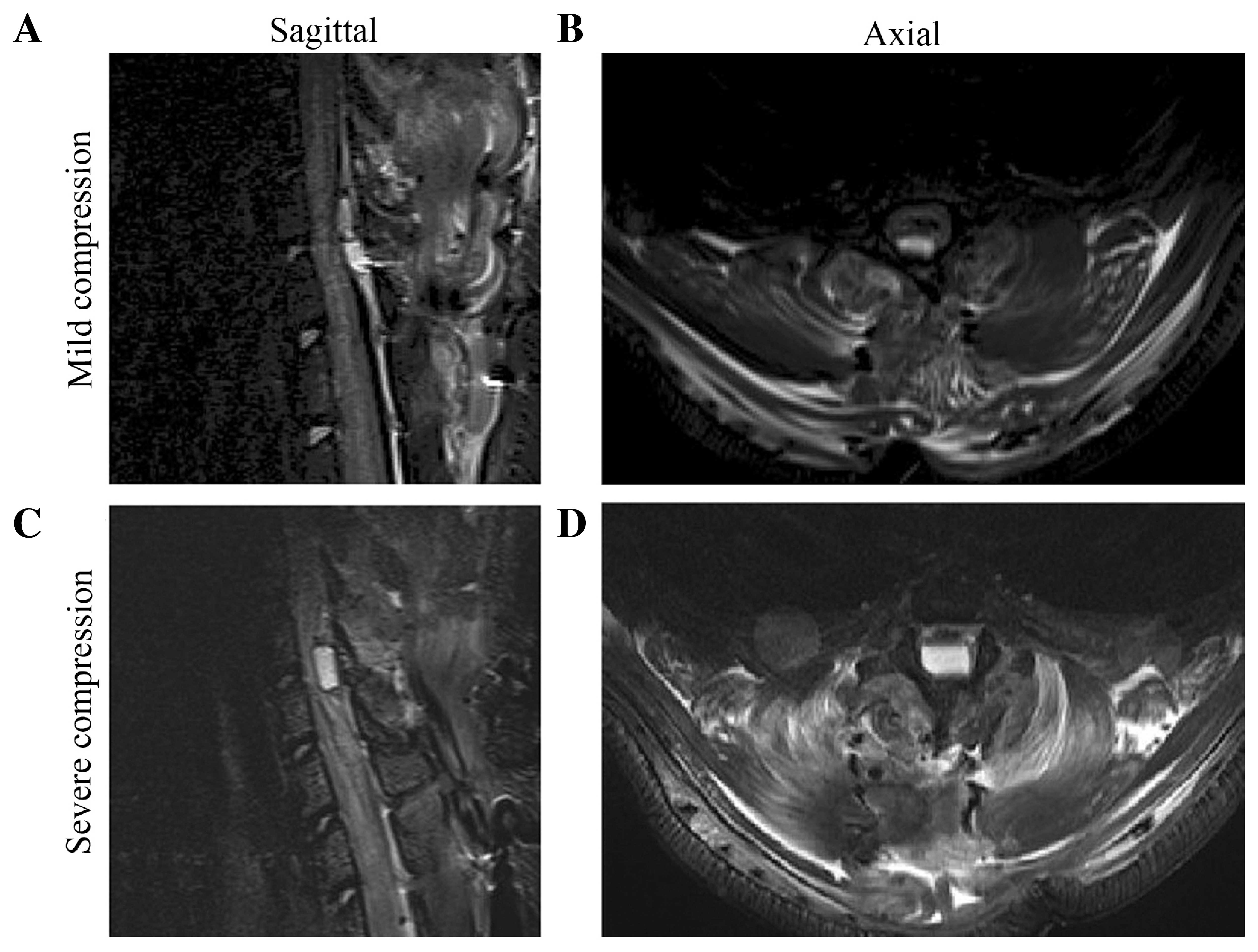
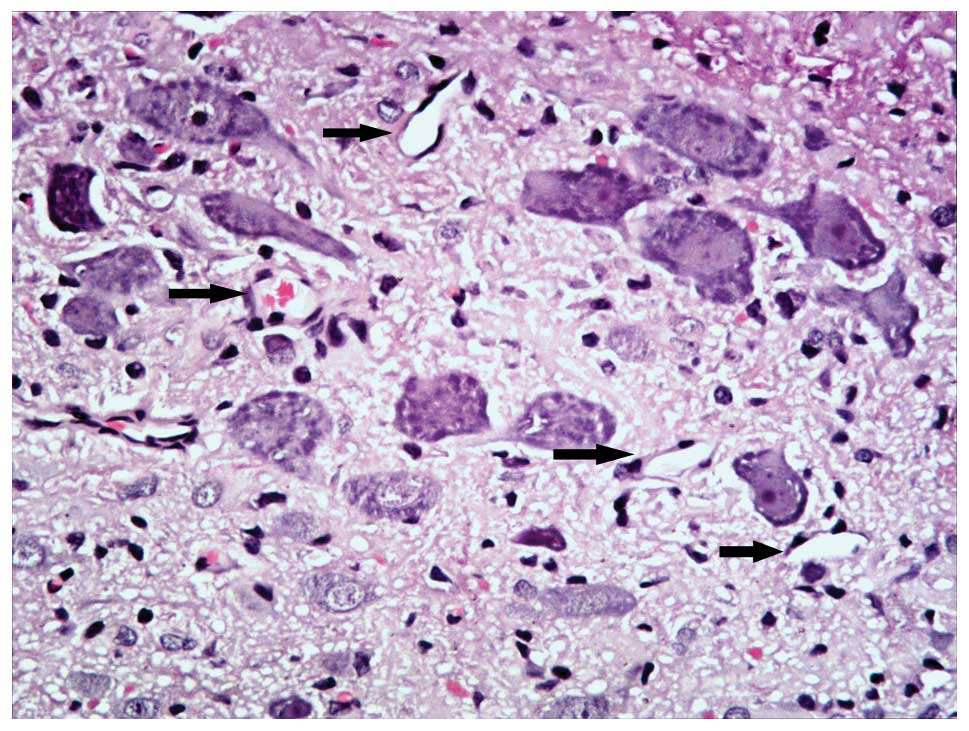
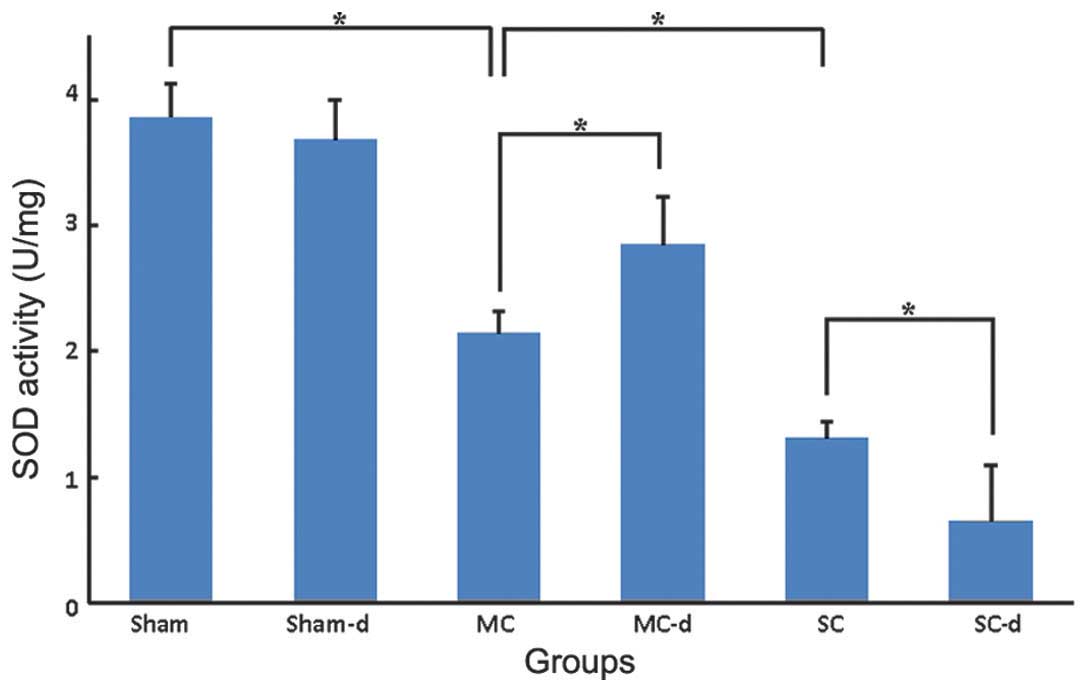
|
1
|
Setzer M, Vatter H, Marquardt G, Seifert V
and Vrionis FD: Management of spinal meningiomas: Surgical results
and a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus. 23:E142007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sandalcioglu IE, Hunold A, Müller O,
Bassiouni H, Stolke D and Asgari S: Spinal meningiomas: Critical
review of 131 surgically treated patients. Eur Spine J.
17:1035–1041. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ambekar S, Sharma M, Kukreja S and Nanda
A: Complications and outcomes of surgery for spinal meningioma: A
nationwide inpatient sample analysis from 2003 to 2010. Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 118:65–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taher F, Lebl DR, Cammisa FP, Pinter DW,
Sun DY and Girardi FP: Transient neurological deficit following
midthoracic decompression for severe stenosis: A series of three
cases. Eur Spine J. 22:2057–2061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uematsu Y, Tokuhashi Y and Matsuzaki H:
Radiculopathy after laminoplasty of the cervical spine. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 23:2057–2062. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chin KR, Seale J and Cumming V: ‘White
cord syndrome’ of acute tetraplegia after anterior cervical
decompression and fusion for chronic spinal cord compression: A
case report. Case Rep Orthop. 2013:6979182013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Orchowski J, Bridwell KH and Lenke LG:
Neurological deficit from a purely vascular etiology after
unilateral vessel ligation during anterior thoracolumbar fusion of
the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:406–410. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee KS, Shim JJ, Doh JW, Yoon SM, Bae HG
and Yun IG: Transient paraparesis after laminectomy in a patient
with multi-level ossification of the spinal ligament. J Korean Med
Sci. 19:624–626. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang T, Wu L, Deng X, Yang C, Zhang Y,
Zhang D and Xu Y: Delayed neurological deterioration with an
unknown cause subsequent to surgery for intraspinal meningiomas.
Oncol Lett. 9:2325–2330. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wisselink W, Money SR, Crockett DE, Nguyen
JH, Becker MO, Farr GH and Hollier LH: Ischemia-reperfusion injury
of the spinal cord: Protective effect of the hydroxyl radical
scavenger dimethylthiourea. J Vasc Surg. 20:444–491. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shan LQ, Ma S, Qiu XC, Zhou Y, Zhang Y,
Zheng LH, Ren PC, Wang YC, Fan QY and Ma BA: Hydroxysafflor Yellow
A protects spinal cords from ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rabbits. BMC Neurosci. 11:982010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chan PH: Role of oxidants in ischemic
brain damage. Stroke. 27:1124–1129. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wilson JX and Gelb AW: Free radicals,
antioxidants and neurologic injury: Possible relationship to
cerebral protection by anesthetics. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol.
14:66–79. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim P, Haisa T, Kawamoto T, Kirino T and
Wakai S: Delayed myelopathy induced by chronic compression in the
rat spinal cord. Ann Neurol. 55:503–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang J, Rong W, Hu X, Liu X, Jiang L, Ma
Y, Dang G, Liu Z and Wei F: Hyaluronan tetrasaccharide in the
cerebrospinal fluid is associated with self-repair of rats after
chronic spinal cord compression. Neuroscience. 210:467–480. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC,
Anderson DK, Faden AI, Gruner JA, Holford TR, Hsu CY, Noble LJ,
Nockels R, et al: MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores:
Effects of experience and teamwork on reliability multicenter
animal spinal cord injury study. J. Neurotrauma. 13:343–359. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kou J, Fischgrund J, Biddinger A and
Herkowitz H: Risk factors for spinal epidural hematoma after spinal
surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:1670–1673. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cramer DE, Maher PC, Pettigrew DB and
Kuntz C IV: Major neurologic deficit immediately after adult spinal
surgery: Incidence and etiology over 10 years at a single training
institution. J Spinal Disord Tech. 22:565–570. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahn JS, Lee JK and Kim BK: Prognostic
factors that affect the surgical outcome of the laminoplasty in
cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Surg. 2:98–104. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Young WF and Baron E: Acute neurologic
deterioration after surgical treatment for thoracic spinal
stenosis. J Clin Neurosci. 8:129–132. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sakaura H, Hosono N, Mukai Y, Ishii T and
Yoshikawa H: C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cervical
myelopathy: Review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
28:2447–2451. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Delattre JY, Arbit E, Thaler HT, Rosenblum
MK and Posner JB: A dose-response study of dexamethasone in a model
of spinal cord compression caused by epidural tumor. J Neurosurg.
70:920–925. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Manabe S, Tanaka H, Higo Y, Park P, Ohno T
and Tateishi A: Experimental analysis of the spinal cord compressed
by spinal metastasis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 14:1308–1315. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ushio Y, Posner R, Posner JB and Shapiro
WR: Experimental spinal cord compression by epidural neoplasm.
Neurology. 27:422–429. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ikeda H, Ushio Y, Hayakawa T and Mogami H:
Edema and circulatory disturbance in the spinal cord compressed by
epidural neoplasms in rabbits. J Neurosurg. 52:203–209. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Delattre JY, Arbit E, Rosenblum MK, Thaler
HT, Lau N, Galicich JH and Posner JB: High dose versus low dose
dexamethasone in experimental epidural spinal cord compression.
Neurosurgery. 22:1005–1007. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harkey HL, al-Mefty O, Marawi I, Peeler
DF, Haines DE and Alexander LF: Experimental chronic compressive
cervical myelopathy: Effects of decompression. J Neurosurg.
83:336–341. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schramm J, Hashizume K, Fukushima T and
Takahashi H: Experimental spinal cord injury produced by slow,
graded compression: Alterations of cortical and spinal evoked
potentials. J Neurosurg. 50:48–57. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baba H, Maezawa Y, Uchida K, Imura S,
Kawahara N, Tomita K and Kudo M: Three-dimensional topographic
analysis of spinal accessory motoneurons under chronic mechanical
compression: An experimental study in the mouse. J Neurol.
244:222–229. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Baba H, Furusawa N, Fukuda M, Maezawa Y,
Imura S, Kawahara N, Nakahashi K and Tomita K: Potential role of
streptozotocin in enhancing ossification of the posterior
longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine in the hereditary
spinal hyperostotic mouse (twy/twy). Eur J Histochem. 41:191–202.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Furusawa N, Baba H, Imura S and Fukuda M:
Characteristics and mechanism of the ossification of posterior
longitudinal ligament in the tip-toe walking Yoshimura (twy) mouse.
Eur J Histochem. 40:199–210. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okawa A, Nakamura I, Goto S, Moriya H,
Nakamura Y and Ikegawa S: Mutation in Npps in a mouse model of
ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine.
Nat Genet. 19:271–273. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tator CH and Koyanagi L: Vascular
mechanisms in the pathophysiology of human spinal cord injury. J
Neurosurg. 86:483–492. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta R, Singh M and Sharma A:
Neuroprotective effect of antioxidants on ischaemia and
reperfusion-induced cerebral in jury. Pharmacol Res. 48:209–215.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ilhan A, Koltuksuz U, Ozen S, Uz E,
Ciralik H and Akyol O: The effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester
(CAPE) on spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury in rabbits. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 16:458–463. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Golding JD, Rigley MacDonald ST, Juurlink
BH and Rosser BW: The effect of glutamine on locomotor performance
and skeletal muscle myosins following spinal cord injury in rats. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 101:1045–1052. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cemil B, Topuz K, Demircan MN, Kurt G, Tun
K, Kutlay M, Ipcioglu O and Kucukodaci Z: Curcumin improves early
functional results after experimental spinal cord injury. Acta
Neurochir (Wien). 152:1583–1590. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ferrari R, Ceconi C, Curello S, Cargnoni
A, Alfiri O, Pardini A, Marzollo P and Visioli O: Oxygen free
radicals and myocardial damage: Protective role of thiol-containing
agents. Am J Med. 91:95S–105S. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Emmez H, Börcek AÖ, Kaymaz M, Kaymaz F,
Durdağ E, Civi S, Gülbahar O, Aykol S and Paşaoğlu A:
Neuroprotective effects of gabapentin in experimental spinal cord
injury. World Neurosurg. 73:729–734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Christie SD, Comeau B, Myers T, Sadi D,
Purdy M and Mendez I: Duration of lipid peroxidation after acute
spinal cord injury in rats and the effect of methylprednisolone.
Neurosurg Focus. 25:E52008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|