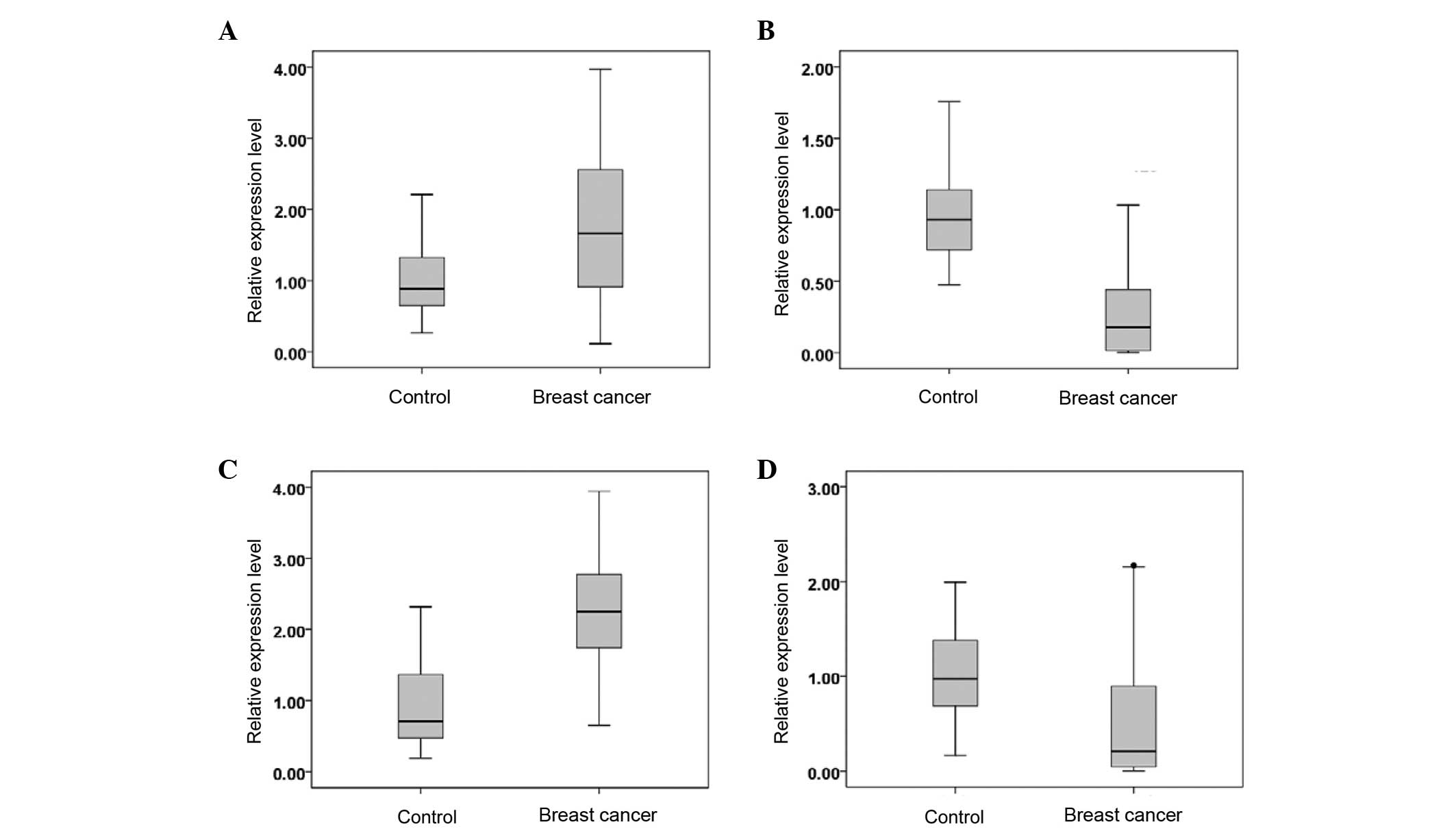
|
1
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mishra S, Srivastava AK, Suman S, Kumar V
and Shukla Y: Circulating miRNAs revealed as surrogate molecular
signatures for the early detection of breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
369:67–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carrington JC and Ambros V: Role of
microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science. 301:336–338.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen H, Xu GZ, Zhao Y, Tian B, Lu H, Yu X,
Xu Z, Ying N, Hu S and Hua Y: A novel OxyR sensor and regulator of
hydrogen peroxide stress with one cysteine residue in
Deinococcus radiodurans. Plos One. 3:e16022008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen H, Huang LF, Hua XT, Yin L, Hu Y,
Wang C, Chen W, Yu X, Xu Z, Tian B, et al: Pleiotropic effects of
RecQ in Deinococcus radiodurans. Genomics. 94:333–340. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bethke A, Fielenbach N, Wang Z,
Mangelsdorf DJ and Antebi A: Nuclear hormone receptor regulation of
microRNAs controls developmental progression. Science. 324:95–98.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ng EK, Wong CL, Ma ES and Kwong A:
MicroRNAs as new players for diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic
targets in breast cancer. J Oncol. 2009:3054202009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu J, Zheng Z, Wang J, Sun J, Wang P,
Cheng X, Fu L, Zhang L, Wang Z and Li Z: Different miRNA expression
profiles between human breast cancer tumors and serum. Front Genet.
5:1492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gradishar WJ, Anderson BO, Blair SL,
Burstein HJ, Cyr A, Elias AD, Farrar WB, Forero A, Giordano SH,
Goldstein LJ, et al: Breast cancer version 3.2014. J Natl Compr
Canc Netw. 12:542–590. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, Benjamin S,
Lebanony D, Yerushalmi N, Benjamin H, Kushnir M, Cholakh H, Melamed
N, et al: Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One.
3:e31482008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brase JC, Wuttig D, Kuner R and Sültmann
H: Serum microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for cancer. Mol
Cancer. 9:3062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun Y, Wang M, Lin G, Sun S, Li X, Qi J
and Li J: Serum MicroRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track
disease in breast cancer. PLoS One. 7:e470032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao FL, Hua GD, Wang XF, Zhang XH, Zhang
YK and Yu ZS: Serum overexpression of microRNA-10b in patients with
bone metastatic primary breast cancer. J Int Med Res. 40:859–866.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zearo S, Kim E, Zhu Y, Zhao JT, Sidhu SB,
Robinson BG and Soon PSh: MicroRNA-484 is more highly expressed in
serum of early breast cancer patients compared to healthy
volunteers. BMC Cancer. 14:2002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Si H, Sun X, Chen Y, Cao Y, Chen S, Wang H
and Hu C: Circulating microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel
minimally invasive biomarkers for primary breast cancer. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 139:223–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chan M, Liaw CS, Ji SM, Tan HH, Wong CY,
Thike AA, Tan PH, Ho GH and Lee AS: Identification of circulating
microRNA signatures for breast cancer detection. Clin Cancer Res.
19:4477–4487. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pritchard CC, Kroh E, Wood B, Arroyo JD,
Dougherty KJ, Miyaji MM, Tait JF and Tewari M: Blood cell origin of
circulating microRNAs: A cautionary note for cancer biomarker
studies. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 5:492–497. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao BS, Liu SG, Wang TY, Ji YH, Qi B, Tao
YP, Li HC and Wu XN: Screening of microRNA in patients with
esophageal cancer at same tumor node metastasis stage with
different prognoses. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:139–143. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walter BA, Valera VA, Pinto PA and Merino
MJ: Comprehensive microRNA profiling of prostate cancer. J Cancer.
4:350–357. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mar-Aguilar F, Mendoza-Ramírez JA,
Malagón-Santiago I, Espino-Silva PK, Santuario-Facio SK,
Ruiz-Flores P, Rodríguez-Padilla C and Reséndez-Pérez D: Serum
circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential
breast cancer biomarkers. Dis Markers. 34:163–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li S, Meng H, Zhou F, Zhai L, Zhang L, Gu
F, Fan Y, Lang R, Fu L, Gu L and Qi L: MicroRNA-132 is frequently
down-regulated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of breast and
acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Pathol
Res Pract. 209:179–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Piepoli A, Tavano F, Copetti M, Mazza T,
Palumbo O, Panza A, di Mola FF, Pazienza V, Mazzoccoli G, Biscaglia
G, et al: Mirna expression profiles identify drivers in colorectal
and pancreatic cancers. PLoS One. 7:e336632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takeshita N, Hoshino I, Mori M, Akutsu Y,
Hanari N, Yoneyama Y, Ikeda N, Isozaki Y, Maruyama T, Akanuma N, et
al: Serum microRNA expression profile: MiR-1246 as a novel
diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oesophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Brit J Cancer. 108:644–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen J, Yao D, Li Y, Chen H, He C, Ding N,
Lu Y, Ou T, Zhao S, Li L and Long F: Serum microRNA expression
levels can predict lymph node metastasis in patients with
early-stage cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med.
32:557–567. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun Z, Meng C, Wang S, Zhou N, Guan M, Bai
C, Lu S, Han Q and Zhao RC: MicroRNA-1246 enhances migration and
invasion through CADM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
14:6162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pigati L, Yaddanapudi SC, Iyengar R, Kim
DJ, Hearn SA, Danforth D, Hastings ML and Duelli DM: Selective
release of MicroRNA species from normal and malignant mammary
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 5:e135152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|