Spandidos Publications style
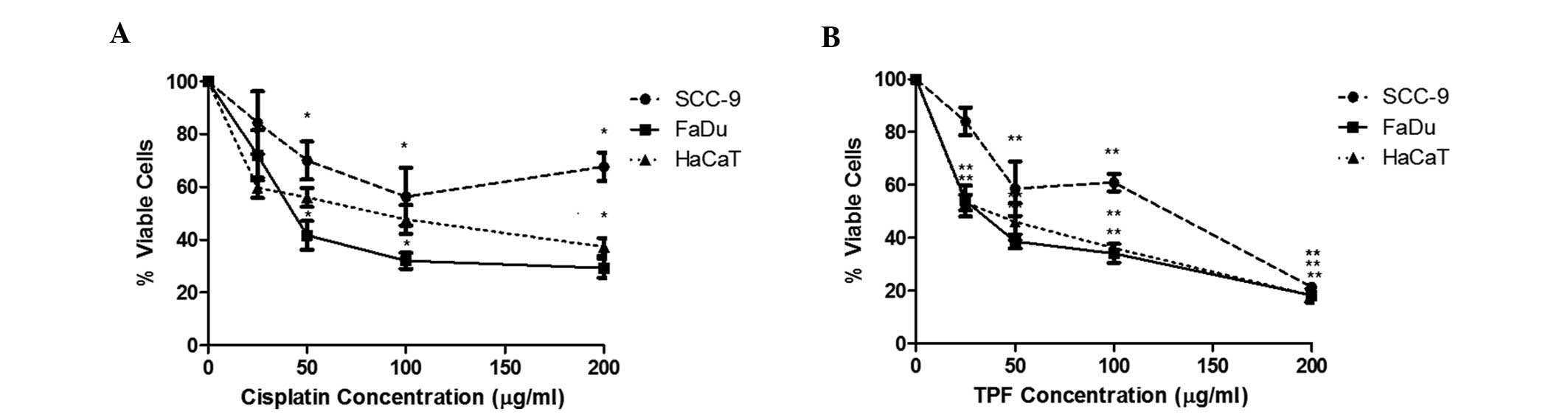
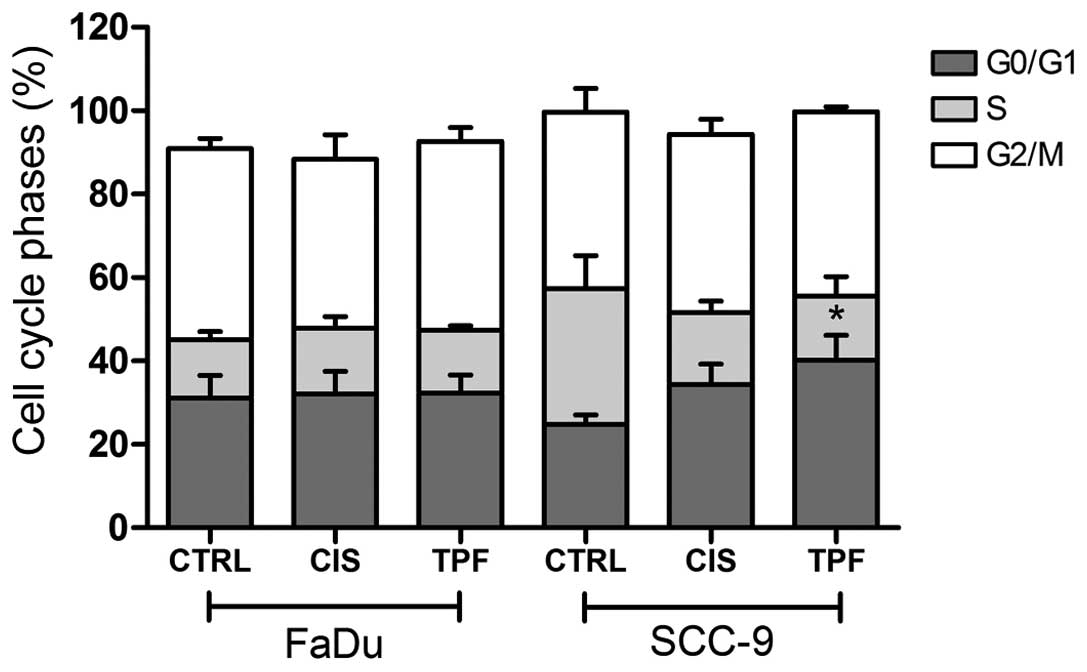
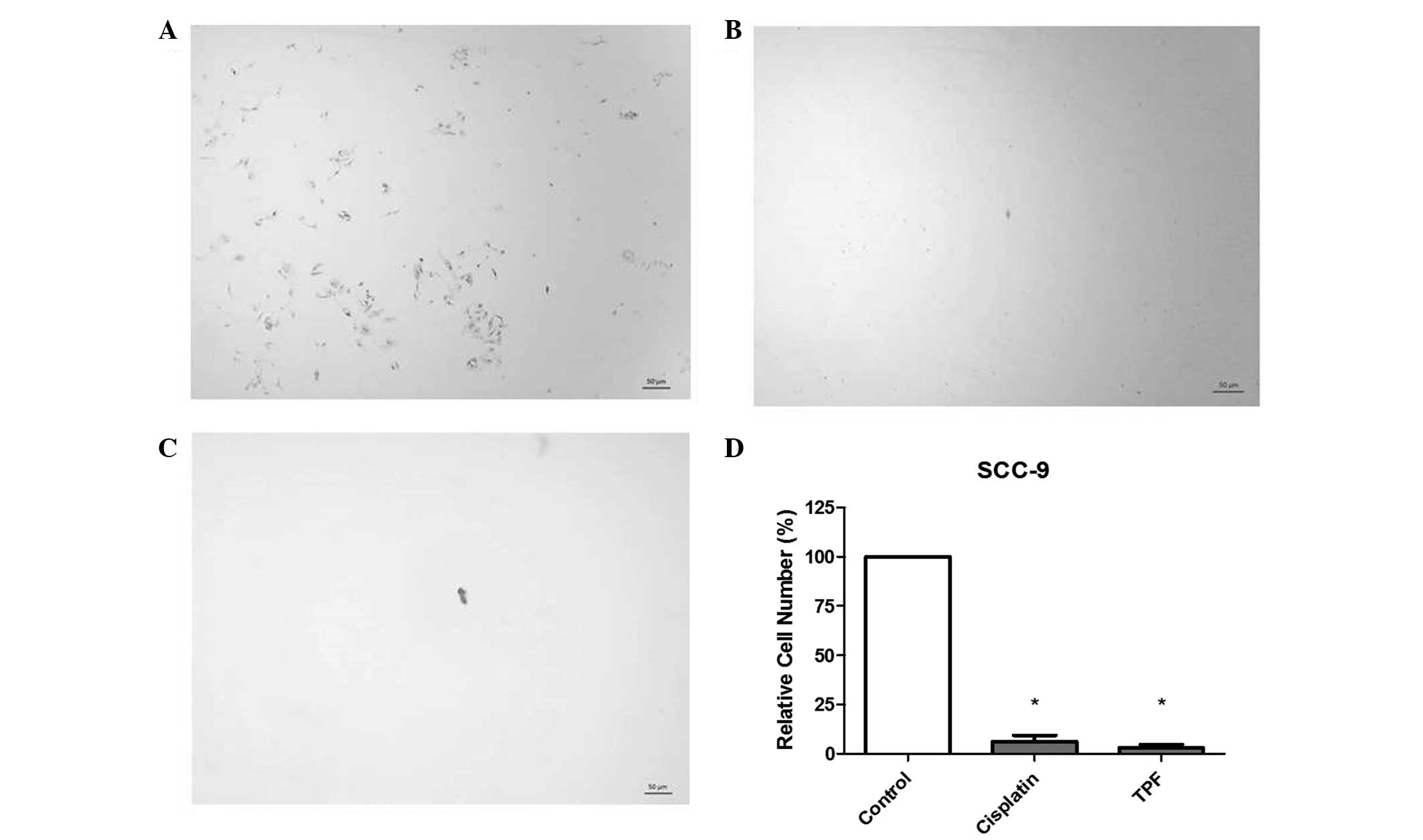
Elias ST, Borges GA, Rêgo DF, Oliveira E Silva LF, Avelino S, Nunes de Matos Neto J, Simeoni LA and Guerra EN: Combined paclitaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil therapy enhances ionizing radiation effects, inhibits migration and induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral carcinoma cell lines. Oncol Lett 10: 1721-1727, 2015.
APA
Elias, S.T., Borges, G.A., Rêgo, D.F., Oliveira E Silva, L.F., Avelino, S., Nunes de Matos Neto, J. ... Guerra, E.N. (2015). Combined paclitaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil therapy enhances ionizing radiation effects, inhibits migration and induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral carcinoma cell lines. Oncology Letters, 10, 1721-1727. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3458
MLA
Elias, S. T., Borges, G. A., Rêgo, D. F., Oliveira E Silva, L. F., Avelino, S., Nunes de Matos Neto, J., Simeoni, L. A., Guerra, E. N."Combined paclitaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil therapy enhances ionizing radiation effects, inhibits migration and induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral carcinoma cell lines". Oncology Letters 10.3 (2015): 1721-1727.
Chicago
Elias, S. T., Borges, G. A., Rêgo, D. F., Oliveira E Silva, L. F., Avelino, S., Nunes de Matos Neto, J., Simeoni, L. A., Guerra, E. N."Combined paclitaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil therapy enhances ionizing radiation effects, inhibits migration and induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral carcinoma cell lines". Oncology Letters 10, no. 3 (2015): 1721-1727. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3458