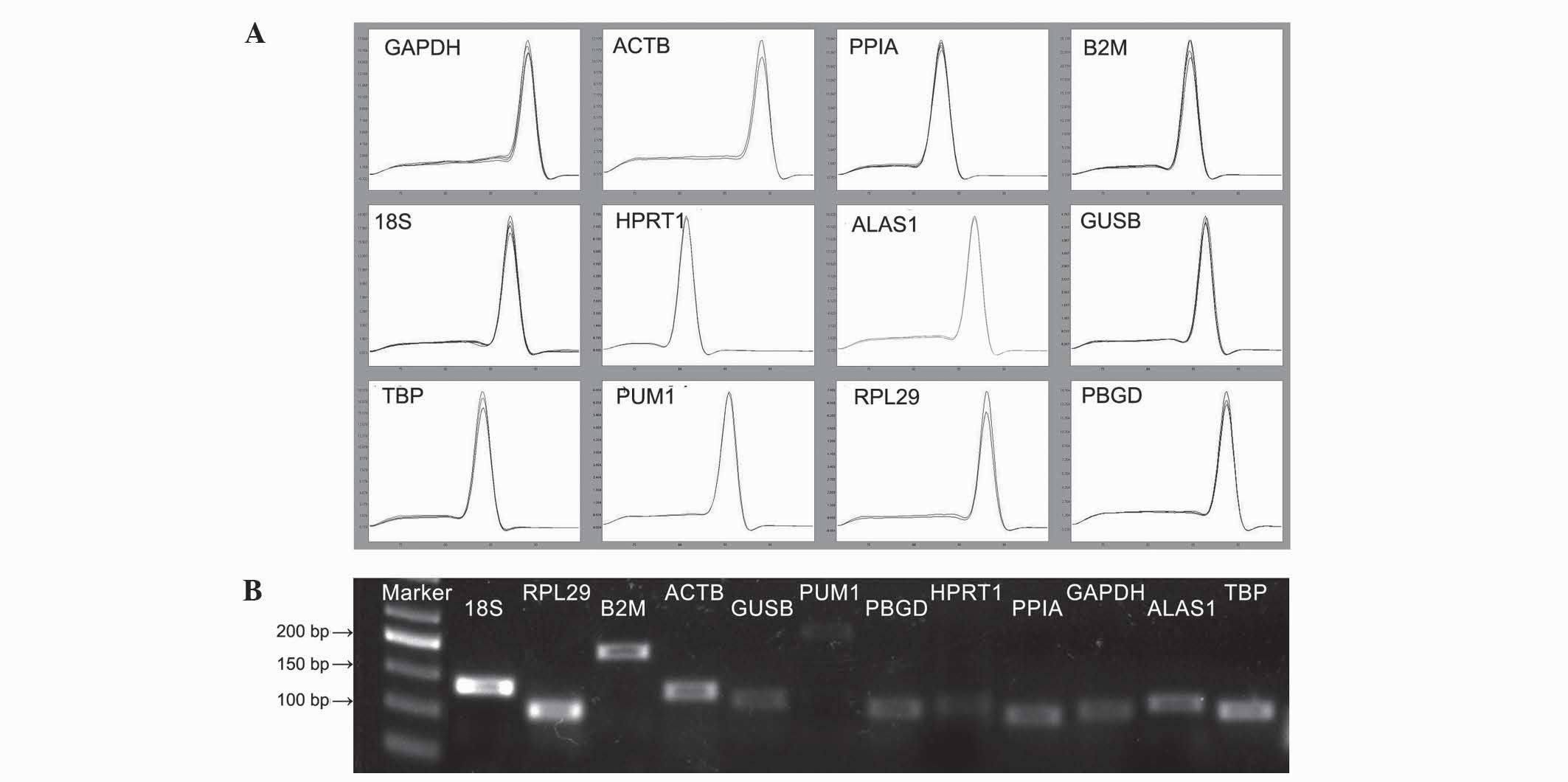
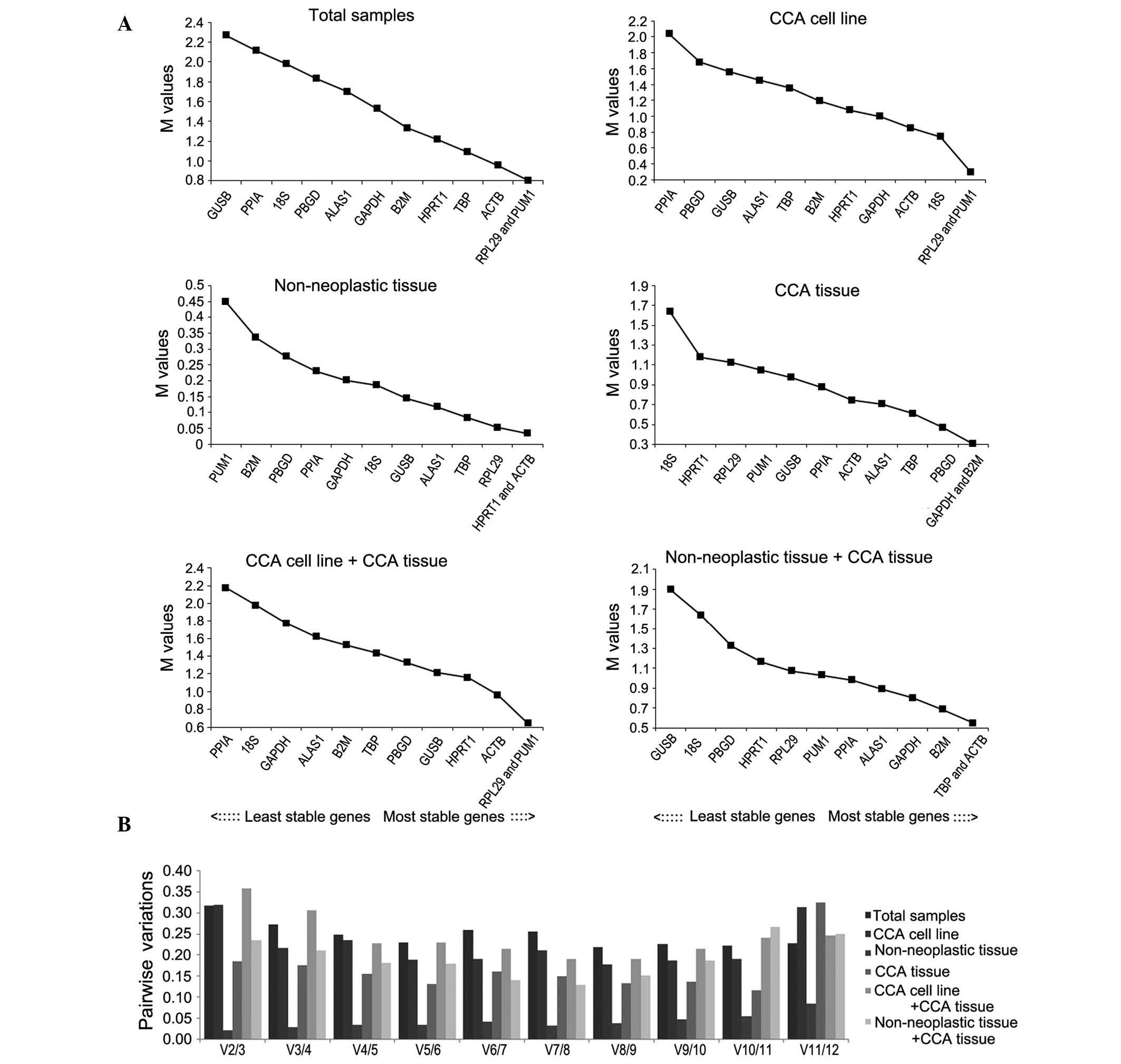
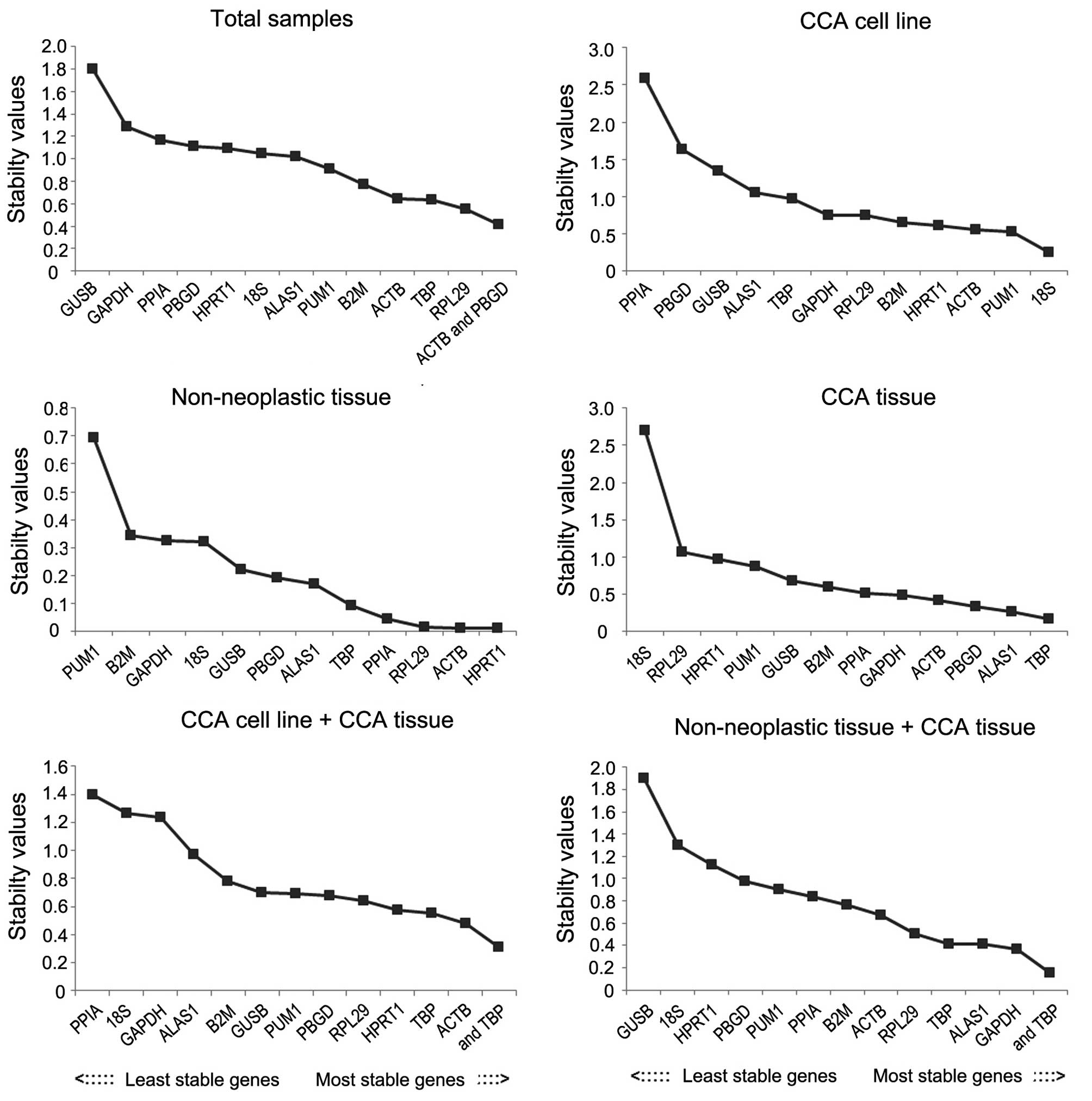
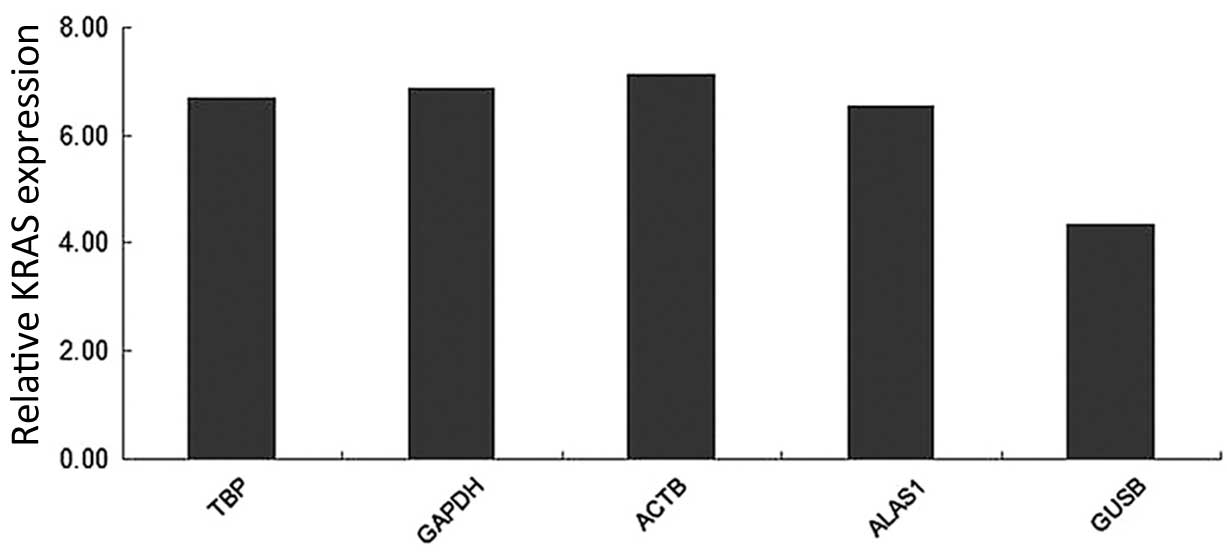
|
1
|
Lazaridis KN and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 128:1655–1667. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friman S: Cholangiocarcinoma - current
treatment options. Scand J Surg. 100:30–34. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cardinale V, Semeraro R, Torrice A, Gatto
M, Napoli C, Bragazzi MC, Gentile R and Alvaro D: Intra-hepatic and
extra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma: New insight into epidemiology and
risk factors. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2:407–416. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown KM: Multidisciplinary approach to
tumors of the pancreas and biliary tree. Surg Clin North Am.
89:115–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bustin SA: Absolute quantification of mRNA
using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
assays. J Mol Endocrinol. 25:169–193. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T and Pfaffl MW:
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR-a perspective. J Mol Endocrinol.
34:597–601. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Derveaux S, Vandesompele J and Hellemans
J: How to do successful gene expression analysis using real-time
PCR. Methods. 50:227–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F,
Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F: Accurate
normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric
averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol.
3:RESEARCH00342002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Jonge HJ, Fehrmann RS, de Bont ES,
Hofstra RM, Gerbens F, Kamps WA, de Vries EG, van der Zee AG, te
Meerman GJ and ter Elst A: Evidence based selection of housekeeping
genes. PLoS One. 2:e8982007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ho-Pun-Cheung A, Bascoul-Mollevi C,
Assenat E, Bibeau F, Boissière-Michot F, Cellier D, Ychou M and
Lopez-Crapez E: Validation of an appropriate reference gene for
normalization of reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase
chain reaction data from rectal cancer biopsies. Anal Biochem.
388:348–350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bustin SA and Mueller R: Real-time reverse
transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and its potential use in clinical
diagnosis. Clin Sci (Lond). 109:365–379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hruz T, Wyss M, Docquier M, Pfaffl MW,
Masanetz S, Borghi L, Verbrugghe P, Kalaydjieva L, Bleuler S, Laule
O, et al: RefGenes: Identification of reliable and condition
specific reference genes for RT-qPCR data normalization. BMC
Genomics. 12:1562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kimmitt PT, Tabrizi SN, Crosatti M,
Garland SM, Schober PC, Rajakumar K and Chapman CA: Pilot study of
the utility and acceptability of tampon sampling for the diagnosis
of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by
duplex realtime polymerase chain reaction in United Kingdom sex
workers. Int J STD AIDS. 21:279–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tannapfel A, Benicke M, Katalinic A,
Uhlmann D, Köckerling F, Hauss J and Wittekind C: Frequency of
p16(INK4A) alterations and K-ras mutations in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma of the liver. Gut. 47:721–727. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ginzinger DG: Gene quantification using
real-time quantitative PCR: An emerging technology hits the
mainstream. Exp Hematol. 30:503–512. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wan H, Zhao Z, Qian C, Sui Y, Malik AA and
Chen J: Selection of appropriate reference genes for gene
expression studies by quantitative real-time polymerase chain
reaction in cucumber. Anal Biochem. 399:257–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohl F, Jung M, Xu C, Stephan C, Rabien A,
Burkhardt M, Nitsche A, Kristiansen G, Loening SA, Radonić A and
Jung K: Gene expression studies in prostate cancer tissue: Which
reference gene should be selected for normalization? J Mol Med
(Berl). 83:1014–1024. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu S, Zhu P, Zhang L, Ding S, Zheng S,
Wang Y and Lu F: Selection of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis
in tumor tissues from male hepatocellular carcinoma patients with
hepatitis B infection and cirrhosis. Cancer Biomark. 13:345–349.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Isa T, Tomita S, Nakachi A, Miyazato H,
Shimoji H, Kusano T, Muto Y and Furukawa M: Analysis of
microsatellite instability, K-ras gene mutation and p53 protein
overexpression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Hepatogastroenterology. 49:604–608. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar V, Sharma R, Trivedi PC, Vyas GK and
Khandelwal V: Traditional and novel references towards systematic
normalization of qRT-PCR data in plants. Australian J Crop Sci.
5:1455–1468. 2011.
|