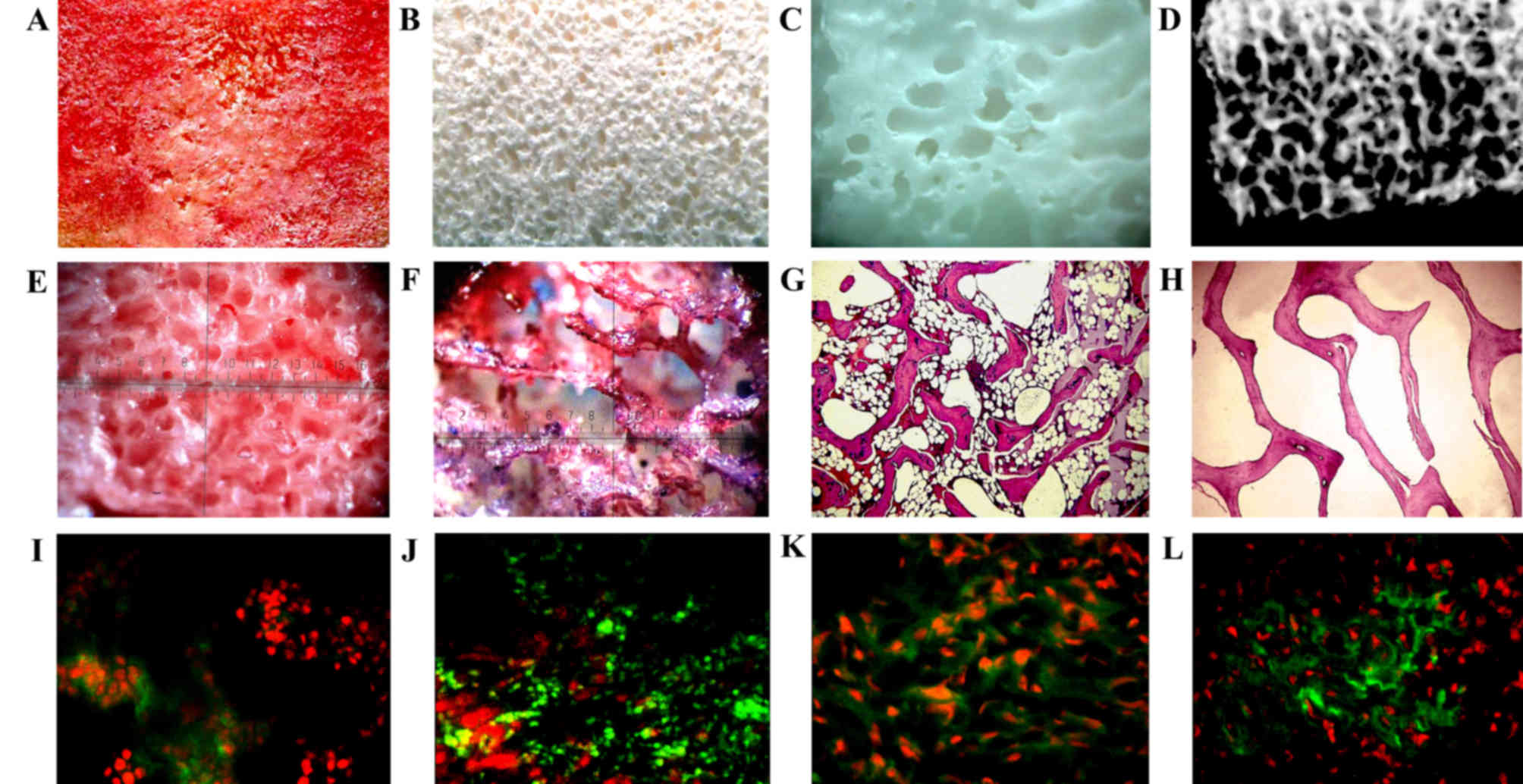
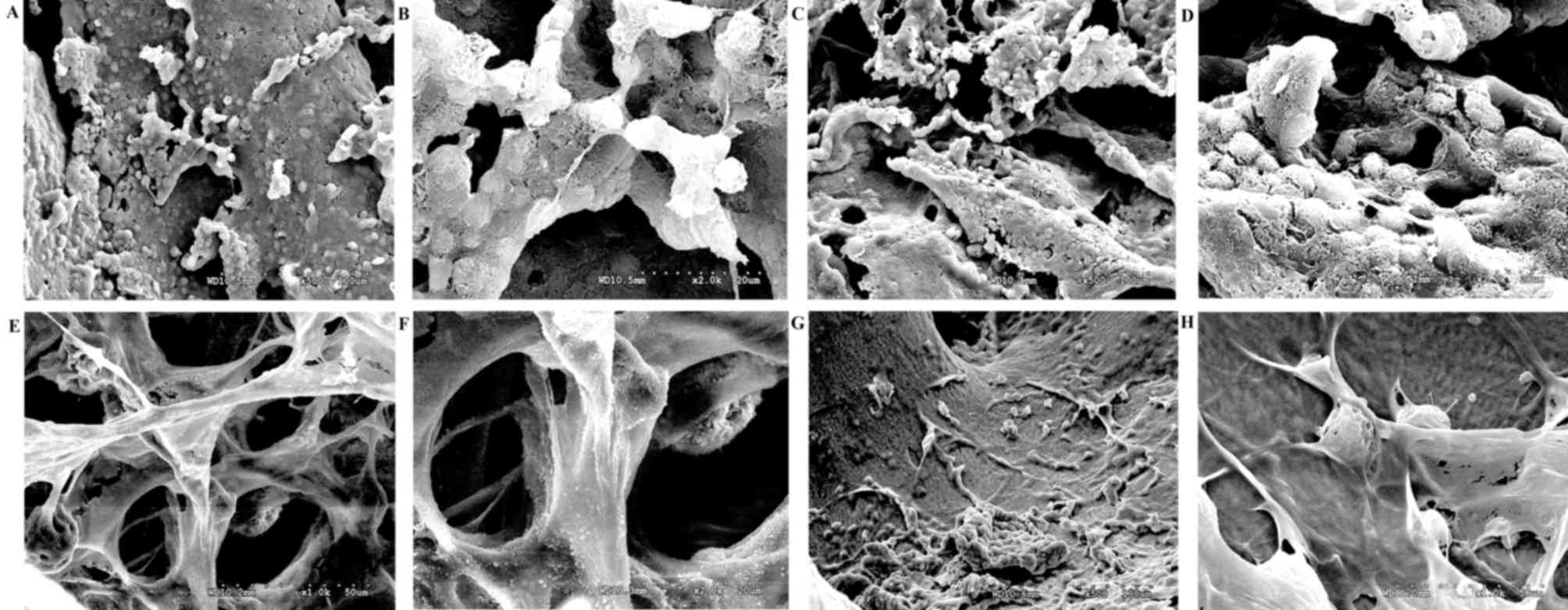
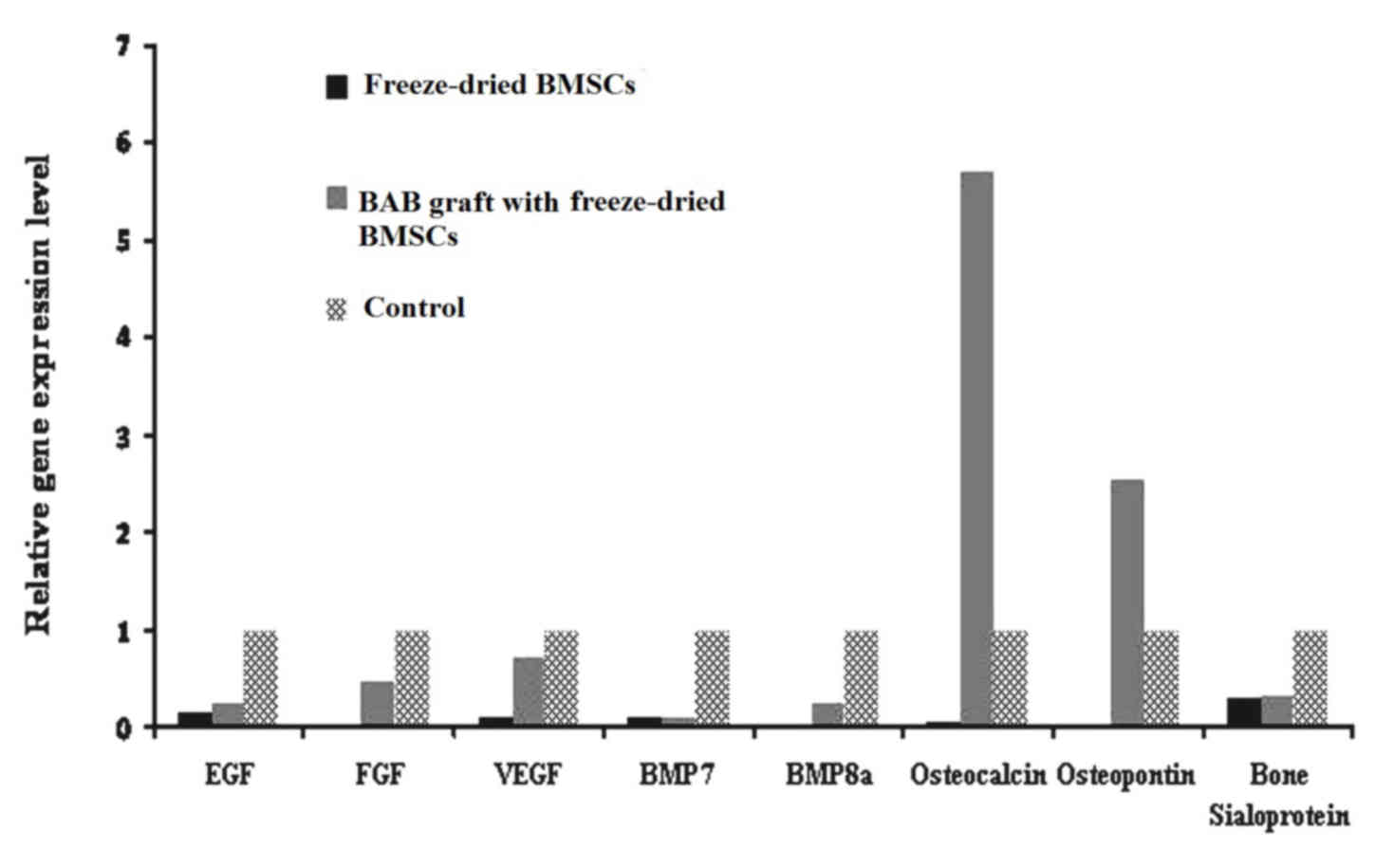
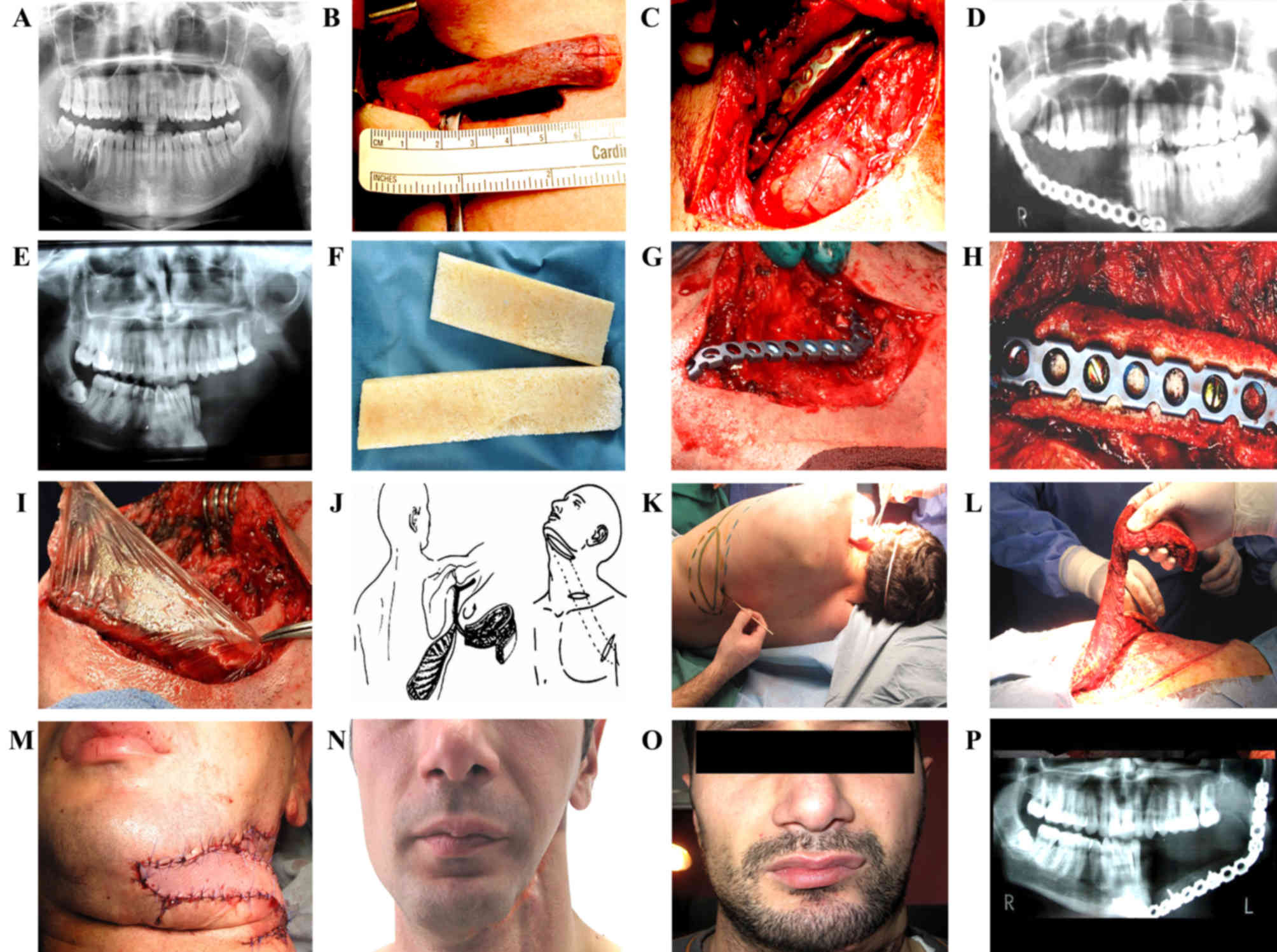
|
1
|
Chim H, Salgado CJ, Mardini S and Chen HC:
Reconstruction of mandibular defects. Semin Plast Surg. 24:188–197.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yap YL, Lim J, Ong WC, Yeo M, Lee H and
Lim TC: Stabilization of mobile mandibular segments in mandibular
reconstruction: Use of spanning reconstruction plate.
Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 5:123–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clokie CM and Sándor GK: Reconstruction of
10 major mandibular defects using bioimplants containing BMP-7. J
Can Dent Assoc. 4:67–72. 2008.
|
|
4
|
Frohlich M, Grayson WL, Wan LQ, Marolt D,
Drobnic M and Vunjak-Novakovic G: Tissue engineered bone grafts:
Biological requirements, tissue culture and clinical relevance.
Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 3:254–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Finkemeier CG: Bone-grafting and
bone-graft substitutes. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A. 454–464. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kaláb M, Karkoška J, Kamínek M and Šantavý
P: Successful three-year outcome in a patient with allogenous
sternal bone graft in the treatment of massive post-sternotomy
defects. Int J Surg Case Rep 7C. 6–9. 2014.
|
|
7
|
Schleicher I, Lips KS, Sommer U, Schappat
I, Martin AP, Szalay G and Schnettler R: Allogenous bone with
collagen for repair of deep osteochondral defects. J Surg Res.
185:667–675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gomes KU, Carlini JL, Biron C, Rapoport A
and Dedivitis RA: Use of allogeneic bone graft in maxillary
reconstruction for installation of dental implants. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 66:2335–2358. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oryan A, Alidadi S, Moshiri A and Maffulli
N: Bone regenerative medicine: Classic options, novel strategies
and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res. 9:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Friesenbichler J, Maurer-Ertl W, Sadoghi
P, Pirker-Fruehauf U, Bodo K and Leithner A: Adverse reactions of
artificial bone graft substitutes: Lessons learned from using
tricalcium phosphate geneXR. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 472:976–682.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han F, Dong Y, Su Z, Yin R, Song A and Li
S: Preparation, characteristics and assessment of a novel
gelatin-chitosan sponge scaffold as skin tissue engineering
material. Int J Pharm. 476:124–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Noth U, Schupp K, Heymer A, Kall S, Jakob
F, Schütze N, Baumann B, Barthel T, Eulert J and Hendrich C:
Anterior cruciate ligament constructs fabricated from human
mesenchymal stem cells in a collagen type I hydrogel. Cytotherapy.
7:447–455. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mohan N, Nair PD and Tabata Y: A 3D
biodegradable protein based matrix for cartilage tissue engineering
and stem cell differentiation to cartilage. J Mater Sci Mater Med.
20:(Suppl 1). S49–S60. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fröhlich M, Grayson WL, Marolt D, Gimble
JM, Kregar-Velikonja N and Vunjak-Novakovic G: Bone grafts
engineered from human adipose-derived stem cells in perfusion
bioreactor culture. Tissue Eng Part A. 16:179–189. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Ahmad S, Shu XZ, Sanders RK,
Kopesec SA and Prestwich GD: Accelerated repair of cortical bone
defects using a synthetic extracellular matrix to deliver human
demineralized bone matrix. J Orthop Res. 24:1454–1462. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kinoshita Y and Maeda H: Recent
developments of functional scaffolds for craniomaxillofacial bone
tissue engineering applications. ScientificWorldJournal.
2013:8631572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang SZ, Qian H, Wang Z, Fan JL, Zhou Q,
Chen GM, Li R, Fu S and Sun J: Preliminary study on the
freeze-drying of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 11:889–894. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fisher JN, Peretti GM and Scotti C: Stem
cells for bone regeneration: From cell-based therapies to
decellularised engineered extracellular matrices. Stem Cells Int.
2016:93525982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ward MA, Kaneko T, Kusakabe H, Biggers JD,
Whittingham DG and Yanagimachi R: Long-term preservation of mouse
spermatozoa after freeze-drying and freezing without
cryoprotection. Biol Reprod. 69:2100–2108. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Natan D, Nagler A and Arav A:
Freeze-drying of mononuclear cells derived from umbilical cord
blood followed by colony formation. PLoS One. 4:e52402009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Linero I and Chaparro O: Paracrine effect
of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue in bone
regeneration. PLoS One. 9:e1070012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nowotny J, Farack J, Vater C, Johnsen M,
Gelinsky M, Tonn T and Kasten P: Translation of cell therapy into
clinical practice: Validation of an application procedure for bone
marrow progenitor cells and platelet rich plasma. J Appl Biomater
Funct Mater. 14:e1–e8. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Liang X, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Tse HF and Lian
Q: Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy:
Current status and perspectives. Cell Transplant. 23:1045–1059.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng Y, Xuan M, Zou J, Liu H, Zhuo Z, Wan
Y and Cheng B: Freeze-dried rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
paracrine factors: A simplified novel material for skin wound
therapy. Tissue Eng Part A. 21:1036–1046. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Burdon TJ, Paul A, Noiseux N, Prakash S
and Shum-Tim D: Bone marrow stem cell derived paracrine factors for
regenerative medicine: Current perspectives and therapeutic
potential. Bone Marrow Res. 2011:2073262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kakabadze Z, Mardaleishvili K, Loladze G,
Javakhishvili I, Chakhunashvili K, Karalashvili L, Sukhitashvili N,
Chutkerashvili G, Kakabadze A and Chakhunashvili D: Clinical
application of decellularized and lyophilized human amnion/chorion
membrane grafts for closing post-laryngectomy pharyngocutaneous
fistulas. J Surg Oncol. 113:538–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu S, Zhu Q, Liu X, Yang W, Jian Y, Zhou
X, He B, Gu L, Yan L, Lin T, et al: Three-dimensional
reconstruction of the microstructure of human acellular nerve
allograft. Sci Rep. 6:306942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim BR, Nam HY, Kim SU, Kim SI and Chang
YJ: Normalization of reverse transcription quantitative-PCR with
housekeeping genes in rice. Biotechnol Lett. 25:1869–1872. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–88. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lawrence BJ and Madihally SV: Cell
colonization in degradable 3D porous matrices. Cell Adh Migr.
2:9–16. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sterling JA and Guelcher SA: Biomaterial
scaffolds for treating osteoporotic bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep.
12:48–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zou W and Chen X: Osteogenesis and
ototoxicity of a novel preparation of autogenous bone cement:
Implications for mastoid obliteration. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
151:1020–1027. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tde M Tera, Prado RF, De Marco AC,
Santamaria MP and Jardini MA: The RANK/RANKL/OPG interaction in the
repair of autogenous bone grafts in female rats with estrogen
deficiency. Braz Oral Res. 28:S1806-83242014000100261. 2014.
|
|
34
|
Bastos AS, Spin-Neto R, Conte-Neto N,
Galina K, Boeck-Neto RJ, Marcantonio C, Marcantonio E and
Marcantonio E Jr: Calvarial autogenous bone graft for maxillary
ridge and sinus reconstruction for rehabilitation with dental
implants. J Oral Implantol. 40:469–478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Al-Nawas B and Schiegnitz E: Augmentation
procedures using bone substitute materials or autogenous bone-a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Oral Implantol. 7:(Suppl
2). S219–S234. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Koerdt S, Siebers J, Bloch W, Ristow O,
Kuebler AC and Reuther T: Immunohistochemial study on the
expression of von Willebrand factor (vWF) after onlay autogenous
iliac grafts for lateral alveolar ridge augmentation. Head Face
Med. 9:402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pogrel MA, Podlesh S, Anthony JP and
Alexander J: A comparison of vascularized and nonvascularized bone
grafts for reconstruction of mandibular continuity defects. J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 55:1200–1206. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pennington EC, Dionigi B, Gray FL, Ahmed
A, Brazzo J, Dolinko A, Calderon N, Darrah T, Zurakowski D,
Nazarian A, et al: Limb reconstruction with decellularized,
non-demineralized bone in a young leporine model. Biomed Mater.
10:0150212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gawlitta D, Benders KE, Visser J, van der
Sar AS, Kempen DH, Theyse LF, Malda J and Dhert WJ: Decellularized
cartilage-derived matrix as substrate for endochondral bone
regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 21:694–703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hoffman MD, Van Hove AH and Benoit DS:
Degradable hydrogels for spatiotemporal control of mesenchymal stem
cells localized at decellularized bone allografts. Acta Biomater.
10:3431–3441. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gardin C, Ricci S, Ferroni L, Guazzo R,
Sbricoli L, De Benedictis G, Finotti L, Isola M, Bressan E and
Zavan B: Decellularization and delipidation protocols of bovine
bone and pericardium for bone grafting and guided bone regeneration
procedures. PLoS One. 10:e01323442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Quan TM, Vu DN, My NTN and Ha TLB:
Decellularization of xenogenic bone grafts for potential use as
tissue engineering scaffolds. International Journal of Life Science
and Medical Research Aug. 4:38–45. 2014.
|
|
43
|
Chatterjea A, Meijer G, van Blitterswijk C
and de Boer J: Clinical application of human mesenchymal stromal
cells for bone tissue engineering. Stem Cells Int. 215–625.
2010.
|
|
44
|
Salem HK and Thiemermann C: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: Current understanding and clinical status. Stem
Cells. 28:585–596. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen Y, Shao JZ, Xiang LX, Dong XJ and
Zhang GR: Mesenchymal stem cells: A promising candidate in
regenerative medicine. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:815–820. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lda S Meirelles, Fontes AM, Covas DT and
Caplan AI: Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of
mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:419–427.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hocking AM and Gibran NS: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Paracrine signaling and differentiation during cutaneous
wound repair. Exp Cell Res. 316:2213–2219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, Lee CW,
Barr S, Fuchs S and Epstein SE: Marrow-derived stromal cells
express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines
and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine
mechanisms. Circ Res. 94:678–685. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rehman J, Traktuev D, Li J, Merfeld-Clauss
S, Temm-Grove CJ, Bovenkerk JE, Pell CL, Johnstone BH, Considine RV
and March KL: Secretion of angiogenic and antiapoptotic factors by
human adipose stromal cells. Circulation. 109:1292–1298. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Takahashi M, Li TS, Suzuki R, Kobayashi T,
Ito H, Ikeda Y, Matsuzaki M and Hamano K: Cytokines produced by
bone marrow cells can contribute to functional improvement of the
infarcted heart by protecting cardiomyocytes from ischemic injury.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H8862006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li W, Ma G, Brazile B, Li N, Dai W, Butler
JR, Claude AA, Wertheim JA, Liao J and Wang B: Investigating the
potential of amnion-based scaffolds as a barrier membrane for
guided bone regeneration. Langmuir. 31:8642–8653. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ducheyne P, De Meester P and Aernoudt E:
Influence of a functional dynamic loading on bone ingrowth into
surface pores of orthopedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res.
11:811–838. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Heck D, Nakajima I, Kelly P and Chao E:
The effect of load alteration on the biological and biomechanical
performance of a titanium fiber-metal segmental prosthesis. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 68:118–126. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gutta R, Baker RA, Bartolucci AA and Louis
PJ: Barrier membranes used for ridge augmentation: Is there an
optimal pore size? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 67:1218–1225. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Amano Y, Ota M, Sekiguchi K, Shibukawa Y
and Yamada S: Evaluation of a poly-l-lactic acid membrane and
membrane fixing pin for guided tissue regeneration on bone defects
in dogs. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
97:155–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
von Arx T, Cochran DL, Hermann JS, Schenk
RK and Buser D: Lateral ridge augmentation using different bone
fillers and barrier membrane application. A histologic and
histomorphometric pilot study in the canine mandible. Clin Oral
Implants Res. 12:260–269. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|