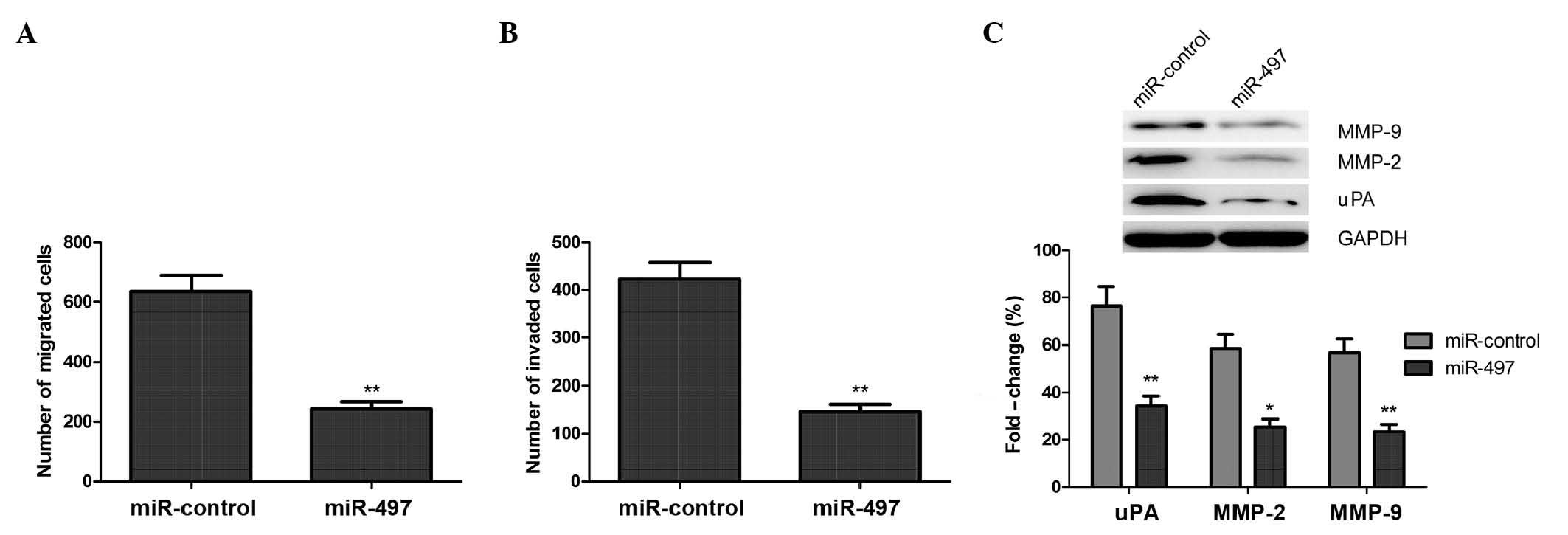
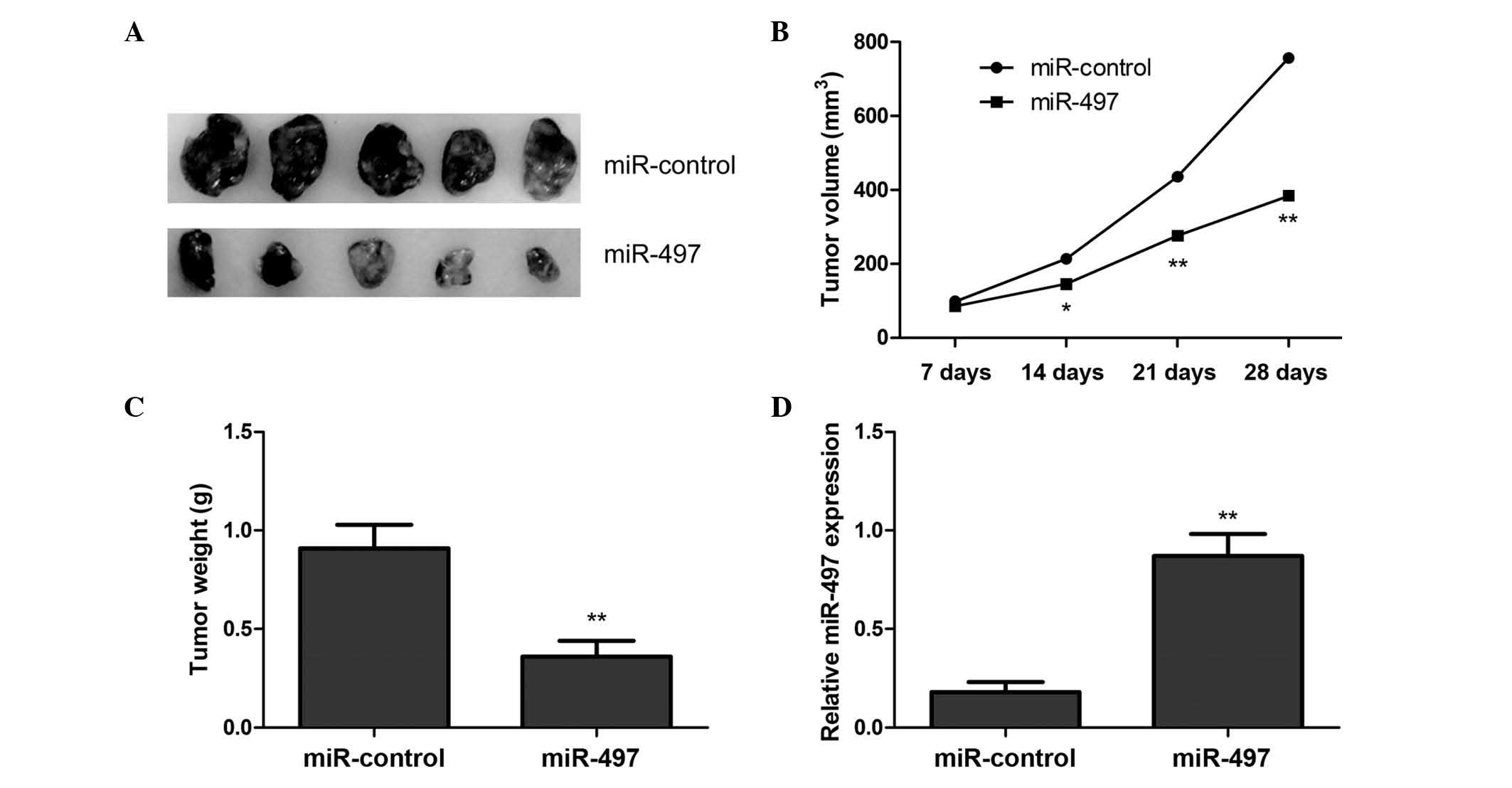
|
1
|
Ottaviani G, Robert RS, Huh WW, Palla S
and Jaffe N: Sociooccupational and physical outcomes more than 20
years after the diagnosis of osteosarcoma in children and
adolescents: Limb salvage versus amputation. Cancer. 119:3727–3736.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The etiology of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:15–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
PosthumaDeBoer J, Witlox MA, Kaspers GJ
and van Royen BJ: Molecular alterations as target for therapy in
metastatic osteosarcoma: A review of literature. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 28:493–503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chou AJ, Kleinerman ES, Krailo MD, Chen Z,
Betcher DL, Healey JH, Conrad EU III, Nieder ML, Weiner MA, Wells
RJ, et al: Children's Oncology Group: Addition of muramyl
tripeptide to chemotherapy for patients with newly diagnosed
metastatic osteosarcoma: A report from the Children's Oncology
Group. Cancer. 115:5339–5348. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grignani G, Palmerini E, Dileo P, Asaftei
SD, D'Ambrosio L, Pignochino Y, Mercuri M, Picci P, Fagioli F,
Casali PG, et al: A phase II trial of sorafenib in relapsed and
unresectable high-grade osteosarcoma after failure of standard
multimodal therapy: An Italian Sarcoma Group study. Ann Oncol.
23:508–516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment - where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kato M and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs: Small
molecules with big roles - C. elegans to human cancer. Biol
Cell. 100:71–81. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nana-Sinkam SP and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Opportunities for the development of
microRNA-based drugs. IDrugs. 13:843–846. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E and Kai
M: Epigenetic alteration and microRNA dysregulation in cancer.
Front Genet. 4:2582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cho WC: OncomiRs: The discovery and
progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer. 6:602007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Finnerty JR, Wang WX, Hébert SS, Wilfred
BR, Mao G and Nelson PT: The miR-15/107 group of microRNA genes:
Evolutionary biology, cellular functions, and roles in human
diseases. J Mol Biol. 402:491–509. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang W, Ren F, Wu Q, Jiang D, Li H, Peng
Z, Wang J and Shi H: MicroRNA-497 inhibition of ovarian cancer cell
migration and invasion through targeting of SMAD specific E3
ubiquitin protein ligase 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
449:432–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang
Y, Zou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang X, et al: Analysis of MiR-195 and
MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1722–1730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo M, Shen D, Zhou X, Chen X and Wang W:
MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical
cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Surgery. 153:836–847. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo ST, Jiang CC, Wang GP, Li YP, Wang CY,
Guo XY, Yang RH, Feng Y, Wang FH, Tseng HY, et al: MicroRNA-497
targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and has a tumour
suppressive role in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene.
32:1910–1920. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Creevey L, Ryan J, Harvey H, Bray IM,
Meehan M, Khan AR and Stallings RL: MicroRNA-497 increases
apoptosis in MYCN amplified neuroblastoma cells by targeting the
key cell cycle regulator WEE1. Mol Cancer. 12:232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Jin X, Deng X, Zhang G, Zhang B and
Ma L: The putative tumor suppressor microRNA-497 modulates gastric
cancer cell proliferation and invasion by repressing eIF4E. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 449:235–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Ren F, Wu Q, Jiang D, Li H and Shi
H: MicroRNA-497 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor A through the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK
pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2127–2133.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Barøy T,
Østensen IH, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, Serra M, Bürger H,
Cleton-Jansen AM and Myklebost O: Modulation of the osteosarcoma
expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 7:e480862012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li E, Zhang J, Yuan T and Ma B: MiR-145
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion by targeting
ROCK1. Tumour Biol. 35:7645–7650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun XH, Geng XL, Zhang J and Zhang C:
miRNA-646 suppresses osteosarcoma cell metastasis by downregulating
fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2). Tumour Biol. 36:2127–2134. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao D, Jia P, Wang W and Zhang G:
VEGF-mediated suppression of cell proliferation and invasion by
miR-410 in osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:87–95. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Ren K, Zhao G, Yan K and
Ma B: MicroRNA-101 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
downregulation of EZH2 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:2143–2149.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu W, Zhu D, Lu S, Wang T, Wang J, Jiang
B, Shu Y and Liu P: miR-497 modulates multidrug resistance of human
cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2. Med Oncol. 29:384–391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yadav S, Pandey A, Shukla A, Talwelkar SS,
Kumar A, Pant AB and Parmar D: miR-497 and miR-302b regulate
ethanol-induced neuronal cell death through BCL2 protein and cyclin
D2. J Biol Chem. 286:37347–37357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou TB, Jiang ZP, Liu ZS and Zhao ZZ:
Roles of miR-497 and its potential signaling pathway in diseases
and with vascular endothelial growth factor. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 35:303–306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie Y, Wei RR, Huang GL, Zhang MY, Yuan YF
and Wang HY: Checkpoint kinase 1 is negatively regulated by miR-497
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:8442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao WY, Wang Y, An ZJ, Shi CG, Zhu GA,
Wang B, Lu MY, Pan CK and Chen P: Downregulation of miR-497
promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting HDGF in
non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
435:466–471. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|