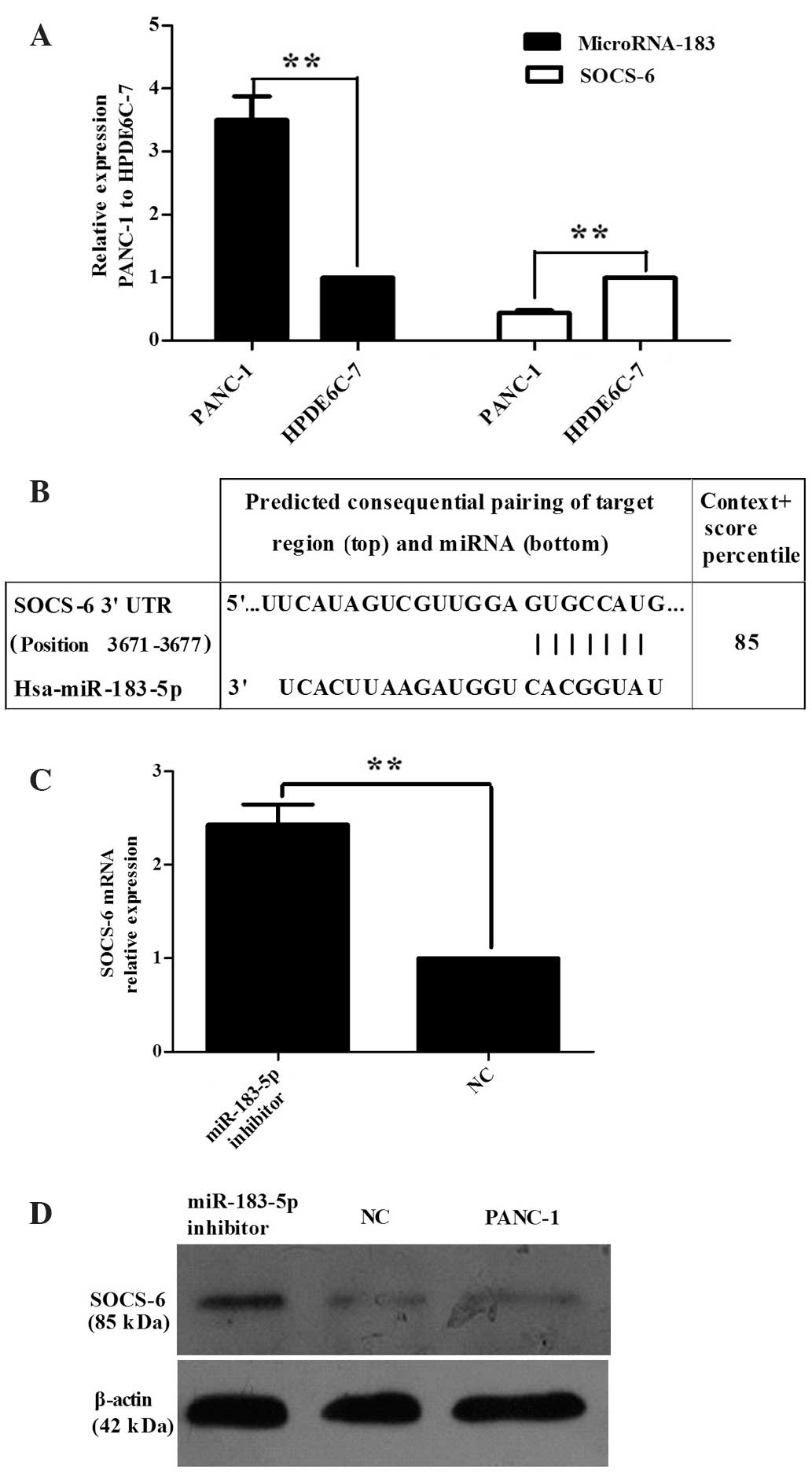
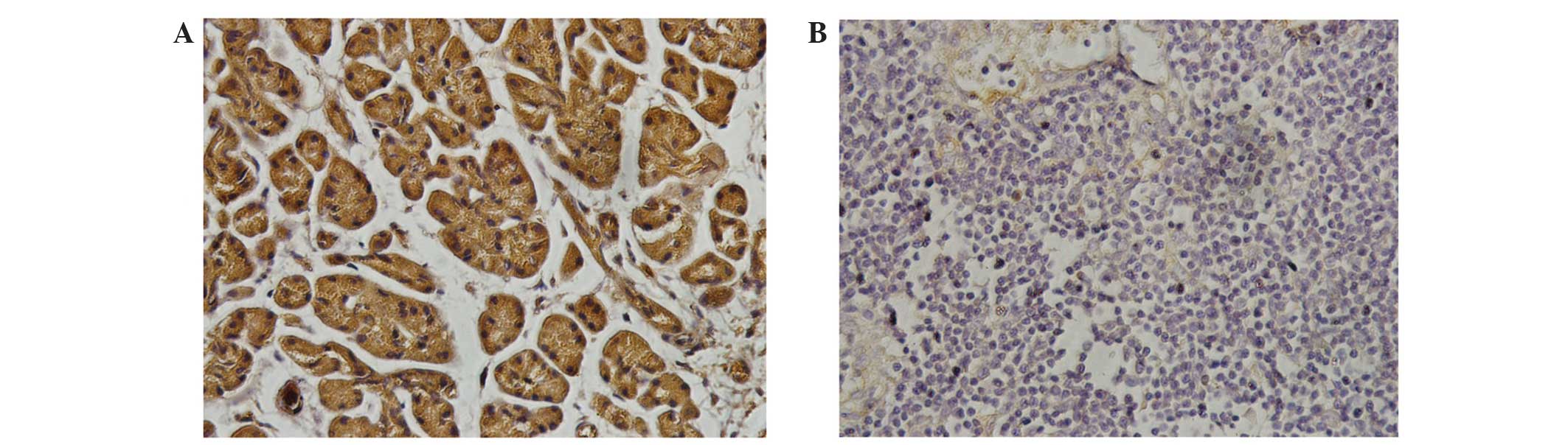
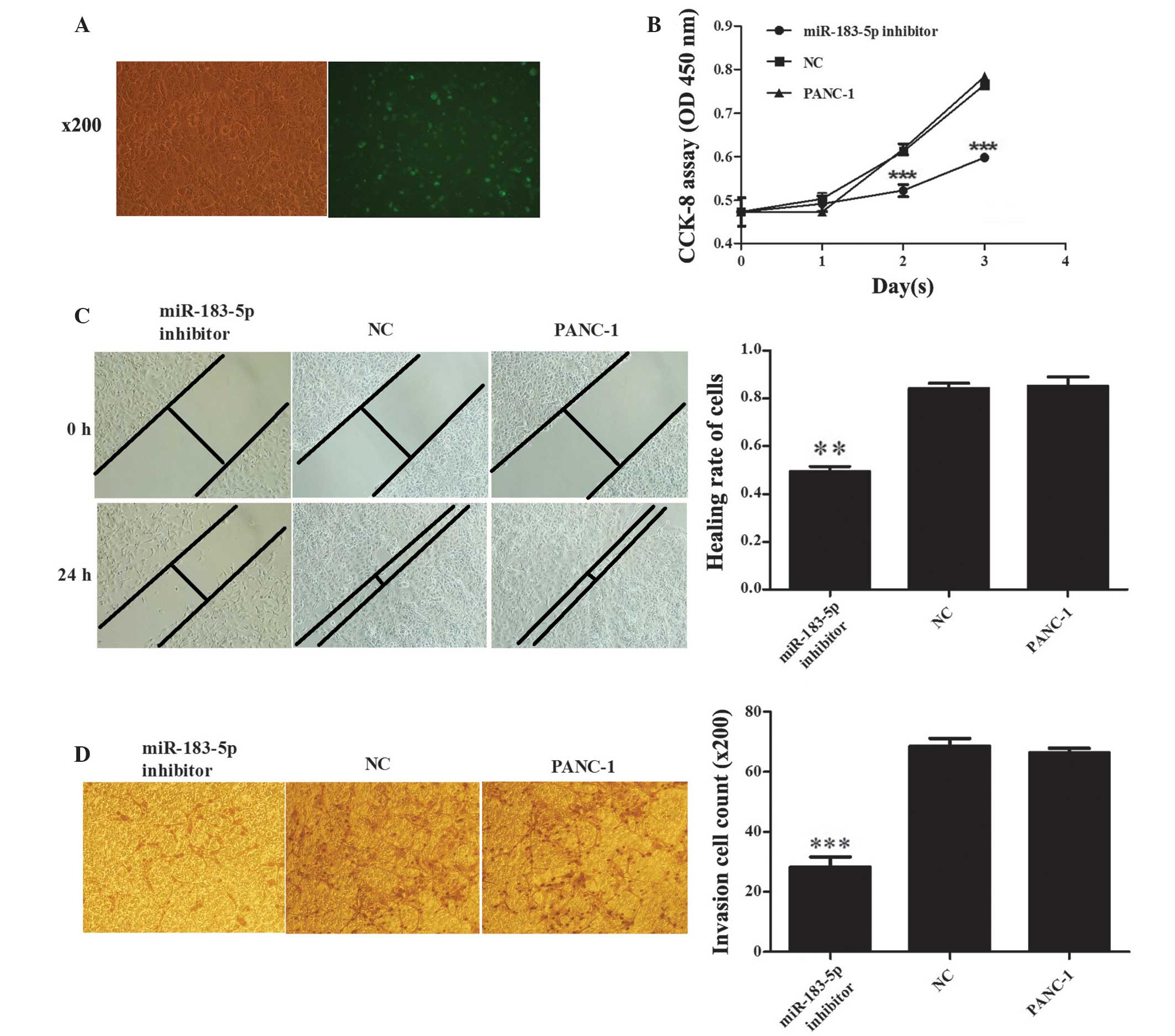
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P and Lowenfels
AB: Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: An overview. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:699–708. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R and Abbruzzese JL:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 363:1049–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maitra A, Kern SE and Hruban RH: Molecular
pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 20:211–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szafranska AE, Doleshal M, Edmunds HS,
Gordon S, Luttges J, Munding JB, Barth RJ Jr, Gutmann EJ,
Suriawinata AA and Marc Pipas J: Analysis of microRNAs in
pancreatic fine-needle aspirates can classify benign and malignant
tissues. Clin Chem. 54:1716–1724. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li A, Omura N, Hong SM, Vincent A, Walter
K, Griffith M, Borges M and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancers
epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress
miR-200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR-200a and
miR-200b levels. Cancer Res. 70:5226–5237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, et
al: MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic
adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA.
297:1901–1908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kent OA, Mullendore M, Wentzel EA,
López-Romero P, Tan AC, Alvarez H, West K, Ochs MF, Hidalgo M and
Arking DE: A resource for analysis of microRNA expression and
function in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Biol
Ther. 8:2013–2024. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sarkar S, Dubaybo H, Ali S, Goncalves P,
Kollepara SL, Sethi S, Philip PA and Li Y: Down-regulation of
miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through
up-regulation of PTEN, p27 (kip1), p57 (kip2) and PUMA. Am J Cancer
Res. 3:465–477. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lumayag S, Haldin CE, Corbett NJ, et al:
Inactivation of the microRNA-183/96/182 cluster results in
syndromic retinal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:E507–E516. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leung WK, He M, Chan AW, Law PT and Wong
N: Wnt/β-Catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett.
362:97–105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Quan H, Wang S, Li X and Che X:
MiR-183 promotes growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells through
FoxO1 inhibition. Tumour Biol. May 17–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Di W, Dong Y, et al: High serum
miR-183 level is associated with poor responsiveness of renal
cancer to natural killer cells. Tumour Biol. Jun 20–2015.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
16
|
Kundu ST, Byers LA, Peng DH, et al: The
miR-200 family and the miR-183~96~182 cluster target Foxf2 to
inhibit invasion and metastasis in lung cancers. Oncogene. Mar
23–2015.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ouyang M, Li Y, Ye S, Ma J, Lu L, Lv W,
Chang G, Li X, Li Q, Wang S and Wang W: MicroRNA profiling implies
new markers of chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancer.
PLoS One. 9:e962282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mihelich BL, Khramtsova EA, Arva N,
Vaishnav A, Johnson DN, Giangreco AA, Martens-Uzunova E, Bagasra O,
Kajdacsy-Balla A and Nonn L: MiR-183-96-182 cluster is
overexpressed in prostate tissue and regulates zinc homeostasis in
prostatecells. J Biol Chem. 286:44503–44511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wojtas B, Ferraz C, Stokowy T, Hauptmann
S, Lange D, Dralle H, Musholt T, Jarzab B, Paschke R and Eszlinger
M: Differential miRNA expression defines migration and reduced
apoptosis in follicular thyroid carcinomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
388:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Dwyer RM and Kerin
MJ: Dysregulated miR-183 inhibits migration in breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 10:5022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Wang X, Li Z, Liu H and Teng Y:
MicroRNA-183 suppresses retinoblastoma cell growth, invasion and
migration by targeting LRP6. FEBS J. 281:1355–1365. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang G, Mao W and Zheng S: MicroRNA-183
regulates Ezrin expression in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
582:3663–3668. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Deng G,
Tanaka Y, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R: MicroRNA-183 is an
oncogene targeting Dkk-3 and SMAD4 in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer.
108:1659–1667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tanaka H, Sasayama T, Tanaka K, et al:
MicroRNA-183 upregulates HIF-1α by targeting isocitrate
dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) in glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 111:273–283.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sarver AL, Li L and Subramanian S:
MicroRNA miR-183 functions as an oncogene by targeting the
transcription factor EGR1 and promoting tumor cell migration.
Cancer Res. 70:9570–9580. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park YG, Lee KH, Lee JK, et al: MicroRNA
expression pattern in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Korean J Gastroenterol. 58:190–200. 2011.(In Korean). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D146–D152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jia A, Xiao J and Liu X: Serum tumor
marker CA199, CA125, CA242 and CEA. Correlational analysis and
detection of different stages of pancreatic cancer. Chongqing Med.
35:3605–3607. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Hwang JH, Voortman J, Giovannetti E, et
al: Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for
chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in
resectable pancreatic cancer. PloS One. 5:e106302010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trengove MC and Ward AC: SOCS proteins in
development and disease. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2:1–29.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Torrisani J, Bournet B, du Rieu MC,
Bouisson M, Souque A, Escourrou J, Buscail L and Cordelier P: Let-7
microRNA transfer in pancreatic cancer-derived cells inhibits in
vitro cell proliferation but fails to alter tumor progression.
Hu Gene Ther. 20:831–844. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yan H, Wu J, Liu W, Zuo Y, Chen S, Zhang
S, Zeng M and Huang W: MicroRNA-20a overexpression inhibited
proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Hum
Gene Ther. 21:1723–1734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu Y, Ou Y, Wu K, Chen Y and Sun W:
miR-143 inhibits the metastasis of pancreatic cancer and an
associated signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 33:1863–1870. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F,
Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C and Croce
CM: MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic
adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA.
297:1901–1908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Panarelli NC, Chen YT, Zhou XK,
Kitabayashi N and Yantiss RK: MicroRNA expression aids the
preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Pancreas. 41:685–690. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang JI, Chen J, Chang P, LeBlanc A, Li D,
Abbruzzesse JL, Frazier ML, Killary AM and Sen S: MicroRNAs in
plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel
blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
2:807–813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W, Croce C and
Bloomston M: MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and
a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg.
12:2171–2176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moriyama T, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J,
Sato N, Nabae T, Takahata S, Toma H, Nagai E and Tanaka M:
MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer
cells including their proliferation, invasion and chemoresistance.
Mo Cancer Ther. 8:1067–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Moriyama T, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J,
Sato N, Nabae T, Takahata S, Toma H, Nagai E and Tanaka M:
MicroRNA-10a is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer and
involved in its invasiveness partially via suppression of the HOXA1
gene. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2394–2402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He H, Hao SJ, Yao L, Yang F, Di Y, Li J,
Jiang YJ, Jin C and Fu DL: MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell invasion and
migration of pancreatic cancer via regulating ROBO1. Cancer Biol
Ther. 15:1333–1339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li W, Yuan Y, Huang L, Qiao M and Zhang Y:
Metformin alters the expression profiles of microRNAs in human
pancreatic cancer cells. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 96:187–195. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hamada S, Satoh K, Fujibuchi W, Hirota M,
Kanno A, Unno J, Masamune A, Kikuta K, Kume K and Shimosegawa T:
MiR-126 acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer cells via
the regulation of ADAM9. Mol Cancer Res. 10:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mees ST, Mardin WA, Sielker S, Willscher
E, Senninger N, Schleicher C, Colombo-Benkmann M and Haier J:
Involvement of CD40 targeting miR-224 and miR-486 on the
progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol.
16:2339–2350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chang CW, Wu HC, Terry MB and Santella RM:
microRNA expression in prospectively collected blood as a potential
biomarker of breast cancer risk in the BCFR. Anticancer Res.
35:3969–3977. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pak MG, Lee CH, Lee WJ, Shin DH and Roh
MS: Unique microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma groups according to
major TKI sensitive EGFR mutation status. Diagn Pathol. 10:992015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Van Keuren-Jensen K, Malenica I,
Courtright A, et al: microRNA changes in liver tissue associated
with fibrosis progression in patients with Hepatitis-C. Liver Int.
Jul 19–2015.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li G, Luna C, Qiu J, Epstein DL and
Gonzalez P: Targeting of integrin beta1 and kinesin 2alpha by
microRNA 183. J Biol Chem. 285:5461–5471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cao Z, Zhang N, Lou T, et al: microRNA-183
down-regulates the expression of BKCaβ1 protein that is related to
the severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hippokratia.
18:328–332. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hilton DJ, Richardson RT, Alexander WS,
Viney EM, Willson TA, Sprigg NS, Starr R, Nicholson SE, Metcalf D
and Nicola NA: Twenty proteins containing a C-terminal SOCS box
form five structural classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:114–119.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Krebs DL, Uren RT, Metcalf D, Rakar S,
Zhang JG, Starr R, De Souza DP, Hanzinikolas K, Eyles J, Connolly
LM, et al: SOCS-6 binds to insulin receptor substrate 4 and mice
lacking the SOCS-6 gene exhibit mild growth retardation. Mol Cell
Biol. 22:4567–4578. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sriram KB, Larsen JE, Savarimuthu Francis
SM, Wright CM, Clarke BE, Duhig EE, Brown KM, Hayward NK, Yang IA,
Bowman RV and Fong KM: Array-comparative genomic hybridization
reveals loss of SOCS6 is associated with poor prognosis in primary
lung squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e303982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lai RH, Hsiao YW, Wang MJ, Lin HY, Wu CW,
Chi CW, Li AF, Jou YS and Chen JY: SOCS6, down-regulated in gastric
cancer, inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation. Cancer
Lett. 288:75–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Storojeva I, Boulay JL, Heinimann K,
Ballabeni P, Terracciano L, Laffer U, Mild G, Herrmann R and
Rochlitz C: Prognostic and predictive relevance of microsatellite
instability in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 14:241–249.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wu K, Hu G, He X, Zhou P, Li J, He B and
Sun W: MicroRNA-424-5p suppresses the expression of SOCS6 in
pancreatic cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 19:739–748. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Park YG, Lee KH, Lee JK, Lee KT, Choi DW,
Choi SH, Heo JS, Jang KT, Lee EM, Kim JO, et al: MicroRNA
expression pattern in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Korean J Gastroenterol. 58:190–200. 2011.(In Korean). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|