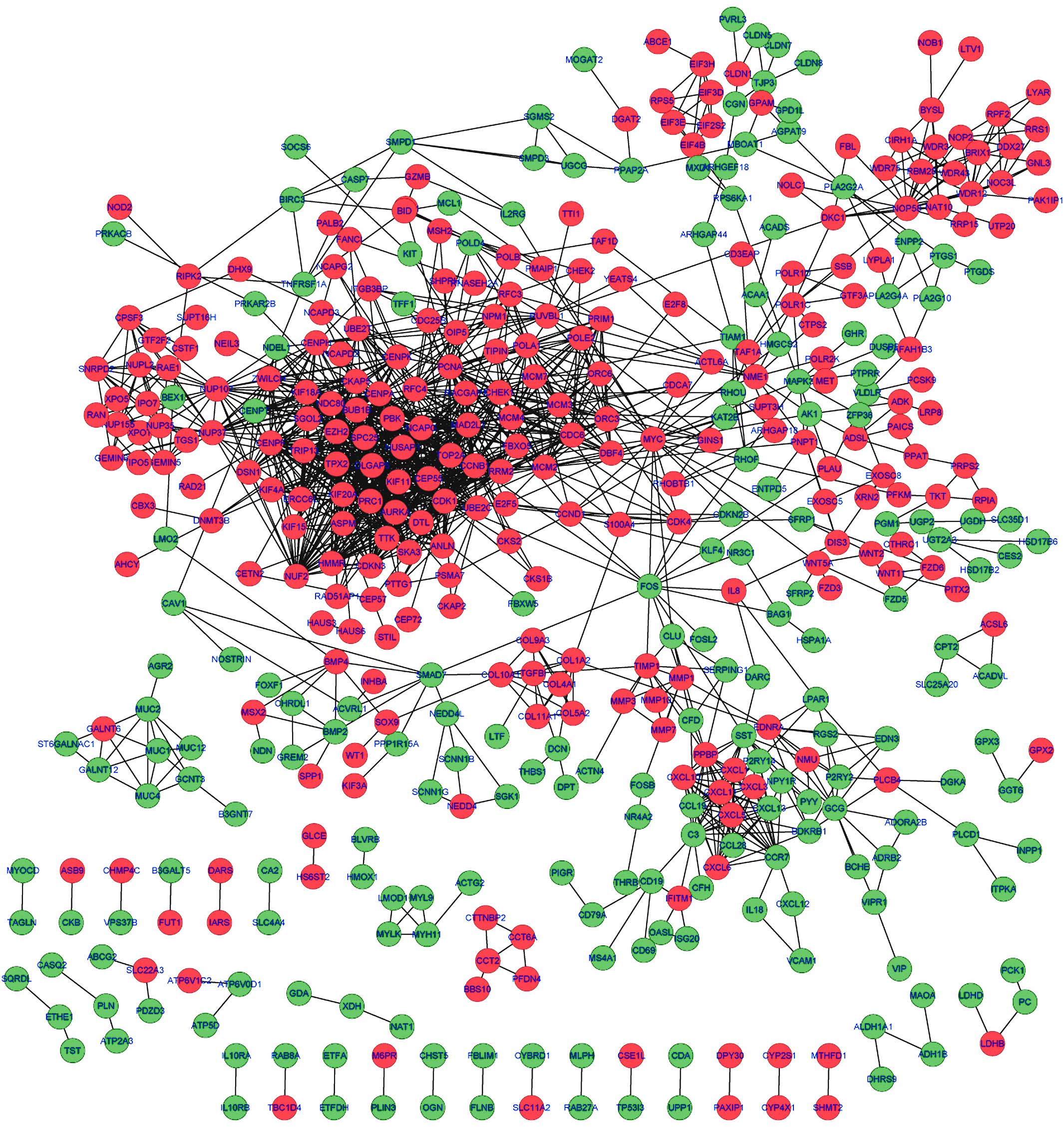
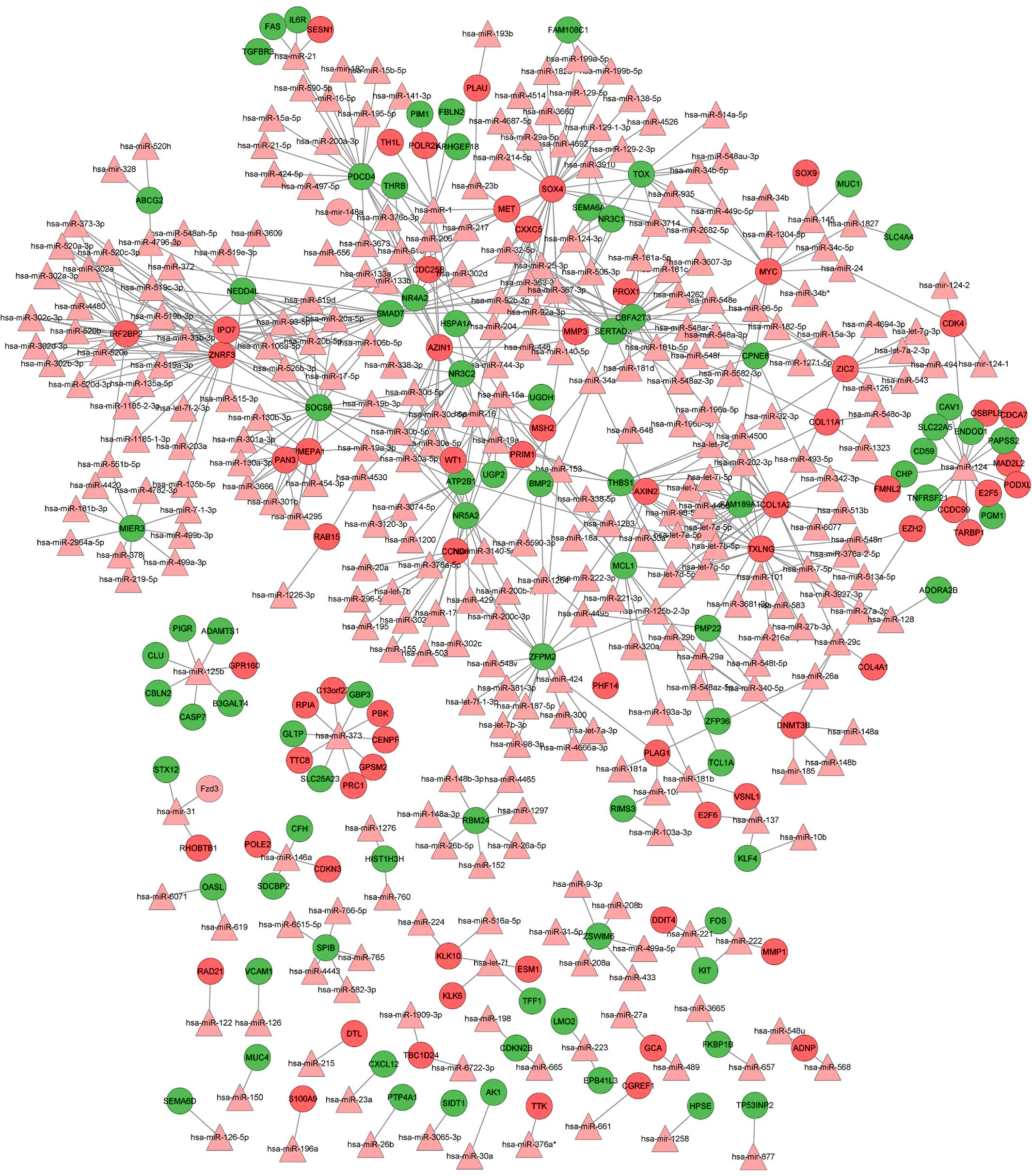
|
1
|
Qiu Y, Patwa TH, Xu L, Shedden K, Misek
DE, Tuck M, Jin G, Ruffin MT, Turgeon DK, Synal S, et al: Plasma
glycoprotein profiling for colorectal cancer biomarker
identification by lectin glycoarray and lectin blot. J Proteome
Res. 7:1693–1703. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cajuso T, Hänninen UA, Kondelin J, Gylfe
AE, Tanskanen T, Katainen R, Pitkänen E, Ristolainen H, Kaasinen E
and Taipale M: Exome sequencing reveals frequent inactivating
mutations in ARID1A, ARID1B, ARID2 and ARID4A in microsatellite
unstable colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 135:611–623. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mendenhall WM, Amos EH, Rout WR, Zlotecki
RA, Hochwald SN and Cance WG: Adjuvant postoperative radiotherapy
for colon carcinoma. Cancer. 101:1338–1344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Quintero E, Castells A, Bujanda L,
Cubiella J, Salas D, Lanas Á, Andreu M, Carballo F, Morillas JD,
Hernández C, et al: Colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical testing
in colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 366:697–706. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W
and Du X: Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early
detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:118–126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pino MS and Chung DC: The chromosomal
instability pathway in colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2059–2072. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peeters M, Douillard JY, Van Cutsem E,
Siena S, Zhang K, Williams R and Wiezorek J: Mutant KRAS codon 12
and 13 alleles in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer:
Assessment as prognostic and predictive biomarkers of response to
panitumumab. J Clin Oncol. 31:759–765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S,
Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham
D, Jassem J, et al: Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations
in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 369:1023–1034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Smith G, Carey FA, Beattie J, Wilkie MJ,
Lightfoot TJ, Coxhead J, Garner RC, Steele RJ and Wolf CR:
Mutations in APC, Kirsten-ras, and p53-alternative genetic pathways
to colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:9433–9438. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang L and Zhang X:
NF-kappaB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer.
Cell Mol Immunol. 6:327–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, Smerdova T,
Knoflickova D, Bednarikova M, Nenutil R and Vyzula R: Altered
expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to
clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology.
72:397–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Khamas A, Ishikawa T, Shimokawa K, Mogushi
K, Iida S, Ishiguro M, Mizushima H, Tanaka H, Uetake H and Sugihara
K: Screening for epigenetically masked genes in colorectal cancer
Using 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine, microarray and gene expression
profile. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:67–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bolstad BM: Package ‘preprocessCore’: A
collection of pre-processing functions. R Package version 1.28.0.
http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/3.0/bioc/html/preprocessCore.html2013.Accessed
May 7, 2015.
|
|
16
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear models for
microarray dataBioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using {R} and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S,
Irizarry R and Huber W: Springer; New York: pp. 397–420. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Duncan D, Shi Z and Zhang B:
WEB-based GEne SeT AnaLysis Toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41:W77–W83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hong BS, Cho JH, Kim H, Choi EJ, Rho S,
Kim J, Kim JH, Choi DS, Kim YK, Hwang D, et al: Colorectal cancer
cell-derived microvesicles are enriched in cell cycle-related mRNAs
that promote proliferation of endothelial cells. BMC Genomics.
10:5562009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Santamaría D, Barrière C, Cerqueira A,
Hunt S, Tardy C, Newton K, Cáceres JF, Dubus P, Malumbres M and
Barbacid M: Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle.
Nature. 448:811–815. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu P, Kao TP and Huang H: CDK1 promotes
cell proliferation and survival via phosphorylation and inhibition
of FOXO1 transcription factor. Oncogene. 27:4733–4744. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SJ, Nakayama S, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T,
Tamaki Y, Matsushima T, Torikoshi Y, Tanaka S, Yoshida T, Ishihara
H and Noguchi S: Determination of the specific activity of CDK1 and
CDK2 as a novel prognostic indicator for early breast cancer. Ann
Oncol. 19:68–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hansel DE, Dhara S, Huang RC, Ashfaq R,
Deasel M, Shimada Y, Bernstein HS, Harmon J, Brock M, Forastiere A,
et al: CDC2/CDK1 expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma and
precursor lesions serves as a diagnostic and cancer progression
marker and potential novel drug target. Am J Surg Pathol.
29:390–399. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang JT, Wang HM, Chang KW, Chen WH, Wen
MC, Hsu YM, Yung BY, Chen IH, Liao CT, Hsieh LL and Cheng AJ:
Identification of differentially expressed genes in oral squamous
cell carcinoma (OSCC): Overexpression of NPM, CDK1 and NDRG1 and
underexpression of CHES1. Int J Cancer. 114:942–949. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thoms HC, Dunlop MG and Stark LA:
p38-mediated inactivation of cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4
stimulates nucleolar translocation of RelA and apoptosis in
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:1660–1669. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang WW, Ko SW, Tsai HY, Chung JG, Chiang
JH, Chen KT, Chen YC, Chen HY, Chen YF and Yang JS: Cantharidin
induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer
colo 205 cells through inhibition of CDK1 activity and
caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 38:1067–1073.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soria JC, Jang SJ, Khuri FR, Hassan K, Liu
D, Hong WK and Mao L: Overexpression of cyclin B1 in early-stage
non-small cell lung cancer and its clinical implication. Cancer
Res. 60:4000–4004. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koon N, Schneider-Stock R, Sarlomo-Rikala
M, Lasota J, Smolkin M, Petroni G, Zaika A, Boltze C, Meyer F,
Andersson L, et al: Molecular targets for tumour progression in
gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Gut. 53:235–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ding K, Li W, Zou Z, Zou X and Wang C:
CCNB1 is a prognostic biomarker for ER+ breast cancer. Med
Hypotheses. 83:359–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang IP, Tsai HL, Hou MF, Chen KC, Tsai
PC, Huang SW, Chou WW, Wang JY and Juo SH: MicroRNA-93 inhibits
tumor growth and early relapse of human colorectal cancer by
affecting genes involved in the cell cycle. Carcinogenesis.
33:1522–1530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Scintu M, Vitale R, Prencipe M, Gallo AP,
Bonghi L, Valori VM, Maiello E, Rinaldi M, Signori E, Rabitti C, et
al: Genomic instability and increased expression of BUB1B and
MAD2L1 genes in ductal breast carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 254:298–307.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shichiri M, Yoshinaga K, Hisatomi H,
Sugihara K and Hirata Y: Genetic and epigenetic inactivation of
mitotic checkpoint genes hBUB1 and hBUBR1 and their relationship to
survival. Cancer Res. 62:13–17. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan B, Xu Y, Woo JH, Wang Y, Bae YK, Yoon
DS, Wersto RP, Tully E, Wilsbach K and Gabrielson E: Increased
expression of mitotic checkpoint genes in breast cancer cells with
chromosomal instability. Clin Cancer Res. 12:405–410. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Andersen CL, Christensen LL, Thorsen K,
Schepeler T, Sørensen FB, Verspaget HW, Simon R, Kruhøffer M,
Aaltonen LA, Laurberg S and Ørntoft TF: Dysregulation of the
transcription factors SOX4, CBFB and SMARCC1 correlates with
outcome of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 100:511–523. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang YW, Liu JC, Deatherage DE, Luo J,
Mutch DG, Goodfellow PJ, Miller DS and Huang TH: Epigenetic
repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4
oncogene in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 69:9038–9046. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Mannava S, Grachtchouk V, Zhuang
D, Soengas MS, Gudkov AV, Prochownik EV and Nikiforov MA: c-Myc
depletion inhibits proliferation of human tumor cells at various
stages of the cell cycle. Oncogene. 27:1905–1915. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takatsuno Y, Mimori K, Yamamoto K, Sato T,
Niida A, Inoue H, Imoto S, Kawano S, Yamaguchi R, Toh H, et al: The
rs6983267 SNP is associated with MYC transcription efficiency,
which promotes progression and worsens prognosis of colorectal
cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 20:1395–1402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, Yang Q, Aris
V, Soteropoulos P, Petrelli NJ, Dunn SP and Krueger LJ: MicroRNA
let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt
lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:9762–9770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao P, Tchernyshyov I, Chang TC, Lee YS,
Kita K, Ochi T, Zeller KI, De Marzo AM, Van Eyk JE, Mendell JT and
Dang CV: c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial
glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature.
458:762–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen Z, Zeng H, Guo Y, Liu P, Pan H, Deng
A and Hu J: miRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell
proliferation by targeting c-Myc. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
29:1512010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Smith MJ, Culhane AC, Donovan M, Coffey
JC, Barry BD, Kelly MA, Higgins DG, Wang JH, Kirwan WO, Cotter TG
and Redmond HP: Analysis of differential gene expression in
colorectal cancer and stroma using fluorescence-activated cell
sorting purification. Br J Cancer. 100:1452–1464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ and Bond GL:
The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 7:979–987. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Al-Kuraya K, Novotny H, Bavi P, Siraj AK,
Uddin S, Ezzat A, Sanea NA, Al-Dayel F, Al-Mana H, Sheikh SS, et
al: HER2, TOP2A, CCND1, EGFR and C-MYC oncogene amplification in
colorectal cancer. J Clin Pathol. 60:768–772. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang HY, Illei PB, Zhao Z, Mazumdar M,
Huvos AG, Healey JH, Wexler LH, Gorlick R, Meyers P and Ladanyi M:
Ewing sarcomas with p53 mutation or p16/p14ARF homozygous deletion:
A highly lethal subset associated with poor chemoresponse. J Clin
Oncol. 23:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Choi EJ and Kim GH: Apigenin causes G(2)/M
arrest associated with the modulation of p21(Cip1) and Cdc2 and
activates p53-dependent apoptosis pathway in human breast cancer
SK-BR-3 cells. J Nutr Biochem. 20:285–290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li CJ, Li RW, Wang YH and Elsasser TH:
Pathway analysis identifies perturbation of genetic networks
induced by butyrate in a bovine kidney epithelial cell line. Funct
Integr Genomics. 7:193–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen J, Feilotter HE, Paré GC, Zhang X,
Pemberton JG, Garady C, Lai D, Yang X and Tron VA: MicroRNA-193b
represses cell proliferation and regulates cyclin D1 in melanoma.
Am J Pathol. 176:2520–2529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xia W, Li J, Chen L, Huang B, Li S, Yang
G, Ding H, Wang F, Liu N, Zhao Q, et al: MicroRNA-200b regulates
cyclin D1 expression and promotes S-phase entry by targeting RND3
in HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 344:261–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Sang Y, Xu S, Hu K,
Wu M, Liang Y, Liu P, Tang J, et al: MiR-138 suppressed
nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and tumorigenesis by targeting the
CCND1 oncogene. Cell Cycle. 11:2495–2506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S
and Kunz M: MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules
in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with
anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res. 18:549–557. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|