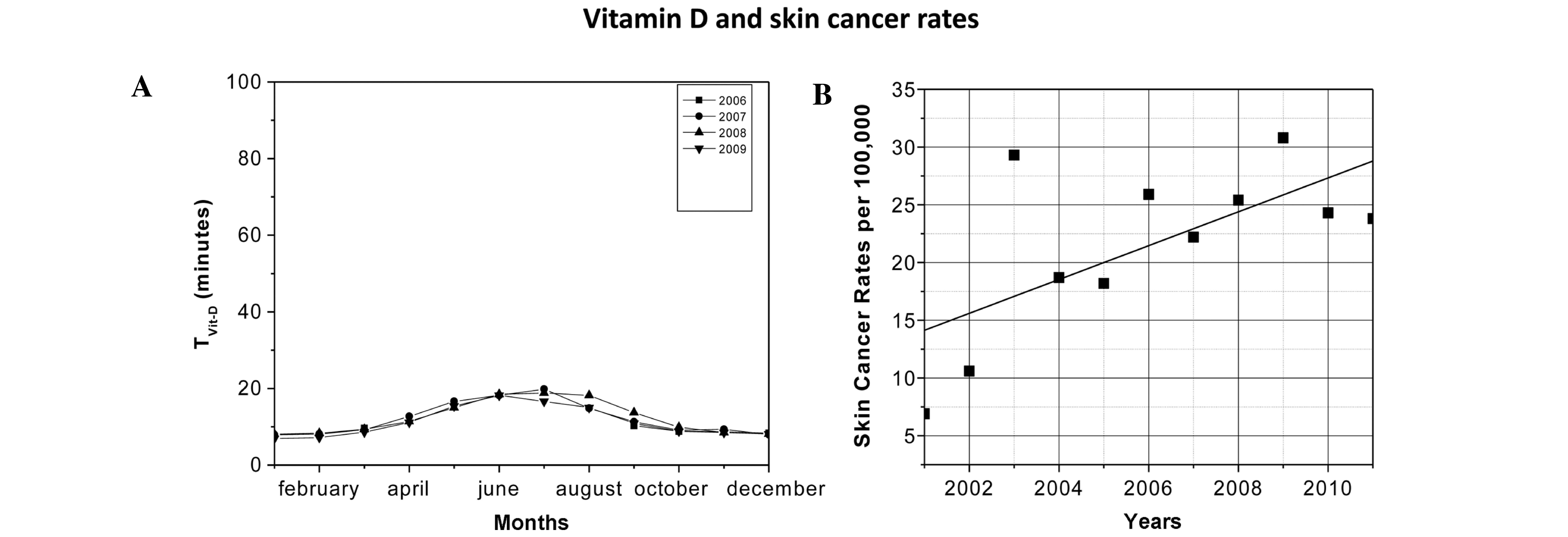
|
1
|
Elwood JM and Jopson J: Melanoma and sun
exposure: An overview of published studies. Int J Cancer.
73:198–203. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D: Importance in the
prevention of cancers, type I diabetes, heart disease and
osteoporosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 79:362–371. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mckenzie L, Liley JB and Bjorn LO: UV
Radiation: Balancing Risk and Benefits. Photochem Photobiol.
85:88–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garland CF, Comstock GW, Garland FC,
Helsing KJ, Shaw EK and Gorham ED: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and
colon cancer: Eight year prospective study. Lancet. 2:1176–1178.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Banwell CM, Singh R, Stewart PM, Uskokovic
MR and Campbell MJ: Antiproliferative signalling by 1,25(OH)2D3 in
prostate and breast cancer is suppressed by a mechanism involving
histone deacetylation. Recent Results Cancer Res. 164:83–98. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grant WB: An ecologic study of dietary and
solar ultraviolet-B links to breast carcinoma mortality rates.
Cancer. 94:272–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grant WB: An estimate of premature cancer
mortality in the U.S. due to inadequate doses of solar
ultraviolet-B radiation. Cancer. 94:1867–1875. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zittermann A, Schleithoff SS, Tenderich H,
Berthold HK, Körfer R and Stehle P: Low vitamin D status: A
contributing factor in the pathogenesis of congestive heart
failure? J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:105–112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Holick MF: Shedding new light on the role
of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: The lncRNA-skin cancer
connection. Exp Dermatol. 23:391–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matkovic V: Calcium metabolism and calcium
requirements during skeletal modeling and consolidation of bone
mass. Am J Clin Nutr. 54:245S–260S. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leccia MT: Skin, sun exposure and vitamin
D: Facts and controversies. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 140:176–182.
2013.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ralph AP, Lucas RM and Norval M: Vitamin D
and solar ultraviolet radiation in the risk and treatment of
tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 13:77–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ooms ME, Roos JC, Bezemer PD, van der Vijh
WJ, Bouter LM and Lips P: Prevention of bone lost by vitamin D
supplementation in elderly women: A randomized double blindtrial. J
Clin Endoc & Metab. 80:1052–1085. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rivas M, Araya MC, Caba F, Rojas E and
Calaf GM: Ultraviolet light exposure influences skin cancer in
association with latitude. Oncol Rep. 25:1153–1159. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rivas M, Rojas E and Calaf GM: Prediction
of skin cancer ocurrence by ultraviolet solar index. Oncol Lett.
3:893–896. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rivas M, Rojas E and Calaf GM: Skin cancer
risk influenced by ultraviolet solar irradiance. Oncol Lett.
7:483–486. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rivas M, Leiva C and Rojas E: Estudio de
series temporales de energía solar UVB de 305 nm y espesor de la
capa de ozono estratosférico en Arica, norte de Chile. Ingeniare.
19:168–173. 2011.(In Spanish).
|
|
18
|
World Meteorological Organization (WMO), .
Report of the WMO Meeting of Experts on UV-B Measurements, Data
Quality and Standardization Of UV IndicesLes Diablerets. WHO;
Geneva, Switzerland: pp. 361994, (WMO TD no. 625).
|
|
19
|
Fitzpatrick TB: The validity and
practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Arch
Dermatol. 124:869–871. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sachdeva S: Fitzpatrick skin typing.
Applications in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol.
75:93–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Madronich S, McKenzie RL, Björn LO and
Caldwell MM: Changes in biologically active ultraviolet radiation
reaching the Earth's surface. J Photochem Photobiol B. 46:5–19.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peters RD, Krueger AJ, Bhartia PK and
Herman JR: Earth probe total ozone mapping spectrometer (TOMS) Data
Products User's GuideNASA Reference Publication 1998-206895.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration; Washington, DC:
1998
|
|
23
|
Rivas M, Araya MC, Durán V, Rojas E,
Cortes J and Calaf GM: Ultraviolet light exposure and skin cancer
in the city of Arica, Chile. Mol Med Rep. 2:567–572.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bojkov R and Fioletov V: Estimating the
global ozone characteristics during the last 30 years. J Geoph Res.
100:16537–16551. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Schwalfenberg GK: Solar radiation and
vitamin D: Mitigating environmental factors in autoimmune disease.
J Environ Public Health 2012. Article ID. : 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Moan J, Porojnicu AC, Dahlback A and
Setlow RB: Addressing the health benefits and risks, involving
vitamin D or skin cancer of increased sun exposure. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:668–673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|