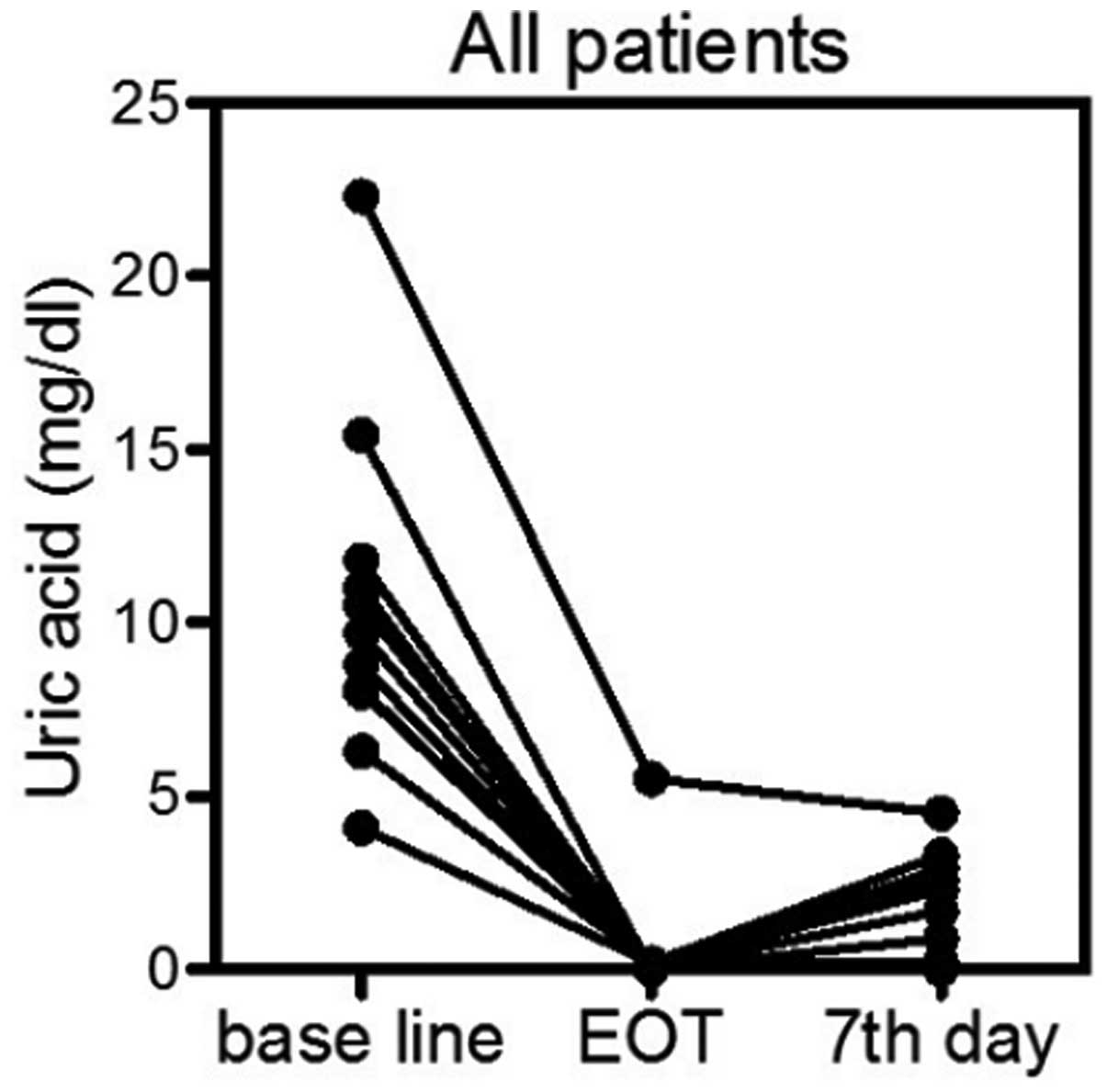
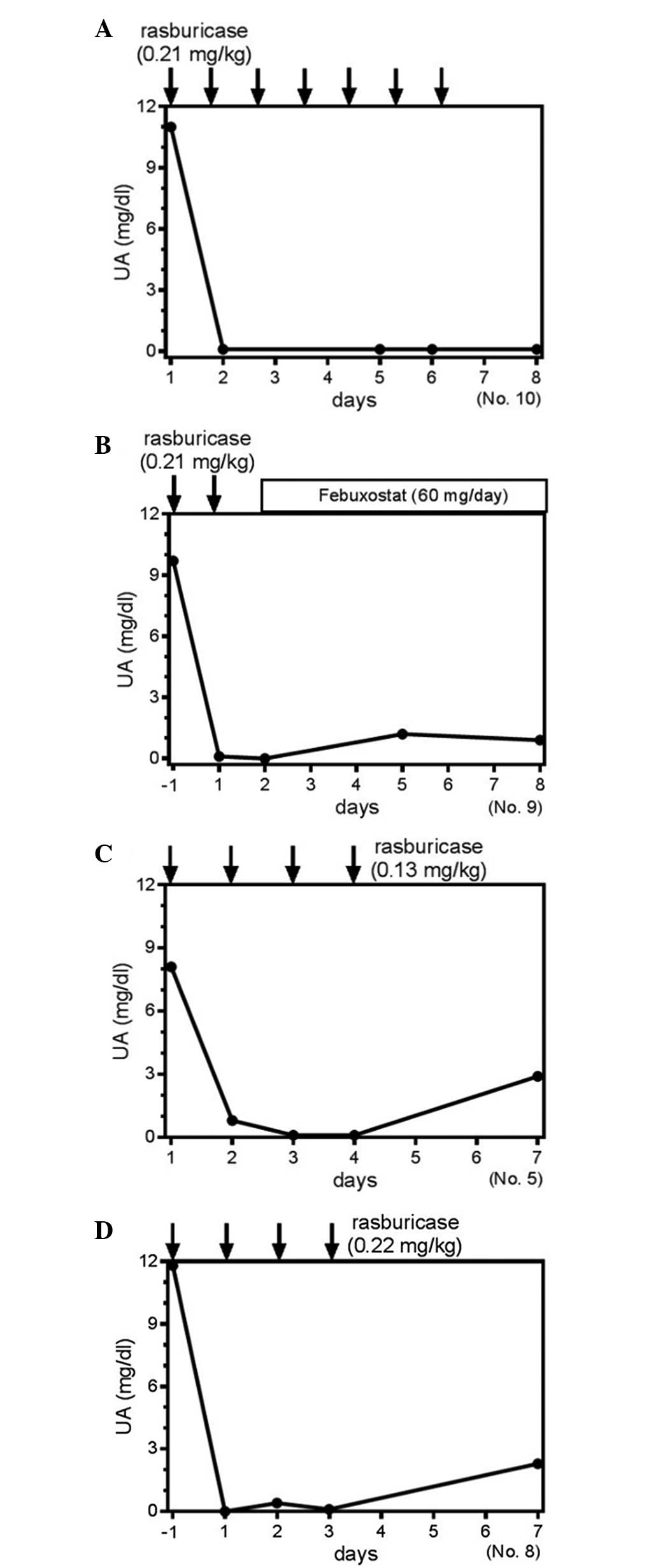
|
1
|
Cairo MS and Bishop M: Tumour lysis
syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J
Haematol. 127:3–11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coiffier B, Altman A, Pui CH, Younes A and
Cairo MS: Guidelines for the management of pediatric and adult
tumor lysis syndrome: an evidence-based review. J Clin Oncol.
26:2767–2778. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cairo MS, Coiffier B, Reiter A and Younes
A: TLS expert panel: Recommendations for the evaluation of risk and
prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children
with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J
Haematol. 149:578–586. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Howard SC, Jones DP and Pui CH: The tumor
lysis syndrome. N Engl J Med. 364:1844–1854. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Firwana BM, Hasan R, Hasan N, Alahdab F,
Alnahhas I, Hasan S and Varon J: Tumor lysis syndrome: a systematic
review of case series and case reports. Postgrad Med. 124:92–101.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wilson FP and Berns JS: Onco-nephrology:
tumor lysis syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 7:1730–1739. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pui CH, Mahmoud HH, Wiley JM, Woods GM,
Leverger G, Camitta B, Hastings C, Blaney SM, Relling MV and Reaman
GH: Recombinant urate oxidase for the prophylaxis or treatment of
hyperuricemia in patients with leukemia or lymphoma. J Clin Oncol.
19:697–704. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McDonnel AM, Lenz KL, Frei-Lahr DA,
Hayslip J and Hall PD: Single-dose rasburicase 6 mg in the
management of tumor lysis syndrome in adults. Pharmacotherapy.
26:806–812. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cammalleri L and Malaguarnera M:
Rasburicase represents a new tool for hyperuricemia in tumor lysis
syndrome and in gout. Int J Med Sci. 4:83–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheuk DK, Chiang AK, Chan GC and Ha SY:
Urate oxidase for the prevention and treatment of tumor lysis
syndrome in children with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
16:CD0069452010.
|
|
11
|
Ishizawa K, Ogura M, Hamaguchi M, Hotta T,
Ohnishi K, Sasaki T, Sakamaki H, Yokoyama H, Harigae H and
Morishima Y: Safety and efficacy of rasburicase (SR29142) in a
Japanese phase II study. Cancer Sci. 100:357–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Trifilio S, Gordon L, Singhal S, Tallman
M, Evens A, Rashid K, Fishman M, Masino K, Pi J and Mehta J:
Reduced-dose rasburicase (recombinant xanthine oxidase) in adult
cancer patients with hyperuricemia. Bone Marrow Transplant.
37:997–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jeha S, Kantarjian H, Irwin D, Shen V,
Shenoy S, Blaney S, Camitta B and Pui CH: Efficacy and safety of
rasburicase, a recombinant urate oxidase (Elitek), in the
management of malignancy associated hyperuricemia in pediatric and
adult patients: Final results of a multicenter compassionate use
trial. Leukemia. 19:34–38. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
The guideline revising committee of
Japanese Society of Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism. Digest of the
guideline for management of hyperuricemia and gout. 2nd edition.
Gout Nucleic Acid Metabol. 34:107–143. 2010.(In Japanese).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yamauchi T, Negoro E, Lee S, Takai M,
Matsuda Y, Takagi K, Kishi S, Tai K, Hosono N, Tasaki T, Ikegaya S,
Inai K, Yoshida A, Urasaki Y, Iwasaki H and Ueda T: A high serum
uric acid level is associated with poor prognosis in patients with
acute myeloid leukemia. Anticancer Res. 33:3947–3951.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yeldandi AV, Yeldandi V, Kumar S, Murthy
CV, Wang XD, Alvares K, Rao MS and Reddy JK: Molecular evolution of
the urate oxidase-encoding gene in hominoid primates: Nonsense
mutations. Gene. 109:281–284. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ishizawa K, Ogura M, Hamaguchi M, Hotta T,
Ohnishi K, Sasaki T, Sakamaki H, Yokoyama H, Harigae H and
Morishima Y: Safety and efficacy of rasburicase (SR29142) in a
Japanese phase II study. Cancer Sci. 100:357–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McBride A, Lathon SC, Boehmer L, Augustin
KM, Butler SK and Westervelt P: Comparative evaluation of single
fixed dosing and weight-based dosing of rasburicase for tumor lysis
syndrome. Pharmacotherapy. 33:295–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vadhan-Raj S, Fayad LE, Fanale MA, Pro B,
Rodriguez A, Hagemeister FB, Bueso-Ramos CE, Zhou X, McLaughlin PW,
Fowler N, Shah J, Orlowski RZ, Samaniego F, Wang M, Cortes JE,
Younes A, Kwak LW, Sarlis NJ and Romaguera JE: A randomized trial
of a single-dose rasburicase versus five-daily doses in patients at
risk for tumor lysis syndrome. Ann Oncol. 23:1640–1645. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cortes J, Moore JO, Maziarz RT, Wetzler M,
Craig M, Matous J, Luger S, Dey BR, Schiller GJ, Pham D, Abboud CN,
Krishnamurthy M, Brown A Jr, Laadem A and Seiter K: Control of
plasma uric acid in adults at risk for tumor Lysis syndrome:
efficacy and safety of rasburicase alone and rasburicase followed
by allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone - results of a
multicenter phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 28:4207–4213. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|