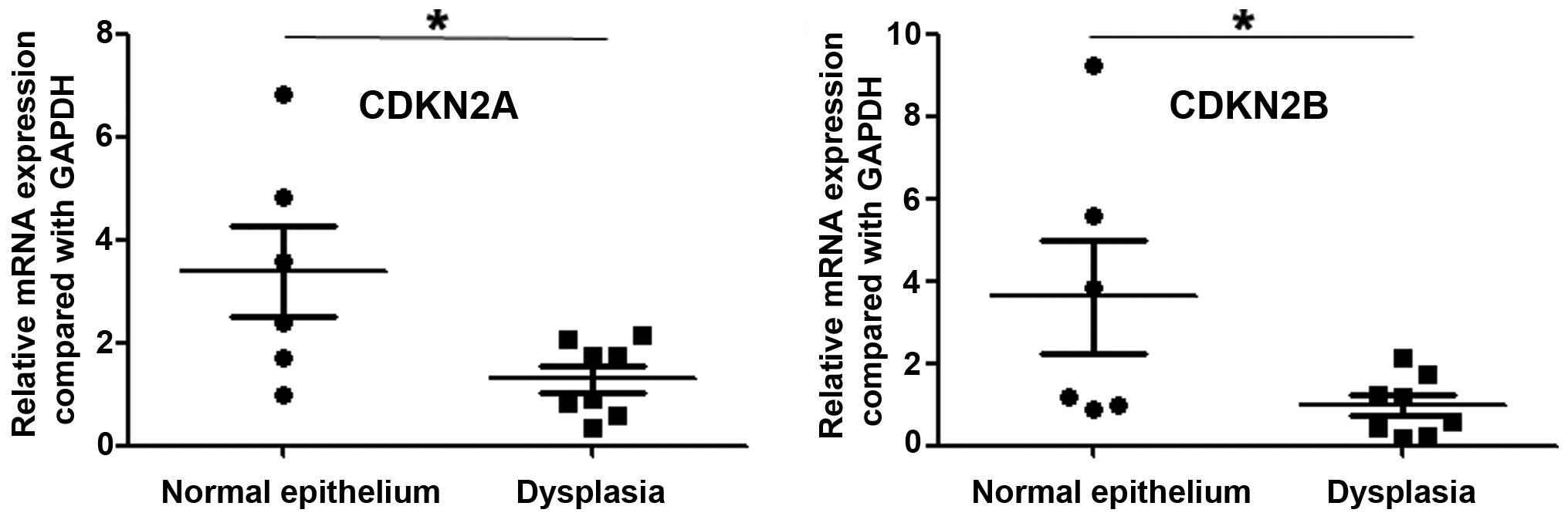
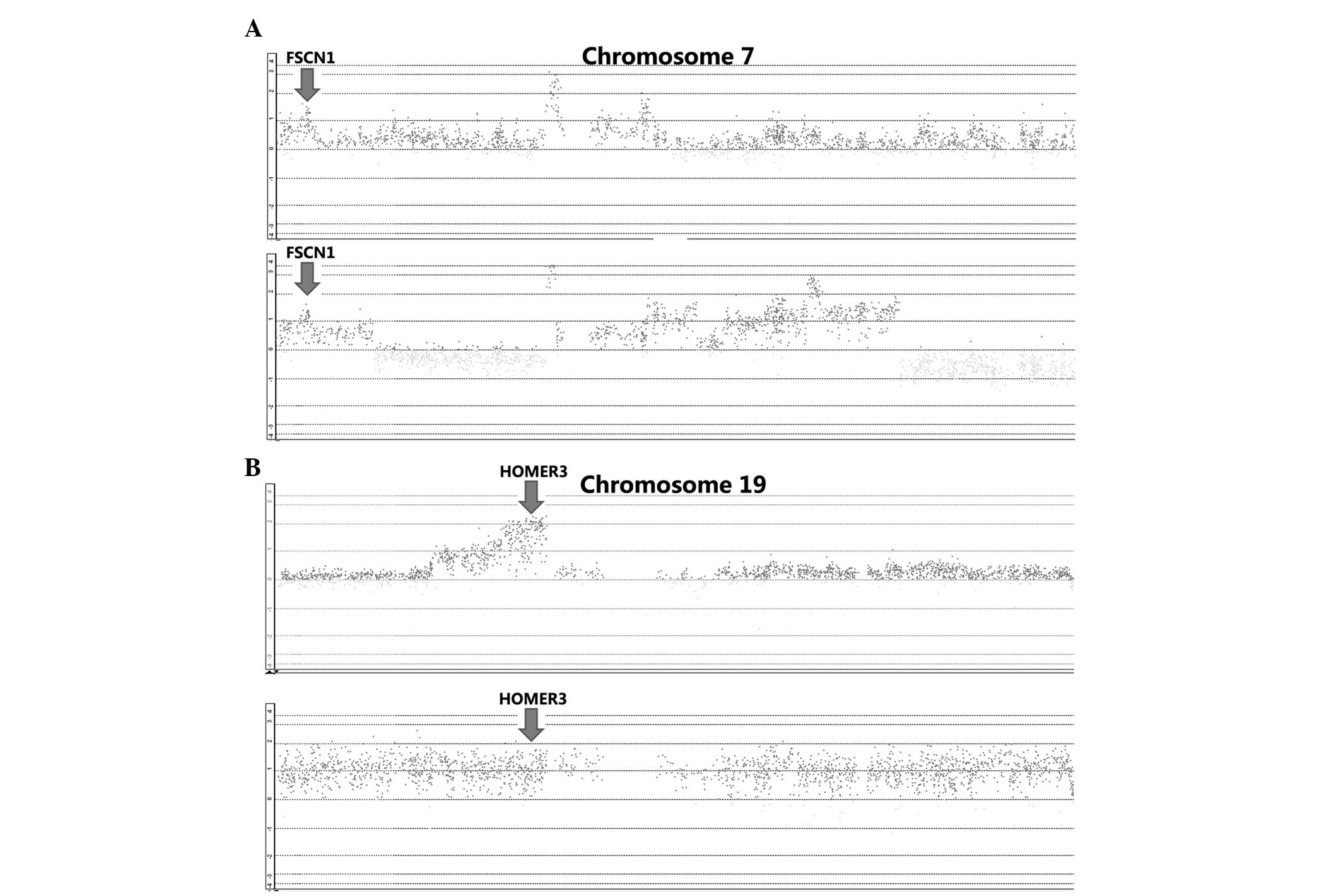
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yen CC, Chen YJ, Chen JT, Hsia JY, Chen
PM, Liu JH, Fan FS, Chiou TJ, Wang WS and Lin CH: Comparative
genomic hybridization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
correlations between chromosomal aberrations and disease
progression/prognosis. Cancer. 92:2769–2777. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi ZZ, Liang JW, Zhan T, Wang BS, Lin DC,
Liu SG, Hao JJ, Yang H, Zhang Y, Zhan QM, et al: Genomic
alterations with impact on survival in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma identified by array comparative genomic hybridization.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 50:518–526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hirasaki S, Noguchi T, Mimori K, Onuki J,
Morita K, Inoue H, Sugihara K, Mori M and Hirano T: BAC clones
related to prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous
carcinoma: an array comparative genomic hybridization study.
Oncologist. 12:406–417. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee HS, Lee K, Jang HJ, Lee GK, Park JL,
Kim SY, Kim SB, Johnson BH, Zo JI, Lee JS and Lee YS: Epigenetic
silencing of the non-coding RNA nc886 provokes oncogenes during
human esophageal tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 5:3472–3481. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Togashi Y, Arao T, Kato H, Matsumoto K,
Terashima M, Hayashi H, de Velasco MA, Fujita Y, Kimura H, Yasuda
T, et al: Frequent amplification of ORAOV1 gene in esophageal
squamous cell cancer promotes an aggressive phenotype via proline
metabolism and ROS production. Oncotarget. 5:2962–2973. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Negrini S, Gorgoulis VG and Halazonetis
TD: Genomic instability - an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 11:220–228. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Riehmer V, Gietzelt J, Beyer U, Hentschel
B, Westphal M, Schackert G, Sabel MC, Radlwimmer B, Pietsch T,
Reifenberger G, et al: Genomic profiling reveals distinctive
molecular relapse patterns in IDH1/2 wild-type glioblastoma. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 53:589–605. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi ZZ, Shang L, Jiang YY, Hao JJ, Zhang
Y, Zhang TT, Lin DC, Liu SG, Wang BS, Gong T, et al: Consistent and
differential genetic aberrations between esophageal dysplasia and
squamous cell carcinoma detected by array comparative genomic
hybridization. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5867–5878. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheung CC, Chung GT, Lun SW, To KF, Choy
KW, Lau KM, Siu SP, Guan XY, Ngan RK, Yip TT, et al: miR-31 is
consistently inactivated in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma
and contributes to its tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer. 13:1842014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tam KW, Zhang W, Soh J, Stastny V, Chen M,
Sun H, Thu K, Rios JJ, Yang C, Marconett CN, et al: CDKN2A/p16
inactivation mechanisms and their relationship to smoke exposure
and molecular features in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 8:1378–1388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
KohonenCorish MR, Tseung J, Chan C, Currey
N, Dent OF, Clarke S, Bokey L and Chapuis PH: KRAS mutations and
CDKN2A promoter methylation show an interactive adverse effect on
survival and predict recurrence of rectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
134:2820–2828. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xing X, Cai W, Shi H, Wang Y, Li M, Jiao J
and Chen M: The prognostic value of CDKN2A hypermethylation in
colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 108:2542–2548.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aravidis C, Panani AD, Kosmaidou Z,
Thomakos N, Rodolakis A and Antsaklis A: Detection of numerical
abnormalities of chromosome 9 and p16/CDKN2A gene alterations in
ovarian cancer with fish analysis. Anticancer Res. 32:5309–5313.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akanuma N, Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Murakami
K, Isozaki Y, Maruyama T, Yusup G, Qin W, Toyozumi T, Takahashi M,
et al: MicroRNA-133a regulates the mRNAs of two invadopodia-related
proteins, FSCN1 and MMP14, in esophageal cancer. Br J Cancer.
110:189–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen MB, Wei MX, Han JY, Wu XY, Li C, Wang
J, Shen W and Lu PH: MicroRNA-451 regulates AMPK/mTORC1 signaling
and fascin1 expression in HT-29 colorectal cancer. Cell Signal.
26:102–109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hanker LC, Karn T, Holtrich U, Graeser M,
Becker S, Reinhard J, Ruckhäberle E, Gevensleben H and Rody A:
Prognostic impact of fascin-1 (FSCN1) in epithelial ovarian cancer.
Anticancer Res. 33:371–377. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu ZS, Wang CQ, Xiang R, Liu X, Ye S, Yang
XQ, Zhang GH, Xu XC, Zhu T and Wu Q: Loss of miR-133a expression
associated with poor survival of breast cancer and restoration of
miR-133a expression inhibited breast cancer cell growth and
invasion. BMC Cancer. 12:512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qin Y, Dang X, Li W and Ma Q: miR-133a
functions as a tumor suppressor and directly targets FSCN1 in
pancreatic cancer. Oncol Res. 21:353–363. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, Fujimura L,
Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Nakagawa M and
Matsubara H: miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive
miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 127:2804–2814. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu R, Liao J, Yang M, Sheng J, Yang H,
Wang Y, Pan E, Guo W, Pu Y, Kim SJ and Yin L: The cluster of
miR-143 and miR-145 affects the risk for esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma through co-regulating fascin homolog 1. PLoS One.
7:e339872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fuse M, Nohata N, Kojima S, Sakamoto S,
Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Naya Y, Ichikawa T
and Seki N: Restoration of miR-145 expression suppresses cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer by
targeting FSCN1. Int J Oncol. 38:1093–1101. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao B, Tu JC, Petralia RS, Yuan JP, Doan
A, Breder CD, Ruggiero A, Lanahan AA, Wenthold RJ and Worley PF:
Homer regulates the association of group 1 metabotropic glutamate
receptors with multivalent complexes of homer-related, synaptic
proteins. Neuron. 21:707–716. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bortoloso E, Pilati N, Megighian A,
Tibaldo E, Sandonà D and Volpe P: Transition of Homer isoforms
during skeletal muscle regeneration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
290:C711–C718. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishiguro K and Xavier R: Homer-3 regulates
activation of serum response element in T cells via its EVH1
domain. Blood. 103:2248–2256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stirewalt DL, Meshinchi S, Kopecky KJ, Fan
W, PogosovaAgadjanyan EL, Engel JH, Cronk MR, Dorcy KS, McQuary AR,
Hockenbery D, et al: Identification of genes with abnormal
expression changes in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 47:8–20. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Valk PJ, Verhaak RG, Beijen MA, Erpelinck
CA, van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani S Barjesteh, Boer JM,
Beverloo HB, Moorhouse MJ, van der Spek PJ, Löwenberg B and Delwel
R: Prognostically useful gene-expression profiles in acute myeloid
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 350:1617–1628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Z, Qiu HY, Jiao Y, Cen JN, Fu CM, Hu
SY, Zhu MQ, Wu DP and Qi XF: Growth and differentiation effects of
Homer3 on a leukemia cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:2525–2528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|