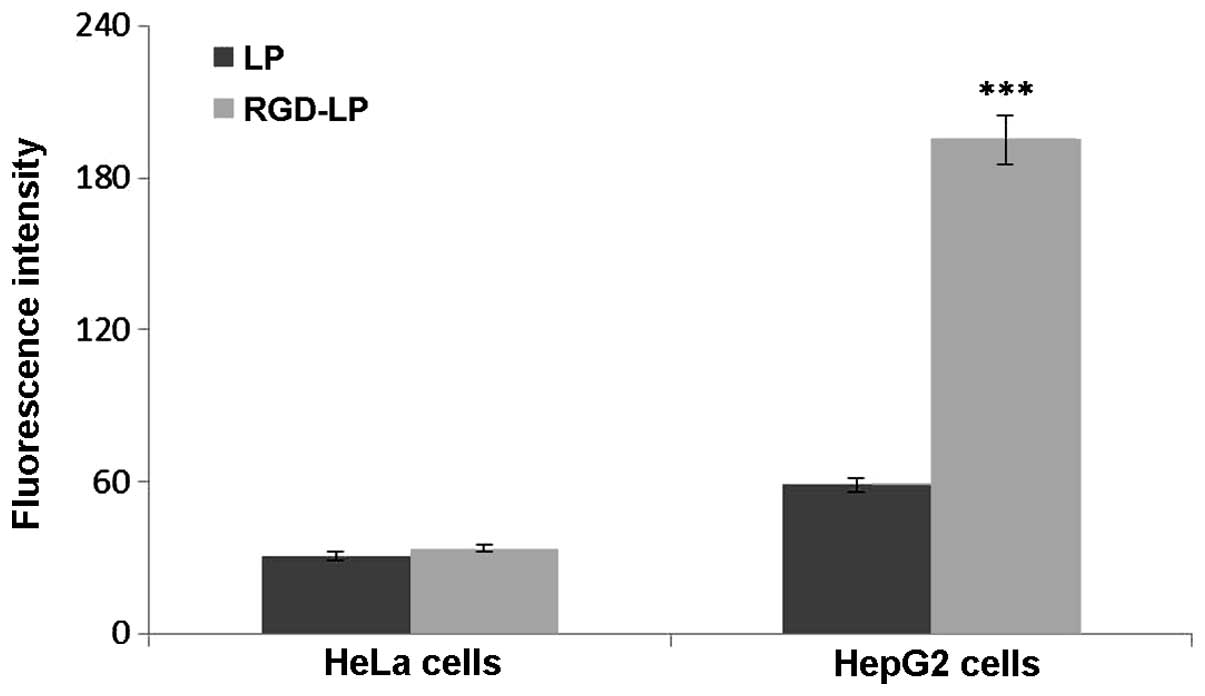
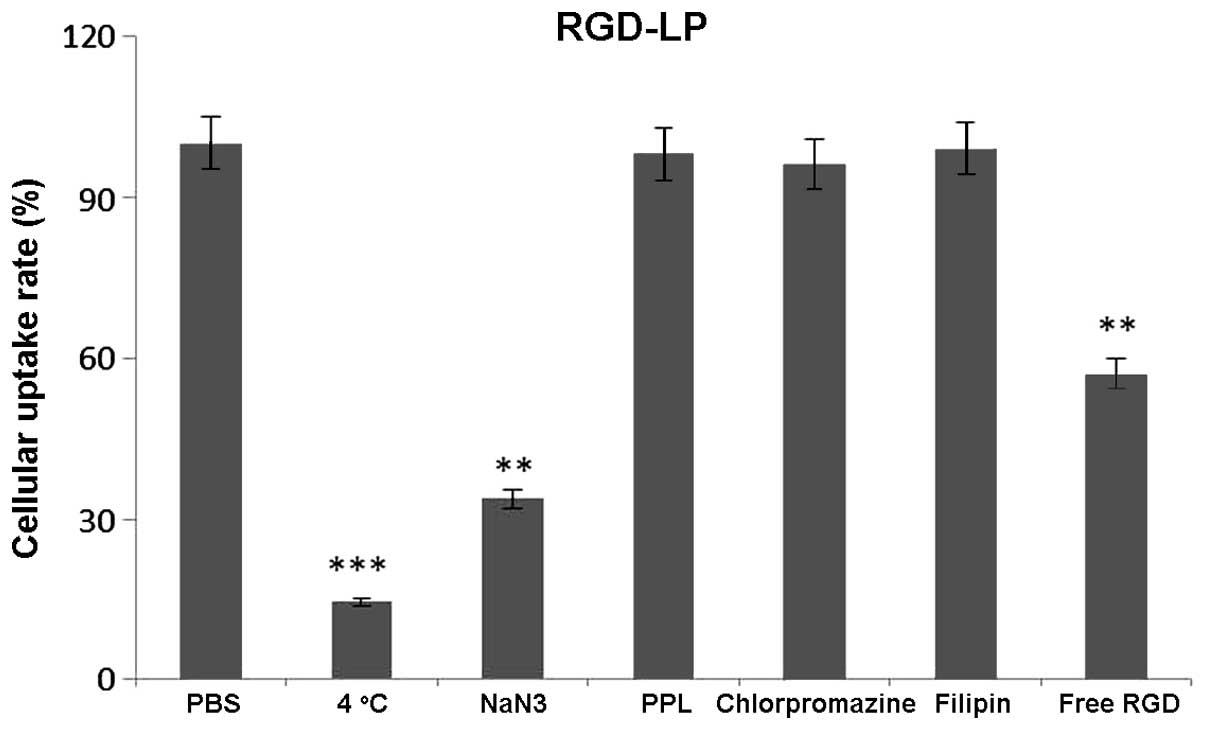
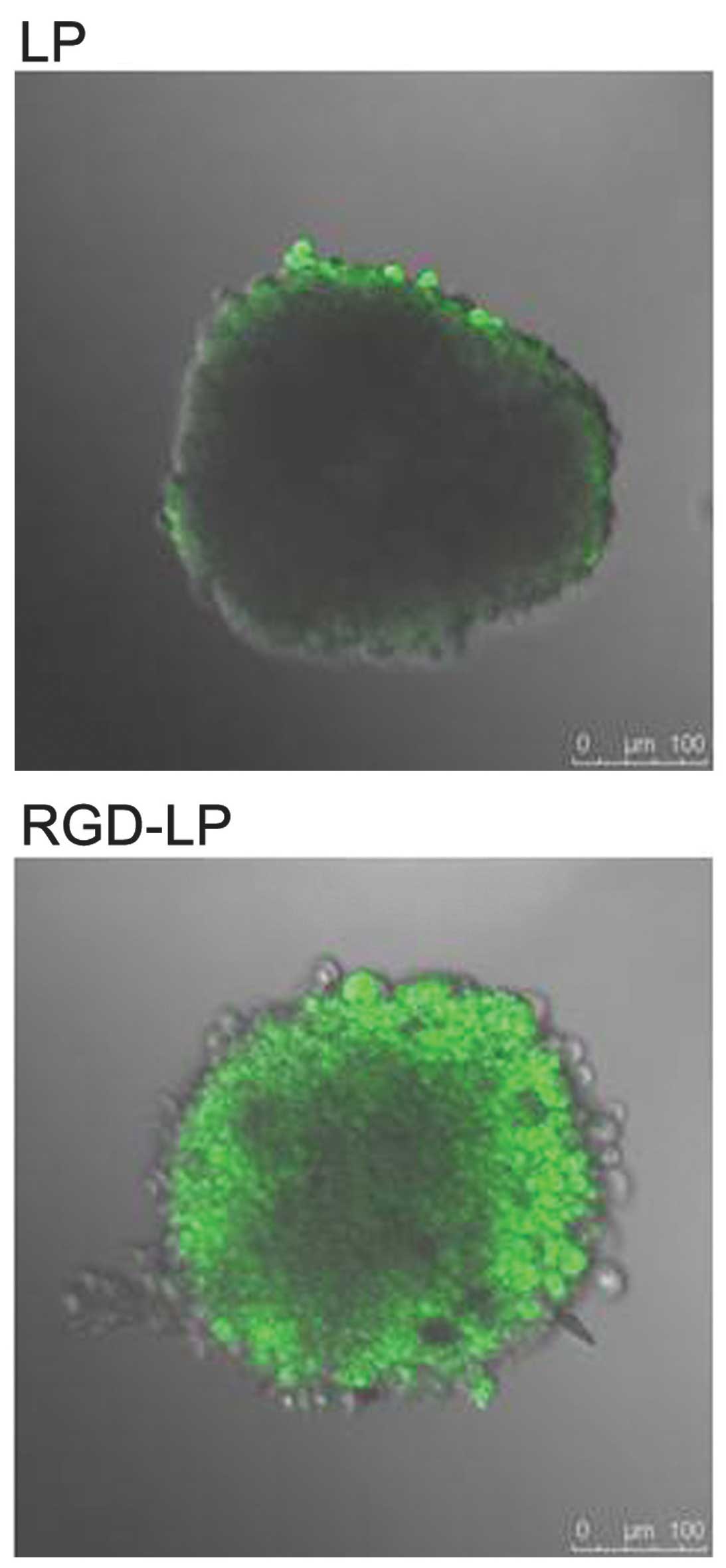
|
1
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu X, Wang W and Wang Z: Recent progress
in understanding the effects of autophagy in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Chin J Hepatobil Surg. 20:69–73. 2014.
|
|
3
|
Pan Y, Ye S, Yuan D, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S)/cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) pathway contributes to
the proliferation of hepatoma cells. Mutat Res. 763–764:10–18.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang C, He H, Zhang H, et al: The
blockage of Ras/ERK pathway augments the sensitivity of SphK1
inhibitor SKI II in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 434:35–41. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baek JS, So JW, Shin SC and Cho CW: Solid
lipid nanoparticles of paclitaxel strengthened by
hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as an oral delivery system. Int J Mol
Med. 30:953–959. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun J, Deng L, Duan Y, et al: Inhibitory
effect of endostatin combined with paclitaxel-cisplatin on breast
cancer in xenograft-bearing mice. Exp Ther Med. 3:159–164.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kimura K, Tanaka S, Iwamoto M, et al:
Safety of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel administered to
breast cancer patients with clinical contraindications to
paclitaxel or docetaxel: Four case reports. Oncol Lett. 6:881–884.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka T, Toujima S and Tanaka J:
Differential sensitivity to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis and growth
suppression in paclitaxel-resistant cell lines established from
HEC-1 human endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
41:1837–1844. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsukada T, Fushida S, Harada S, et al:
Low-dose paclitaxel modulates tumour fibrosis in gastric cancer.
Int J Oncol. 42:1167–1174. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Horwitz SB: Taxol (paclitaxel): Mechanisms
of action. Ann Oncol. 5 (Suppl 6):S3–S6. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liebmann J, Cook JA and Mitchell JB:
Cremophor EL, solvent for paclitaxel and toxicity. Lancet.
342:14281993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gou Y, Wang L, Lv P and Zhang P:
Transferrin-conjugated doxorubicin-loaded lipid-coated
nanoparticles for the targeting and therapy of lung cancer. Oncol
Lett. 9:1065–1072. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Despierre E, Lambrechts D, Neven P, et al:
The molecular genetic basis of ovarian cancer and its roadmap
towards a better treatment. Gynecol Oncol. 117:358–365. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Curtin JP, Blessing JA, Webster KD, Rose
PG, Mayer AR, Fowler WC Jr, Malfetano JH and Alvarez RD:
Paclitaxel, an active agent in nonsquamous carcinomas of the
uterine cervix: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol.
19:1275–1278. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McGuire WP, Blessing JA, Moore D, Lentz SS
and Photopulos G: Paclitaxel has moderate activity in squamous
cervix cancer. A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol.
14:792–795. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rose PG, Blessing JA, Gershenson DM and
McGehee R: Paclitaxel and cisplatin as first-line therapy in
recurrent or advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix: A
gynecologic oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 17:2676–2680.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chua DT, Sham JS and Au GK: A phase II
study of docetaxel and cisplatin as first line chemotherapy in
patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
41:589–595. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McCarthy JS, Tannock IF, Degendorfer P,
Panzarella T, Furlan M and Siu LL: A Phase II trial of docetaxel
and cisplatin in patients with recurrent or metastatic
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 38:686–690. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yin Y, Wu X, Yang Z, et al: The potential
efficacy of R8-modified paclitaxel-loaded liposomes on pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Pharm Res. 30:2050–2062. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wender PA, Galliher WC, Goun EA, Jones LR
and Pillow TH: The design of guanidinium-rich transporters and
their internalization mechanisms. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 60:452–472.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JH, Engler JA, Collawn JF and Moore
BA: Receptor mediated uptake of peptides that bind the human
transferrin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 268:2004–2012. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oba M, Fukushima S, Kanayama N, et al:
Cyclic RGD peptide-conjugated polyplex micelles as a targetable
gene delivery system directed to cells possessing alphavbeta3 and
alphavbeta5 integrins. Bioconjug Chem. 18:1415–1423. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li S, Wei J, Yuan L, et al: RGD-modified
endostatin peptide 530 derived from endostatin suppresses invasion
and migration of HepG2 cells through the αvβ3 pathway. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 26:529–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kibria G, Hatakeyama H, Ohga N, et al:
Dual-ligand modification of PEGylated liposomes shows better cell
selectivity and efficient gene delivery. J Control Release.
153:141–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sharma G, Modgil A, Sun C and Singh J:
Grafting of cell-penetrating peptide to receptor-targeted liposomes
improves their transfection efficiency and transport across
blood-brain barrier model. J Pharm Sci. 101:2468–2478. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang T, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, et al:
Dual-functional liposomes based on pH-responsive cell-penetrating
peptide and hyaluronic acid for tumor-targeted anticancer drug
delivery. Biomaterials. 33:9246–9258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maeda N, Takeuchi Y, Takada M, et al:
Anti-neovascular therapy by use of tumor neovasculature-targeted
long-circulating liposome. J Control Release. 100:41–52. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Q, Tang J, Fu L, et al: A
pH-responsive α-helical cell penetrating peptide-mediated liposomal
delivery system. Biomaterials. 34:7980–7993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin Y, Chen H, Yuan W, et al: Liposome
formulated with TAT-modified cholesterol for enhancing the brain
delivery. Int J Pharm. 419:85–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Borgne-Sanchez A, Dupont S, Langonné A, et
al: Targeted Vpr-derived peptides reach mitochondria to induce
apoptosis of alphaVbeta3-expressing endothelial cells. Cell Death
Differ. 14:422–435. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lewis CE and Pollard JW: Distinct role of
macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res.
66:605–612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fukumura D, Xu L, Chen Y, et al: Hypoxia
and acidosis independently up-regulate vascular endothelial growth
factor transcription in brain tumors in vivo. Cancer Res.
61:6020–6024. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jain RK: Delivery of molecular and
cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 46:149–168.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|