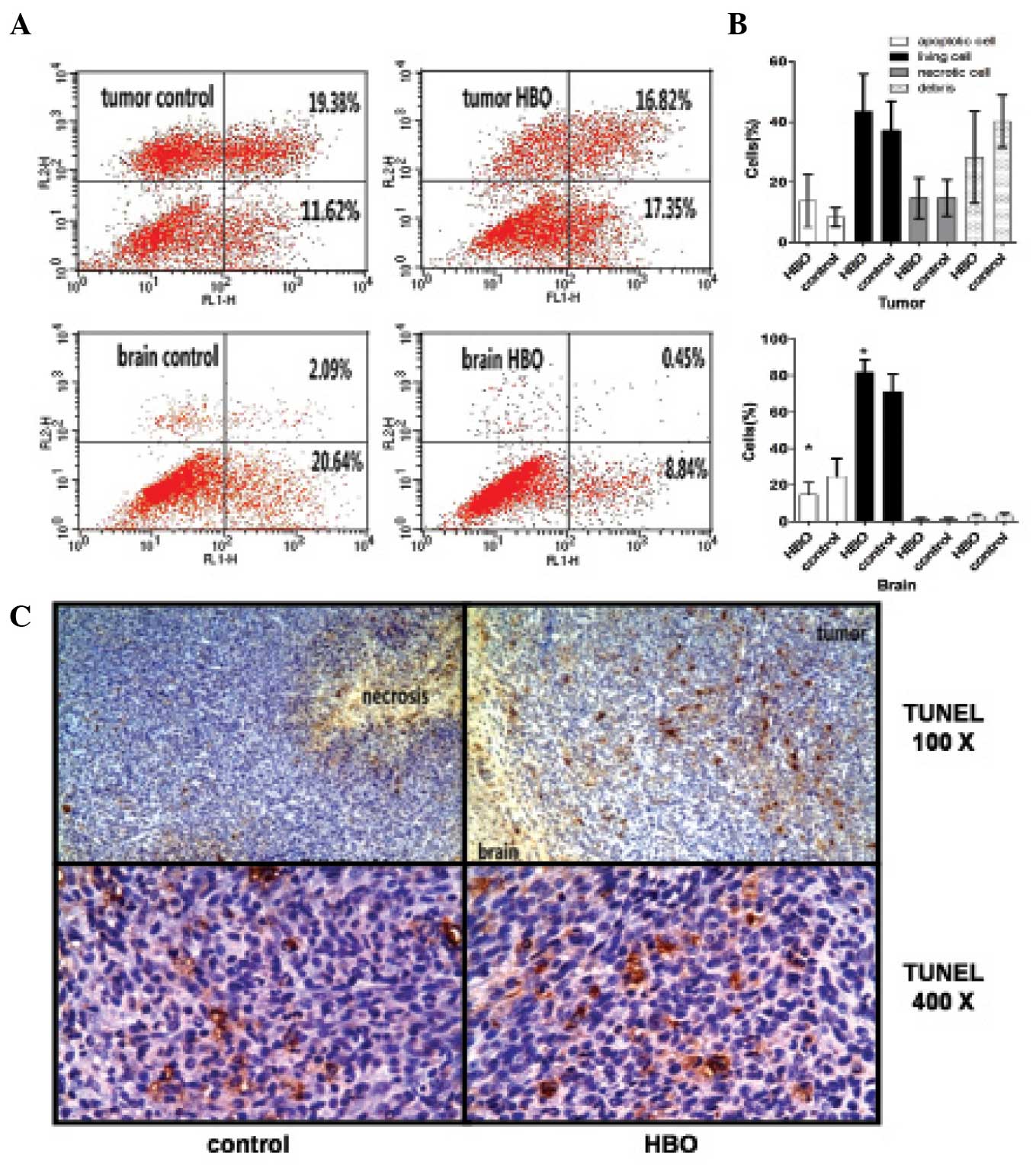
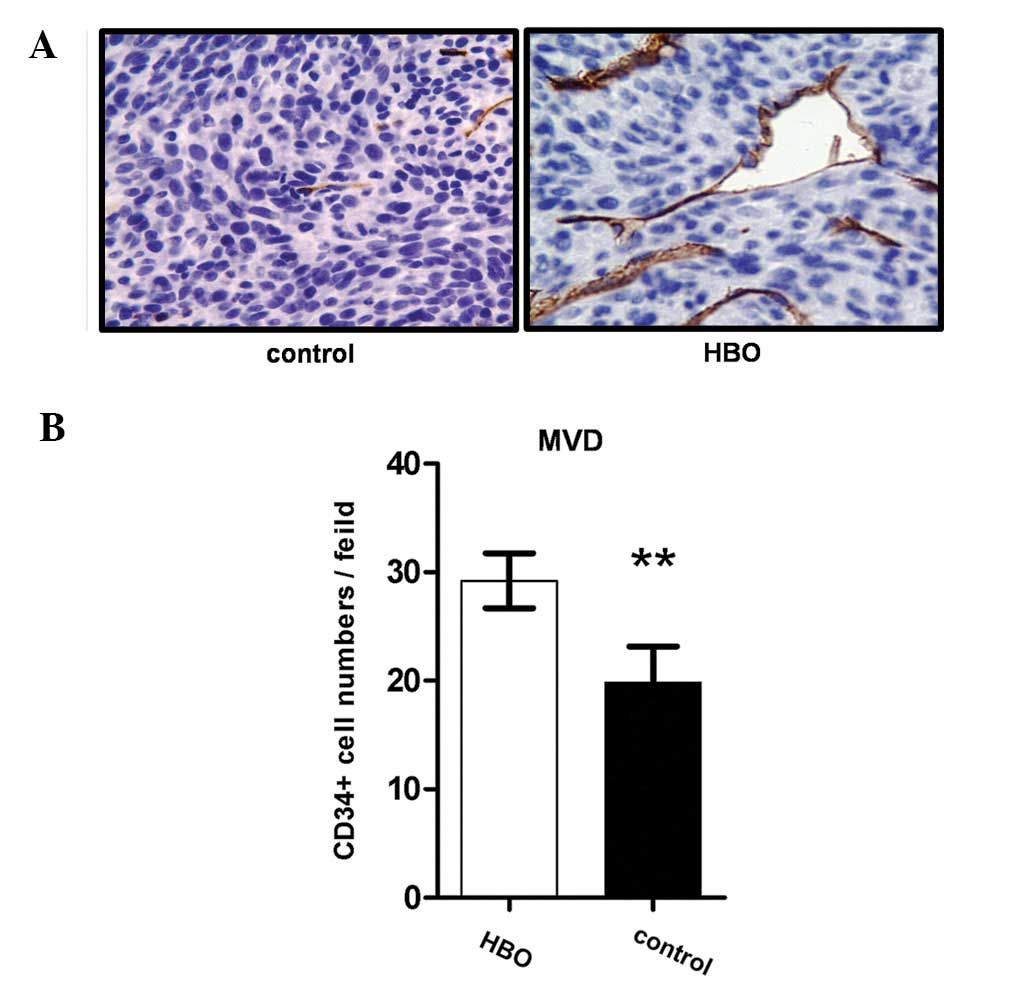
|
1
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al
European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain
Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada
Clinical Trials Group: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant
temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnson DR and O'Neill BP: Glioblastoma
survival in the United States before and during the temozolomide
era. J Neurooncol. 107:359–364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sayegh ET, Kaur G, Bloch O and Parsa AT:
Systematic review of protein biomarkers of invasive behavior in
glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. 49:1212–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chamberlain MC: Neuro-oncology: A selected
review of ASCO 2014 abstracts. CNS Oncology. 3:321–325. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sathornsumetee S, Cao Y, Marcello JE, et
al: Tumor angiogenic and hypoxic profiles predict radiographic
response and survival in malignant astrocytoma patients treated
with bevacizumab and irinotecan. J Clin Oncol. 26:271–278. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jensen RL: Brain tumor hypoxia:
Tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, imaging, pseudoprogression, and as a
therapeutic target. J Neurooncol. 92:317–335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Shingu T, et al: Metabolic
alterations in highly tumorigenic glioblastoma cells: Preference
for hypoxia and high dependency on glycolysis. J Biol Chem.
286:32843–32853. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bar EE: Glioblastoma, cancer stem cells
and hypoxia. Brain Pathol. 21:119–129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Persano L, Rampazzo E, Della Puppa A,
Pistollato F and Basso G: The three-layer concentric model of
glioblastoma: Cancer stem cells, microenvironmental regulation, and
therapeutic implications. ScientificWorldJournal. 11:1829–1841.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brizel DM, Lin S, Johnson JL, Brooks J,
Dewhirst MW and Piantadosi CA: The mechanisms by which hyperbaric
oxygen and carbogen improve tumour oxygenation. Br J Cancer.
72:1120–1124. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beppu T, Kamada K, Yoshida Y, Arai H,
Ogasawara K and Ogawa A: Change of oxygen pressure in glioblastoma
tissue under various conditions. J Neurooncol. 58:47–52. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Beppu T, Kamada K, Nakamura R, et al: A
phase II study of radiotherapy after hyperbaric oxygenation
combined with interferon-β and nimustine hydrochloride to treat
supratentorial malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol. 61:161–170. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kohshi K, Kinoshita Y, Imada H, et al:
Effects of radiotherapy after hyperbaric oxygenation on malignant
gliomas. Br J Cancer. 80:236–241. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ogawa K, Ishiuchi S, Inoue O, et al: Phase
II trial of radiotherapy after hyperbaric oxygenation with
multiagent chemotherapy (procarbazine, nimustine, and vincristine)
for high-grade gliomas: Long-term results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 82:732–738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kohshi K, Yamamoto H, Nakahara A, Katoh T
and Takagi M: Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using gamma
unit after hyperbaric oxygenation on recurrent high-grade gliomas.
J Neurooncol. 82:297–303. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun S, Lee D, Lee NP, et al: Hyperoxia
resensitizes chemoresistant human glioblastoma cells to
temozolomide. J Neurooncol. 109:467–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu XY, Cao K, Li QY, Yuan ZC and Lu PS:
The synergistic therapeutic effect of temozolomide and hyperbaric
oxygen on glioma U251 cell lines is accompanied by alterations in
vascular endothelial growth factor and multidrug
resistance-associated protein-1 levels. J Int Med Res. 40:995–1004.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stuhr LE, Raa A, Oyan AM, et al: Hyperoxia
retards growth and induces apoptosis, changes in vascular density
and gene expression in transplanted gliomas in nude rats. J
Neurooncol. 85:191–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Biollaz G, Bernasconi L, Cretton C, et al:
Site-specific anti-tumor immunity: Differences in DC function,
TGF-β production and numbers of intratumoral Foxp3+ Treg. Eur J
Immunol. 39:1323–1333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Conconi MT, Baiguera S, Guidolin D, et al:
Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on proliferative and apoptotic
activities and reactive oxygen species generation in mouse
fibroblast 3T3/J2 cell line. J Investig Med. 51:227–232. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Milovanova TN, Bhopale VM, Sorokina EM, et
al: Hyperbaric oxygen stimulates vasculogenic stem cell growth and
differentiation in vivo. J Appl Physiol. (1985)106:711–728.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kohshi K, Kinoshita Y, Terashima H, Konda
N, Yokota A and Soejima T: Radiotherapy after hyperbaric
oxygenation for malignant gliomas: A pilot study. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 122:676–678. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maes W, Deroose C, Reumers V, et al: In
vivo bioluminescence imaging in an experimental mouse model for
dendritic cell based immunotherapy against malignant glioma. J
Neurooncol. 91:127–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stafford P, Abdelwahab MG, Kim Y, Preul
MC, Rho JM and Scheck AC: The ketogenic diet reverses gene
expression patterns and reduces reactive oxygen species levels when
used as an adjuvant therapy for glioma. Nutr Metab (Lond). 7:74.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, et al:
A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell.
11:69–82. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zagzag D, Amirnovin R, Greco MA, et al:
Vascular apoptosis and involution in gliomas precede
neovascularization: A novel concept for glioma growth and
angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 80:837–849. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deb P, Boruah D and Dutta V: Morphometric
study of microvessels in primary CNS tumors and its correlation
with tumor types and grade. Microvasc Res. 84:34–43. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leon SP, Folkerth RD and Black PM:
Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with
astroglial brain tumors. Cancer. 77:362–372. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moen I, Jevne C, Wang J, et al: Gene
expression in tumor cells and stroma in dsRed 4T1 tumors in
eGFP-expressing mice with and without enhanced oxygenation. BMC
Cancer. 12:21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Preusser M, Heinzl H, Gelpi E, et al
European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain
Tumor Group: Histopathologic assessment of hot-spot microvessel
density and vascular patterns in glioblastoma: Poor observer
agreement limits clinical utility as prognostic factors: A
translational research project of the European Organization for
Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor Group. Cancer.
107:162–170. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|