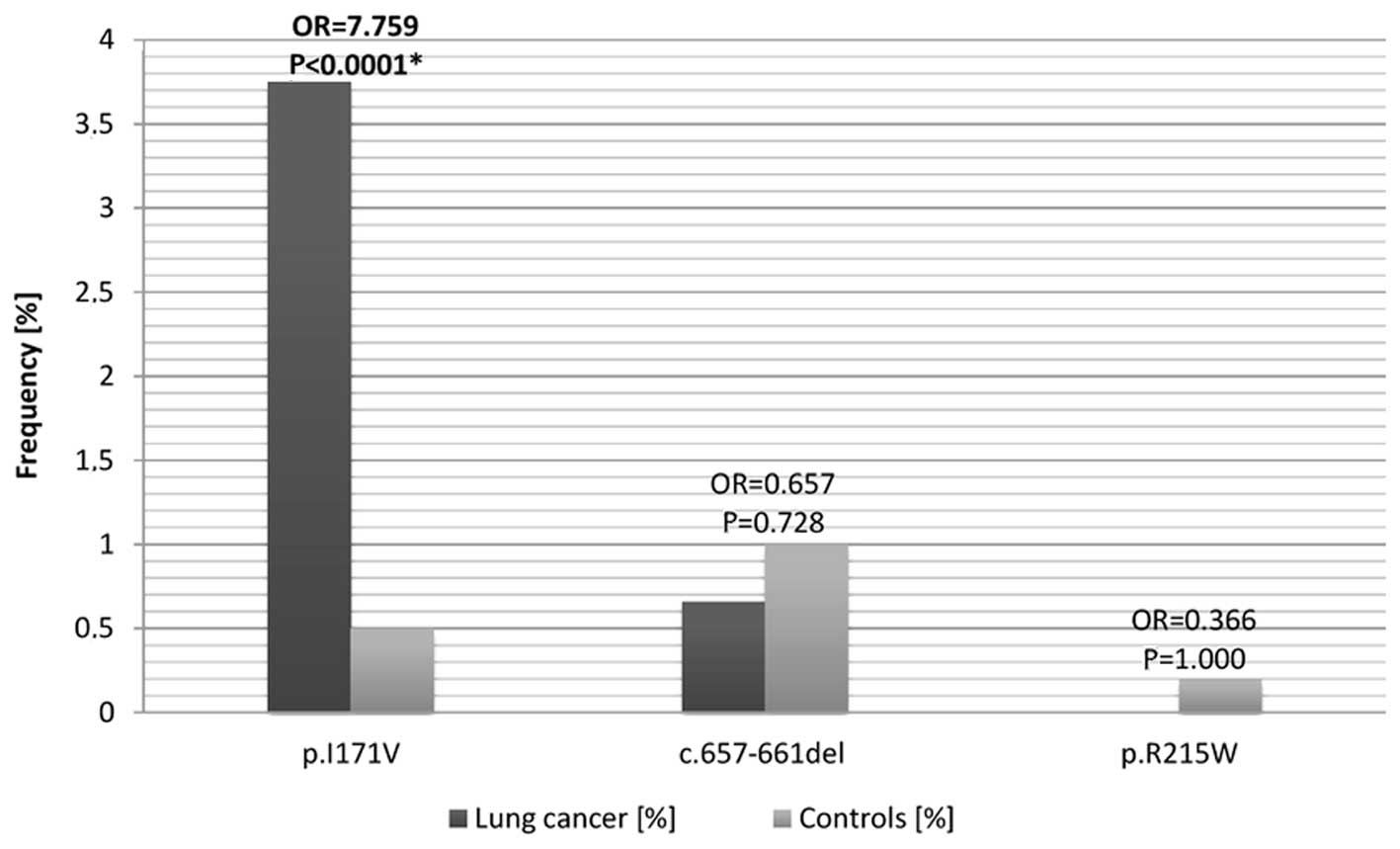
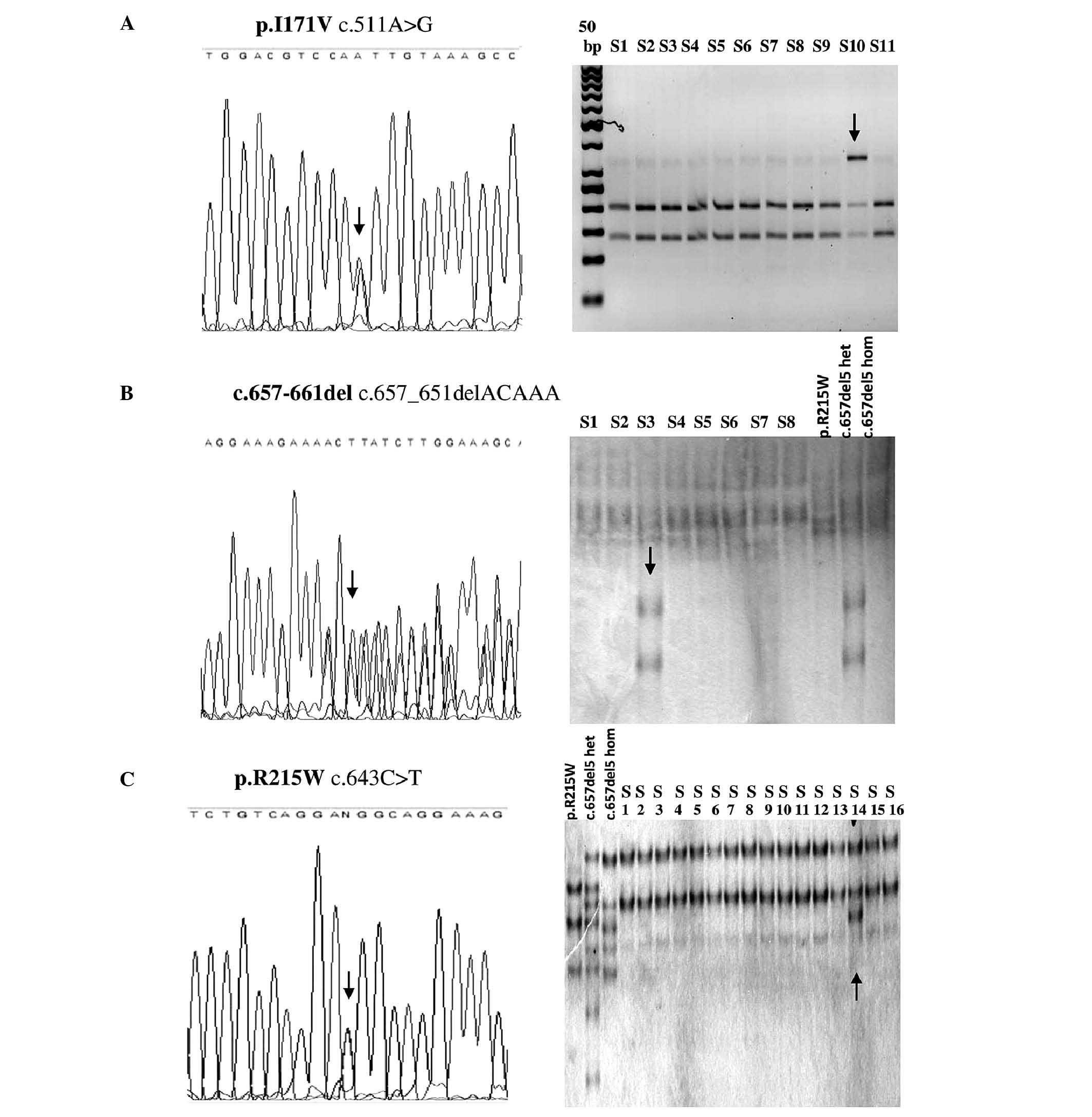
|
1
|
Weizmann Institute of Science: GeneCards:
NBN gene. Rehovot, Israel: Weizmann Institute of Science. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Assenmacher N and Hopfner KP:
MRE11/RAD50/NBS1: Complex activities. Chromosoma. 113:157–166.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
D'Amours D and Jackson SP: The Mre11
complex: At the crossroads of dna repair and checkpoint signalling.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:317–327. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tauchi H, Matsuura S, Kobayashi J,
Sakamoto S and Komatsu K: Nijmegen breakage syndrome gene, NBS1,
and molecular links to factors for genome stability. Oncogene.
21:8967–8980. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carney JP, Maser RS, Olivares H, Davis EM,
Le Beau M, Yates JR III, Hays L, Morgan WF and Petrini JH: The
hMre11/hRad50 protein complex and Nijmegen breakage syndrome:
Linkage of double-strand break repair to the cellular DNA damage
response. Cell. 93:477–486. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matsuura S, Tauchi H, Nakamura A, Kondo N,
Sakamoto S, Endo S, Smeets D, Solder B, Belohradsky BH, Der
Kaloustian VM, et al: Positional cloning of the gene for Nijmegen
breakage syndrome. Nat Genet. 19:179–181. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Varon R, Vissinga C, Platzer M,
Cerosaletti KM, Chrzanowska KH, Saar K, Beckmann G, Seemanová E,
Cooper PR, Nowak NJ, et al: Nibrin, a novel DNA double-strand break
repair protein, is mutated in Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Cell.
93:467–476. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mosor M, Ziółkowska I, Pernak-Schwarz M,
Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D and Nowak J: Association of the
heterozygous germline I171V mutation of the NBS1 gene with
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 20:1454–1456.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Roznowski K, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D,
Mosor M, Pernak M, Litwiniuk M and Nowak J: I171V germline mutation
in the NBS1 gene significantly increases risk of breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 110:343–348. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ziólkowska I, Mosor M, Wierzbicka M,
Rydzanicz M, Pernak-Schwarz M and Nowak J: Increased risk of larynx
cancer in heterozygous carriers of the I171V mutation of the NBS1
gene. Cancer Sci. 98:1701–1705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nowak J, Mosor M, Nowicka K, Rembowska J
and Januszkiewicz D: Is the NBN gene mutation I171V a potential
risk factor for malignant solid tumors in children? J Pediatr
Hematol Oncol. 33:e248–e249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cybulski C, Górski B, Debniak T,
Gliniewicz B, Mierzejewski M, Masojć B, Jakubowska A, Matyjasik J,
Złowocka E, Sikorski A, et al: NBS1 is a prostate cancer
susceptibility gene. Cancer Res. 64:1215–1219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mosor M, Ziółkowska-Suchanek I, Nowicka K,
Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D and Nowak J:
Germline variants in MRE11/RAD50/NBN complex genes in childhood
leukemia. BMC Cancer. 13:457–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ziółkowska I, Mosor M and Nowak J:
Regional distribution of heterozygous 657del5 mutation carriers of
the NBS1 gene in Wielkopolska province (Poland). J Appl Genet.
47:269–272. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nowak J, Mosor M, Ziółkowska I, Wierzbicka
M, Pernak-Schwarz M, Przyborska M, Roznowski K, Pławski A, Słomski
R and Januszkiewicz D: Heterozygous carriers of the I171V mutation
of the NBS1 gene have a significantly increased risk of solid
malignant tumours. Eur J Cancer. 44:627–630. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao P, Ma N, Li M, Tian Q-B and Liu DW:
Functional variants in NBS1 and cancer risk: Evidence from a
meta-analysis of 60 publications with 11 individual studies.
Mutagenesis. 28:683–697. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bork P, Hofmann K, Bucher P, Neuwald AF,
Altschul SF and Koonin EV: A superfamily of conserved domains in
DNA damage-responsive cell cycle checkpoint proteins. FASEB J.
11:68–76. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cerosaletti KM and Concannon P: Nibrin
forkhead-associated domain and breast cancer C-terminal domain are
both required for nuclear focus formation and phosphorylation. J
Biol Chem. 278:21944–21951. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ciara E, Piekutowska-Abramczuk D, Popowska
E, Grajkowska W, Barszcz S, Perek D, Dembowska-Bagińska B,
Perek-Polnik M, Kowalewska E, Czajńska A, et al: Heterozygous
germ-line mutations in the NBN gene predispose to medulloblastoma
in pediatric patients. Acta Neuropathol. 119:325–334. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Mosor M,
Januszkiewicz D and Nowak J: Impact of heterozygous c.657-661del,
p.I171V and p.R215W mutations in NBN on nibrin functions.
Mutagenesis. 27:337–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seemanová E, Jarolim P, Seeman P, Varon R,
Digweed M, Swift M and Sperling K: Cancer risk of heterozygotes
with the NBN founder mutation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1875–1880.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steffen J, Varon R, Mosor M, Maneva G,
Maurer M, Stumm M, Nowakowska D, Rubach M, Kosakowska E, Ruka W, et
al: Increased cancer risk of heterozygotes with NBS1 germline
mutations in Poland. Int J Cancer. 111:67–71. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seemanová E, Sperling K, Neitzel H, Varon
R, Hadac J, Butova O, Schröck E, Seeman P and Digweed M: Nijmegen
breakage syndrome (NBS) with neurological abnormalities and without
chromosomal instability. J Med Genet. 43:218–224. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Varon R, Reis A, Henze G, von Einsiedel
HG, Sperling K and Seeger K: Mutations in the Nijmegen Breakage
Syndrome gene (NBS1) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
(ALL). Cancer Res. 61:3570–3572. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hebbring SJ, Fredriksson H, White KA,
Maier C, Ewing C, McDonnell SK, Jacobsen SJ, Cerhan J, Schaid DJ,
Ikonen T, et al: Role of the Nijmegen breakage syndrome gene in
familial and sporadic prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 15:935–938. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|