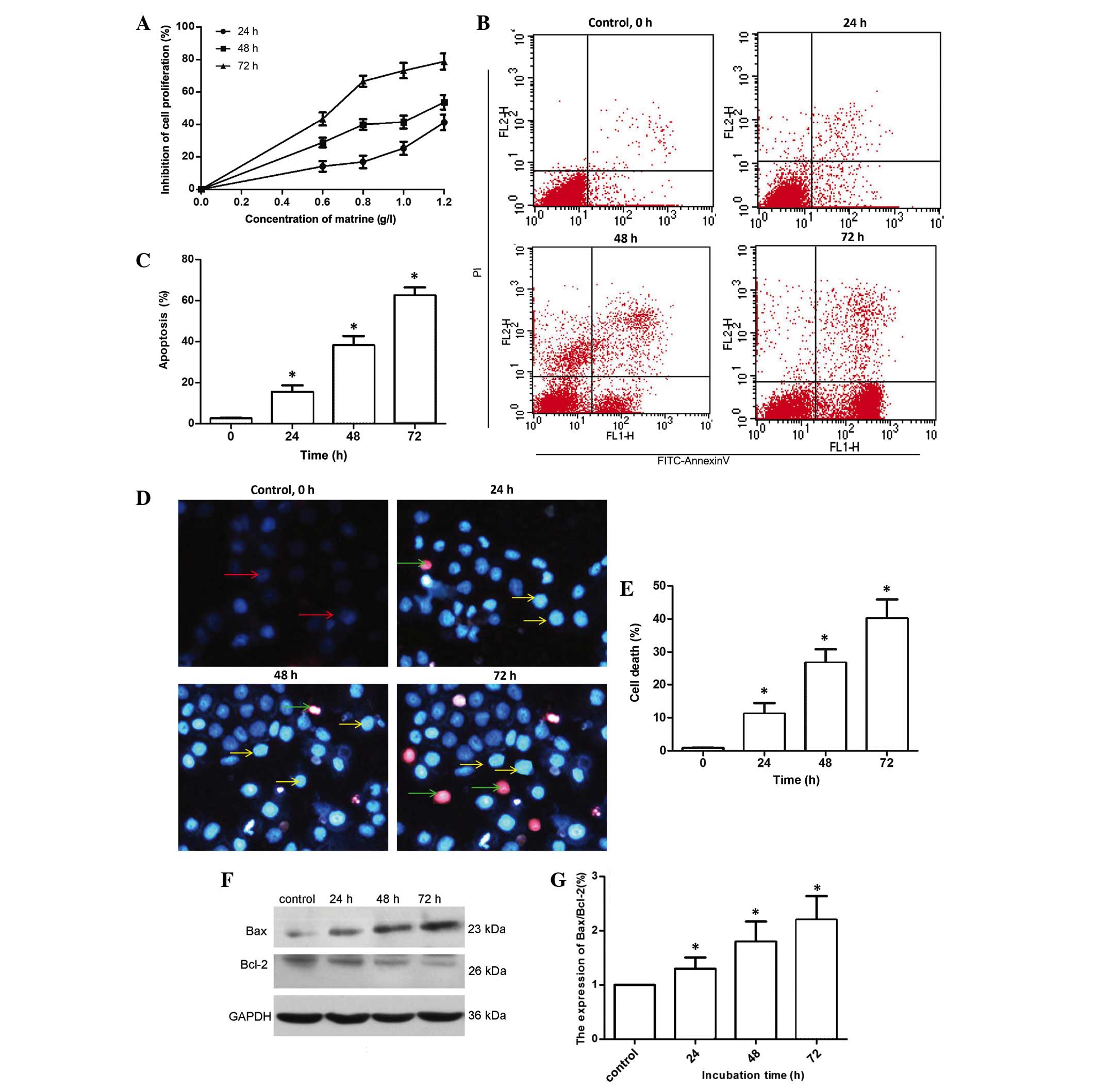
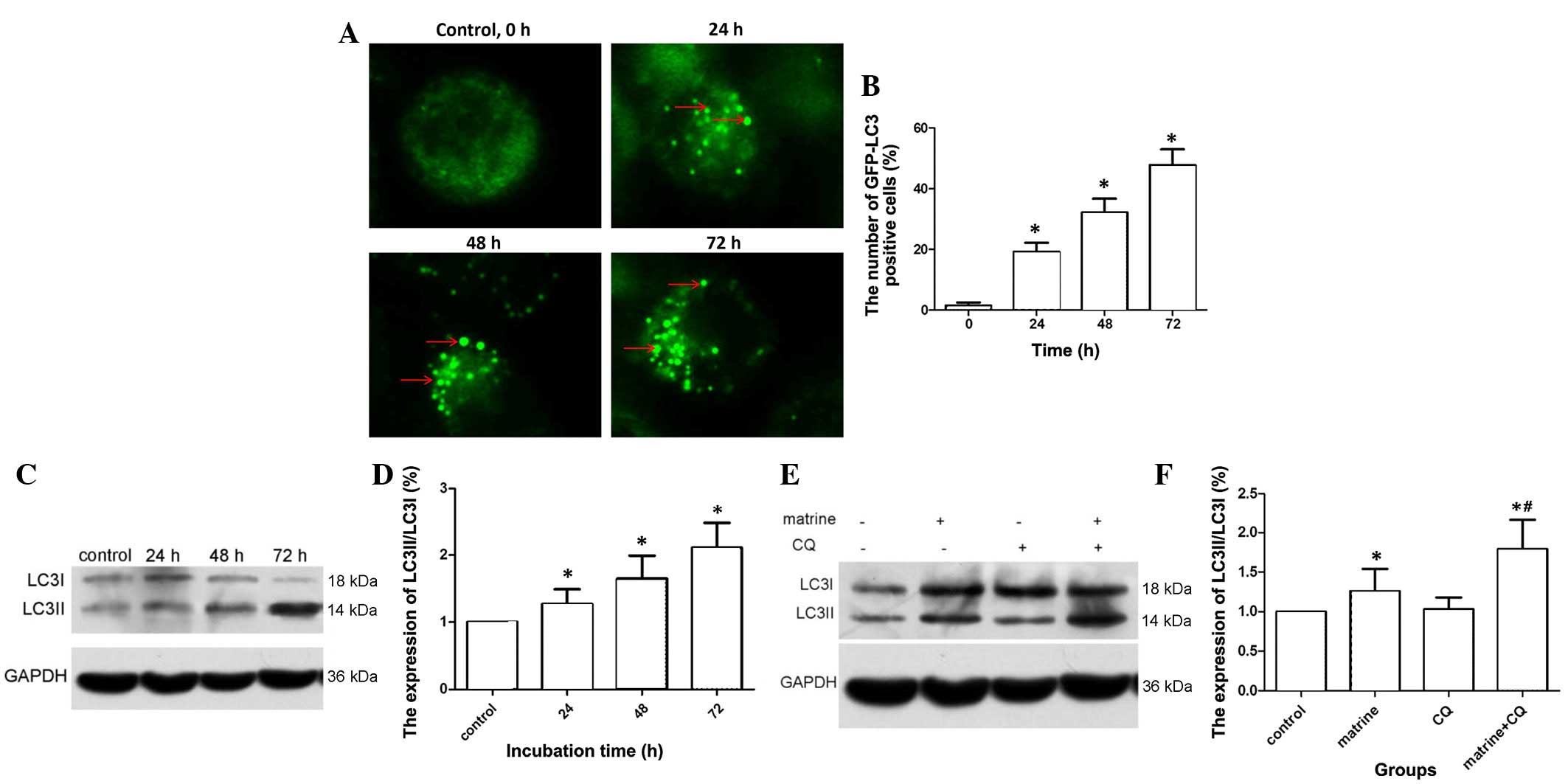
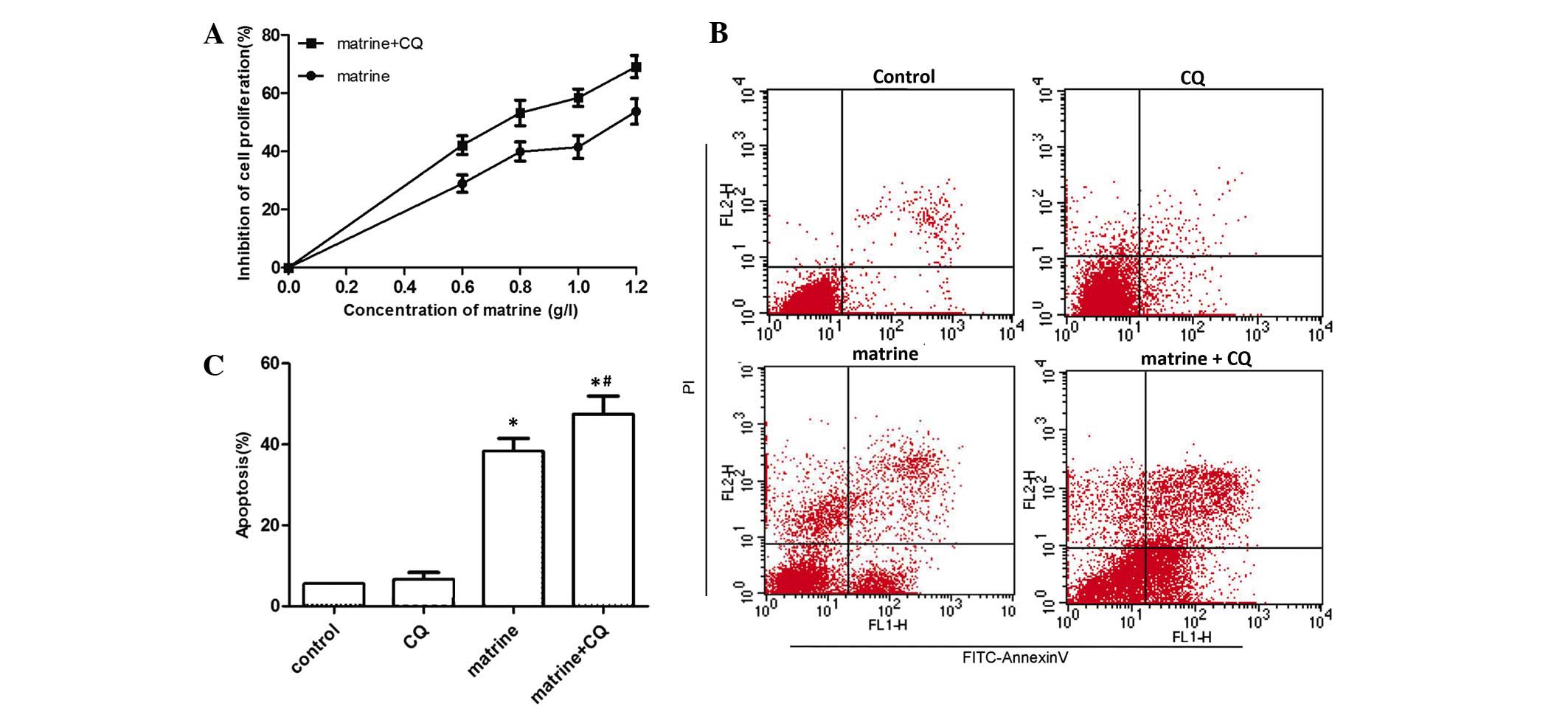
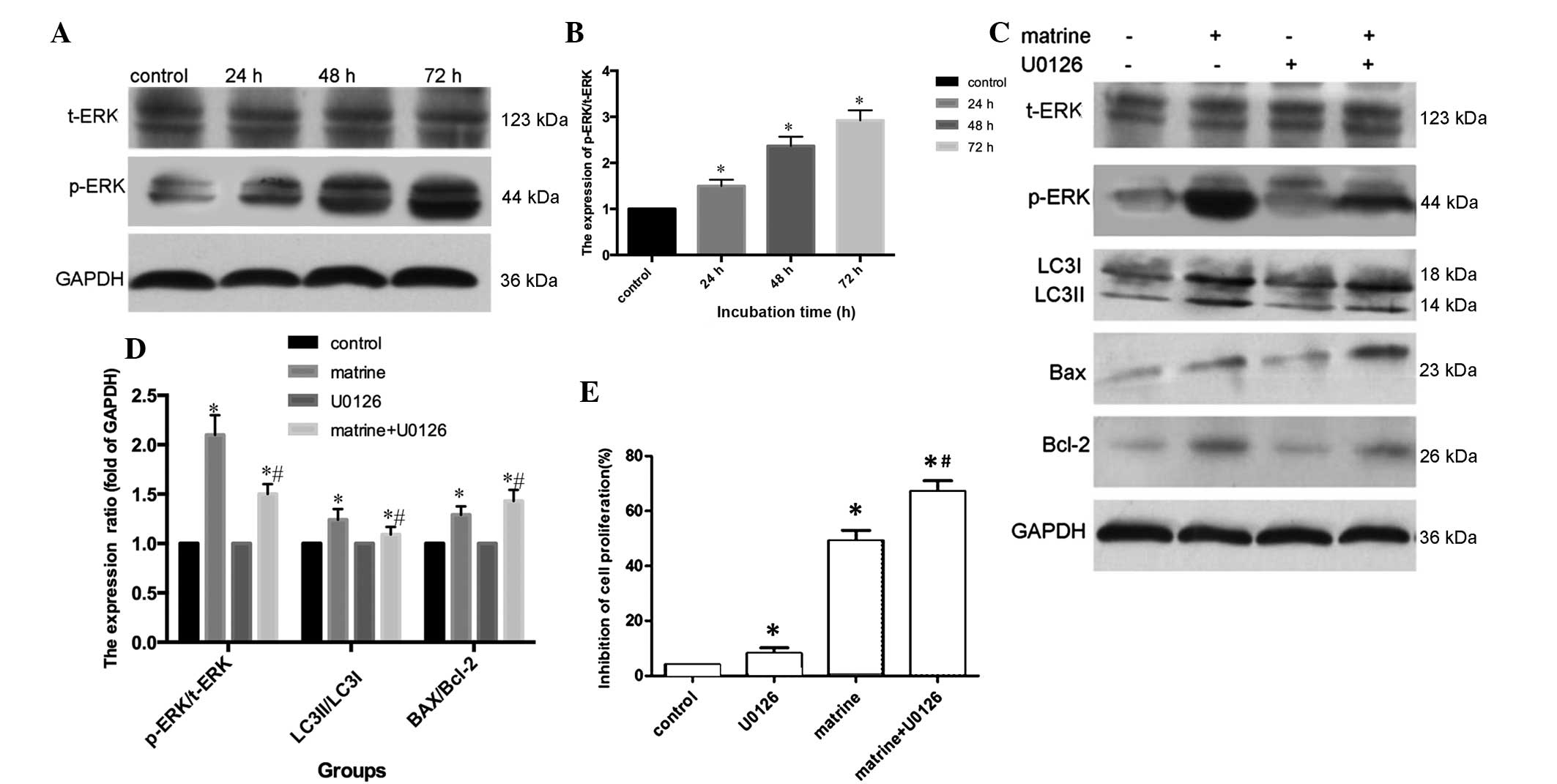
|
1
|
Yang C, Hornicek FJ, Wood KB, Schwab JH,
Mankin H and Duan Z: RAIDD expression is impaired in multidrug
resistant osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
64:607–614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao W, Zhou SF, Zhang ZPXGP, Li XB and
Yan JL: Gambogic acid inhibits the growth of osteosarcoma cells in
vitro by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep.
25:1289–1295. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lai JP, He XW, Jiang Y and Chen F:
Preparative separation and determination of matrine from the
Chinese medical plant Sophara flavescens Ait, by molecularly
imprinted solidphase extraction. Anal Bioanal Chem. 375:264–269.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang B, Liu ZY, Li YY, Luo Y, Liu ML,
Dong HY, Wang YX, Liu Y, Zhao PT, Jin FG and Li ZC:
Antiinflammatory effects of matrine in LPS-induceded acute lung
injury in mice. Eur J Pharm Sci. 44:573–579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li CQ, Zhu YT, Zhang FX, Fu LC, Li XH,
Cheng Y and Li XY: Anti-HBV effect of liposome-encapsulated matrine
in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 11:426–428. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren LL, Lan T and Wang XJ: Zhejiang
Provincial Tumor Hospital; Hangzhou Hospital of TCM: Antitumor
effect of matrine in human breast cancer Bcap-37 cells by apoptosis
and autophagy. Chin J Trad Chin Med Pharm. 32:2756–2759. 2014.(In
Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Liu XS, Jiang J, Jiao XY, Wu YE and Lin
JH: Matrine-induced apoptosis in leukemia U937 cells: Involvement
of caspases activation and MAPK-independent pathways. Planta Med.
72:501–506. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang JQ, Li YM, Liu T, He WT, Chen YT,
Chen XH, Li X, Zhou WC, Yi JF and Ren ZJ: Antitumor effect of
matrine in human hepatoma G2 cells by inducing apoptosis and
autophagy. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4281–4290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Ma H, Chen X, Liu T, Jiao
Z, He W, Wang F, Liu X and Zeng X: Protective role of autophagy in
matrine-induced gastric cancer cell death. Int J Oncol.
42:1417–1426. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Gao C, Yao S and Xie B: Blocking
autophagic flux enhances matrine-induced apoptosis in human
hepatoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 14:23212–23230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yorimitsu T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy:
Molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ. 12(Suppl
2): S1542–S1552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Booth LA, Tavallai S, Hamed HA,
Cruickshanks N and Dent P: The role of cell signalling in the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Signal. 26:549–555.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang CZ, Zhang JK, Shi Z, Liu B, Shen CQ
and Tao HM: Matrine induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human
osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo through the upregulation of
Bax and Fas/FasL and downregulation of Bcl-2. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 69:317–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carew JS, Medina EC, Esquivel JA II,
Mahalingam D, Swords R, Kelly K, Zhang H, Huang P, Mita AC, Mita
MM, et al: Autophagy inhibition enhances vorinostat-induced
apoptosis via ubiquitinated protein accumulation. J Cell Mol Med.
14:2448–2459. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Whiteman MW, Lian H, Wang G, Singh
A, Huang D and Denmark T: A non-canonical MEK/ERK signaling pathway
regulates autophagy via regulating Beclin-1. J Biol Chem.
284:21412–21424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bacci G, Longhi A, Bertoni F, Bacchini P,
Ruggeri P, Versari M and Picci P: Primary high-grade osteosarcoma:
Comparison between preadolescent and older patients. J Pediatr
Hematol Oncol. 27:129–134. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang C, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Wood KB,
Schwab JH, Liu X, Mankin H and Duan Z: Histone deacetylase
inhibitor (HDACI) PCI-24781 potentiates cytotoxic effects of
doxorubicin in bone sarcoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
67:439–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan F, Liu Y and Wang W: Matrine inhibited
the growth of rat osteosarcoma UMR-108 cells by inducing apoptosis
in a mitochondrial caspase-dependent pathway. Tumour Biol.
34:2135–2140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu GP, Zhao W, Zhuang JP, Zu JN, Wang DY,
Han F, Zhang ZP and Yan JL: Matrine inhibits the growth and induces
apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells in vitro by inactivating the Akt
pathway. Tumor Biol. 36:1653–1659. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Oral O, Akkoc Y, Bayraktar O and Gozuacik
D: Physiological and pathological significance of the molecular
cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Histology Histopathol.
31:479–498. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Apel A, Zentgraf H, Büchler MW and Herr I:
Autophagy-A double-edged sword in oncology. Int J Cancer.
125:991–995. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: An innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hou W, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Chen R, Zeh HJ III,
Kang R, Lotze MT and Tang D: Strange attractors: DAMPs and
autophagy link tumor cell death and immunity. Cell Death Dis.
4:e9662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu Z and Xu S: ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell
survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life. 58:621–631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haieh MJ, Tsai TL, Hsieh YS, Wang CJ and
Chiou HL: Dioscin-induced autophagy mitigated cell apoptosis
through modulation of PI13K/Akt and ERK and JNK signaling pathways
in human lung cancer cell lines. Arch Toxicol. 87:1927–1937. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|