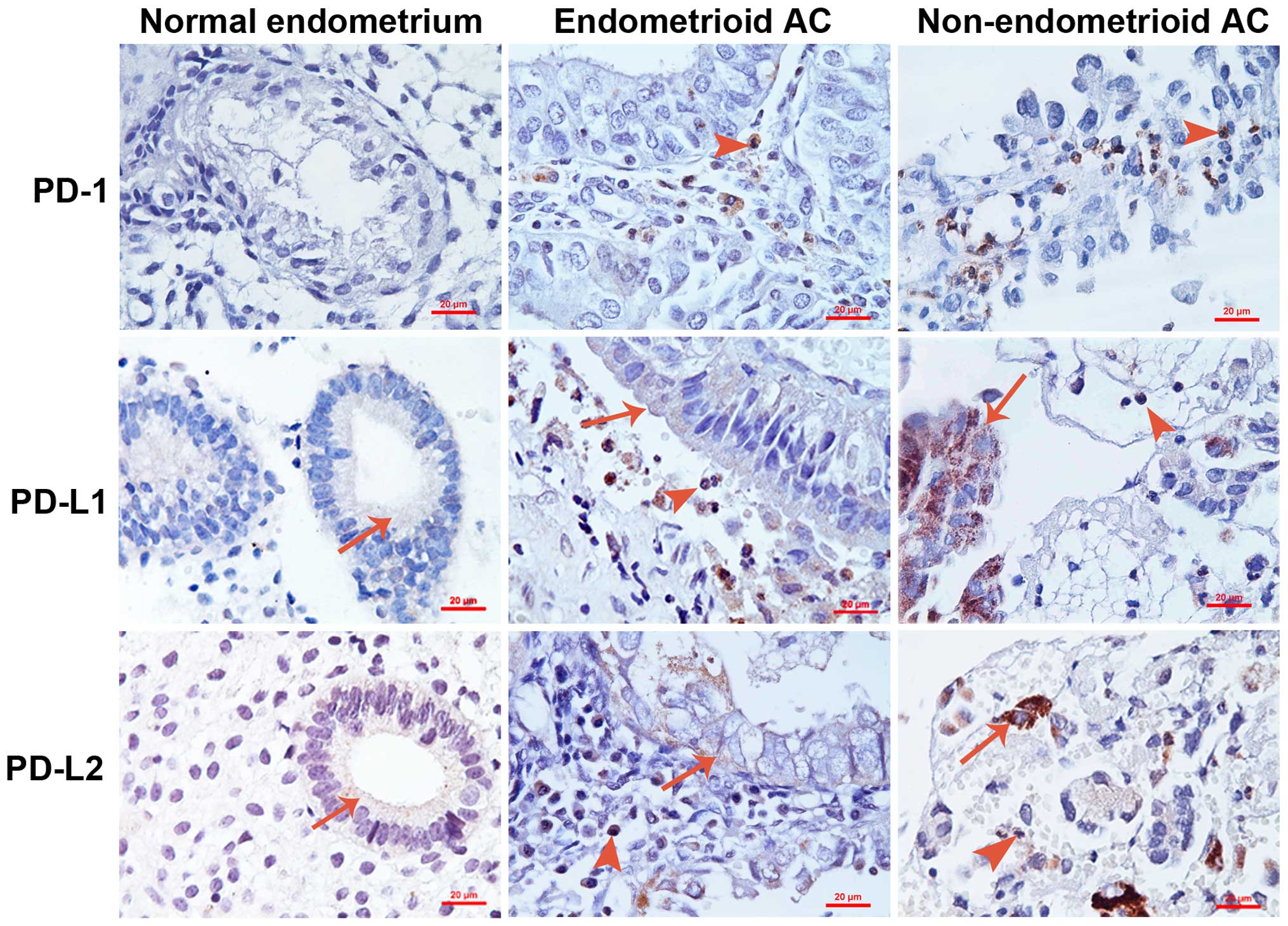
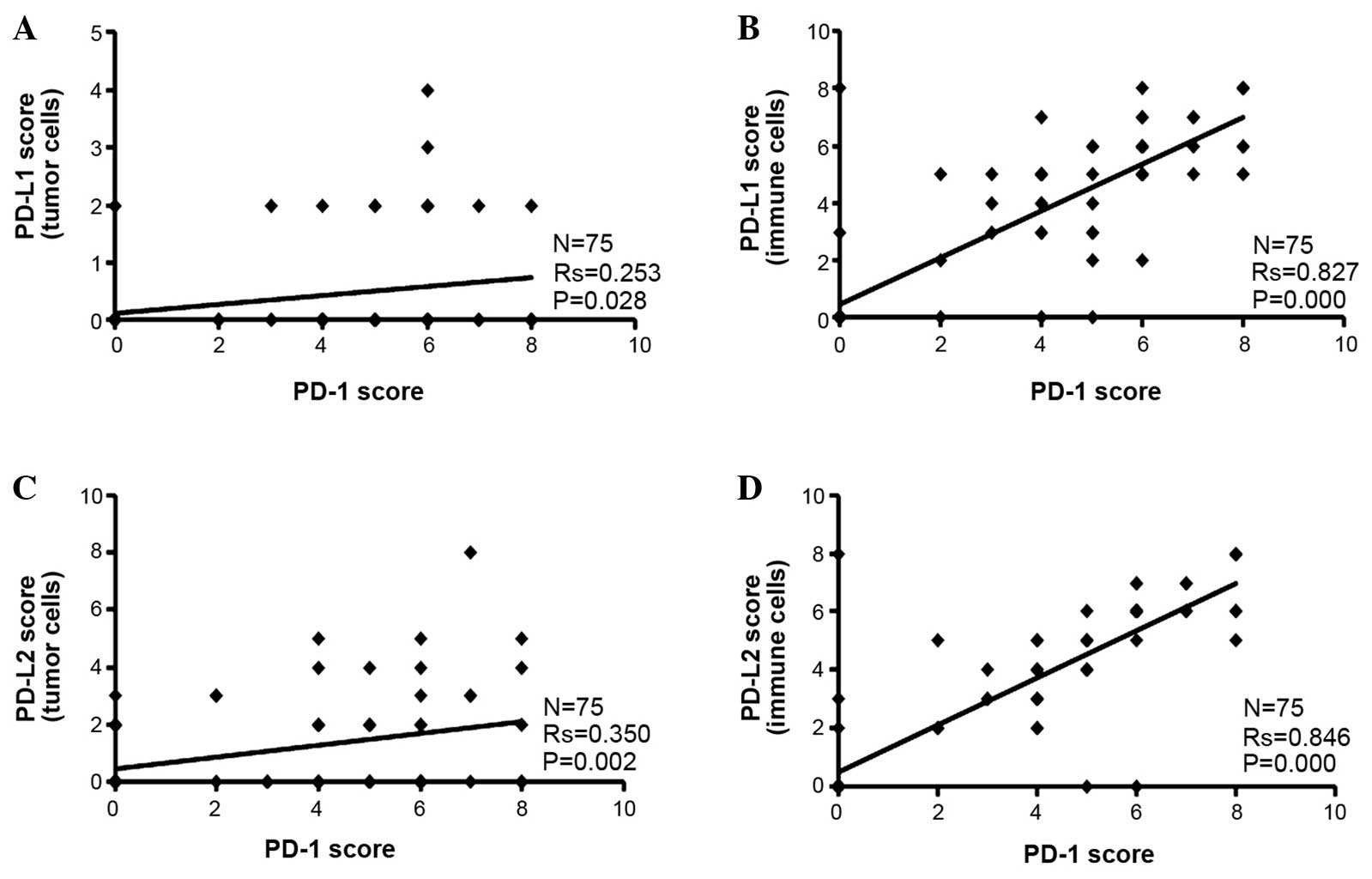
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Loos AH, Oostindier M and
Weiderpass E: Geographic and temporal variations in cancer of the
corpus uteri: Incidence and mortality in pre- and postmenopausal
women in Europe. Int J Cancer. 117:123–131. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bokhman JV: Two pathogenetic types of
endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 15:10–17. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mendivil A, Schuler KM and Gehrig PA:
Non-endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterine corpus: A review of
selected histological subtypes. Cancer Control. 16:46–52.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rasool N, Fader AN, Seamon L, Neubauer NL,
Shahin FA, Alexander HA, Moore K, Moxley K, Secord AA, Kunos C, et
al: Stage I, grade III endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the
endometrium: An analysis of clinical outcomes and patterns of
recurrence. Gynecol Oncol. 116:10–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goff BA, Kato D, Schmidt RA, Ek M, Ferry
JA, Muntz HG, Cain JM, Tamimi HK, Figge DC and Greer BE: Uterine
papillary serous carcinoma: Patterns of metastatic spread. Gynecol
Oncol. 54:264–268. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hidaka T, Kato K, Yonezawa R, Shima T,
Nakashima A, Nagira K, Nakamura T and Saito S: Omission of
lymphadenectomy is possible for low-risk corpus cancer. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 33:86–90. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soslow RA, Bissonnette JP, Wilton A,
Ferguson SE, Alektiar KM, Duska LR and Oliva E: Clinicopathologic
analysis of 187 high-grade endometrial carcinomas of different
histologic subtypes: Similar outcomes belie distinctive biologic
differences. Am J Surg Pathol. 31:979–987. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petignat P, Usel M, Gauthier P, Popowski
Y, Pelte MF, Bouchardy C and Verkooijen HM: Outcome of uterine
clear cell carcinomas compared to endometrioid carcinomas and
poorly-differentiated endometrioid carcinomas. Eur J Gynaecol
Oncol. 29:57–60. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hamilton CA, Cheung MK, Osann K, Chen L,
Teng NN, Longacre TA, Powell MA, Hendrickson MR, Kapp DS and Chan
JK: Uterine papillary serous and clear cell carcinomas predict for
poorer survival compared to grade III endometrioid corpus cancers.
Br J Cancer. 94:642–646. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brinton LA, Berman ML, Mortel R, Twiggs
LB, Barrett RJ, Wilbanks GD, Lannom L and Hoover RN: Reproductive,
menstrual, and medical risk factors for endometrial cancer: Results
from a case-control study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 167:1317–1325.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McPherson CP, Sellers TA, Potter JD,
Bostick RM and Folsom AR: Reproductive factors and risk of
endometrial cancer. The iowa women's health study. Am J Epidemiol.
143:1195–1202. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K and Honjo
T: Induced expression of pd-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin
gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 11:3887–3895.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: Pd-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sharpe AH and Freeman GJ: The b7-cd28
superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:116–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blank C, Gajewski TF and Mackensen A:
Interaction of PD-L1 on tumor cells with PD-1 on tumor-specific T
cells as a mechanism of immune evasion: Implications for tumor
immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 54:307–314. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1
antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary
D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, et al:
PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation.
Nat Immunol. 2:261–268. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Day CL, Kaufmann DE, Kiepiela P, Brown JA,
Moodley ES, Reddy S, Mackey EW, Miller JD, Leslie AJ, DePierres C,
et al: PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with
T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature. 443:350–354.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Okazaki T and Honjo T: PD-1 and PD-1
ligands: From discovery to clinical application. Int Immunol.
19:813–824. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N,
Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L,
et al: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 372:2018–2028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu
WJ, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph RW, Weber JS, et al:
Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 369:134–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lipson EJ, Sharfman WH, Drake CG, Wollner
I, Taube JM, Anders RA, Xu H, Yao S, Pons A, Chen L, et al: Durable
cancer regression off-treatment and effective reinduction therapy
with an anti-PD-1 antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 19:462–468. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A,
Grob JJ, Mortier L, Daud A, Carlino MS, McNeil C, Lotem M, et al:
Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med.
372:2521–2532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow
MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, Segal NH, Ariyan CE, Gordon RA, Reed K,
et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J
Med. 369:122–133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
FDA News Release: FDA approves Keytruda
for advanced melanoma. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm412802.htmAccessed.
January. 2016
|
|
29
|
FDA News Release: FDA approves Opdivo to
treat advanced form of kidney cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm473971.htmAccessed.
January. 2016
|
|
30
|
Nivolumab (Opdivo). http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm436566.htmAccessed.
January. 2016
|
|
31
|
http://www.onclive.com/web-exclusives/fda-grants-priority-review-to-pembrolizumab-in-lung-cancerAccessed.
January. 2016
|
|
32
|
Cha E, Wallin J and Kowanetz M: PD-L1
inhibition with MPDL3280A for solid tumors. Semin Oncol.
42:484–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Howitt BE, Shukla SA, Sholl LM,
Ritterhouse LL, Watkins JC, Rodig S, Stover E, Strickland KC,
D'Andrea AD, Wu CJ, et al: Association of polymerase e-mutated and
microsatellite-instable endometrial cancers with neoantigen load,
number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and expression of PD-1
and PD-L1. JAMA Oncol. 1:1319–1323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vanderstraeten A, Luyten C, Verbist G,
Tuyaerts S and Amant F: Mapping the immunosuppressive environment
in uterine tumors: Implications for immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 63:545–557. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Allred DC, Clark GM, Elledge R, Fuqua SA,
Brown RW, Chamness GC, Osborne CK and McGuire WL: Association of
p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and
clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 85:200–206. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|