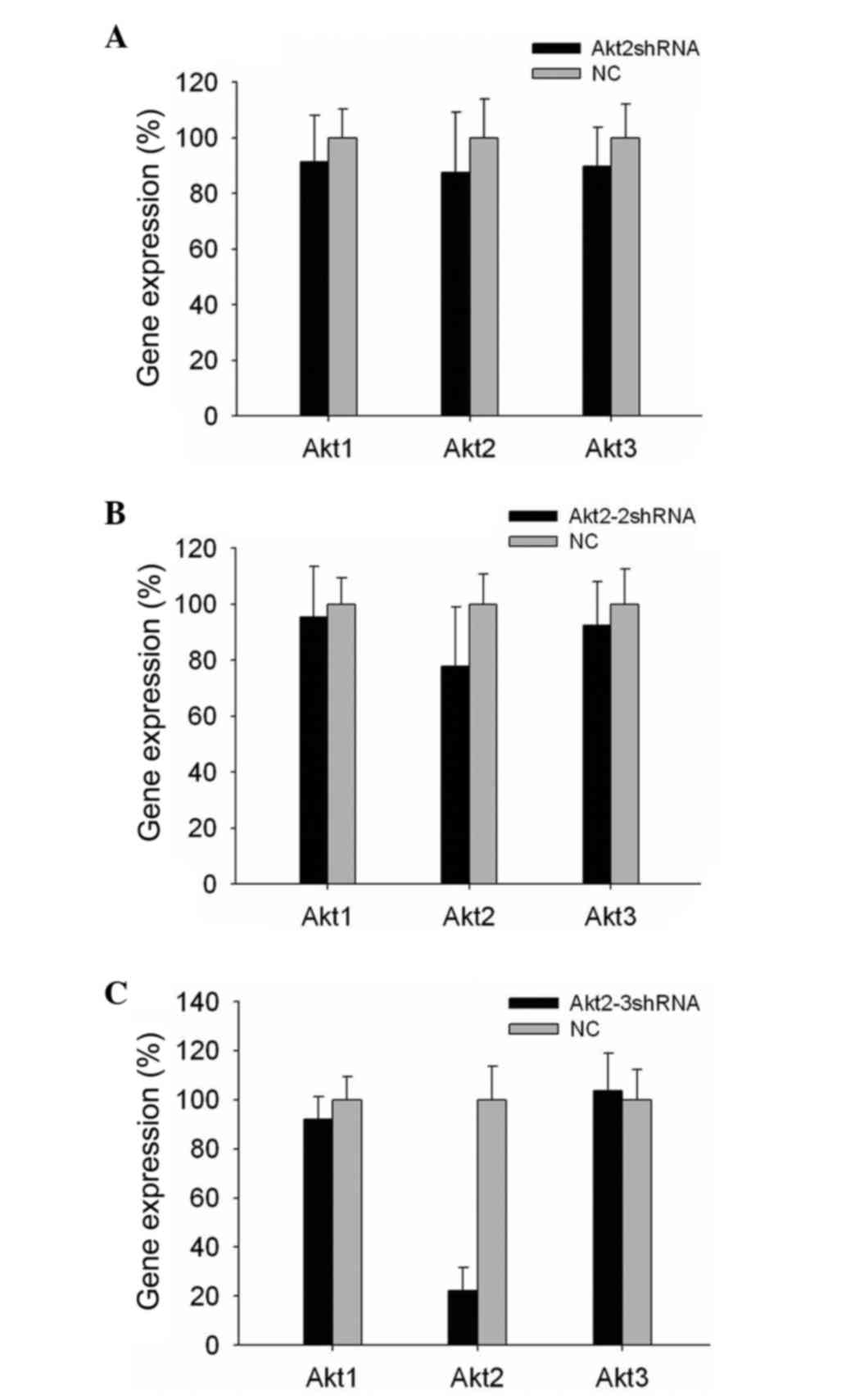
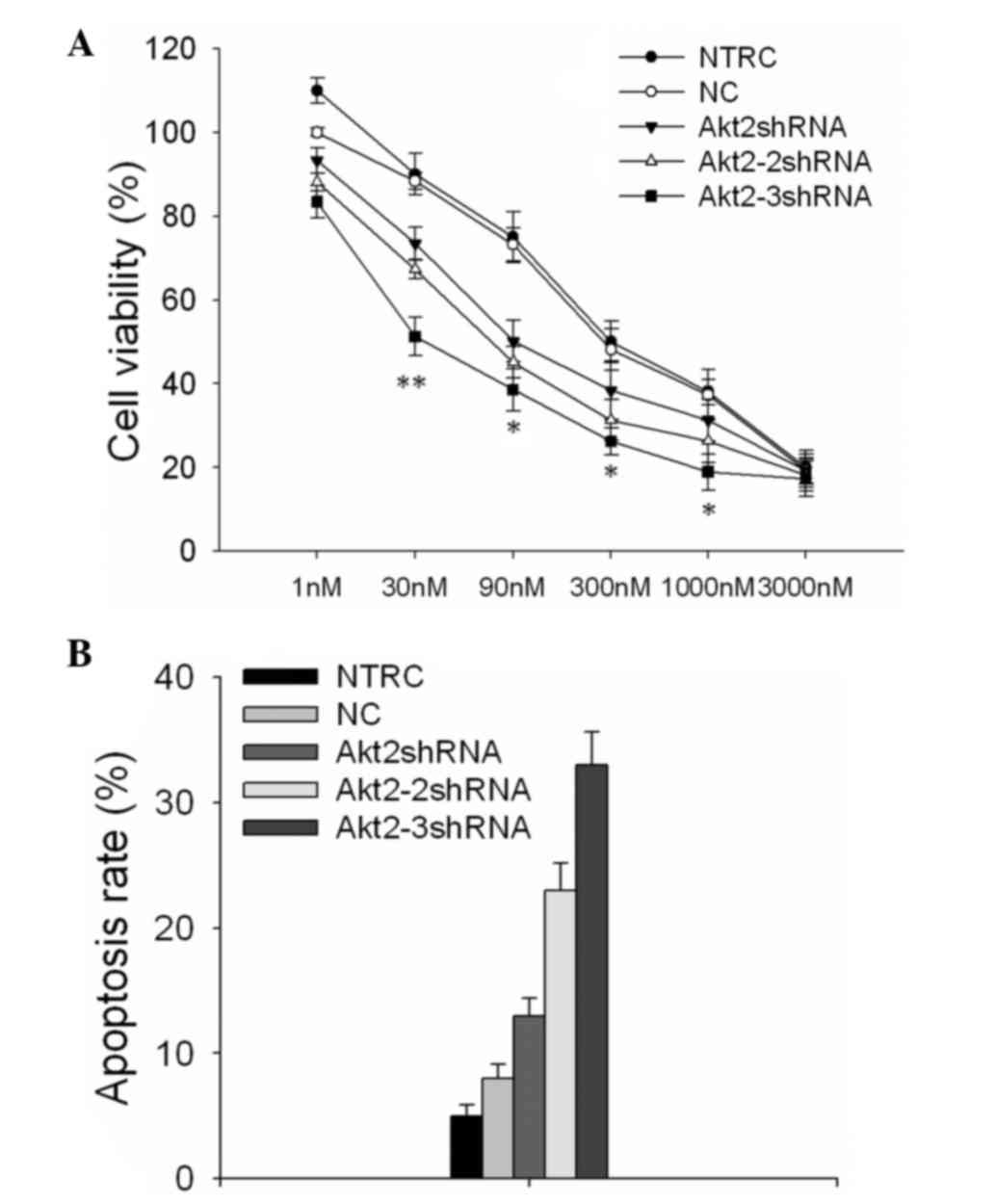
|
1
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W,
Yalcin A, Weber K and Tuschl T: Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs
mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature.
411:494–498. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Crombez L and Divita G: A non-covalent
peptide-based strategy for siRNA delivery. Methods Mol Biol.
683:349–360. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shan G, Li Y, Zhang J, Li W, Szulwach KE,
Duan R, Faghihi MA, Khalil AM, Lu L, Paroo Z, et al: A small
molecule enhances RNA interference and promotes microRNA
processing. Nat Biotechnol. 26:933–940. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, Kim SY,
Kloepfer AM, Hinkle G, Piqani B, Eisenhaure TM, Luo B, Grenier JK,
et al: A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied
to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell. 124:1283–1298. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ku SH, Jo SD, Lee YK, Kim K and Kim SH:
Chemical and structural modifications of RNAi therapeutics. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 104:16–28. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khandelwal N, Breinig M, Speck T, Michels
T, Kreutzer C, Sorrentino A, Sharma AK, Umansky L, Conrad H,
Poschke I, et al: A high-throughput RNAi screen for detection of
immune-checkpoint molecules that mediate tumor resistance to
cytotoxic T lymphocytes. EMBO Mol Med. 7:450–463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cho JS, Kim YC and Morrison SL: Inhibitors
of MyD88-dependent proinflammatory cytokine production identified
utilizing a novel RNA interference screening approach. PLoS One.
4:e70292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du C, Ge B, Liu Z, Fu K, Chan WC and
McKeithan TW: PCR-based generation of shRNA libraries from cDNAs.
BMC Biotechnol. 6:282006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scherer LJ, Yildiz Y, Kim J, Cagnon L,
Heale B and Rossi JJ: Rapid assessment of anti-HIV siRNA efficacy
using PCR-derived pol III shRNA cassettes. Mol Ther. 10:597–603.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berns K, Hijmans EM, Mullenders J,
Brummelkamp TR, Velds A, Heimerikx M, Kerkhoven RM, Madiredjo M,
Nijkamp W, Weigelt B, et al: A large-scale RNAi screen in human
cells identifies new components of the p53 pathway. Nature.
428:431–437. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stewart SA, Dykxhoorn DM, Palliser D,
Mizuno H, Yu EY, An DS, Sabatini DM, Chen IS, Hahn WC, Sharp PA, et
al: Lentivirus-delivered stable gene silencing by RNAi in primary
cells. RNA. 9:493–501. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klinghoffer RA, Roberts B, Annis J,
Frazier J, Lewis P, Linsley PS and Cleary MA: An optimized
lentivirus-mediated RNAi screen reveals kinase modulators of
kinesin-5 inhibitor sensitivity. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 6:105–119.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang YH, Wang ZX, Qiu Y, Xiong J, Chen YX,
Miao DS and De W: Lentivirus-mediated RNAi knockdown of
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibits growth, reduces
invasion, and enhances radiosensitivity in human osteosarcoma
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 327:257–266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xing H, Weng D, Chen G, Tao W, Zhu T, Yang
X, Meng L, Wang S, Lu Y and Ma D: Activation of
fibronectin/PI-3K/Akt2 leads to chemoresistance to docetaxel by
regulating survivin protein expression in ovarian and breast cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 261:108–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weng D, Song X, Xing H, Ma X, Xia X, Weng
Y, Zhou J, Xu G, Meng L, Zhu T, et al: Implication of the
Akt2/survivin pathway as a critical target in paclitaxel treatment
in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 273:257–265. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Manche L, Green SR, Schmedt C and Mathews
MB: Interactions between double-stranded-RNA regulators and the
protein-kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 12:5238–5248. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Williams BR: Role of the double-stranded
RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) in cell regulation. Biochem Soc
Trans. 25:509–513. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uprichard SL: The therapeutic potential of
RNA interference. FEBS Lett. 579:5996–6007. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jaitin DA and Schreiber G: Upregulation of
a small subset of genes drives type I interferon-induced antiviral
memory. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 27:653–664. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leung RK and Whittaker PA: RNA
interference: From gene silencing to gene-specific therapeutics.
Pharmacol Ther. 107:222–239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K and
Tuschl T: Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells
using small interfering RNAs. Methods. 26:199–213. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rubinson DA, Dillon CP, Kwiatkowski AV,
Sievers C, Yang L, Kopinja J, Rooney DL, Zhang M, Ihrig MM, McManus
MT, et al: A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence genes
in primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by RNA
interference. Nat Genet. 33:401–406. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tiscornia G, Singer O and Verma IM: Design
and cloning of lentiviral vectors expressing small interfering
RNAs. Nat Protoc. 1:234–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roelz R, Pilz IH, Mutschler M and Pahl HL:
Of mice and men: Human RNA polymerase III promoter U6 is more
efficient than its murine homologue for shRNA expression from a
lentiviral vector in both human and murine progenitor cells. Exp
Hematol. 38:792–797. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miest T, Saenz D, Meehan A, Llano M and
Poeschla EM: Intensive RNAi with lentiviral vectors in mammalian
cells. Methods. 47:298–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jackson AL, Burchard J, Leake D, Reynolds
A, Schelter J, Guo J, Johnson JM, Lim L, Karpilow J, Nichols K, et
al: Position-specific chemical modification of siRNAs reduces
‘off-target’ transcript silencing. RNA. 12:1197–1205. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sledz CA, Holko M, de Veer MJ, Silverman
RH and Williams BR: Activation of the interferon system by
short-interfering RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 5:834–839. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boudreau RL, Monteys AM and Davidson BL:
Minimizing variables among hairpin-based RNAi vectors reveals the
potency of shRNAs. RNA. 14:1834–1844. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Feinbaum R: Introduction to plasmid
biology. Curr Protoc Mol Biol Chapter. 1:Unit1.5. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xia XG, Zhou H and Xu Z: Multiple shRNAs
expressed by an inducible pol II promoter can knock down the
expression of multiple target genes. Biotechniques. 41:64–68. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stove V, Smits K, Naessens E, Plum J and
Verhasselt B: Multiple gene knock-down by a single lentiviral
vector expressing an array of short hairpin RNAs. Electron J
Biotechnol. 9:572–579. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xu XM, Yoo MH, Carlson BA, Gladyshev VN
and Hatfield DL: Simultaneous knockdown of the expression of two
genes using multiple shRNAs and subsequent knock-in of their
expression. Nat Protoc. 4:1338–1348. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Root DE, Hacohen N, Hahn WC, Lander ES and
Sabatini DM: Genome-scale loss-of-function screening with a
lentiviral RNAi library. Nat Methods. 3:715–719. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song J, Giang A, Lu Y, Pang S and Chiu R:
Multiple shRNA expressing vector enhances efficiency of gene
silencing. BMB Rep. 41:358–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim SM, Lee KN, Lee SJ, Ko YJ, Lee HS,
Kweon CH, Kim HS and Park JH: Multiple shRNAs driven by U6 and CMV
promoter enhances efficiency of antiviral effects against
foot-and-mouth disease virus. Antiviral Res. 87:307–317. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|