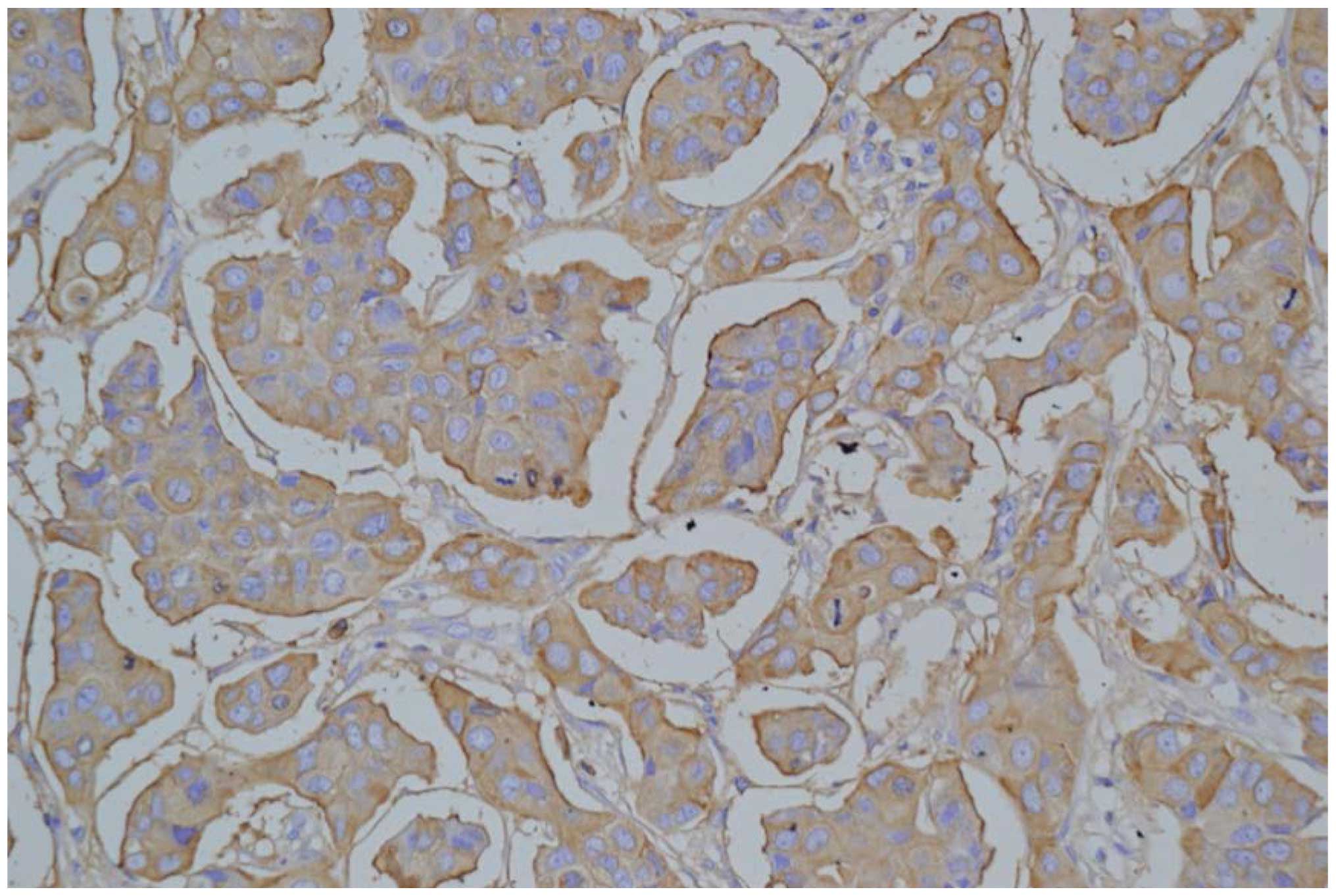
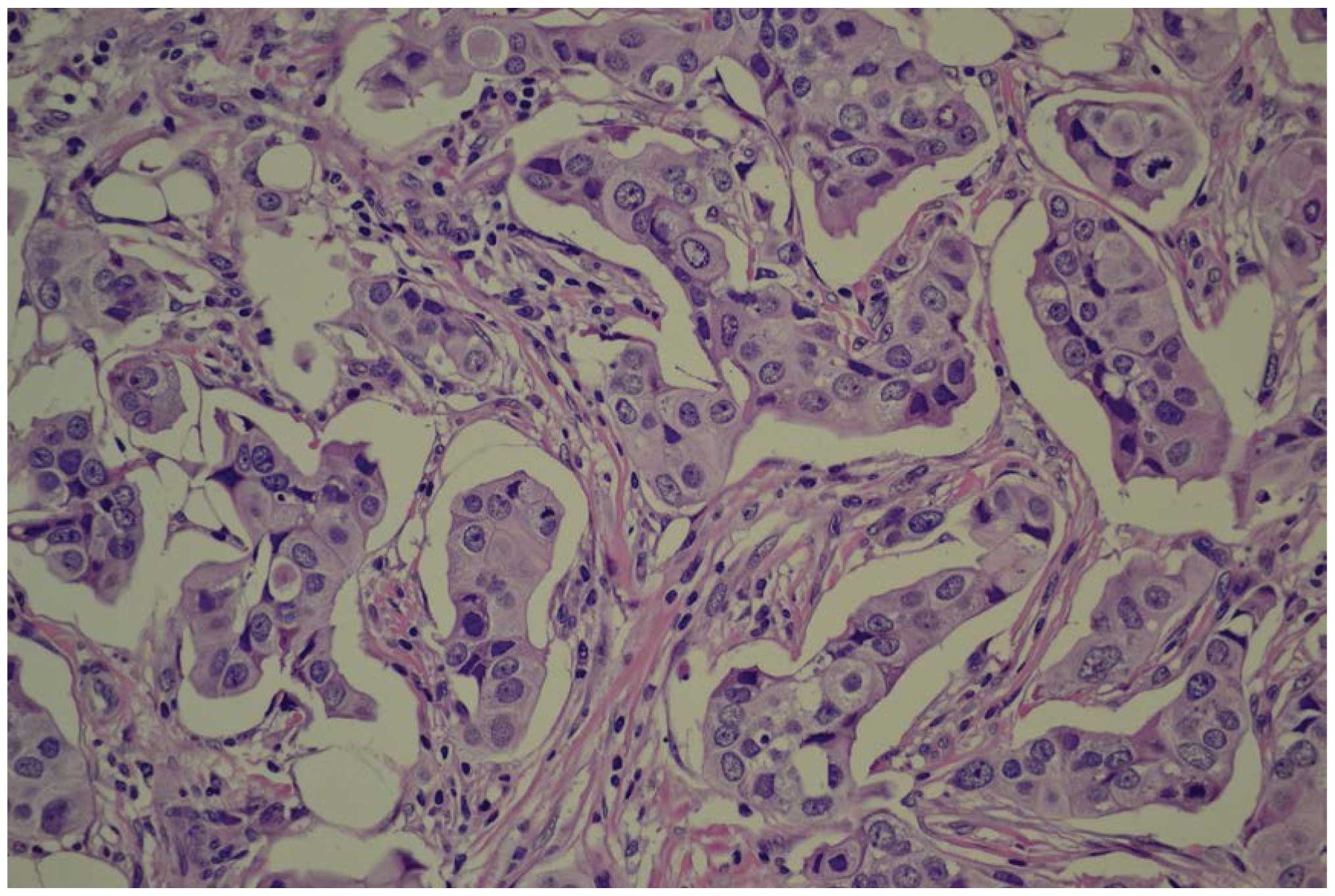
|
1
|
Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Sastre-Garau X, et
al: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma. Pathology and Genetics of
Tumors of the Breast and Female Genital Organs (IARC WHO
Classification of Tumours). Tavassoli FA and Devilee P: IARC Press;
Lyon: pp. 35–36. 2003
|
|
2
|
Pettinato G, Manivel CJ, Panico L, Sparano
L and Petrella G: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast:
clinicopathologic study of 62 cases of a poorly recognized variant
with highly aggressive behavior. Am J Clin Pathol. 121:857–866.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petersen JL: Breast carcinomas with an
unexpected inside-out growth pattern: rotation of polarization
associated with angioinvasion. Pathol Res Pract. 189:A7801993.
|
|
4
|
Tavassoli FA and Devilee P: World Health
Organization Classification of Tumors. Pathology and Genetics of
Tumors of the Breast and Female Genital Organs. IARC Press; Lyon:
2003
|
|
5
|
Siriaunkgul S and Tavassoli FA: Invasive
micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. Mod Patho. 6:660–662.
1993.
|
|
6
|
Yun SU, Choi BB, Shu KS, et al: Imaging
findings of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. J
Breast Cancer. 15:57–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fisher ER, Palekar AS, Redmond C, Barton B
and Fisher B: Pathologic findings from the National Surgical
Adjuvant Breast Project (protocol no. 4) VI Invasive papillary
cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 73:313–322. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Wolff AG, Mangu PB
and Temin S: American society of clinical oncology/college of
American pathologists guideline recommendations for
immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors
in breast cancer. J Oncol Pract. 6:195–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
American College of Radiology. BI-RADS:
Ultrasound. Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS
atlas). 4th edition. American College of Radiology; Reston, VA: pp.
196–198. 2003
|
|
10
|
Ide Y, Horii R, Osako T, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of invasive micropapillary
carcinoma component in invasive breast carcinoma. Pathol Int.
61:731–736. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Fan Y, Lang RG, et al: Breast
carcinoma with micropapillary features: clinicopathological study
and long-term follow-up of 100 cases. Int J Surg Pathol.
16:155–163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu JI, Choi DH, Park W, et al: Differences
in prognostic factors and patterns of failure between invasive
micropapillary carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma of the
breast: matched case-control study. Breast. 19:231–237. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo X, Chen L, Lang R, et al: Invasive
micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: association of pathologic
features with lymph node metastasis. Am J Clin Pathol. 126:740–746.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adrada B, Arribas E, Gilcrease M and Yang
WT: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: mammographic,
sonographic, and MRI features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 193:W58–W63.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim DS, Cho N, Ko ES, et al: Imaging and
the clinical-pathologic features of invasive miropapillary
carcinoma of the breast. J Korean Radio Soc. 56:497–503. 2007.
|
|
16
|
Zekioglu O, Erhan Y, Ciris M, Bayramoglu H
and Ozdemir N: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast:
high incidence of lymph node metastasis with extranodal extension
and its immunohistochemical profile compared with invasive ductal
carcinoma. Histopathology. 44:18–23. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li YS, Kaneko M, Sakamoto DG, Takeshima Y
and Inai K: The reversed apical pattern of MUC1 expression is
characteristics of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast.
Breast Cancer. 13:58–63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao X, Qian XL, Li YQ, Ren MJ and Fu L:
Expression and significance of Hsp27 in invasive micropapillary
carcinoma of the breast. Chin J Clin Oncol. 40:525–528. 2013.
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Fan Y, Li WD, et al: Expression
and significance of L1-CAM in invasive micropapillary carcinoma of
the breast. Chin J Clin Oncol. 40:198–201. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Kristiansen G, Sammar M and Altevogt P:
Tumour biological aspects of CD24, a mucin-like adhesion molecule.
J Mol Histol. 35:255–262. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Simonetti S, Terracciano L, Zlobec I, et
al: Immunophenotyping analysis in invasive micropapillary carcinoma
of the breast: role of CD24 and CD44 isoforms expression. Breast.
21:165–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tressrra F, Grases PJ, Fábregas R,
Férnandez-Cid A and Dexeus S: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma.
Distinct features of a poorly recognized variant of breast
carcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 20:205–208. 1999.
|
|
23
|
Walsh MM and Bleiweiss IJ: Invasive
micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: eighty cases of an
underrecognized entity. Hum Pathol. 32:583–589. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rosen PP: Rosen’s Breast Pathology. 2nd
edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: pp.
561–564. 2001
|