review of randomized controlled trials. Lung Cancer. 59:1–11.
2008.
|
|
19
|
Choi YH, Zhang L, Lee WH and Park KY:
Genistein-induced G2/M arrest is associated with the inhibition of
cyclin B1 and the induction of p21 in human breast carcinoma cells.
Int J Oncol. 13:391–396. 1998.
|
|
20
|
Choi YH, Lee WH, Park KY and Zhang L:
p53-independent induction of p21 (WAF1/CIP1), reduction of cyclin
B1 and G2/M arrest by the isoflavone genistein in human prostate
carcinoma cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 91:164–173. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Sarkar FH, Adsule S, Padhye S, Kulkarni S
and Li Y: The role of genistein and synthetic derivatives of
isoflavone in cancer prevention and therapy. Mini Rev Med Chem.
6:401–407. 2006.
|
|
22
|
Thasni KA, Rojini G, Rakesh SN, et al:
Genistein induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via different
molecular pathways depending on Breast Cancer Susceptibility gene-1
(BRCA1) status. Eur J Pharmacol. 588:158–164. 2008.
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Ahmed F, Ali S, et al: Inactivation
of nuclear factor kappaB by soy isoflavone genistein contributes to
increased apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in human
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:6934–6942. 2005.
|
|
24
|
Jeong SY and Seol DW: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. BMB Rep. 41:11–22. 2008.
|
|
25
|
Cohen GM: Caspases: the executioners of
apoptosis. Biochem J. 326(Pt 1): 1–16. 1997.
|
|
26
|
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM and Kaufmann SH:
Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and
functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:383–424. 1999.
|
|
27
|
Gagnon V, Van Themsche C, Turner S,
Leblanc V and Asselin E: AKT and XIAP regulate the sensitivity of
human uterine cancer cells to cisplatin, doxorubicin and taxol.
Apoptosis. 13:259–271. 2008.
|
|
28
|
McDonald GT, Sullivan R, Paré GC and
Graham CH: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase promotes
tumor cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents via a mechanism
involving delay in cell cycle progression. Exp Cell Res.
316:3197–3206. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Chekenya M, Krakstad C, Svendsen A, et al:
The progenitor cell marker NG2/MPG promotes chemoresistance by
activation of integrin-dependent PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncogene.
27:5182–5194. 2008.
|
|
30
|
Li Y and Sarkar FH: Inhibition of nuclear
factor kappaB activation in PC3 cells by genistein is mediated via
AKT signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2369–2377. 2002.
|
|
31
|
Park SY and Seol DW: Regulation of AKT by
EGF-R inhibitors, a possible mechanism of EGF-R inhibitor-enhanced
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 295:515–518.
2002.
|