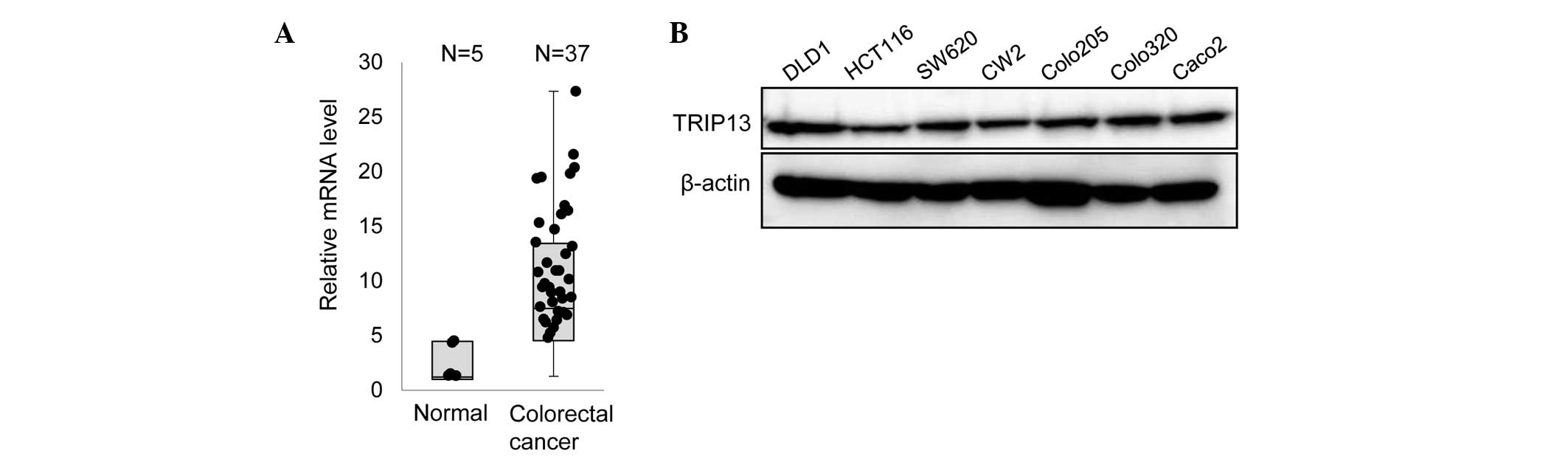
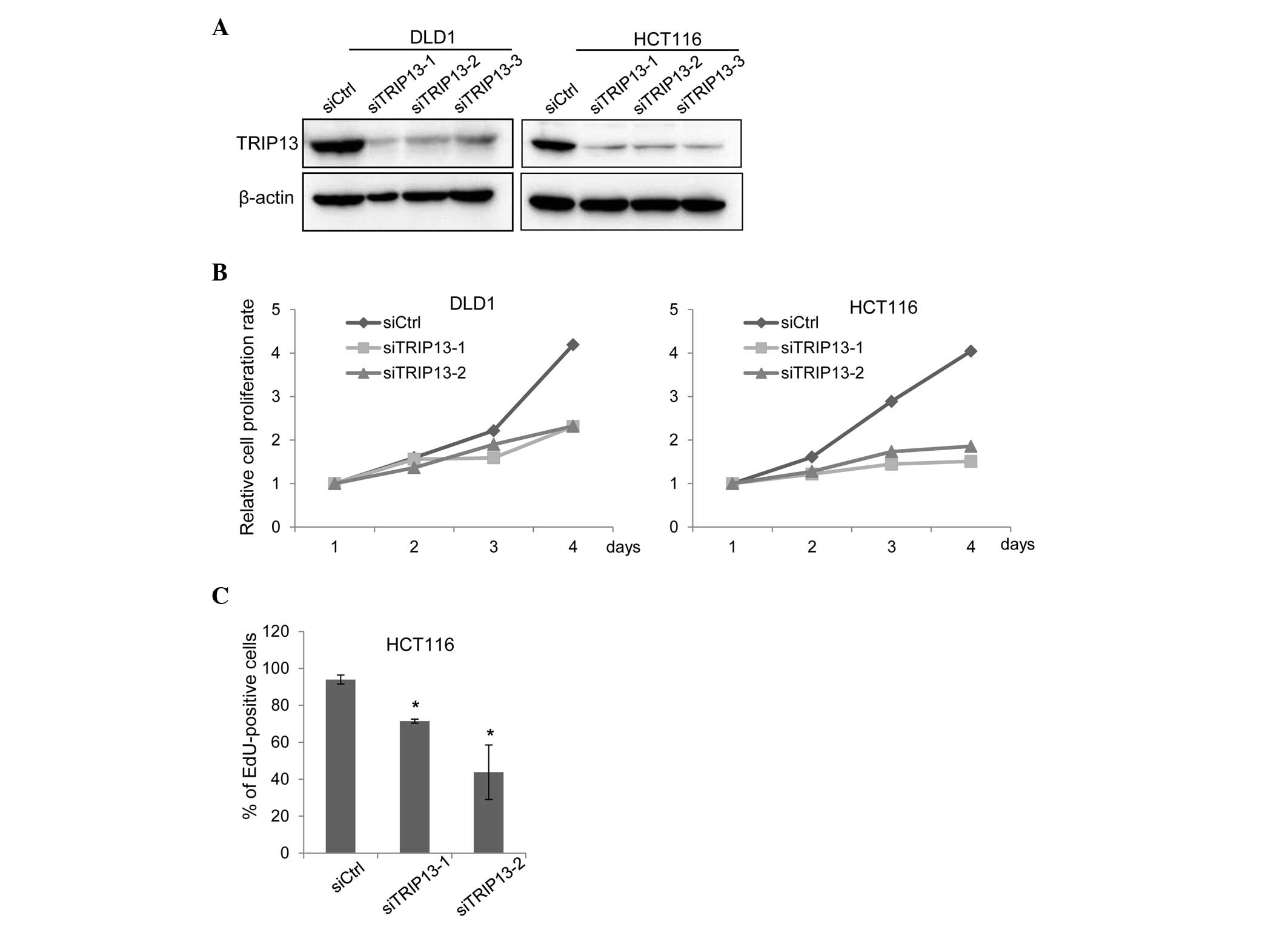
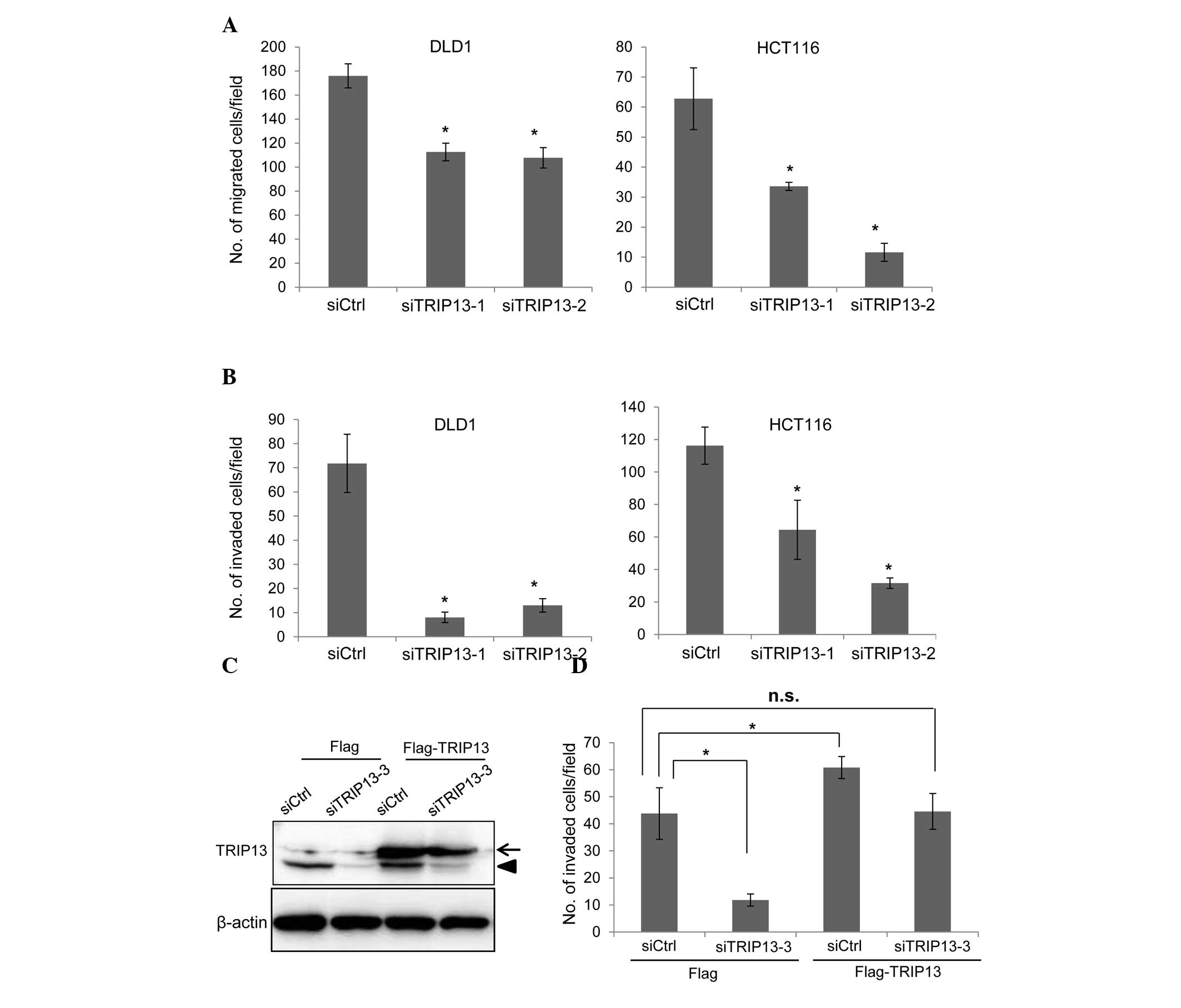
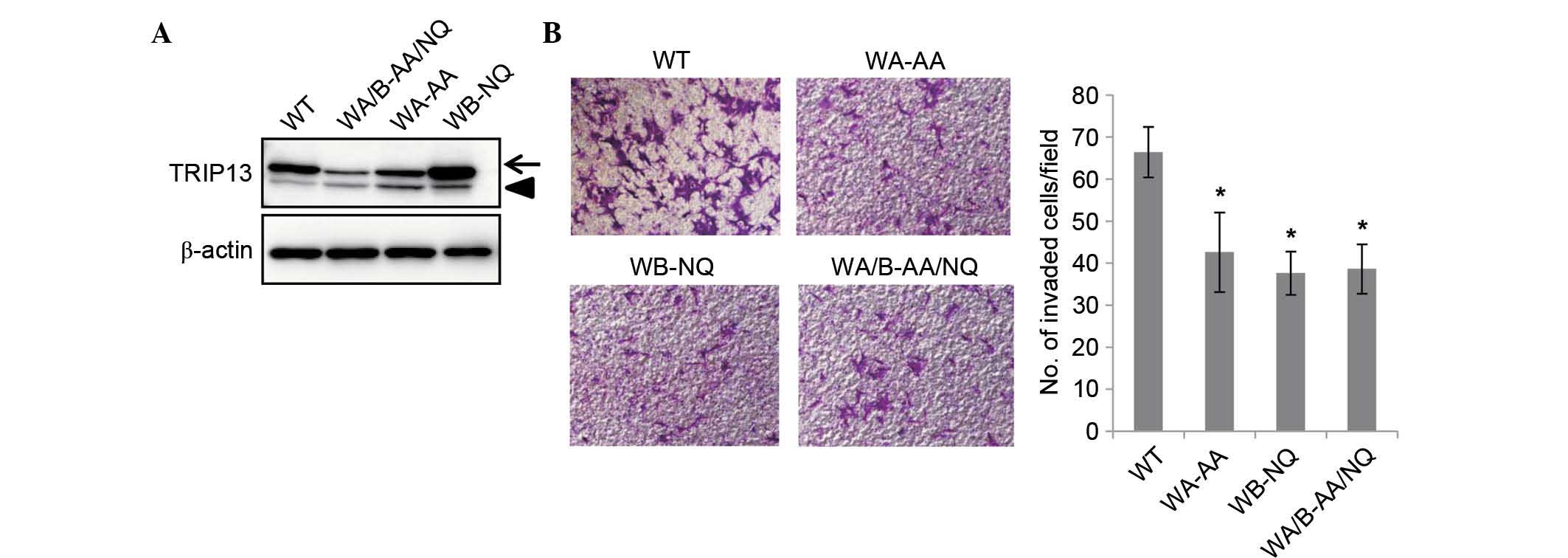
|
1
|
Ogura T and Wilkinson AJ: AAA+ superfamily
ATPases: Common structure-diverse function. Genes Cells. 6:575–597.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanson PI and Whiteheart SW: AAA+
proteins: Have engine, will work. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:519–529.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Snider J and Houry WA: AAA+ proteins:
Diversity in function, similarity in structure. Biochem Soc Trans.
36:72–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wendler P, Ciniawsky S, Kock M and Kube S:
Structure and function of the AAA+ nucleotide binding pocket.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:2–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grigoletto A, Lestienne P and Rosenbaum J:
The multifaceted proteins Reptin and Pontin as major players in
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1815:147–157. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huber O, Ménard L, Haurie V, Nicou A,
Taras D and Rosenbaum J: Pontin and reptin, two related ATPases
with multiple roles in cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6873–6876. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JW, Choi HS, Gyuris J, Brent R and
Moore DD: Two classes of proteins dependent on either the presence
or absence of thyroid hormone for interaction with the thyroid
hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 9:243–254. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li XC and Schimenti JC: Mouse pachytene
checkpoint 2 (trip13) is required for completing meiotic
recombination but not synapsis. PLoS Genet. 3:e1302007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Roig I, Dowdle JA, Toth A, de Rooij DG,
Jasin M and Keeney S: Mouse TRIP13/PCH2 is required for
recombination and normal higher-order chromosome structure during
meiosis. PLoS Genet. 6:e10010622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ho HC and Burgess SM: Pch2 acts through
Xrs2 and Tel1/ATM to modulate interhomolog bias and checkpoint
function during meiosis. PLoS Genet. 7:e10023512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wojtasz L, Daniel K, Roig I, Bolcun-Filas
E, Xu H, Boonsanay V, Eckmann CR, Cooke HJ, Jasin M, Keeney S, et
al: Mouse HORMAD1 and HORMAD2, two conserved meiotic chromosomal
proteins, are depleted from synapsed chromosome axes with the help
of TRIP13 AAA-ATPase. PLoS Genet. 5:e10007022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Farmer S, Hong EJ, Leung WK, Argunhan B,
Terentyev Y, Humphryes N, Toyoizumi H and Tsubouchi H: Budding
yeast Pch2, a widely conserved meiotic protein, is involved in the
initiation of meiotic recombination. PLoS One. 7:e397242012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen C, Jomaa A, Ortega J and Alani EE:
Pch2 is a hexameric ring ATPase that remodels the chromosome axis
protein Hop1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E44–E53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tipton AR, Wang K, Oladimeji P, Sufi S, Gu
Z and Liu ST: Identification of novel mitosis regulators through
data mining with human centromere/kinetochore proteins as group
queries. BMC Cell Biol. 13:152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang K, Sturt-Gillespie B, Hittle JC,
Macdonald D, Chan GK, Yen TJ and Liu ST: Thyroid hormone receptor
interacting protein 13 (TRIP13) AAA-ATPase is a novel mitotic
checkpoint-silencing protein. J Biol Chem. 289:23928–23937. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eytan E, Wang K, Miniowitz-Shemtov S,
Sitry-Shevah D, Kaisari S, Yen TJ, Liu ST and Hershko A:
Disassembly of mitotic checkpoint complexes by the joint action of
the AAA-ATPase TRIP13 and p31 (comet). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:12019–12024. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye Q, Rosenberg SC, Moeller A, Speir JA,
Su TY and Corbett KD: TRIP13 is a protein-remodeling AAA+ ATPase
that catalyzes MAD2 conformation switching. Elife. 4:2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lara-Gonzalez P, Westhorpe FG and Taylor
SS: The spindle assembly checkpoint. Curr Biol. 22:R966–R980. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rao CV, Yamada HY, Yao Y and Dai W:
Enhanced genomic instabilities caused by deregulated microtubule
dynamics and chromosome segregation: A perspective from genetic
studies in mice. Carcinogenesis. 30:1469–1474. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Banerjee R, Russo N, Liu M, Basrur V,
Bellile E, Palanisamy N, Scanlon CS, van Tubergen E, Inglehart RC,
Metwally T, et al: TRIP13 promotes error-prone nonhomologous end
joining and induces chemoresistance in head and neck cancer. Nat
Commun. 5:45272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wong M, Hyodo T, Asano E, Funasaka K,
Miyahara R, Hirooka Y, Goto H, Hamaguchi M and Senga T: Silencing
of STRN4 suppresses the malignant characteristics of cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 105:1526–1532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Giet R, Petretti C and Prigent C: Aurora
kinases, aneuploidy and cancer, a coincidence or a real link?
Trends Cell Biol. 15:241–250. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gautschi O, Heighway J, Mack PC, Purnell
PR, Lara PN Jr and Gandara DR: Aurora kinases as anticancer drug
targets. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1639–1648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nguyen HG, Makitalo M, Yang D, Chinnappan
D, St Hilaire C and Ravid K: Deregulated Aurora-B induced
tetraploidy promotes tumorigenesis. FASEB J. 23:2741–2748. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang LY, Chang CC, Lee YS, Chang JM,
Huang JJ, Chuang SH, Kao KJ, Lau GM, Tsai PY, Liu CW, et al:
Activity of a novel Hec1-targeted anticancer compound against
breast cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:1419–1430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang LY, Chang CC, Lee YS, Huang JJ,
Chuang SH, Chang JM, Kao KJ, Lau GM, Tsai PY, Liu CW, et al:
Inhibition of Hec1 as a novel approach for treatment of primary
liver cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 74:511–520. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maachani UB, Kramp T, Hanson R, Zhao S,
Celiku O, Shankavaram U, Colombo R, Caplen NJ, Camphausen K and
Tandle A: Targeting MPS1 enhances Radiosensitization of human
Glioblastoma by modulating DNA repair proteins. Mol Cancer Res.
13:852–862. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Larkin SE, Holmes S, Cree IA, Walker T,
Basketter V, Bickers B, Harris S, Garbis SD, Townsend PA and
Aukim-Hastie C: Identification of markers of prostate cancer
progression using candidate gene expression. Br J Cancer.
106:157–165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sudakin V, Chan GK and Yen TJ: Checkpoint
inhibition of the APC/C in HeLa cells is mediated by a complex of
BUBR1, BUB3, CDC20, and MAD2. J Cell Biol. 154:925–936. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tipton AR, Tipton M, Yen T and Liu ST:
Closed MAD2 (C-MAD2) is selectively incorporated into the mitotic
checkpoint complex (MCC). Cell Cycle. 10:3740–3750. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sotillo R, Schvartzman JM, Socci ND and
Benezra R: Mad2-induced chromosome instability leads to lung tumour
relapse after oncogene withdrawal. Nature. 464:436–440. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iwanaga Y, Chi YH, Miyazato A, Sheleg S,
Haller K, Peloponese JM Jr, Li Y, Ward JM, Benezra R and Jeang KT:
Heterozygous deletion of mitotic arrest-deficient protein 1 (MAD1)
increases the incidence of tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 67:160–166.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chapman E, Maksim N, de la Cruz F and La
Clair JJ: Inhibitors of the AAA+ chaperone p97. Molecules.
20:3027–3049. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|