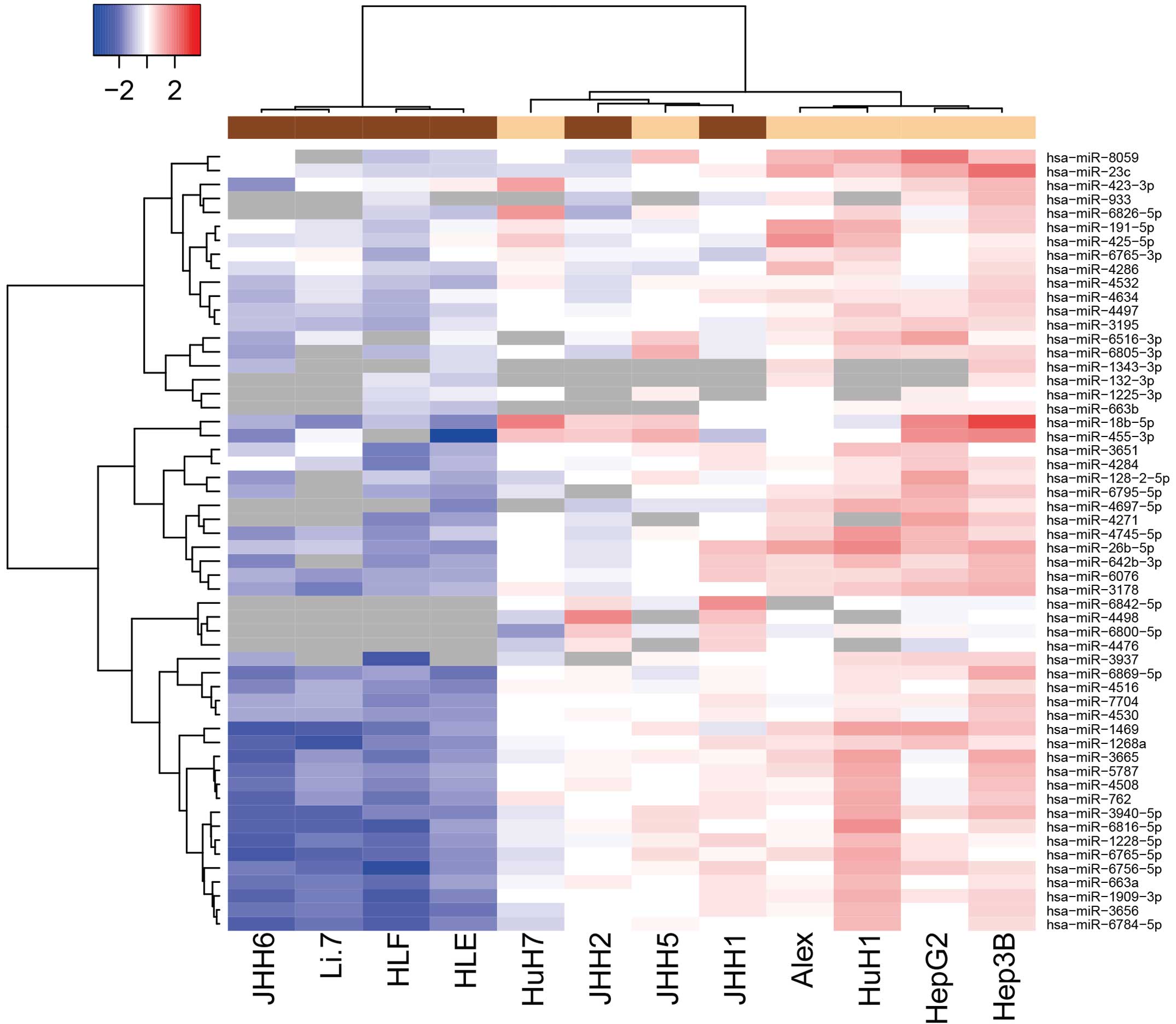
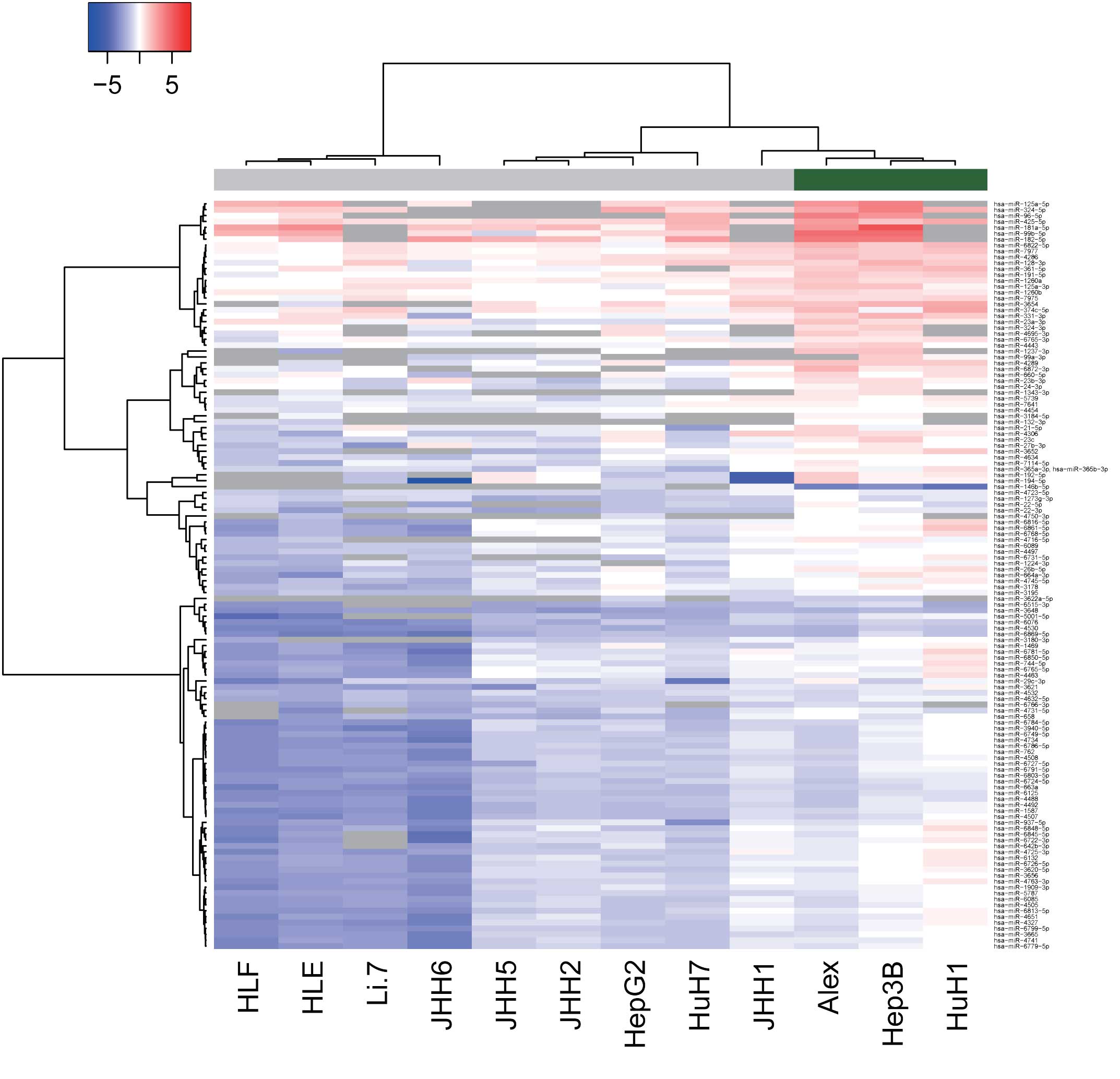
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Małkowski P, Pacholczyk M, Łagiewska B,
Adadyński L, Wasiak D, Kwiatkowski A, Chmura A and Czerwiński J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma-epidemiology and treatment. Przegl
Epidemiol. 60:731–740. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Belghiti J and Kianmanesh R: Surgical
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 7:42–49. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee PH, Lin WJ, Tsang YM, Hu RH, Sheu JC,
Lai MY, Hsu HC, May W and Lee CS: Clinical management of recurrent
hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 222:670–676. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Masaki T: MicroRNA and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 39:751–752. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15
and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Michael MZ, O'Connor SM, van Holst
Pellekaan NG, Young GP and James RJ: Reduced accumulation of
specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res.
1:882–891. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner
MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ and Schmittgen
TD: Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in
pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 120:1046–1054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K,
Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H, Harano T, Yatabe Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y,
et al: Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung
cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival.
Cancer Res. 64:3753–3756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F,
Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG, Calin GA, Giovannini C, Ferrazzi E,
Grazi GL, et al: Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA
frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 67:6092–6099. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong QW, Lung RW, Law PT, Lai PB, Chan KY,
To KF and Wong N: MicroRNA-223 is commonly repressed in
hepatocellular carcinoma and potentiates expression of Stathmin1.
Gastroenterology. 135:257–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F,
Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP and Odenthal M: MicroRNA gene
expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:1223–1232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li L and Li W: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human cancer: Comprehensive reprogramming of
metabolism, epigenetics, and differentiation. Pharmacol Ther.
150:33–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Y, Lu Y, Zhang Q, Liu JJ, Li TJ, Yang
JR, Zeng C and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-26a/b and their host genes
cooperate to inhibit the G1/S transition by activating the pRb
protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:4615–4625. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Renjie W and Haiqian L: MiR-132, miR-15a
and miR-16 synergistically inhibit pituitary tumor cell
proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting Sox5. Cancer
Lett. 356:568–578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kojima M, Sudo H, Kawauchi J, Takizawa S,
Kondou S, Nobumasa H and Ochiai A: MicroRNA markers for the
diagnosis of pancreatic and biliary-tract cancers. PLoS One.
10:e01182202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feber A, Xi L, Pennathur A, Gooding WE,
Bandla S, Wu M, Luketich JD, Godfrey TE and Litle VR: MicroRNA
prognostic signature for nodal metastases and survival in
esophageal adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 91:1523–1530. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang W, Zhao LJ, Tan YX, Ren H and Qi ZT:
Identification of deregulated miRNAs and their targets in hepatitis
B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
18:5442–5453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|