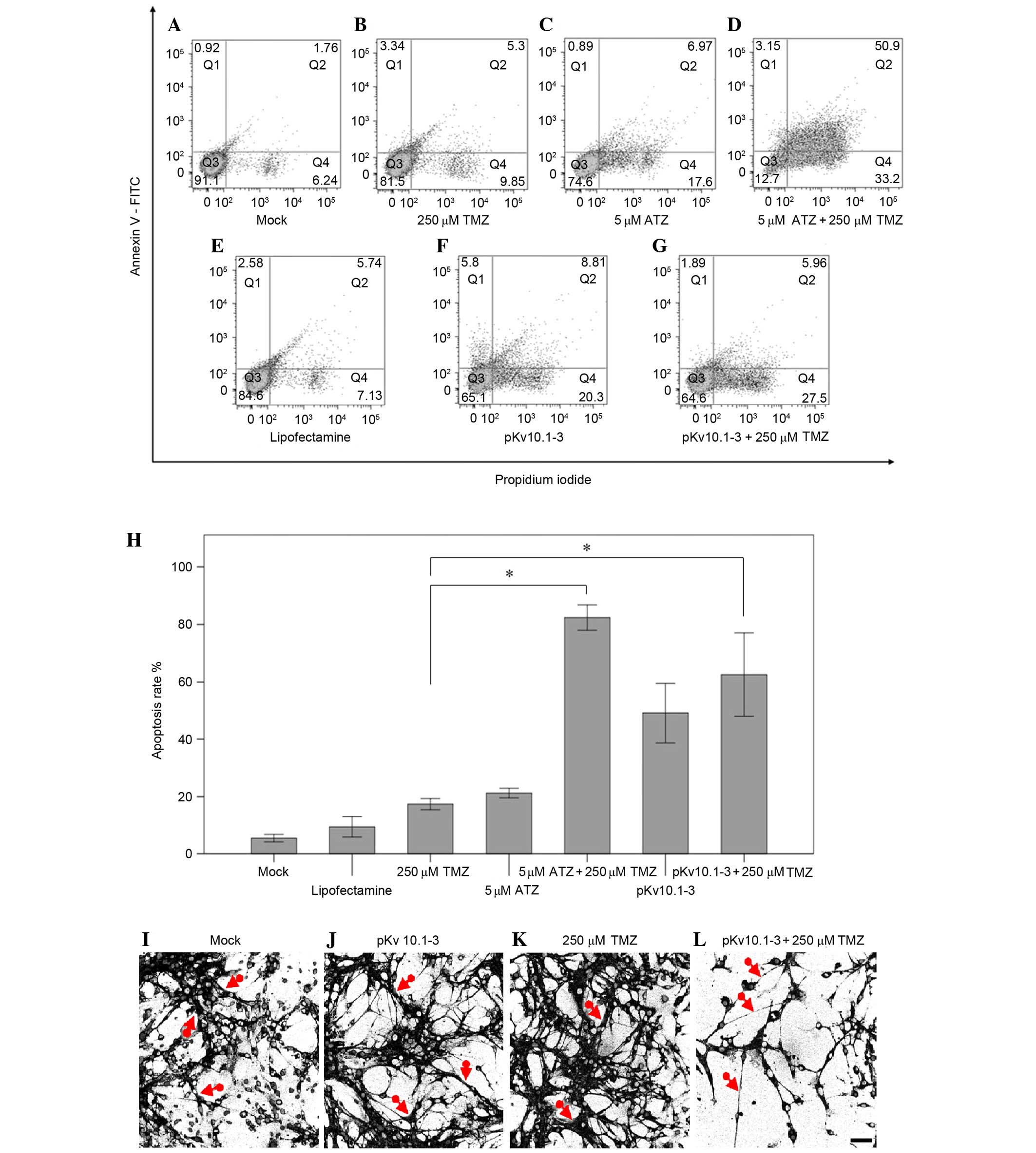
|
1
|
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch
DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK and DePinho RA: Malignant glioma: Genetics
and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 15:1311–1333. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lassman AB: Molecular biology of gliomas.
Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 4:228–233. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gladson CL, Prayson RA and Liu WM: The
pathobiology of glioma tumors. Annu Rev Pathol. 5:33–50. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nagasawa DT, Chow F, Yew A, Kim W, Cremer
N and Yang I: Temozolomide and other potential agents for the
treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurg Clin N Am.
23:307–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chamberlain MC: Temozolomide: Therapeutic
limitations in the treatment of adult high-grade gliomas. Expert
Rev Neurother. 10:1537–1544. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pardo LA and Stümer W: The roles of K (+)
channels in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:39–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pardo LA, del Camino D, Sánchez A, Alves
F, Brüggemann A, Beckh S and Stühmer W: Oncogenic potential of EAG
K(+) channels. EMBO J. 18:5540–5547. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hemmerlein B, Weseloh RM, de Queiroz F
Mello, Knötgen H, Sánchez A, Rubio ME, Martin S, Schliephacke T,
Jenke M, Heinz-Joachim-Radzun, et al: Overexpression of Eag1
potassium channels in clinical tumours. Mol Cancer. 5:412006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Patt S, Preussat K, Beetz C, Kraft R,
Schrey M, Kalff R, Schönherr K and Heinemann SH: Expression of
ether à go-go potassium channels in human gliomas. Neurosci Lett.
368:249–253. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hermisson M, Klumpp A, Wick W, Wischhusen
J, Nagel G, Roos W, Kaina B and Weller M: O6-methylguanine DNA
methyltransferase and p53 status predict temozolomide sensitivity
in human malignant glioma cells. J Neurochem. 96:766–776. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim SS, Rait A, Kim E, Pirollo KF, Nishida
M, Farkas N, Dagata JA and Chang EH: A nanoparticle carrying the
p53 gene targets tumors including cancer stem cells, sensitizes
glioblastoma to chemotherapy and improves survival. ACS Nano.
8:5494–5514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin H, Li Z, Chen C, Luo X, Xiao J, Dong
D, Lu Y, Yang B and Wang Z: Transcriptional and
post-transcriptional mechanisms for oncogenic overexpression of
ether à go-go K+ channel. PLoS One. 6:e203622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Essmann F and Schulze-Osthoff K:
Translational approaches targeting the p53 pathway for anticancer
therapy. Br J Pharmacol. 165:328–344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pardo LA and Stühmer W: EAG1: An emerging
oncological target. Cancer Res. 68:1611–1613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gavrilova-Ruch O, Schönherr K, Gessner G,
Schönherr R, Klapperstück T, Wohlrab W and Heinemann SH: Effects of
imipramine on ion channels and proliferation of IGR1 melanoma
cells. J Membr Biol. 188:137–149. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
García-Ferreiro RE, Kerschensteiner D,
Major F, Monje F, Stühmer W and Pardo LA: Mechanism of block of
hEag1 K+ channels by imipramine and astemizole. J Gen Physiol.
124:301–317. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roy J, Vantol B, Cowley EA, Blay J and
Linsdell P: Pharmacological separation of hEAG and hERG K+ channel
function in the human mammary carcinoma cell line MCF-7. Oncol Rep.
19:1511–1516. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gómez-Varela D, Zwick-Wallasch E, Knötgen
H, Sánchez A, Hettmann T, Ossipov D, Weseloh R, Contreras-Jurado C,
Rothe M, Stühmer W and Pardo LA: Monoclonal antibody blockade of
the human Eag1 potassium channel function exerts antitumor
activity. Cancer Res. 67:7343–7349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Burnett JC and Rossi JJ: RNA-based
therapeutic: Current progress and future prospects. Chem Biol.
19:60–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weber C, de Queiroz F Mello, Downie BR,
Suckow A, Stühmer W and Pardo LA: Silencing the activity and
proliferative properties of the human EagI potassium channel by RNA
interference. J Biol Chem. 281:13030–13037. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cunha LC, Del Bel E, Pardo L, Stühmer W
and Titze-DE-Almeida R: RNA interference with EAG1 enhances
interferon gamma injury to glioma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res.
33:865–870. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kane A and Yang I: Interferon-gamma in
brain tumor immunotherapy. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 21:77–86. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mareschi K, Novara M, Rustichelli D,
Ferrero I, Guido D, Carbone E, Medico E, Madon E, Vercelli A and
Fagioli F: Neural differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells:
Evidence for expression of neural markers and each K+ channel type.
Exp Hematol. 34:1563–1572. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kwon MJ, Oh E, Lee S, Roh MR, Kim SE, Lee
Y, Choi YL, In YH, Park T, Koh SS and Shin YK: Identification of
novel reference genes using multiplatform expression data and their
validation for quantitative gene expression analysis. PLoS One.
4:e61622009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kunzelmann K: Ion channels and cancer. J
Membr Biol. 205:159–173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kondratskyi A, Kondratska K, Skryma R and
Prevarskaya N: Ion channels in the regulation of apoptosis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1848:2532–2546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lang F, Föller M, Lang KS, Lang PA, Ritter
M, Gulbins E, Vereninov A and Huber SM: Ion channels in cell
proliferation and apoptotic cell death. J Membr Biol. 205:147–157.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Menéndez ST, Villaronga MA, Rodrigo JP,
Alvarez-Teijeiro S, García-Carracedo D, Urdinguio RG, Fraga MF,
Pardo LA, Viloria CG, Suárez C and García-Pedrero JM: Frequent
aberrant expression of the human ether à go-go (hEAG1) potassium
channel in head and neck cancer: Pathobiological mechanisms and
clinical implications. J Mol Med (Berl). 90:1173–1184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ding XW, Yan JJ, An P, Lü P and Luo HS:
Aberrant expression of ether à go-go potassium channel in
colorectal cancer patients and cell lines. World J Gastroenterol.
13:1257–1261. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ousingsawat J, Spitzner M, Puntheeranurak
S, Terracciano L, Tornillo L, Bubendorf L, Kunzelmann K and
Schreiber R: Expression of voltage-gated potassium channels in
human and mouse colonic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:824–831.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ding XW, Luo HS, Jin X, Yan JJ and Ai YW:
Aberrant expression of Eag1 potassium channels in gastric cancer
patients and cell lines. Med Oncol. 24:345–350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ortiz CS, Montante-Montes D, Saqui-Salces
M, Hinojosa LM, Gamboa-Dominguez A, Hernández-Gallegos E,
Martínez-Benítez B, Del Rosario Solís-Pancoatl M, Garcia-Villa E,
Ramírez A, et al: Eag1 potassium channels as markers of cervical
dysplasia. Oncol Rep. 26:1377–1383. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Agarwal JR, Griesinger F, Stühmer W and
Pardo LA: The potassium channel Ether à go-go is a novel prognostic
factor with functional relevance in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol
Cancer. 9:182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ufartes R, Schneider T, Mortensen LS, de
Juan Romero C, Hentrich K, Knoetgen H, Beilinson V, Moebius W,
Tarabykin V, Alves F, et al: Behavioural and functional
characterization of Kv10.1 (Eag1) knockout mice. Hum Mol Genet.
22:2247–2262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
García-Quiroz J and Camacho J: Astemizole:
An old anti-histamine as a new promising anti-cancer drug.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 11:307–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Martínez R, Stühmer W, Martin S, Schell J,
Reichmann A, Rohde V and Pardo L: Analysis of the expression of
Kv10.1 potassium channel in patients with brain metastases and
glioblastoma multiforme: impact on survival. BMC Cancer.
15:8392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Guadalupe Chávez-López M, Pérez-Carreón
JI, Zuñiga-García V, Díaz-Chávez J, Herrera LA, Caro-Sánchez CH,
Acuña-Macías I, Gariglio P, Hernández-Gallegos E, Chiliquinga AJ
and Camacho J: Astemizole-based anticancer therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and Eag1 channels as potential
early-stage markers of HCC. Tumour Biol. 36:6149–6158. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
García-Quiroz J, García-Becerra R,
Santos-Martínez N, Barrera D, Ordaz-Rosado D, Avila E, Halhali A,
Villanueva O, Ibarra-Sánchez MJ, Esparza-López J, et al: In vivo
dual targeting of the oncogenic Ether-à-go-go-1 potassium channel
by calcitriol and astemizole results in enhanced antineoplastic
effects in breast tumors. BMC Cancer. 14:7452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
de Guadalupe Chávez-López M,
Hernández-Gallegos E, Vázquez-Sánchez AY, Gariglio P and Camacho J:
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of astemizole on
cervical cancer cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 24:824–828. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
de Abajo FJ and Rodríguez LA: Risk of
ventricular arrhythmias associated with nonsedating antihistamine
drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 47:307–313. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Oppenheimer JJ and Casale TB: Next
generation antihistamines: Therapeutic rationale, accomplishments
and advances. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 11:807–817. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
González MA and Estes KS: Pharmacokinetic
overview of oral second-generation H1 antihistamines. Int J Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 36:292–300. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
vanTellingen O, Yetkin-Arik B, de Gooijer
MC, Wesseling P, Wurdinger T and de Vries HE: Overcoming the
blood-brain tumor barrier for effective glioblastoma treatment.
Drug Resist Updat. 19:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu J, Wu X, Zhong D, Zhai W, Ding Z and
Zhou Y: Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go 1 (Eag1) inhibition
of human osteosarcoma angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT signaling. Int
J Mol Sci. 13:12573–12583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hui C, Lan Z, Yue-Li L and Li-Lin H and
Li-Lin H: Knockdown of Eag1 expression by RNA interference
increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in ovarian cancer cells.
Reprod Sci. 22:1618–1626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|