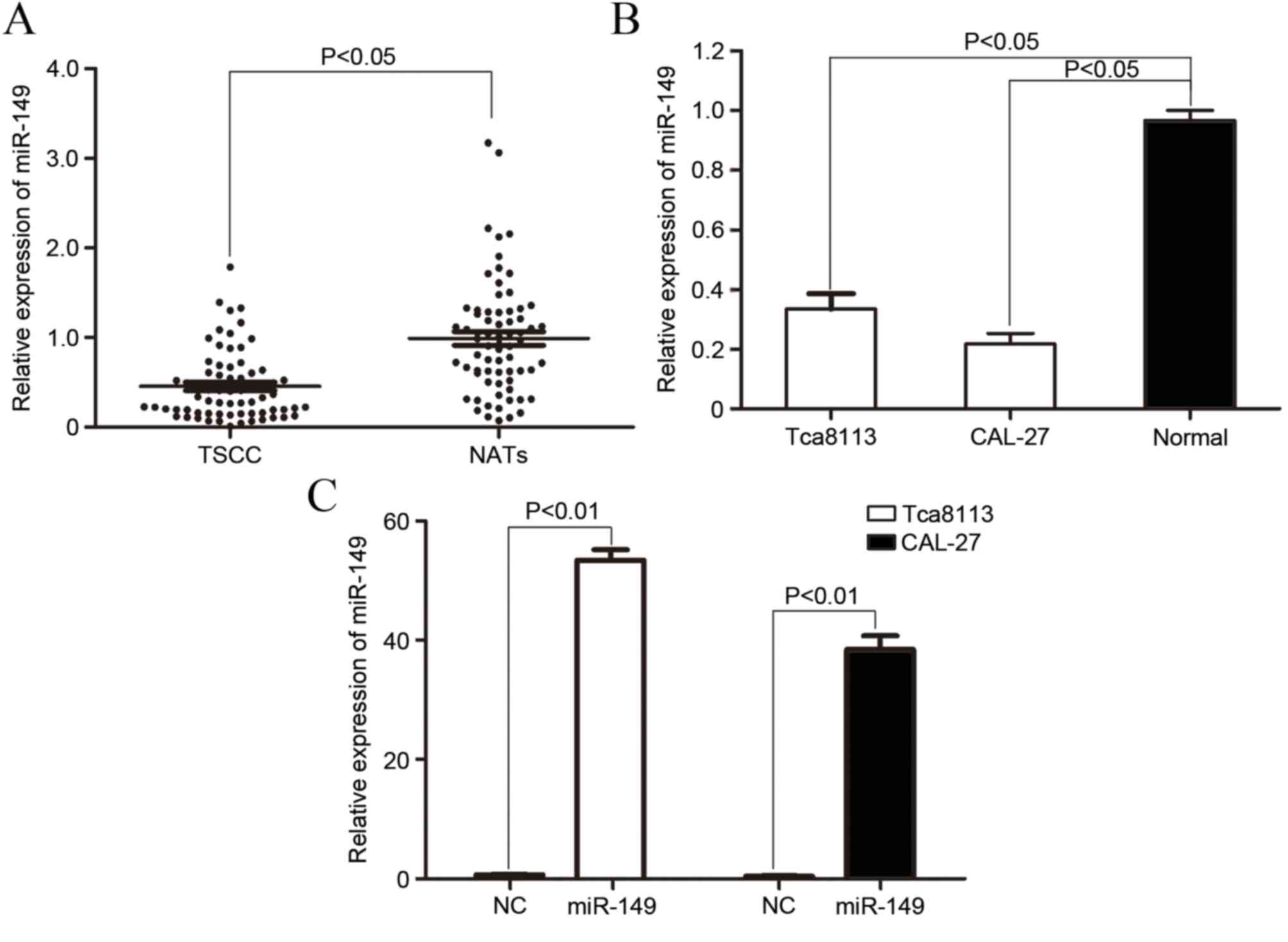
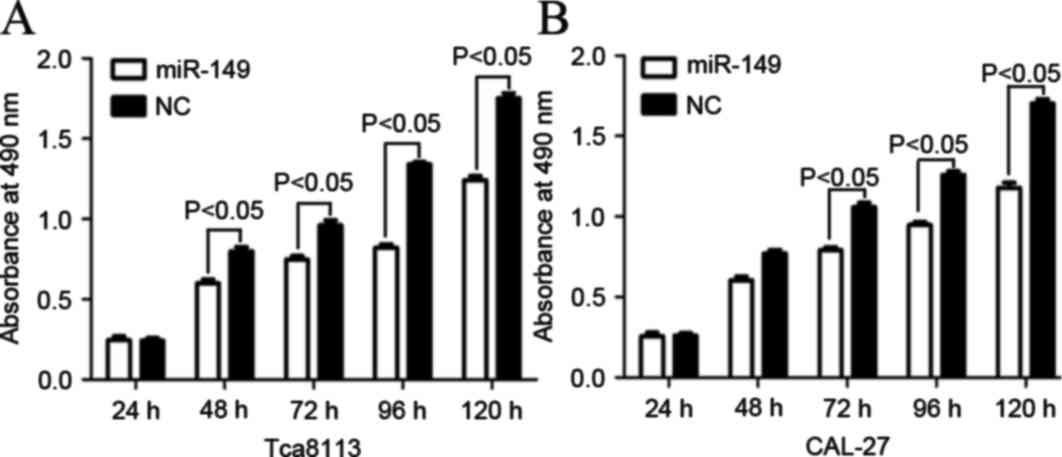
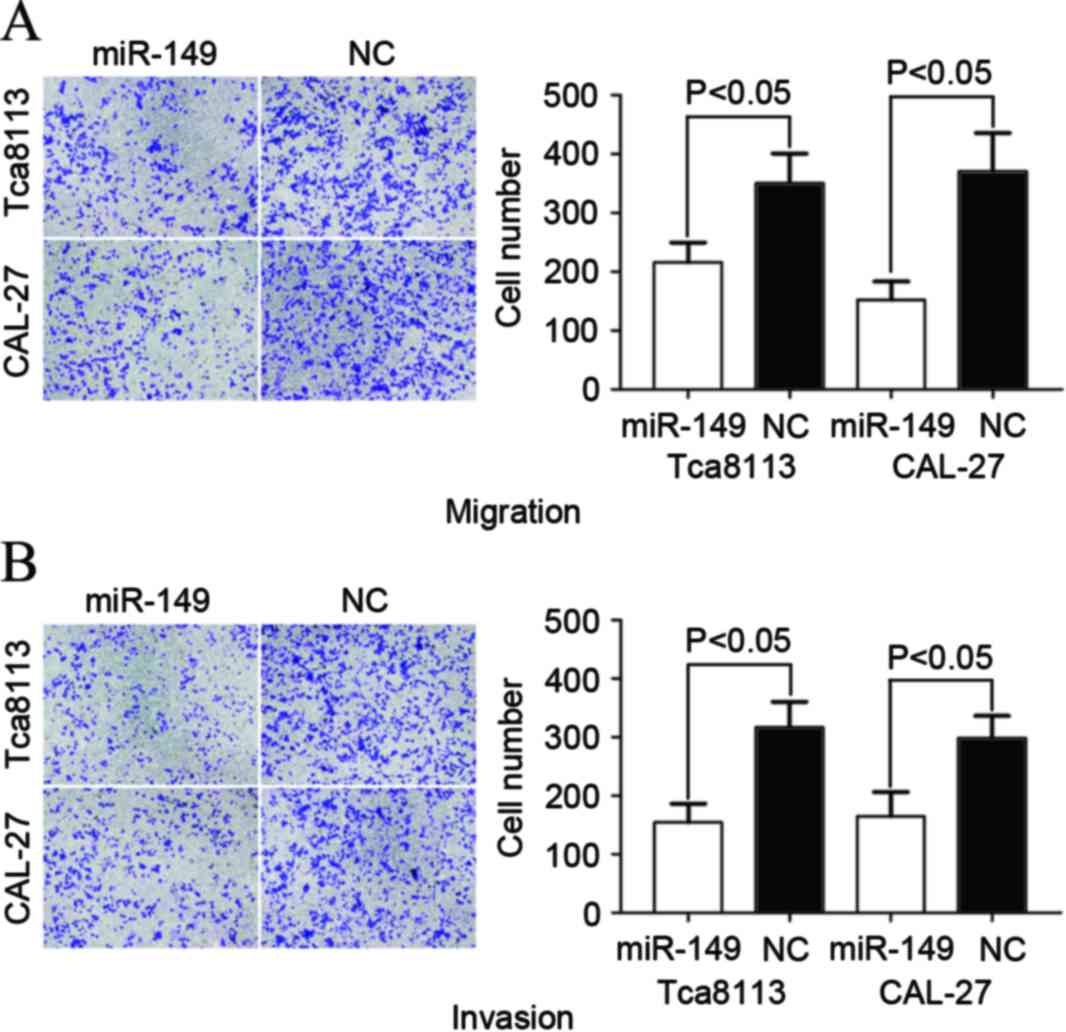
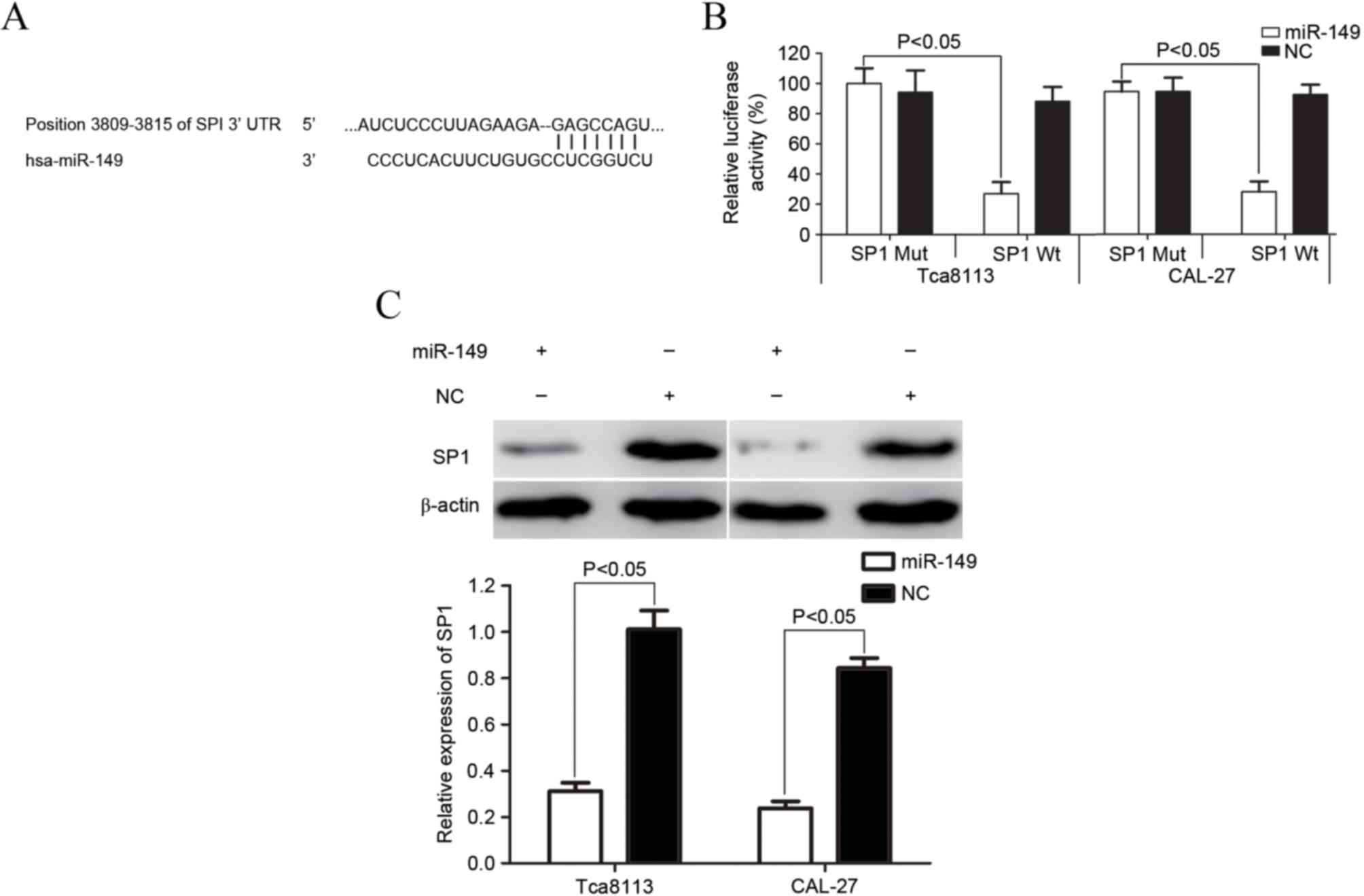
|
1
|
Yu ZW, Zhong LP, Ji T, Zhang P, Chen WT
and Zhang CP: MicroRNAs contribute to the chemoresistance of
cisplatin in tongue squamous cell carcinoma lines. Oral Oncol.
46:317–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yuen PW, Lam KY, Chan AC, Wei WI and Lam
LK: Clinicopathological analysis of local spread of carcinoma of
the tongue. Am J Surg. 175:242–244. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Po Wing Yuen A, Lam KY, Lam LK, Ho CM,
Wong A, Chow TL, Yuen WF and Wei WI: Prognostic factors of
clinically stage I and II oral tongue carcinoma-A comparative study
of stage, thickness, shape, growth pattern, invasive front
malignancy grading, Martinez-Gimeno score, and pathologic features.
Head Neck. 24:513–520. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sano D and Myers JN: Metastasis of
squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:645–662. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song KB, Liu WJ and Jia SS: miR-219
inhibits the growth and metastasis of TSCC cells by targeting
PRKCI. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:2957–2965. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Squarize CH, Castilho RM, Abrahao AC,
Molinolo A, Lingen MW and Gutkind JS: PTEN deficiency contributes
to the development and progression of head and neck cancer.
Neoplasia. 15:461–471. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Knopf A, Lempart J, Bas M, SlottaHuspenina
J, Mansour N and Fritsche MK: Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in young patients.
Oncotarget. 6:3443–3451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Regezi JA, Dekker NP, McMillan A,
RamirezAmador V, MenesesGarcia A, Ruiz-Godoy Rivera LM, Chrysomali
E and Ng IO: p53, p21, Rb, and MDM2 proteins in tongue carcinoma
from patients <35 versus >75 years. Oral Oncol. 35:379–383.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:(Database Issue). D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ryan BM, Robles AI and Harris CC: Genetic
variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:389–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV,
Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, et
al: miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:10.7554/eLife.05005. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP
and Wei WI: Mature miR-184 as Potential Oncogenic microRNA of
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2588–2592.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang L, Liu X, Chen Z, Jin Y, Heidbreder
CE, Kolokythas A, Wang A, Dai Y and Zhou X: MicroRNA-7 targets
IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) in tongue squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Biochem J. 432:199–205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu X, Yu J, Jiang L, Wang A, Shi F, Ye H
and Zhou X: MicroRNA-222 regulates cell invasion by targeting
matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) and manganese superoxide
dismutase 2 (SOD2) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.
Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 6:131–139. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu K, Liu X, Mao X, Xue L, Wang R, Chen L
and Chu X: MicroRNA-149 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration
and invasion by directly targeting forkhead box transcription
factor FOXM1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:499–515. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chan SH, Huang WC, Chang JW, Chang KJ, Kuo
WH, Wang MY, Lin KY, Uen YH, Hou MF, Lin CM, et al: MicroRNA-149
targets GIT1 to suppress integrin signaling and breast cancer
metastasis. Oncogene. 33:4496–4507. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Zheng X, Zhang Z, Zhou J, Zhao G,
Yang J, Xia L, Wang R, Cai X, Hu H, et al: MicroRNA-149 inhibits
proliferation and cell cycle progression through the targeting of
ZBTB2 in human gastric cancer. PLoS One. 7:e416932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pan SJ, Zhan SK, Pei BG, Sun QF, Bian LG
and Sun BM: MicroRNA-149 inhibits proliferation and invasion of
glioma cells via blockade of AKT1 signaling. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:871–881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin L, Hu WL, Jiang CC, Wang JX, Han CC,
Chu P, Zhang LJ, Thorne RF, Wilmott J, Scolyer RA, et al:
MicroRNA-149*, a p53-responsive microRNA, functions as an oncogenic
regulator in human melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:15840–15845. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ke Y, Zhao W, Xiong J and Cao R: miR-149
Inhibits Non-small-cell lung cancer cells EMT by targeting FOXM1.
Biochem Res Int. 2013:5067312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang WC and Hung JJ: Functional role of
post-translational modifications of Sp1 in tumorigenesis. J Biomed
Sci. 19:942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Zou WX and Chang KS: Inhibition of
Sp1 functions by its sequestration into PML nuclear bodies. PLoS
One. 9:e944502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yue L, Li L, Liu F, Hu N, Zhang W, Bai X,
Li Y, Zhang Y, Fu L, Zhang X and Ye L: The oncoprotein HBXIP
activates transcriptional coregulatory protein LMO4 via Sp1 to
promote proliferation of breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
34:927–935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin P, Zhao C, Li Z, Mei C, Yao W, Liu Y,
Li N, Qi J, Wang L, Shi Y, et al: Sp1 is involved in regulation of
cystathionine γ-lyase gene expression and biological function by
PI3K/Akt pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cell
Signal. 24:1229–1240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pathi S, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Nair V,
Lee SO and Safe S: Aspirin inhibits colon cancer cell and tumor
growth and downregulates specificity protein (Sp) transcription
factors. PLoS One. 7:e482082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Black AR, Black JD and Azizkhan-Clifford
J: Sp1 and kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in
cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 188:143–160.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li L, He S, Sun JM and Davie JR: Gene
regulation by Sp1 and Sp3. Biochem Cell Biol. 82:460–471. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mukhopadhyay D and Datta K: Multiple
regulatory pathways of vascular permeability factor/vascular
endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF) expression in tumors. Semin
Cancer Biol. 14:123–130. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu S, Liu Z, Xie Z, Pang J, Yu J, Lehmann
E, Huynh L, Vukosavljevic T, Takeki M, Klisovic RB, et al:
Bortezomib induces DNA hypomethylation and silenced gene
transcription by interfering with Sp1/NF-kappaB-dependent DNA
methyltransferase activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
111:2364–2373. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chadalapaka G, Jutooru I, Chintharlapalli
S, Papineni S, Smith R III, Li X and Safe S: Curcumin decreases
specificity protein expression in bladder cancer cells. Cancer Res.
68:5345–5354. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pathi SS, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G,
Sreevalsan S, Anand S, Thatcher GR and Safe S: GT-094, a NO-NSAID,
inhibits colon cancer cell growth by activation of a reactive
oxygen species-microRNA-27a: ZBTB10-specificity protein pathway.
Mol Cancer Res. 9:195–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hsu TI, Wang MC, Chen SY, Huang ST, Yeh
YM, Su WC, Chang WC and Hung JJ: Betulinic acid decreases
specificity protein 1 (Sp1) level via increasing the sumoylation of
sp1 to inhibit lung cancer growth. Mol Pharmacol. 82:1115–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jia L, Huang Y, Zheng Y, Lyu M, Zhang C,
Meng Z, Gan Y and Yu G: miR-375 inhibits cell growth and correlates
with clinical outcomes in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 33:2061–2071. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jia LF, Huang YP, Zheng YF, Lyu MY, Wei
SB, Meng Z and Gan YH: miR-29b suppresses proliferation, migration,
and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma through PTEN-AKT
signaling pathway by targeting Sp1. Oral Oncol. 50:1062–1071. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qiu T, Zhou X, Wang J, Du Y, Xu J, Huang
Z, Zhu W, Shu Y and Liu P: MiR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b inhibit
proliferation, migration, invasion and cell cycle progression via
targeting transcription factor Sp1 in gastric cancer. FEBS Lett.
588:1168–1177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo MM, Hu LH, Wang YQ, Chen P, Huang JG,
Lu N, He JH and Liao CG: miR-22 is down-regulated in gastric
cancer, and its overexpression inhibits cell migration and invasion
via targeting transcription factor Sp1. Med Oncol. 30:5422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang
X, Jiang L, Sun Z, Miao Z and Xu H: MicroRNA-335 acts as a
metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and
specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 31:1398–1407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu X, Li Y, Xie C, Yin X, Liu Y, Cao Y,
Fang Y, Lin X, Xu Y, Xu W, et al: miR-145 sensitizes ovarian cancer
cells to paclitaxel by targeting Sp1 and Cdk6. Int J Cancer.
135:1286–1296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Li M, Zang W, Ma Y, Wang N, Li P,
Wang T and Zhao G: MiR-429 up-regulation induces apoptosis and
suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal
carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 36:385–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang R, Luo H, Wang S, Chen W, Chen Z,
Wang HW, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhang X, Wu W, et al: MicroRNA-377
inhibited proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by
directly targeting specificity protein 1. Neuro Oncol.
16:1510–1522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cui W, Huang Z, He H, Gu N, Qin G, Lv J,
Zheng T, Sugimoto K and Wu Q: MiR-1188 at the imprinted Dlk1-Dio3
domain acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatoma cells. Mol Biol Cell.
26:1416–1427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|