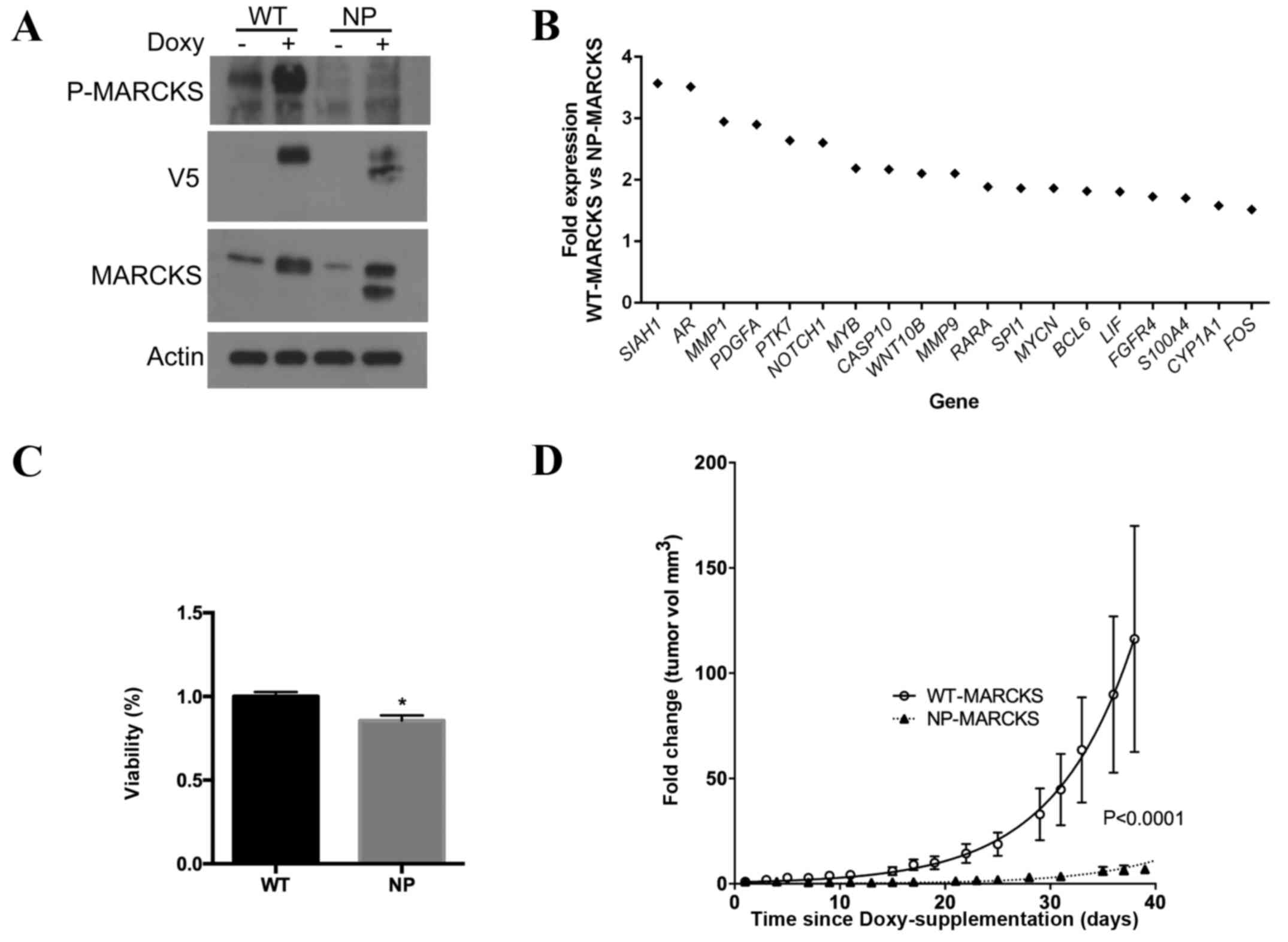
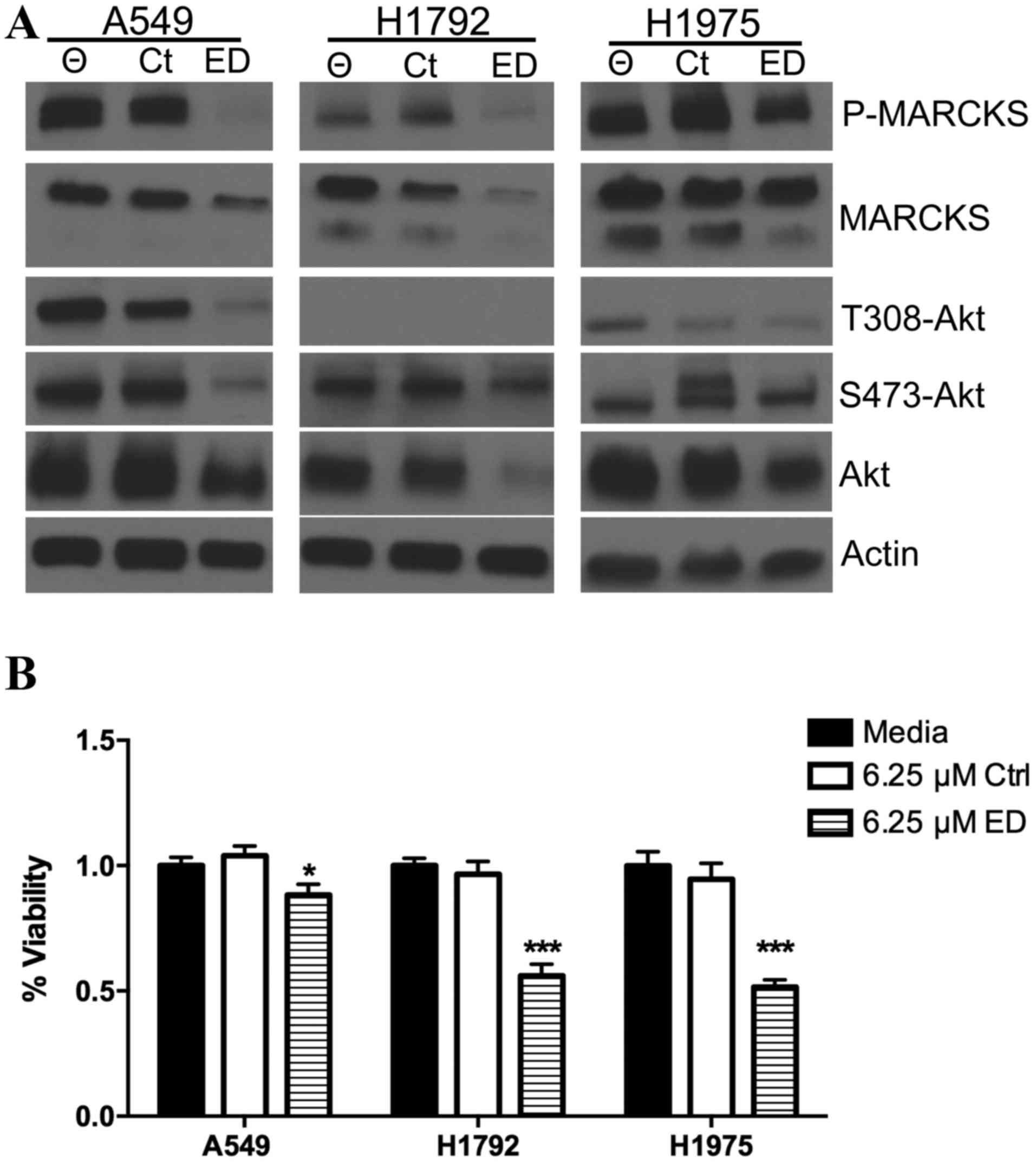
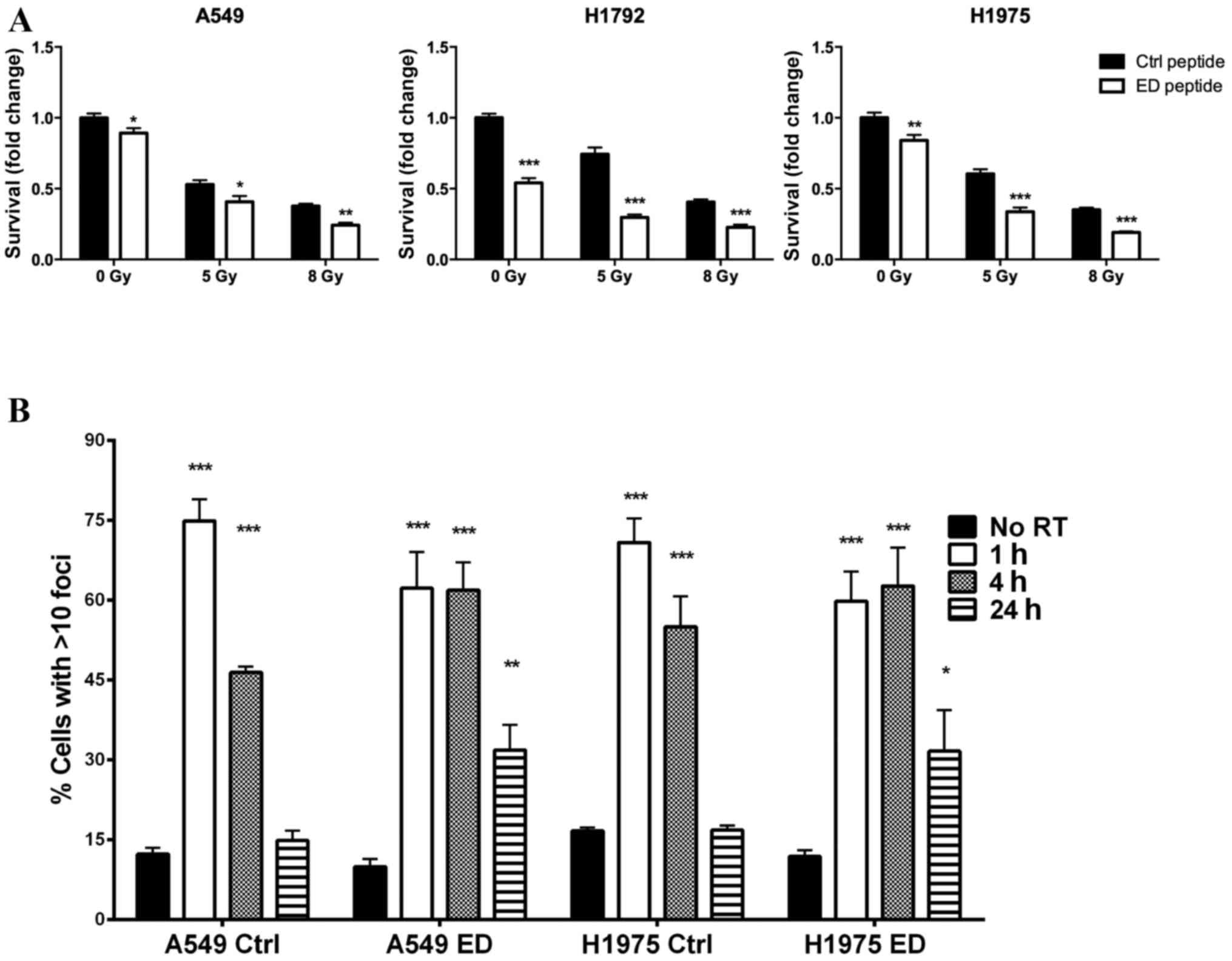
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Davies MA: Regulation, role, and targeting
of Akt in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:4715–4717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jarboe JS, Anderson JC, Duarte CW, Mehta
T, Nowsheen S, Hicks PH, Whitley AC, Rohrbach TD, McCubrey RO, Chiu
S, et al: MARCKS regulates growth and radiation sensitivity and is
a novel prognostic factor for glioma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3030–3041. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glaser M, Wanaski S, Buser CA, Boguslavsky
V, Rashidzada W, Morris A, Rebecchi M, Scarlata SF, Runnels LW,
Prestwich GD, et al: Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate
(MARCKS) produces reversible inhibition of phospholipase C by
sequestering phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in lateral
domains. J Biol Chem. 271:26187–26193. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aderem A: Signal transduction and the
actin cytoskeleton: The roles of MARCKS and profilin. Trends
Biochem Sci. 17:438–443. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stumpo DJ, Graff JM, Albert KA, Greengard
P and Blackshear PJ: Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for the bovine
myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS). Nucleic
Acids Res. 17:3987–3988. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heemskerk FM, Chen HC and Huang FL:
Protein kinase C phosphorylates Ser152, Ser156 and Ser163 but not
Ser160 of MARCKS in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
190:236–241. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gambhir A, Hangyás-Mihályné G, Zaitseva I,
Cafiso DS, Wang J, Murray D, Pentyala SN, Smith SO and McLaughlin
S: Electrostatic sequestration of PIP2 on phospholipid membranes by
basic/aromatic regions of proteins. Biophys J. 86:2188–2207. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Arbuzova A, Hangyás-Mihályné G and
McLaughlin S: The effector domain of myristoylated alanine-rich C
kinase substrate binds strongly to phosphatidylinositol
4,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 276:5012–5019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McLaughlin S and Aderem A: The
myristoyl-electrostatic switch: A modulator of reversible
protein-membrane interactions. Trends Biochem Sci. 20:272–276.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Manenti S, Sorokine O, Van Dorsselaer A
and Taniguchi H: Affinity purification and characterization of
myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS) from
bovine brain. Comparison of the cytoplasmic and the membrane-bound
forms. J Biol Chem. 267:22310–22315. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rohrbach TD, Jarboe JS, Anderson JC,
Trummell HQ, Hicks PH, Weaver AN, Yang ES, Oster RA, Deshane JS,
Steele C, et al: Targeting the effector domain of the myristoylated
alanine rich C-kinase substrate enhances lung cancer radiation
sensitivity. Int J Oncol. 46:1079–1088. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Graff JM, Rajan RR, Randall RR, Nairn AC
and Blackshear PJ: Protein kinase C substrate and inhibitor
characteristics of peptides derived from the myristoylated
alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) protein phosphorylation
site domain. J Biol Chem. 266:14390–14398. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Isayeva T, Xu J, Ragin C, Dai Q, Cooper T,
Carroll W, Dayan D, Vered M, Wenig B, Rosenthal E, et al: The
protective effect of p16(INK4a) in oral cavity carcinomas: p16
(Ink4A) dampens tumor invasion-integrated analysis of expression
and kinomics pathways. Mod Pathol. 28:631–653. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Malkov VA, Serikawa KA, Balantac N,
Watters J, Geiss G, Mashadi-Hossein A and Fare T: Multiplexed
measurements of gene signatures in different analytes using the
Nanostring nCounter Assay System. BMC Res Notes. 2:802009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Willey CD, Xiao D, Tu T, Kim KW, Moretti
L, Niermann KJ, Tawtawy MN, Quarles CC and Lu B: Enzastaurin
(LY317615), a protein kinase C beta selective inhibitor, enhances
antiangiogenic effect of radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
77:1518–1526. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cawthorne C, Swindell R, Stratford IJ,
Dive C and Welman A: Comparison of doxycycline delivery methods for
Tet-inducible gene expression in a subcutaneous xenograft model. J
Biomol Tech. 18:120–123. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ayers GD, McKinley ET, Zhao P, Fritz JM,
Metry RE, Deal BC, Adlerz KM, Coffey RJ and Manning HC: Volume of
preclinical xenograft tumors is more accurately assessed by
ultrasound imaging than manual caliper measurements. J Ultrasound
Med. 29:891–901. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jensen MM, Jørgensen JT, Binderup T and
Kjaer A: Tumor volume in subcutaneous mouse xenografts measured by
microCT is more accurate and reproducible than determined by
18F-FDG-microPET or external caliper. BMC Med Imaging. 8:162008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang ES, Wang H, Jiang G, Nowsheen S, Fu
A, Hallahan DE and Xia F: Lithium-mediated protection of
hippocampal cells involves enhancement of DNA-PK-dependent repair
in mice. J Clin Invest. 119:1124–1135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nowsheen S, Bonner JA and Yang ES: The
poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibitor ABT-888 reduces
radiation-induced nuclear EGFR and augments head and neck tumor
response to radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 99:331–338. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang ES, Nowsheen S, Wang T, Thotala DK
and Xia F: Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibition enhances
repair of DNA double-strand breaks in irradiated hippocampal
neurons. Neuro Oncol. 13:459–470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arbuzova A, Schmitz AA and Vergères G:
Cross-talk unfolded: MARCKS proteins. Biochem J. 362:1–12. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seykora JT, Myat MM, Allen LA, Ravetch JV
and Aderem A: Molecular determinants of the myristoyl-electrostatic
switch of MARCKS. J Biol Chem. 271:18797–18802. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Witsch E, Sela M and Yarden Y: Roles for
growth factors in cancer progression. Physiology (Bethesda).
25:85–101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cascorbi I, Brockmöller J and Roots I: A
C4887A polymorphism in exon 7 of human CYP1A1: Population
frequency, mutation linkages, and impact on lung cancer
susceptibility. Cancer Res. 56:4965–4969. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh
P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S,
et al: miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin
and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 12:247–256. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Westhoff B, Colaluca IN, D'Ario G,
Donzelli M, Tosoni D, Volorio S, Pelosi G, Spaggiari L, Mazzarol G,
Viale G, et al: Alterations of the Notch pathway in lung cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:22293–22298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bickeboller M, Tagscherer KE, Kloor M,
Jansen L, Chang-Claude J, Brenner H, Hoffmeister M, Toth C,
Schirmacher P, Roth W and Bläker H: Functional characterization of
the tumor-suppressor MARCKS in colorectal cancer and its
association with survival. Oncogene. 34:1150–1159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Browne BC, Hochgräfe F, Wu J, Millar EK,
Barraclough J, Stone A, McCloy RA, Lee CS, Roberts C, Ali NA, et
al: Global characterization of signalling networks associated with
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. FEBS J. 280:5237–5257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Techasen A, Loilome W, Namwat N, et al:
Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate phosphorylation
promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis via the
protein kinase C-dependent pathwayCancer Sci. England: pp.
pp658–pp665. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wright PE and Dyson HJ: Intrinsically
unstructured proteins: Re-assessing the protein structure-function
paradigm. J Mol Biol. 293:321–331. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen CH, Chiu CL, Adler KB and Wu R: A
novel predictor of cancer malignancy: Up-regulation of
myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate phosphorylation in
lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 189:1002–1004. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hanada S, Kakehashi A, Nishiyama N, Wei M,
Yamano S, Chung K, Komatsu H, Inoue H, Suehiro S and Wanibuchi H:
Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate as a prognostic
biomarker in human primary lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Biomark. 13:289–298. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen CH, Thai P, Yoneda K, Adler KB, Yang
PC and Wu R: A peptide that inhibits function of Myristoylated
Alanine-Rich C Kinase Substrate (MARCKS) reduces lung cancer
metastasis. Oncogene. 33:3696–3706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang HJ, Kim N, Seong KM, Youn H and Youn
B: Investigation of radiation-induced transcriptome profile of
radioresistant non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells using RNA-seq.
PloS One. 8:e593192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shanker M, Willcutts D and Roth JA: Drug
resistance in lung cancer. Lung Cancer: Targets and Therapy.
1:23–36. 2010.
|
|
41
|
Schuurbiers OC, Kaanders JH, van der
Heijden HF, Dekhuijzen RP, Oyen WJ and Bussink J: The
PI3-K/AKT-pathway and radiation resistance mechanisms in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 4:761–767. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garraway LA and Jänne PA: Circumventing
cancer drug resistance in the era of personalized medicine. Cancer
Discov. 2:214–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|