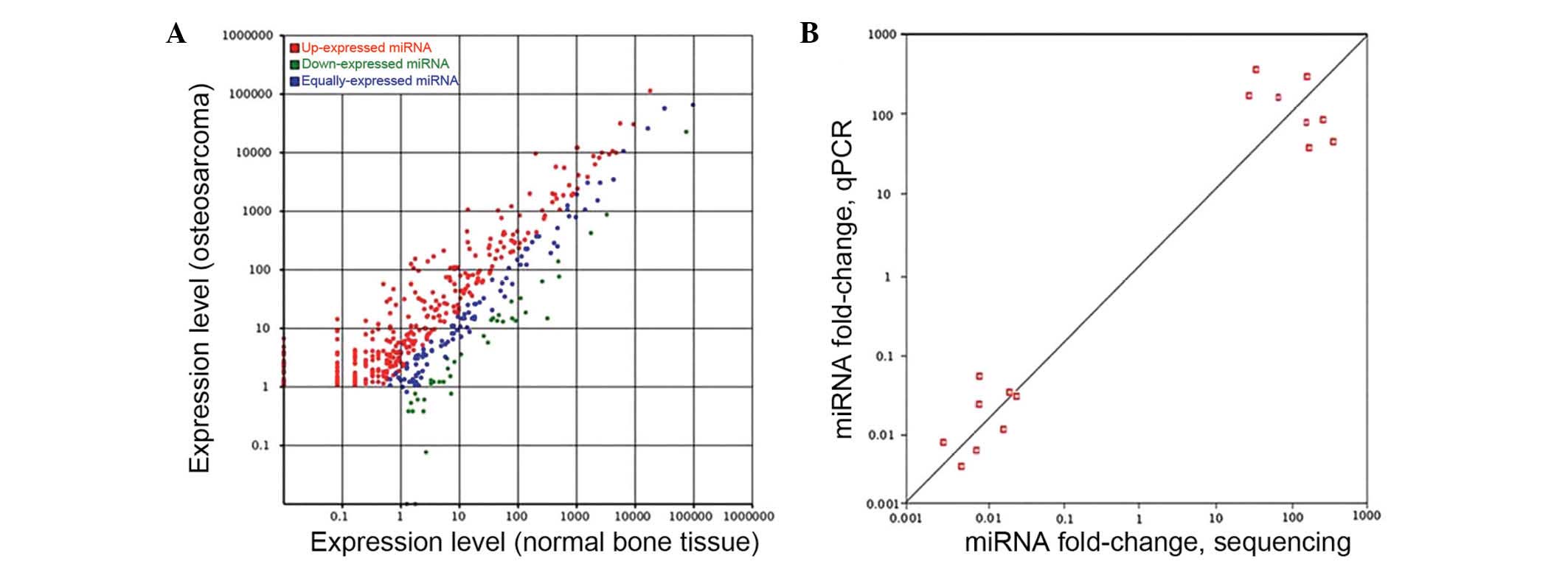
|
1
|
Sweetnam R: Osteosarcoma. Br J Hosp Med.
28:116–121. 1982.
|
|
2
|
Damron TA, Ward WG and Stewart A:
Osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma: National Cancer
Data Base Report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 459:40–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dorfman HD and Czerniak B: Bone cancers.
Cancer. 75 (1 Suppl):S203–S210. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tarkkanen M, Karhu R, Kallioniemi A,
Elomaa I, Kivioja AH, Nevalainen J, Böhling T, Karaharju E,
Hyytinen E, Knuutila S, et al: Gains and losses of DNA sequences in
osteosarcomas by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Res.
55:1334–1338. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
AlRomaih K, Bayani J, Vorobyova J,
Karaskova J, Park PC, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Chromosomal
instability in osteosarcoma and its association with centrosome
abnormalities. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 144:91–99. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ragland BD, Bell WC, Lopez RR and Siegal
GP: Cytogenetics and molecular biology of osteosarcoma. Lab Invest.
82:365–373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He JP, Hao Y, Wang XL, Yang XJ, Shao JF,
Guo FJ and Feng JX: Review of the molecular pathogenesis of
osteosarcoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:5967–5976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Broadhead ML, Clark JC, Myers DE, Dass CR
and Choong PF: The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: A
review. Sarcoma. 2011:9592482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kansara M and Thomas DM: Molecular
pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 26:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tabone MD, Kalifa C, Rodary C, Raquin M,
ValteauCouanet D and Lemerle J: Osteosarcoma recurrences in
pediatric patients previously treated with intensive chemotherapy.
J Clin Oncol. 12:2614–2620. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
KempfBielack B, Bielack SS, Jurgens H,
Branscheid D, Berdel WE, Exner GU, Göbel U, Helmke K, Jundt G,
Kabisch SF, et al: Osteosarcoma relapse after combined modality
therapy: An analysis of unselected patients in the Cooperative
Osteosarcoma Study Group (COSS). J Clin Oncol. 23:559–568. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Davis AM, Bell RS and Goodwin PJ:
Prognostic factors in osteosarcoma: A critical review. J Clin
Oncol. 12:423–431. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
ArteagaVazquez M, CaballeroPerez J and
Vielle-Calzada JP: A family of microRNAs present in plants and
animals. Plant Cell. 18:3355–3369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang B, Wang Q and Pan X: MicroRNAs and
their regulatory roles in animals and plants. J Cell Physiol.
210:279–289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 96
(Suppl):R40–R44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J,
Megraw MS, Giannakakis A, Liang S, Naylor TL, Barchetti A, Ward MR,
et al: microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in
human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:9136–9141. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Voorhoeve PM: MicroRNAs: Oncogenes, tumor
suppressors or master regulators of cancer heterogeneity? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1805:72–86. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada
H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y and
Takahashi T: A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is
overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell
proliferation. Cancer Res. 65:9628–9632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diosdado B, van de Wiel MA, Terhaar Sive
Droste JS, Mongera S, Postma C, Meijerink WJ, Carvalho B and Meijer
GA: MiR-17-92 cluster is associated with 13q gain and c-myc
expression during colorectal adenoma to adenocarcinoma progression.
Br J Cancer. 101:707–714. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: The tumor suppressor
microRNA let-7 represses the HMGA2 oncogene. Genes Dev.
21:1025–1030. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, AlvarezSaavedra E,
Lamb J, Peck D, SweetCordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, et
al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang W, Gao B, Fu P, Xu S, Qian Y and Fu
Q: The miRNAs in the pathgenesis of osteosarcoma. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 18:788–794. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kobayashi E, Hornicek FJ and Duan Z:
MicroRNA involvement in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma. 2012:3597392012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jones KB, Salah Z, Del Mare S, Galasso M,
Gaudio E, Nuovo GJ, Lovat F, LeBlanc K, Palatini J, Randall RL, et
al: miRNA signatures associate with pathogenesis and progression of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 72:1865–1877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lulla RR, Costa FF, Bischof JM, Chou PM,
de F Bonaldo M, Vanin EF and Soares MB: Identification of
differentially expressed microRNAs in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma.
2011:7326902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maire G, Martin JW, Yoshimoto M,
ChiltonMacNeill S, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Analysis of
miRNA-gene expression-genomic profiles reveals complex mechanisms
of microRNA deregulation in osteosarcoma. Cancer Genet.
204:138–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leidinger P, Keller A, Borries A,
Reichrath J, Rass K, Jager SU, Lenhof HP and Meese E:
High-throughput miRNA profiling of human melanoma blood samples.
BMC Cancer. 10:2622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gillis AJ, Stoop HJ, Hersmus R, Oosterhuis
JW, Sun Y, Chen C, Guenther S, Sherlock J, Veltman I, Baeten J, et
al: High-throughput microRNAome analysis in human germ cell
tumours. J Pathol. 213:319–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schotte D, Akbari Moqadam F,
Lange-Turenhout EA, Chen C, van Ijcken WF, Pieters R and den Boer
ML: Discovery of new microRNAs by small RNAome deep sequencing in
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 25:1389–1399.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leptidis S, El Azzouzi H, Lok SI, de Weger
R, Olieslagers S, Kisters N, Silva GJ, Heymans S, Cuppen E,
Berezikov E, et al: A deep sequencing approach to uncover the
miRNOME in the human heart. PLoS One. 8:e578002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Enneking WF, Spanier SS and Goodman MA: A
system for the surgical staging of musculoskeletal sarcoma. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 153:106–120. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Luo X, Li H, Deng L and Wang Y:
Genome-wide uncovering of STAT3-mediated miRNA expression profiles
in colorectal cancer cell lines. Biomed Res Int.
2014:1871052014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Wang Y, Zhen P, Luo X, Zhang C,
Zhou L, Lu Y, Yang Y, Zhang W and Wan J: Genome-wide analysis of
miRNA signature differentially expressed in doxorubicin-resistant
and parental human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. PLoS One.
8:e541112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yekutieli D and Benjamini Y:
Resampling-based false discovery rate controlling multiple test
procedures for correlated test statistics. J Stat Plan Inference.
82:171–196. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goedeke L and Fernández-Hernando C:
microRNAs: A connection between cholesterol metabolism and
neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis. 72:48–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Goedeke L, ValesLara FM, Fenstermaker M,
CireraSalinas D, ChamorroJorganes A, Ramírez CM, Mattison JA, de
Cabo R, Suárez Y and Fernández-Hernando C: A regulatory role for
microRNA 33* in controlling lipid metabolism gene expression. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:2339–2352. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kuo PL, Liao SH, Hung JY, Huang MS and Hsu
YL: MicroRNA-33a functions as a bone metastasis suppressor in lung
cancer by targeting parathyroid hormone related protein. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:3756–3766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Thomas M, LangeGrunweller K, Weirauch U,
Weirauch U, Gutsch D, Aigner A, Grünweller A and Hartmann RK: The
proto-oncogene Pim-1 is a target of miR-33a. Oncogene. 31:918–928.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M,
Grünweller A, Hartmann RK and Aigner A: MicroRNA replacement
therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 71:5214–5224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Iwakiri Y: A role of miR-33 for cell cycle
progression and cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 11:1057–1058. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
CireraSalinas D, Pauta M, Allen RM,
Salerno AG, Ramírez CM, ChamorroJorganes A, Wanschel AC, Lasuncion
MA, MoralesRuiz M, Suarez Y, et al: Mir-33 regulates cell
proliferation and cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle. 11:922–933.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Datta J, Kutay H, Nasser MW, Nuovo GJ,
Wang B, Majumder S, Liu CG, Volinia S, Croce CM, Schmittgen TD, et
al: Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role
in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 68:5049–5058. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wong KY, Yu L and Chim CS: DNA methylation
of tumor suppressor miRNA genes: A lesson from the miR-34 family.
Epigenomics. 3:83–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dela Cruz F and Matushansky I: MicroRNAs
in chromosomal translocation-associated solid tumors: Learning from
sarcomas. Discov Med. 12:307–317. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|