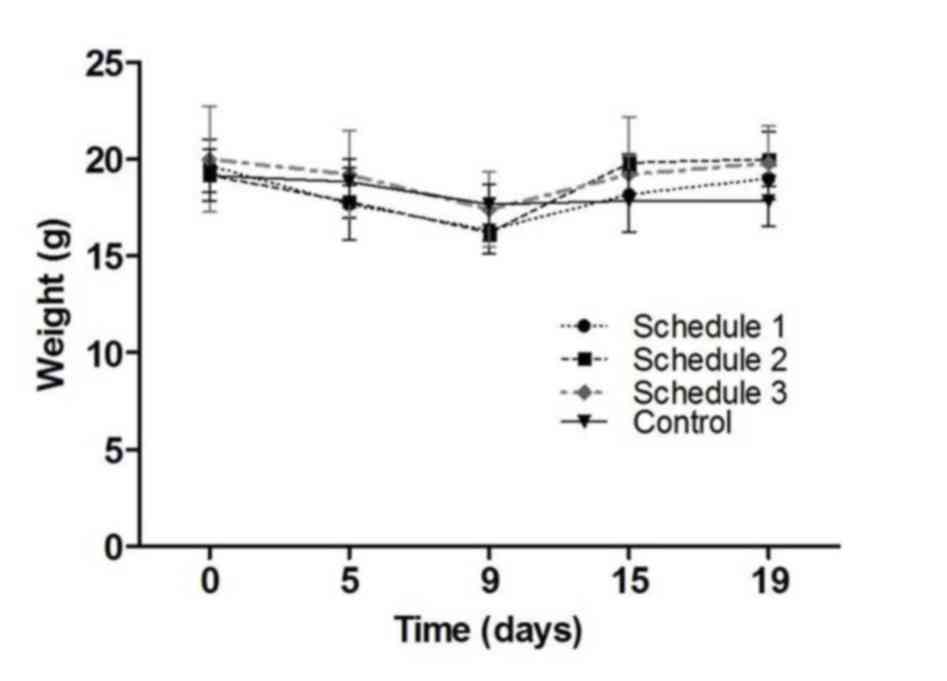
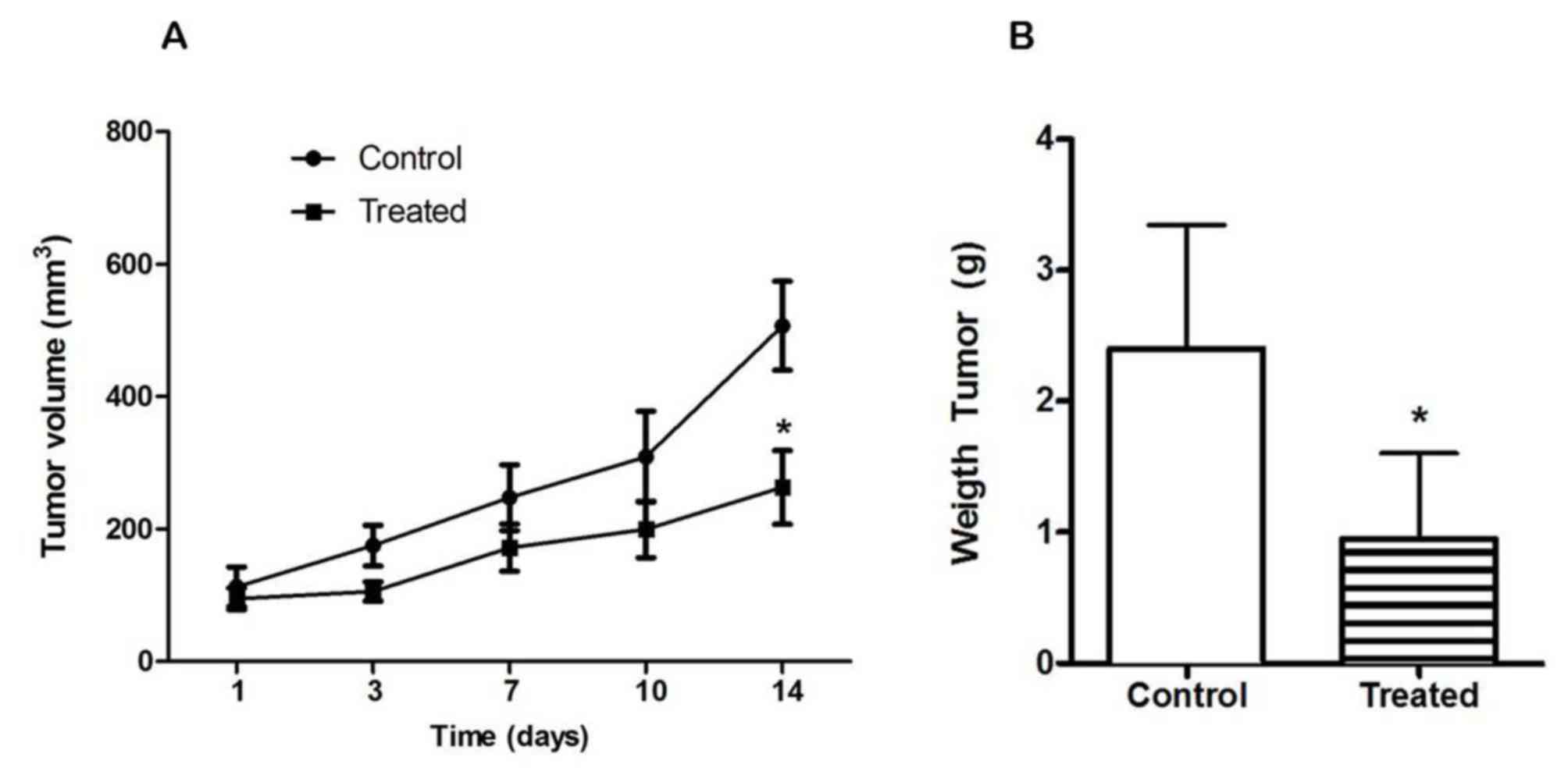
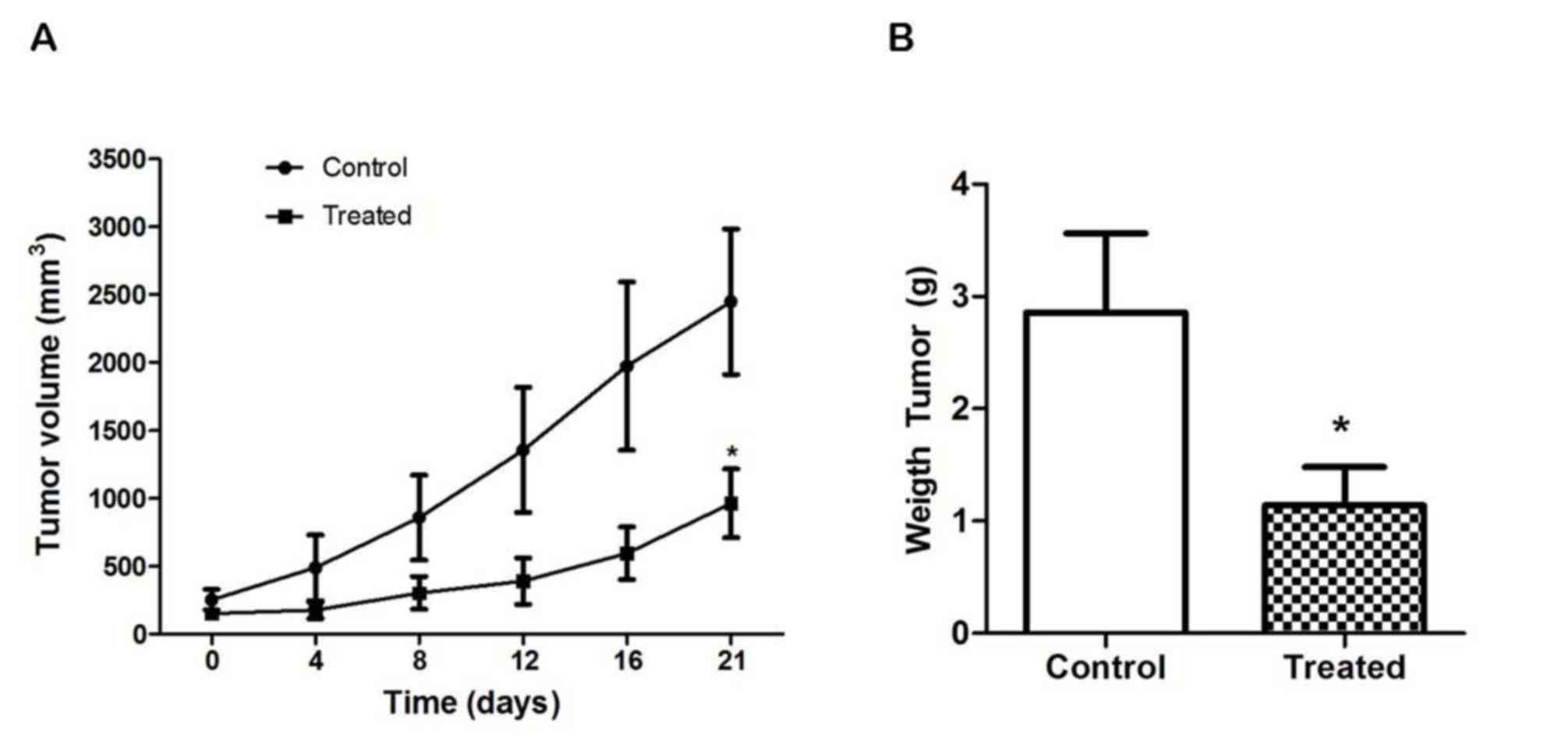
|
1
|
Chen JQ and Russo J: Dysregulation of
glucose transport, glycolysis, TCA cycle and glutaminolysis by
oncogenes and tumor suppressors in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1826:370–384. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moncada S, Higgs EA and Colombo SL:
Fulfilling the metabolic requirements for cell proliferation.
Biochem J. 446:1–7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Fatty acid
synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:763–767. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tan NL and Seyfried TN: Influence of serum
and hypoxia on incorporation of [(14)C]-D-glucose or
[(14)C]-L-glutamine into lipids and lactate in murine glioblastoma
cells. Lipids. 50:1167–1184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cervantes-Madrid D, Romero Y and
Dueñas-González A: Reviving lonidamine and
6-Diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine to be used in combination for metabolic
cancer therapy. Biomed Res Int. 2015:6904922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lupu R and Menendez JA: Pharmacological
inhibitors of fatty acid synthase (FASN)-catalyzed endogenous fatty
acid biogenesis: A new family of anti-cancer agents? Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 7:483–493. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kridel SJ, Axelrod F, Rozenkrantz N and
Smith JW: Orlistat is a novel inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with
antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 64:2070–2075. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Flavin R, Peluso S, Nguyen PL and Loda M:
Fatty acid synthase as a potential therapeutic target in cancer.
Future Oncol. 6:551–562. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cervantes-Madrid D and Dueñas-González A:
Antitumor effects of a drug combination targeting glycolysis,
glutaminolysis and de novo synthesis of fatty acids. Oncol Rep.
34:1533–1542. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M and Ahmad N: Dose
translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J.
22:659–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elf SE and Chen J: Targeting glucose
metabolism in patients with cancer. Cancer. 120:774–780. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin L, Alesi GN and Kang S: Glutaminolysis
as a target for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 35:3619–3625. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deepa PR, Vandhana S, Jayanthi U and
Krishnakumar S: Therapeutic and toxicologic evaluation of
anti-lipogenic agents in cancer cells compared with non-neoplastic
cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 110:494–503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S and Geschwind JF:
Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: Progress and
prospects. Mol Cancer. 12:1522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Di Cosimo S, Ferretti G, Papaldo P,
Carlini P, Fabi A and Cognetti F: Lonidamine: Efficacy and safety
in clinical trials for the treatment of solid tumors. Drugs Today
(Barc). 39:157–174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dwarakanath BS, Singh D, Banerji AK, Sarin
R, Venkataramana NK, Jalali R, Vishwanath PN, Mohanti BK, Tripathi
RP, Kalia VK and Jain V: Clinical studies for improving
radiotherapy with 2-deoxy-D-glucose: Present status and future
prospects. J Cancer Res Ther. 5:(Suppl 1). S21–S26. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garon EB, Christofk HR, Hosmer W, Britten
CD, Bahng A, Crabtree MJ, Hong CS, Kamranpour N, Pitts S,
Kabbinavar F, et al: Dichloroacetate should be considered with
platinum-based chemotherapy in hypoxic tumors rather than as a
single agent in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 140:443–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Catane R, Von Hoff DD, Glaubiger DL and
Muggia FM: Azaserine, DON, and azotomycin: Three diazo analogs of
L-glutamine with clinical antitumor activity. Cancer Treat Rep.
63:1033–1038. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Unger C, Mueller C, Bausch MP,
Krzemieniecki K, Ochenduszko S, Wilk B, Jaeger E and Al-Batran S: A
phase I schedule optimization study of pegylated glutaminase
(PEG-PGA) plus 6-diazo-5-oxo-l-norleucine (DON) in patients (pts)
with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 29:(Suppl) abstr 3049.
2011.
|
|
20
|
Griffiths M, Keast D, Patrick G, Crawford
M and Palmer TN: The role of glutamine and glucose analogues in
metabolic inhibition of human myeloid leukaemia in vitro. Int J
Biochem. 25:1749–1755. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paulmurugan R, Bhethanabotla R, Mishra K,
Devulapally R, Foygel K, Sekar TV, Ananta JS, Massoud TF and Joy A:
Folate receptor targeted polymeric micellar nanocarriers for
delivery of orlistat as a repurposed drug against triple negative
breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:221–231. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhi J, Mulligan TE and Hauptman JB:
Long-term systemic exposure of orlistat, a lipase inhibitor, and
its metabolites in obese patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 39:41–46.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
De Cesare M, Pratesi G, Giusti A, Polizzi
D and Zunino F: Stimulation of the apoptotic response as a basis
for the therapeutic synergism of lonidamine and cisplatin in
combination in human tumour xenografts. Br J Cancer. 77:434–439.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nath K, Nelson DS, Heitjan DF, Leeper DB,
Zhou R and Glickson JD: Lonidamine induces intracellular tumor
acidification and ATP depletion in breast, prostate and ovarian
cancer xenografts and potentiates response to doxorubicin. NMR
Biomed. 28:281–290. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ovejera AA, Houchens DP, Catane R,
Sheridan MA and Muggia FM: Efficacy of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine
and N-(N-gamma-glutamyl-6-diazo-5-oxo-norleucinyl)-6-diazo-5-
oxo-norleucine against experimental tumors in conventional and nude
mice. Cancer Res. 39:3220–3224. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heiden MG Vander: Targeting cancer
metabolism: A therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
10:671–684. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo L, Shestov AA, Worth AJ, Nath K,
Nelson DS, Leeper DB, Glickson JD and Blair IA: Inhibition of
mitochondrial complex II by the anti-cancer agent lonidamine. J
Biol Chem. 291:42–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Assanhou AG, Li W, Zhang L, Xue L, Kong L,
Sun H, Mo R and Zhang C: Reversal of multidrug resistance by
co-delivery of paclitaxel and lonidamine using a TPGS and
hyaluronic acid dual-functionalized liposome for cancer treatment.
Biomaterials. 73:284–295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Olsen RR, Mary-Sinclair MN, Yin Z and
Freeman KW: Antagonizing Bcl-2 family members sensitizes
neuroblastoma and Ewing's sarcoma to an inhibitor of glutamine
metabolism. PLoS One. 10:e01169982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|