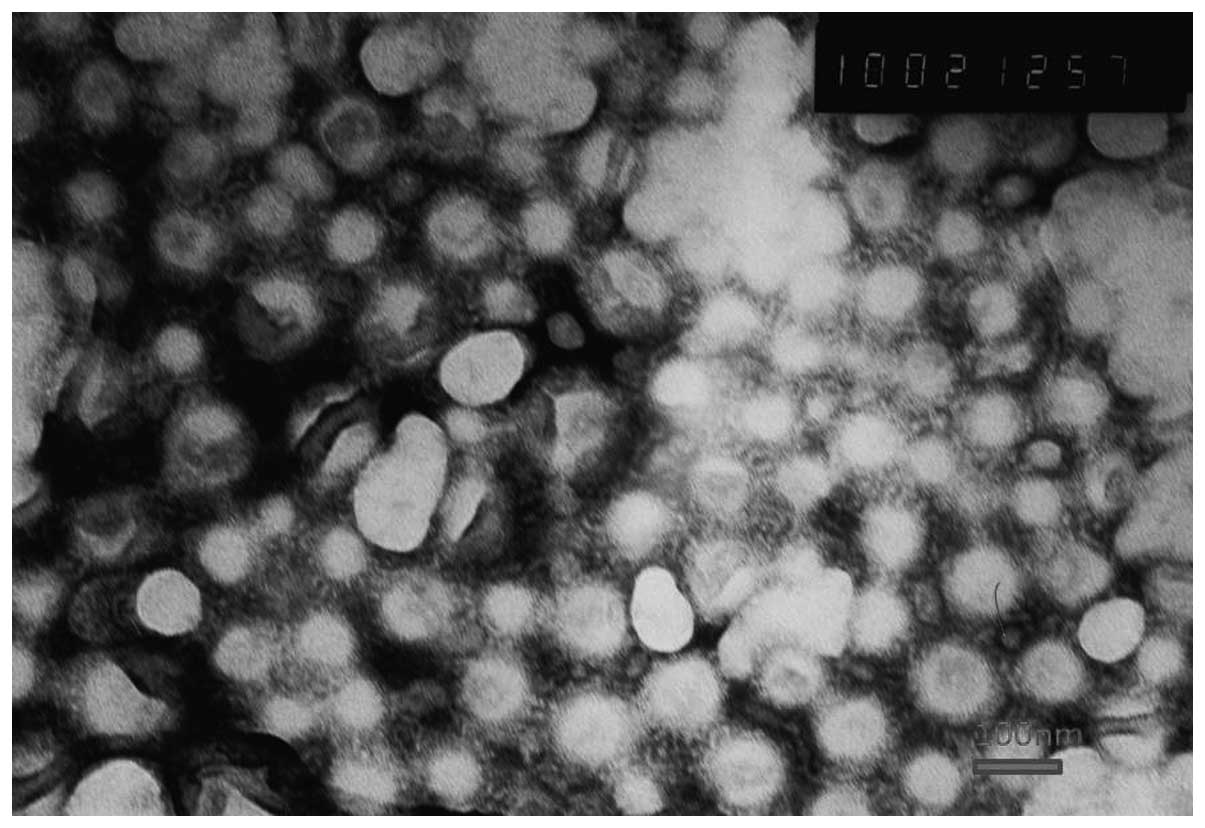
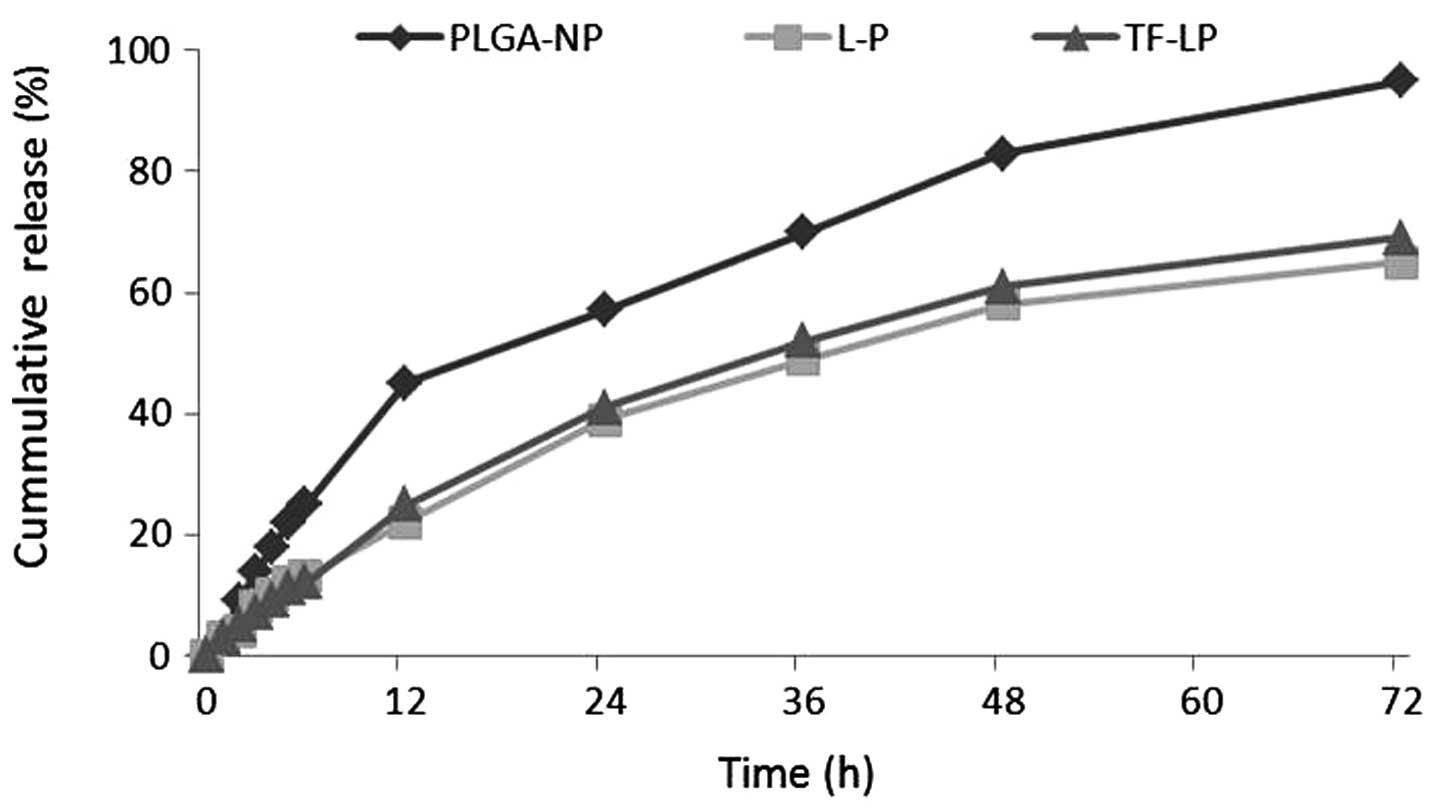
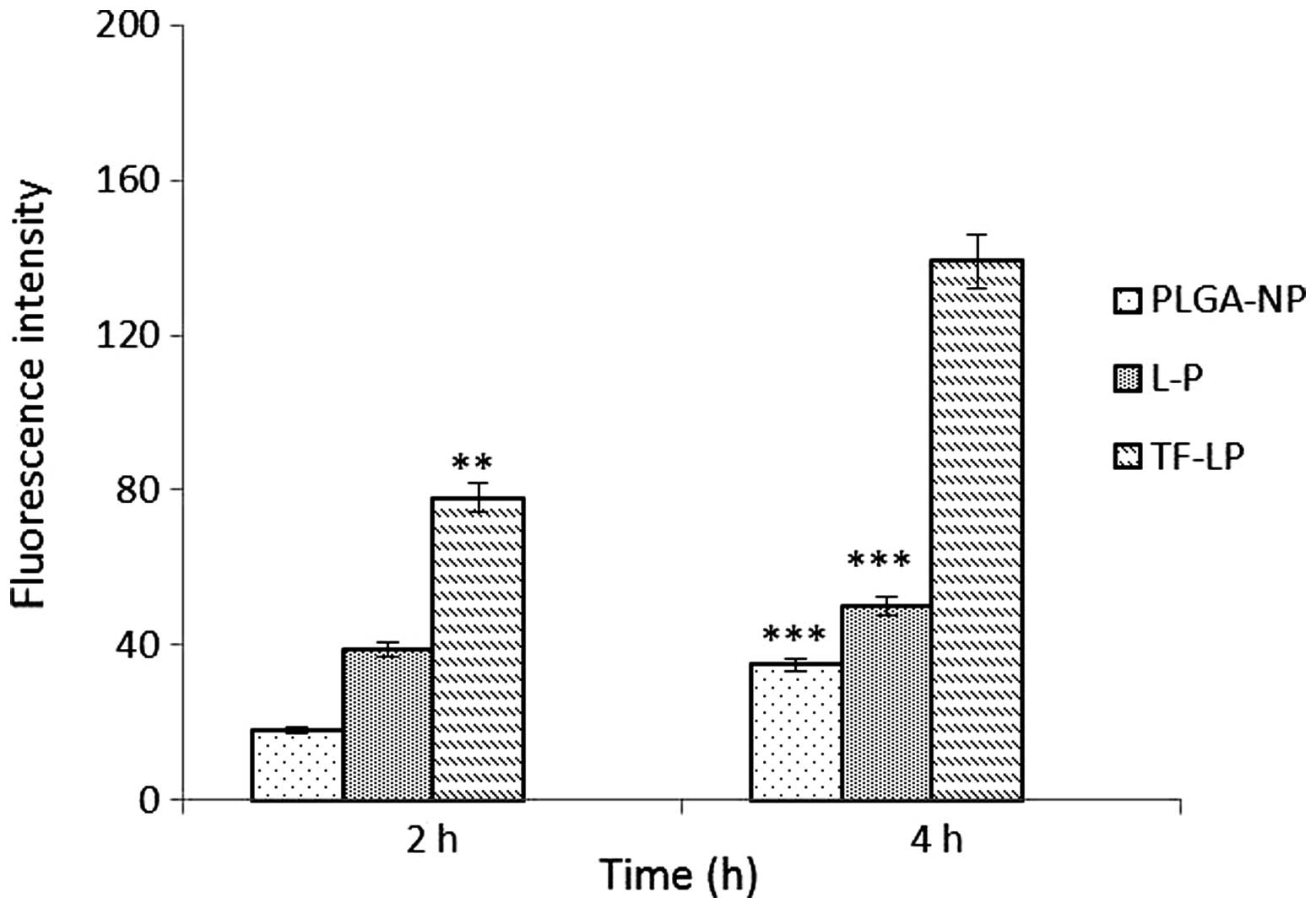
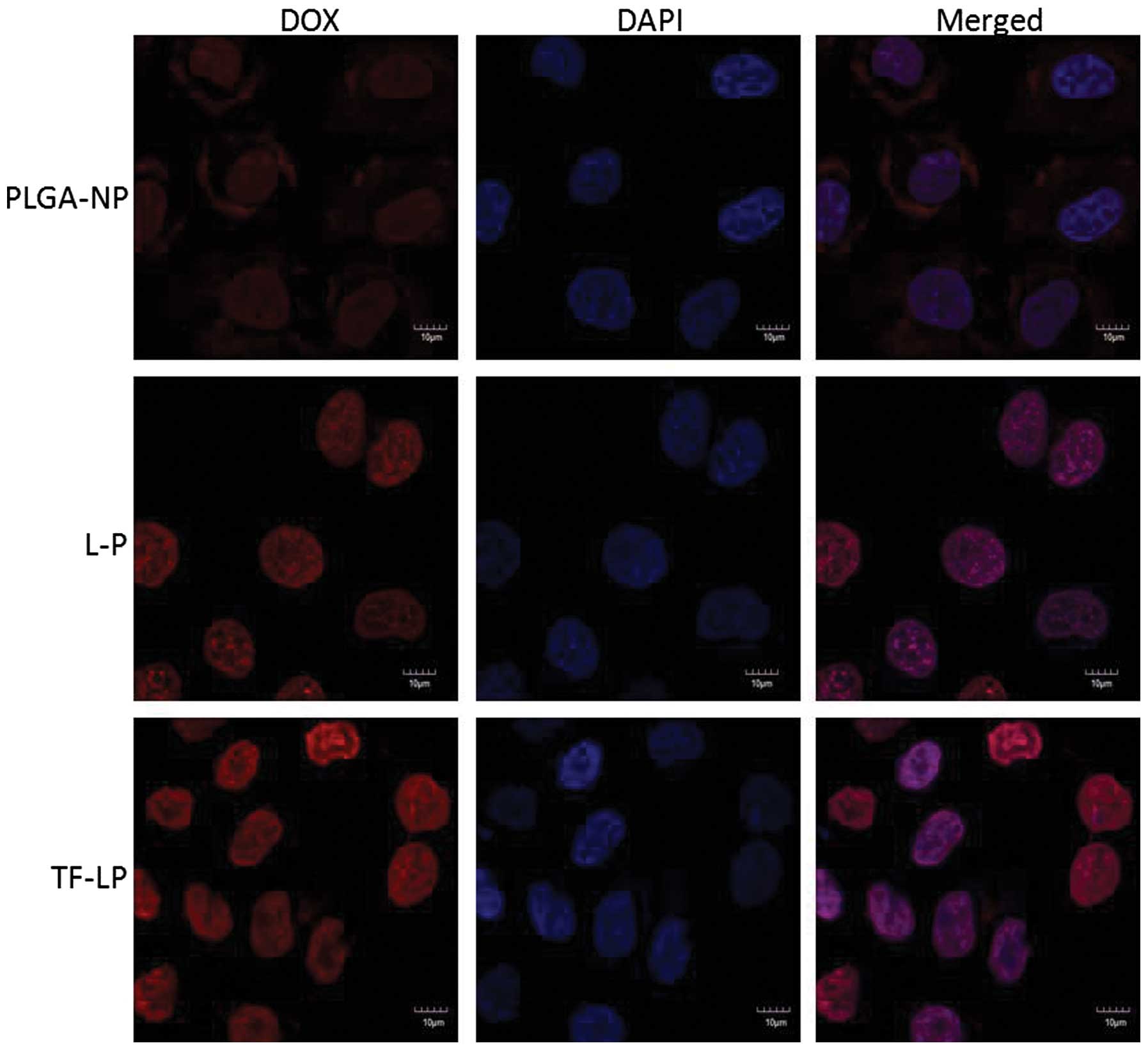
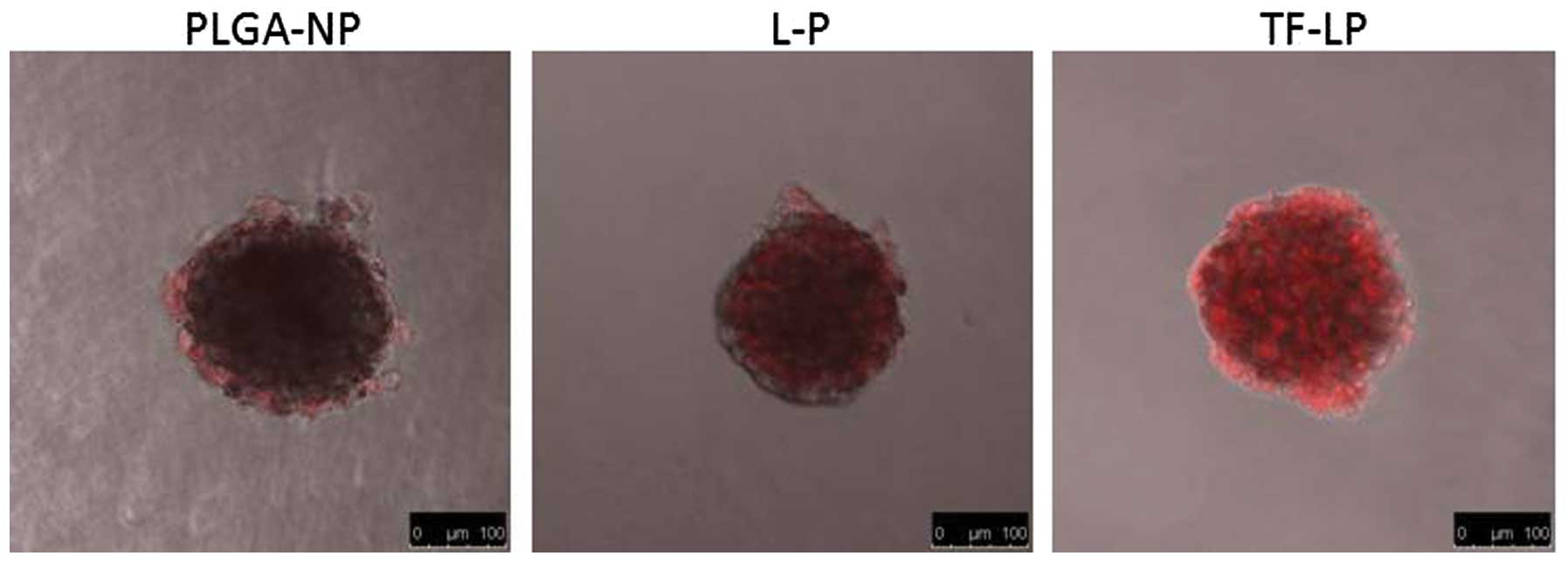
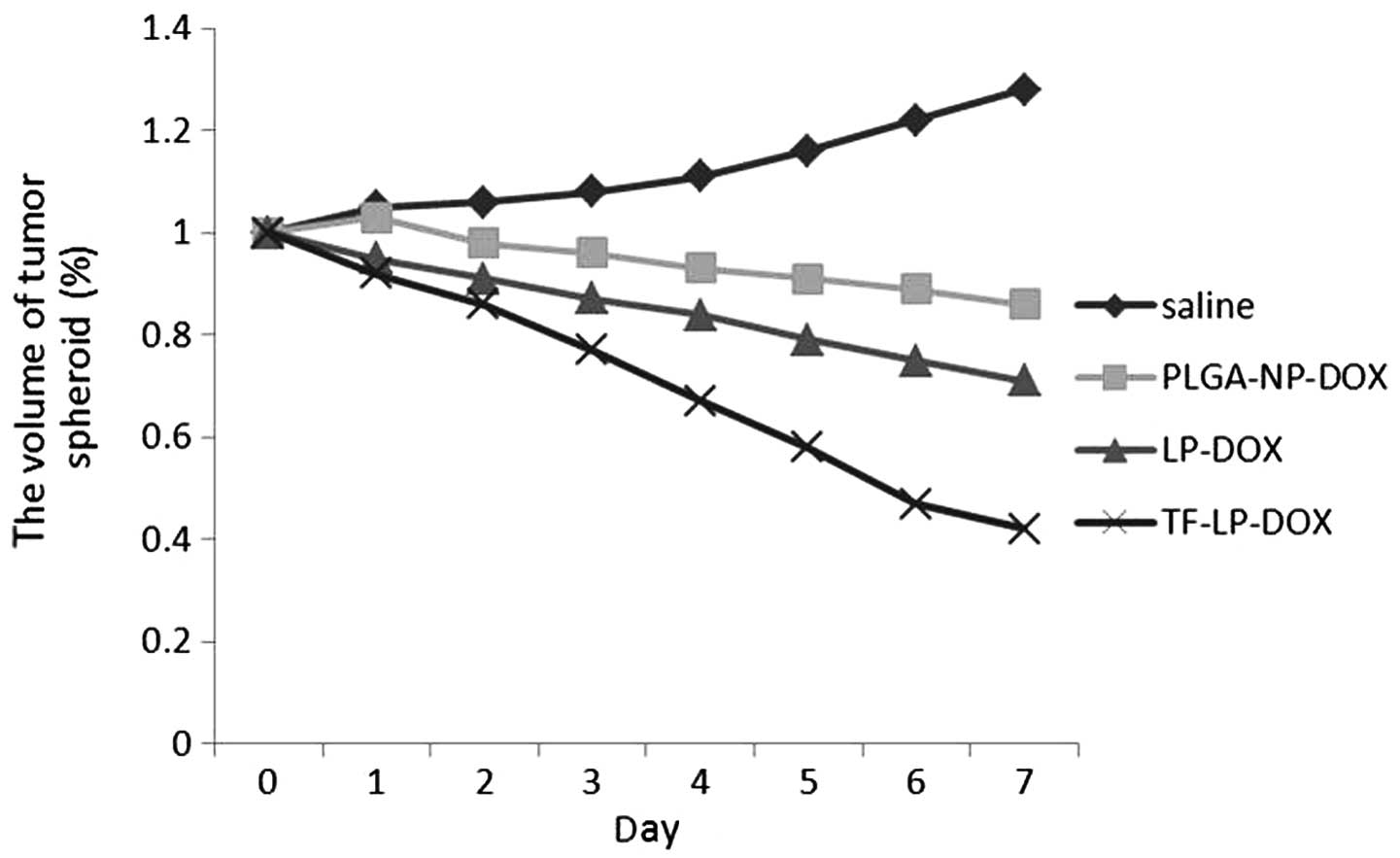
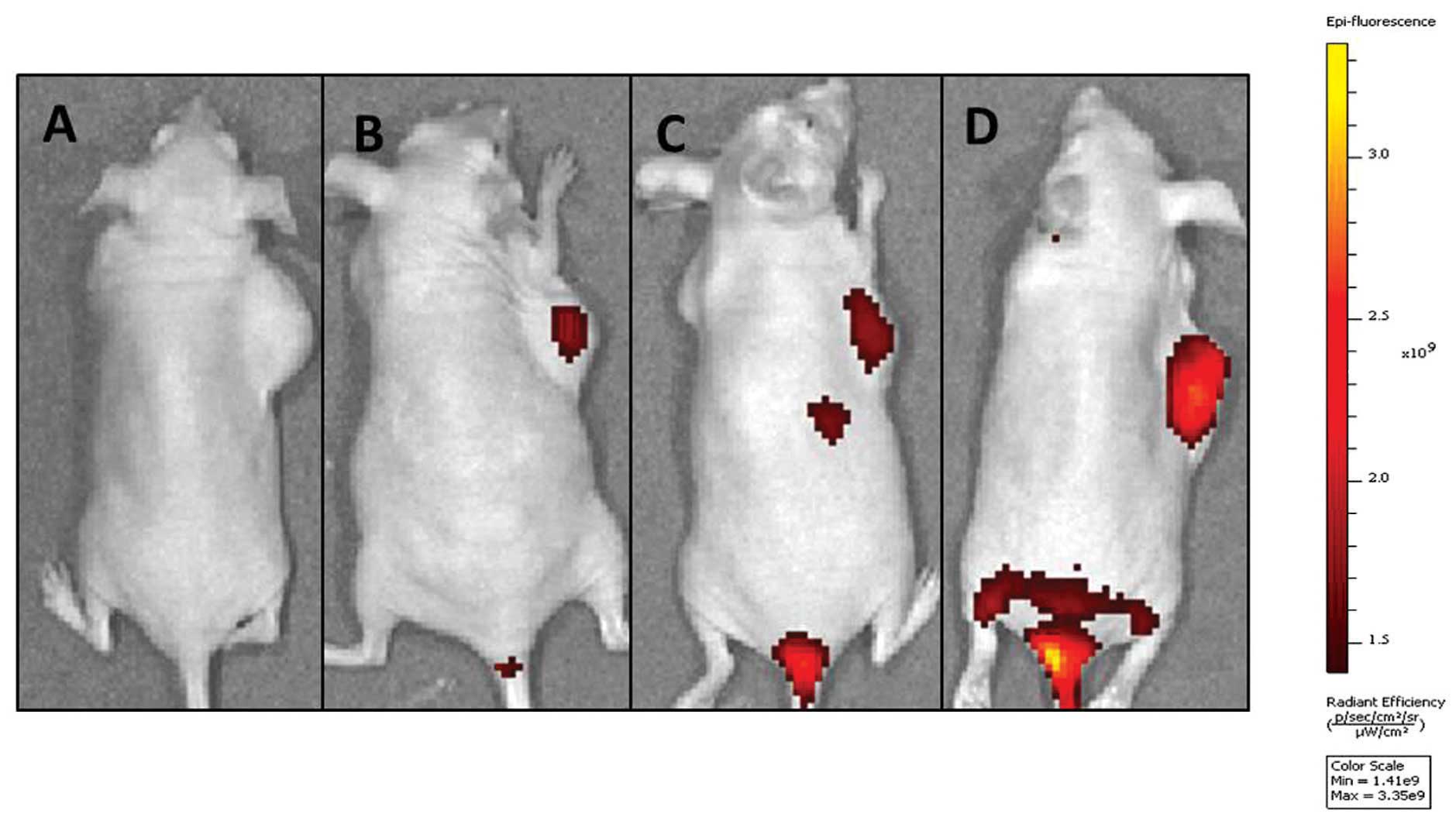
|
1
|
Jinturkar KA, Anish C, Kumar MK, et al:
Liposomal formulations of Etoposide and Docetaxel for p53 mediated
enhanced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines. Biomaterials.
33:2492–2507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sengupta S, Tyagi P, Velpandian T, et al:
Etoposide encapsulated in positively charged liposomes:
pharmacokinetic studies in mice and formulation stability studies.
Pharmacol Res. 42:459–464. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li R, Zhang Q, Wang XY, et al: A targeting
drug delivery system for ovarian carcinoma: transferring modified
lipid coated paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles. Drug Res (Stuttg).
64:541–547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Oh S, Kim BJ, Singh NP, et al: Synthesis
and anti-cancer activity of covalent conjugates of artemisinin and
a transferrin-receptor targeting peptide. Cancer Lett. 274:33–39.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hu CM and Zhang L: Therapeutic
nanoparticles to combat cancer drug resistance. Curr Drug Metab.
10:836–841. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Torchilin VP: Recent advances with
liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
4:145–160. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang AZ, Bagalkot V, Vasilliou CC, et al:
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for
combined prostate cancer imaging and therapy. ChemMedChem.
3:1311–1315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakatsuji T, Kao MC, Zhang L, et al: Sebum
free fatty acids enhance the innate immune defense of human
sebocytes by upregulating beta-defensin-2 expression. J Invest
Dermatol. 130:985–994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hu CM, Kaushal S, Tran Cao HS, et al:
Half-antibody functionalized lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for
targeted drug delivery to carcinoembryonic antigen presenting
pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Pharm. 7:914–920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kibria G, Hatakeyama H, Ohga N, et al:
Dual-ligand modification of PEGylated liposomes shows better cell
selectivity and efficient gene delivery. J Control Release.
153:141–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sharma G, Modgil A, Sun C and Singh J:
Grafting of cell-penetrating peptide to receptor-targeted liposomes
improves their transfection efficiency and transport across
blood-brain barrier model. J Pharm Sci. 101:2468–2478. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wadia JS and Dowdy SF: Protein
transduction technology. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 13:52–56. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Zhao Y, Wu Y, et al: Enhanced
anti-tumor efficacy by co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel
with amphiphilic methoxy PEG-PLGA copolymer nanoparticles.
Biomaterials. 32:8281–8290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cui Y, Xu Q, Chow PK, et al:
Transferrin-conjugated magnetic silica PLGA nanoparticles loaded
with doxorubicin and paclitaxel for brain glioma treatment.
Biomaterials. 34:8511–8520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan JM, Zhang L, Yuet KP, et al:
PLGA-lecithin-PEG core-shell nanoparticles for controlled drug
delivery. Biomaterials. 30:1627–1634. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Chan JM, Gu FX, et al:
Self-assembled lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles: a robust drug
delivery platform. ACS Nano. 2:1696–1702. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang X, Koh CG, Liu S, et al: Transferrin
receptor-targeted lipid nanoparticles for delivery of an antisense
oligodeoxyribonucleotide against Bcl-2. Mol Pharm. 6:221–230. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chiu SJ, Liu S, Perrotti D, et al:
Efficient delivery of a Bcl-2-specific antisense
oligodeoxyribonucleotide (G3139) via transferrin receptor-targeted
liposomes. J Controlled Release. 112:199–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jiang T, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, et al:
Dual-functional liposomes based on pH-responsive cell-penetrating
peptide and hyaluronic acid for tumor-targeted anticancer drug
delivery. Biomaterials. 33:9246–9258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maeda N, Takeuchi Y, Takada M, et al:
Anti-neovascular therapy by use of tumor neovasculature-targeted
long-circulating liposome. J Control Release. 100:41–52. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lewis CE and Pollard JW: Distinct role of
macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res.
66:605–612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fukumura D, Xu L, Chen Y, Gohongi T, et
al: Hypoxia and acidosis independently up-regulate vascular
endothelial growth factor transcription in brain tumors in vivo.
Cancer Res. 61:6020–6024. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jain RK: Delivery of molecular and
cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 64(Suppl):
353–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Yang L, Chen ZG and Shin DM:
Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy and imaging. CA
Cancer J Clin. 58:97–110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen X, Wang X, Wang Y, et al: Improved
tumor-targeting drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy by cationic
liposome modified with truncated bFGF peptide. J Control Release.
145:17–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|