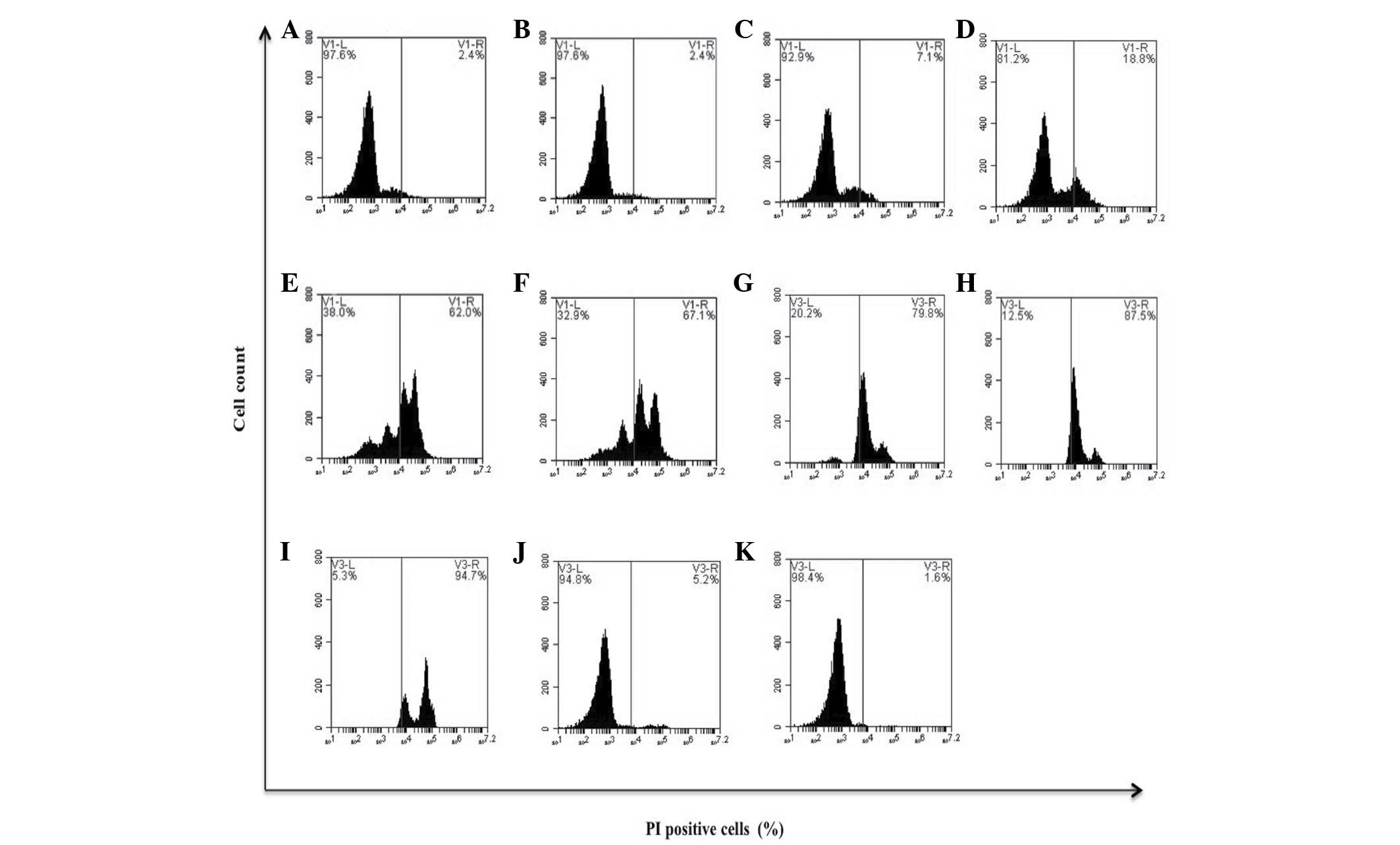
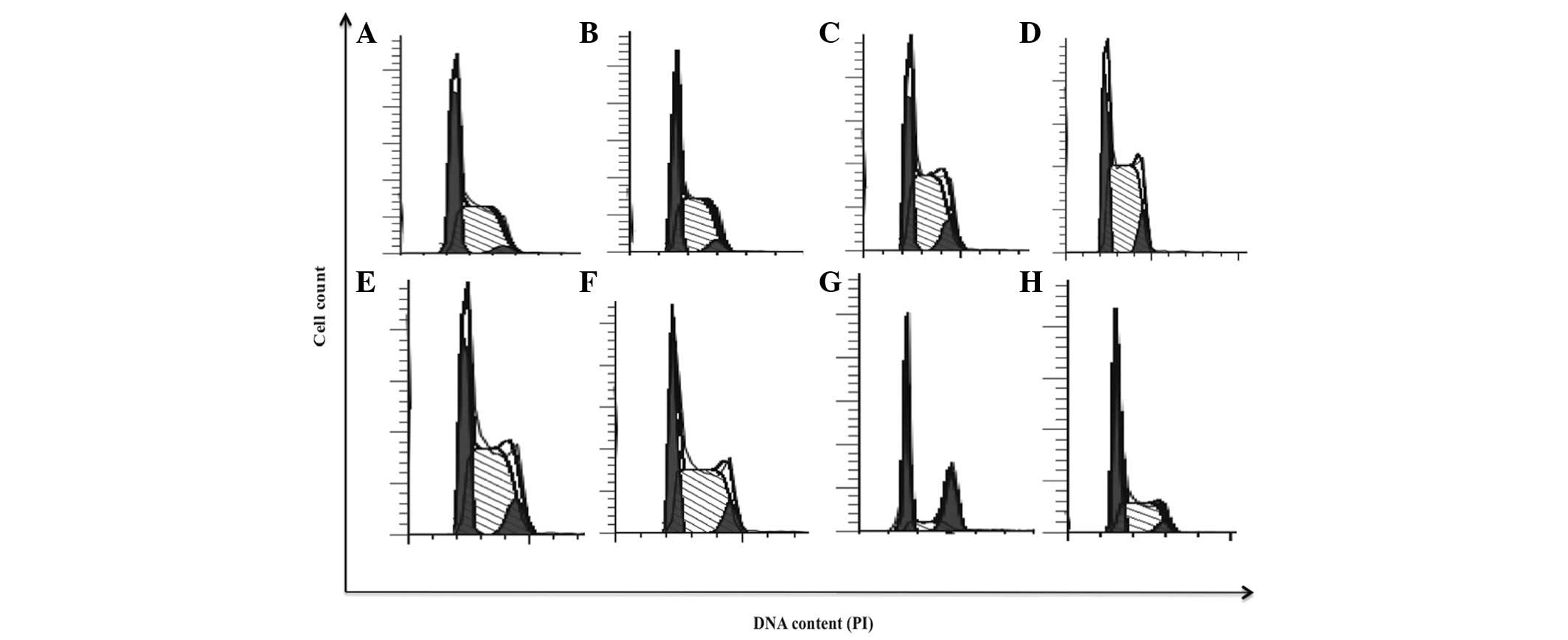
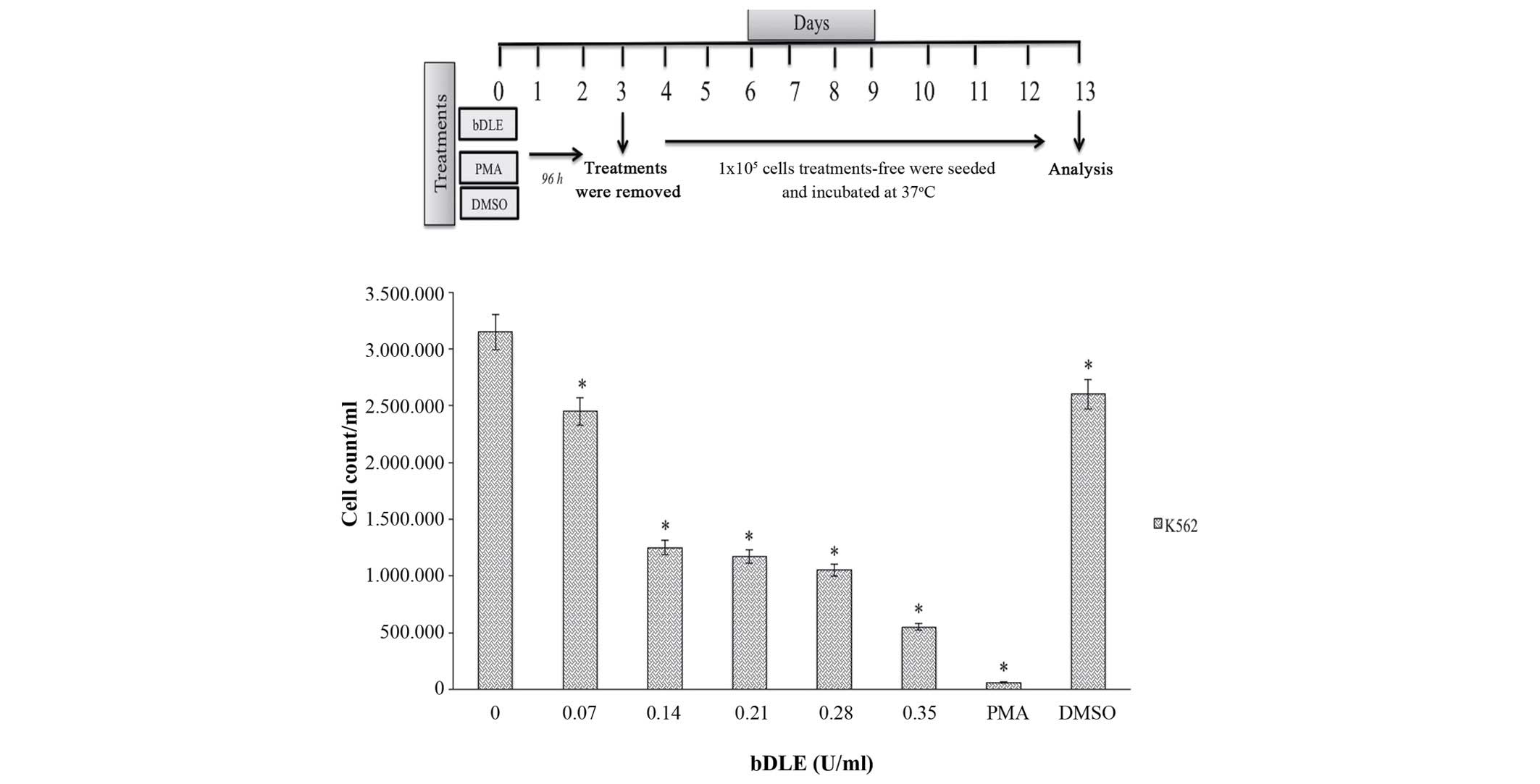
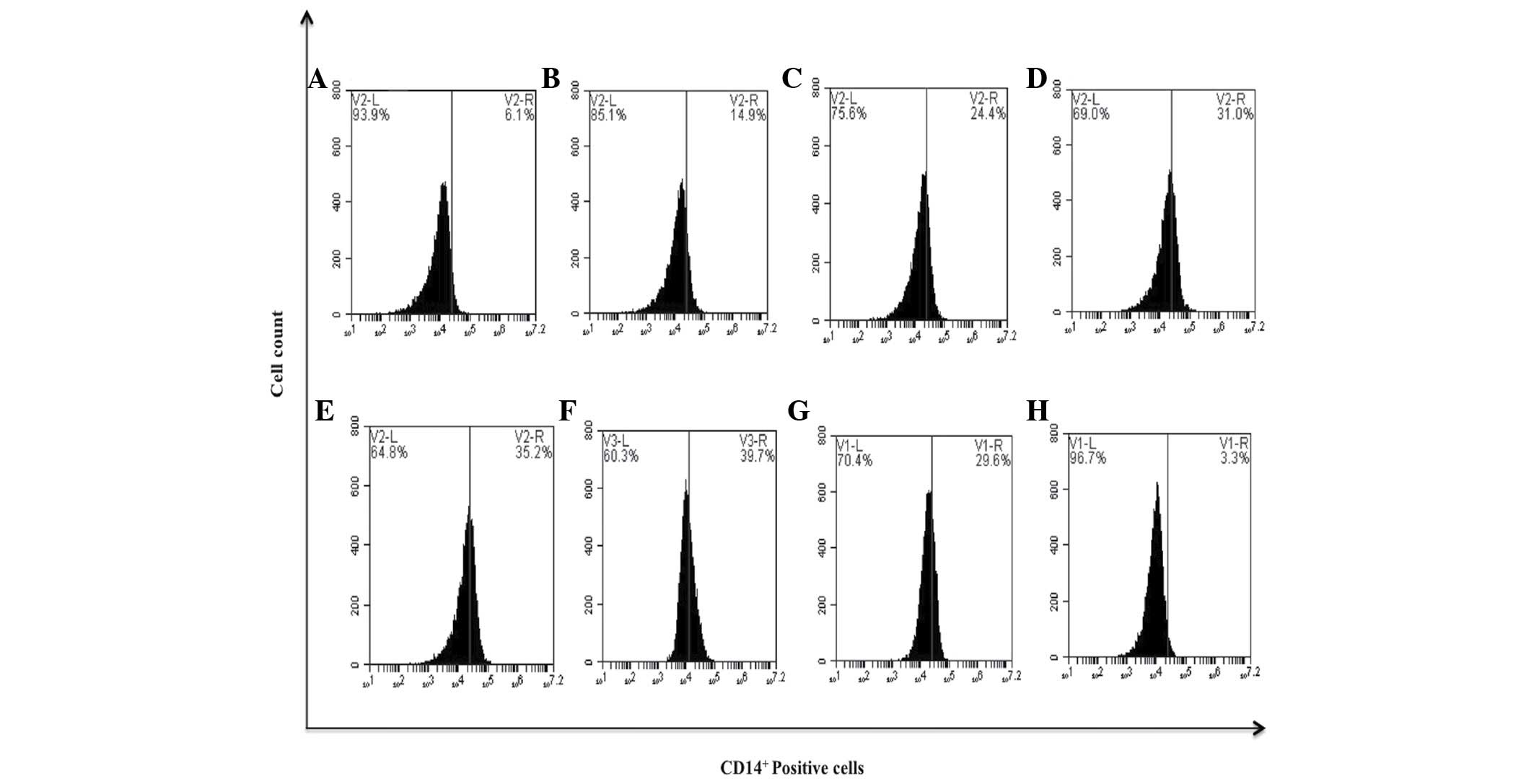
Spandidos Publications style
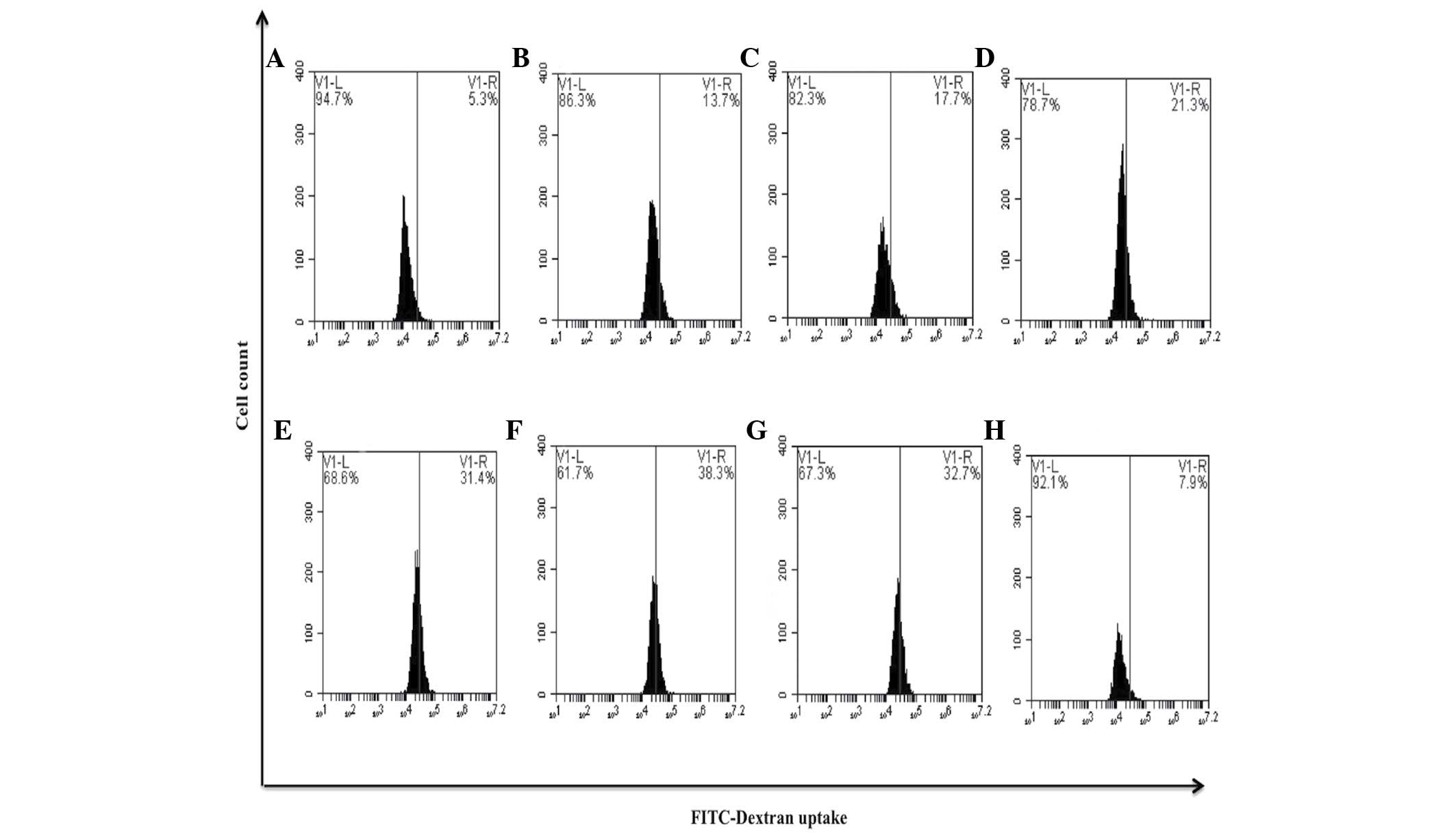
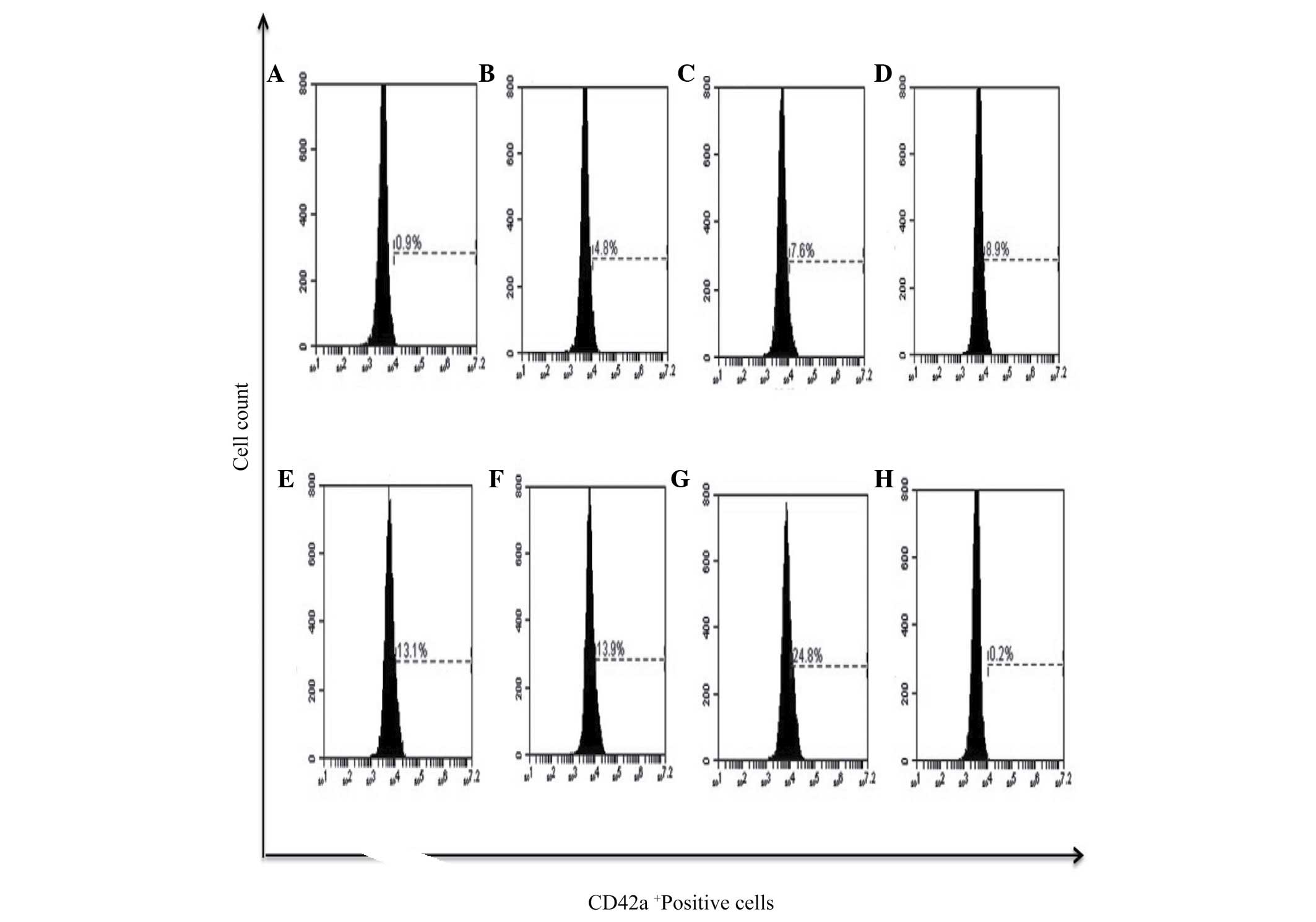
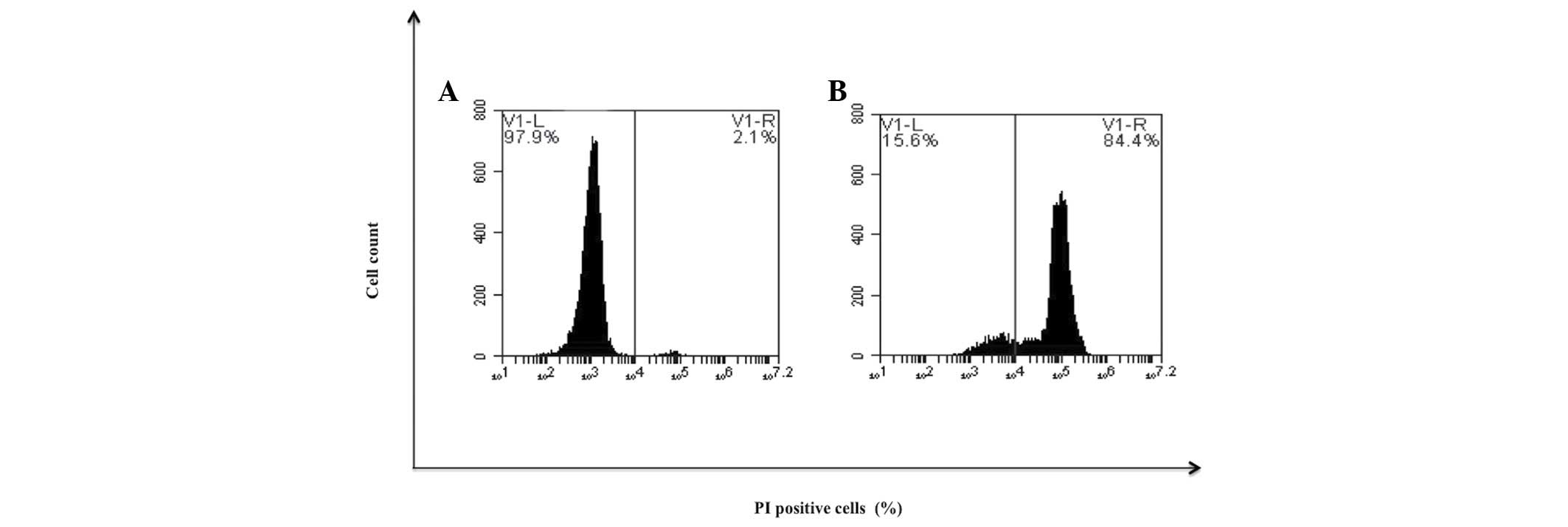
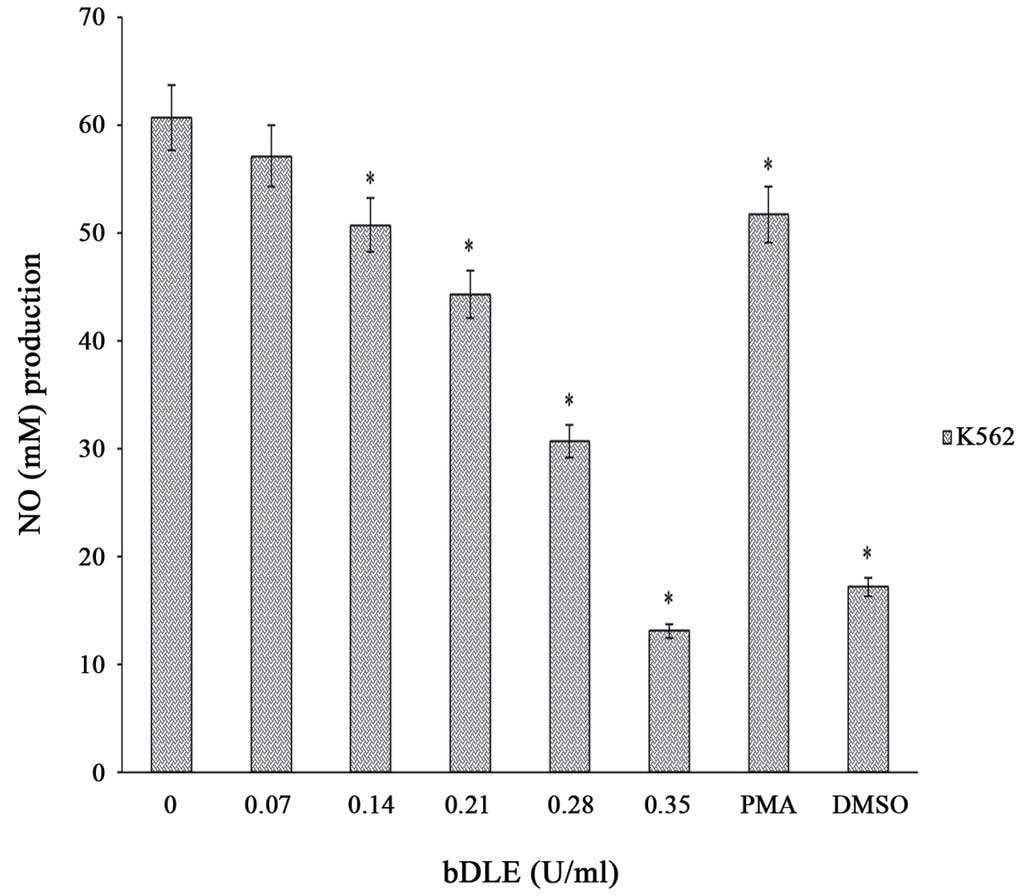
Sierra‑Rivera CA, Franco‑Molina MA, Mendoza‑Gamboa E, Zapata‑Benavides P, Santaolalla‑Tapia J, Coronado‑Cerda EE, Tamez‑Guerra RS and Rodríguez‑Padilla C: Effect of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract on induction of cell differentiation and death in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Oncol Lett 12: 4449-4460, 2016.
APA
Sierra‑Rivera, C.A., Franco‑Molina, M.A., Mendoza‑Gamboa, E., Zapata‑Benavides, P., Santaolalla‑Tapia, J., Coronado‑Cerda, E.E. ... Rodríguez‑Padilla, C. (2016). Effect of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract on induction of cell differentiation and death in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Oncology Letters, 12, 4449-4460. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.5285
MLA
Sierra‑Rivera, C. A., Franco‑Molina, M. A., Mendoza‑Gamboa, E., Zapata‑Benavides, P., Santaolalla‑Tapia, J., Coronado‑Cerda, E. E., Tamez‑Guerra, R. S., Rodríguez‑Padilla, C."Effect of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract on induction of cell differentiation and death in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells". Oncology Letters 12.6 (2016): 4449-4460.
Chicago
Sierra‑Rivera, C. A., Franco‑Molina, M. A., Mendoza‑Gamboa, E., Zapata‑Benavides, P., Santaolalla‑Tapia, J., Coronado‑Cerda, E. E., Tamez‑Guerra, R. S., Rodríguez‑Padilla, C."Effect of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract on induction of cell differentiation and death in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells". Oncology Letters 12, no. 6 (2016): 4449-4460. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.5285