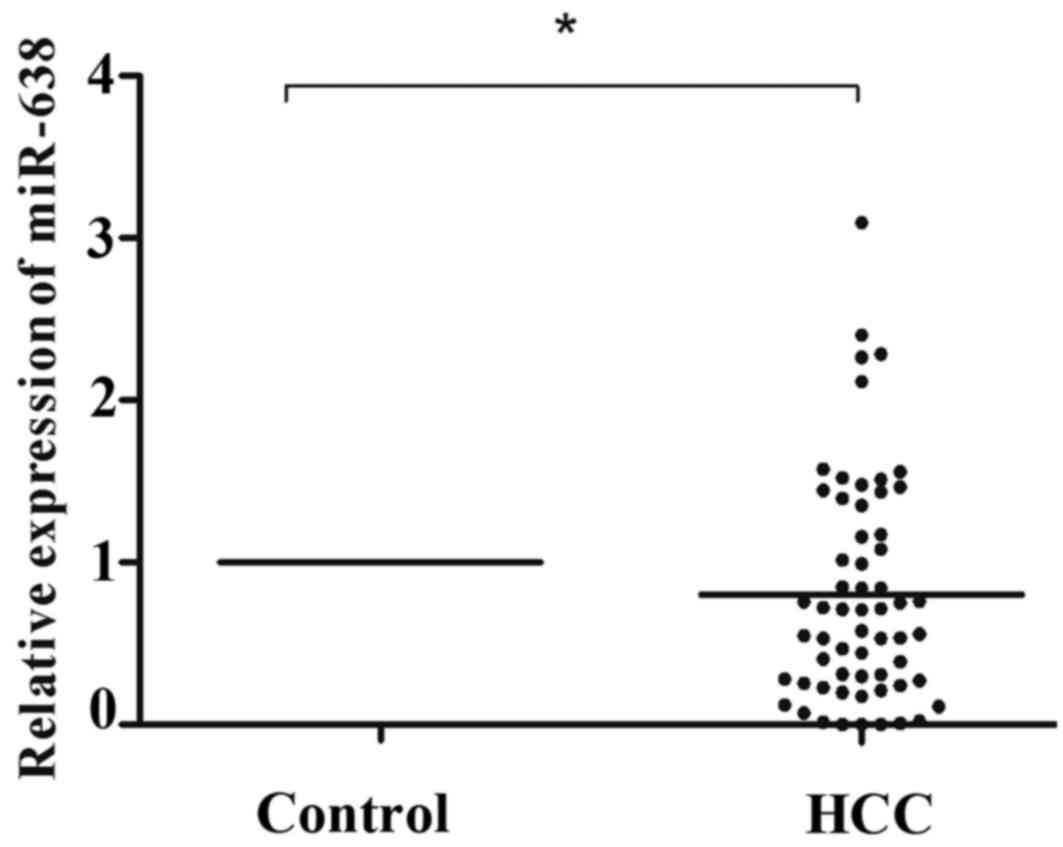
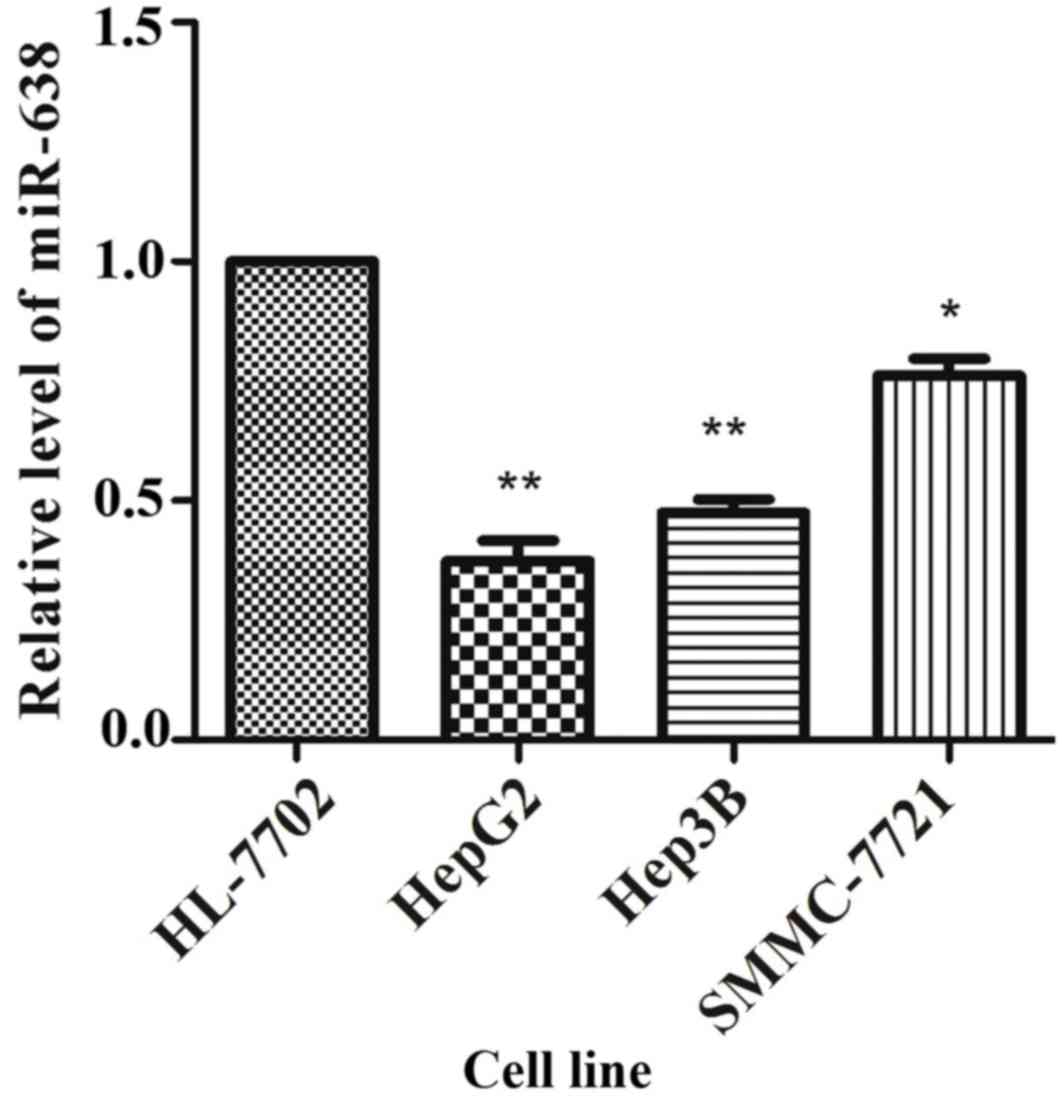
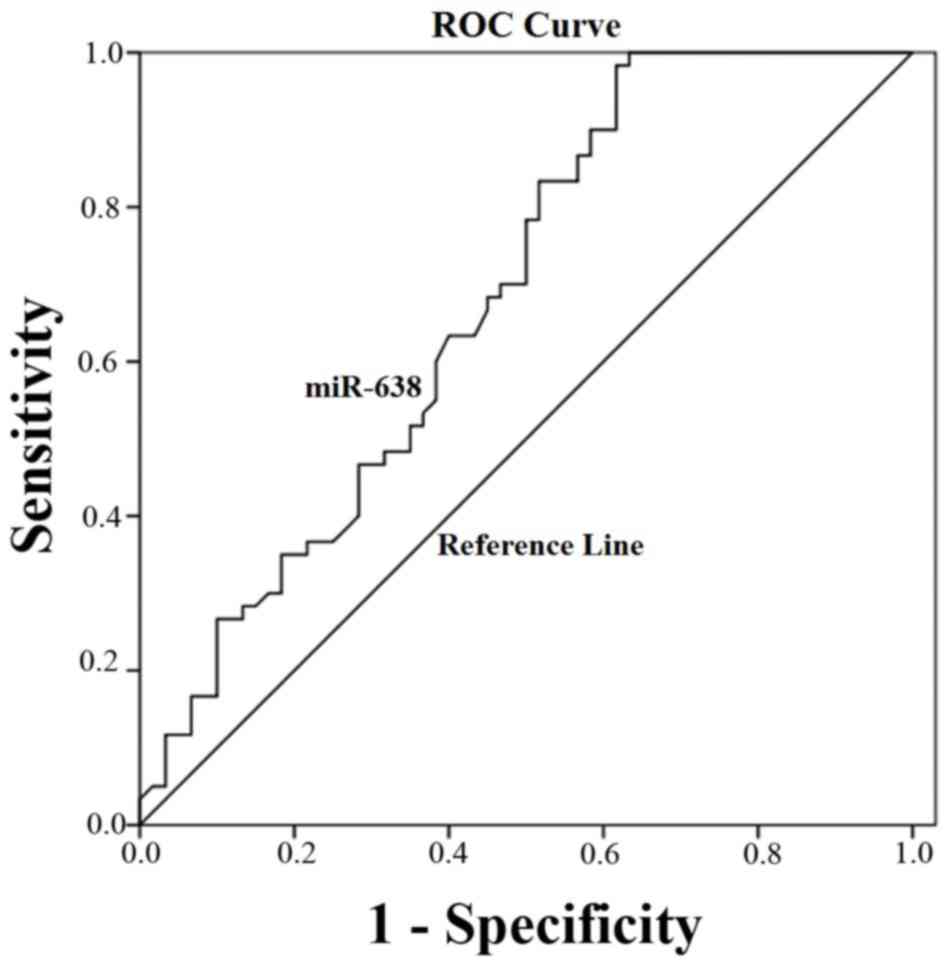
|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Pdel Monroig C,
Pasculli B and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer
diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sen R, Ghosal S, Das S, Balti S and
Chakrabarti J: Competing endogenous RNA: The key to
posttranscriptional regulation. ScientificWorldJournal.
2014:8962062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mendell JT and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao LY, Yao Y, Han J, Yang J, Wang XF,
Tong DD, Song TS, Huang C and Shao Y: miR-638 suppresses cell
proliferation in gastric cancer by targeting Sp2. Dig Dis Sci.
59:1743–1753. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan X, Peng J, Fu Y, An S, Rezaei K,
Tabbara S, Teal CB, Man YG, Brem RF and Fu SW: miR-638 mediated
regulation of BRCA1 affects DNA repair and sensitivity to UV and
cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
16:4352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Sand D, Georgas D, Hahn
SA, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P and Bechara FG: Expression of
microRNAs in basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 167:847–855.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu DX, Zhu W, Fang C, Fan L, Zou ZJ, Wang
YH, Liu P, Hong M, Miao KR, Liu P, et al: miR-181a/b significantly
enhances drug sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via
targeting multiple anti-apoptosis genes. Carcinogenesis.
33:1294–1301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin Y, Zeng Y, Zhang F, Xue L, Huang Z, Li
W and Guo M: Characterization of microRNA expression profiles and
the discovery of novel microRNAs involved in cancer during human
embryonic development. PLoS One. 8:e692302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tao ZH, Wan JL, Zeng LY, Xie L, Sun HC,
Qin LX, Wang L, Zhou J, Ren ZG, Li YX, et al: miR-612 suppresses
the invasive-metastatic cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp
Med. 210:789–803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J, Fei B, Wang Q, Song M, Yin Y,
Zhang B, Ni S, Guo W, Bian Z, Quan C, et al: MicroRNA-638 inhibits
cell proliferation, invasion and regulates cell cycle by targeting
tetraspanin 1 in human colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
5:12083–12096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xia Y, Wu Y, Liu B, Wang P and Chen Y:
Downregulation of miR-638 promotes invasion and proliferation by
regulating SOX2 and induces EMT in NSCLC. FEBS Lett. 588:2238–2245.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Wang T, Wakita T and Yang W:
Systematic identification of microRNA and messenger RNA profiles in
hepatitis C virus-infected human hepatoma cells. Virology.
398:57–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lytle JR, Yario TA and Steitz JA: Target
mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the
5′UTR as in the 3′UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9667–9672. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peiró-Chova L, Peña-Chilet M,
López-Guerrero JA, García-Giménez JL, Alonso-Yuste E, Burgues O,
Lluch A, Ferrer-Lozano J and Ribas G: High stability of microRNAs
in tissue samples of compromised quality. Virchows Arch.
463:765–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Chen J, Radcliffe T, Lebrun DP,
Tron VA and Feilotter H: An array-based analysis of microRNA
expression comparing matched frozen and formalin-fixed
paraffin-embedded human tissue samples. J Mol Diagn. 10:513–519.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Siebolts U, Varnholt H, Drebber U, Dienes
HP, Wickenhauser C and Odenthal M: Tissues from routine pathology
archives are suitable for microRNA analyses by quantitative PCR. J
Clin Pathol. 62:84–88. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu CG, Calin GA, Volinia S and Croce CM:
MicroRNA expression profiling using microarrays. Nat Protoc.
3:563–578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Benes V and Castoldi M: Expression
profiling of microRNA using real-time quantitative PCR, how to use
it and what is available. Methods. 50:244–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin W, Grant J, Stothard P, Moore SS and
Guan LL: Characterization of bovine miRNAs by sequencing and
bioinformatics analysis. BMC Mol Biol. 10:902009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sempere LF and Korc M: A method for
conducting highly sensitive microRNA in situ hybridization and
immunohistochemical analysis in pancreatic cancer. Methods Mol
Biol. 980:43–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, Van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: Mirbase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36:D154–D158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parasramka MA, Ali S, Banerjee S,
Deryavoush T, Sarkar FH and Gupta S: Garcinol sensitizes human
pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to gemcitabine in association with
microRNA signatures. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:235–248. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu N, Cui RX, Sun Y, Guo R, Mao YP, Tang
LL, Jiang W, Liu X, Cheng YK, He QM, et al: A four-miRNA signature
identified from genome-wide serum miRNA profiling predicts survival
in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
134:1359–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang X, Tan J, Li J, Kivimäe S, Yang X,
Zhuang L, Lee PL, Chan MT, Stanton LW, Liu ET, et al: DACT3 is an
epigenetic regulator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colorectal
cancer and is a therapeutic target of histone modifications. Cancer
Cell. 13:529–541. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murphy NC, Biankin AV, Millar EK, McNeil
CM, O'Toole SA, Segara D, Crea P, Olayioye MA, Lee CS, Fox SB, et
al: Loss of STARD10 expression identifies a group of poor prognosis
breast cancers independent of HER2/Neu and triple negative status.
Int J Cancer. 126:1445–1453. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lan J, Guo P, Lin Y, Mao Q, Guo L, Ge J,
Li X, Jiang J, Lin X and Qiu Y: Role of glycosyltransferase PomGnT1
in glioblastoma progression. Neuro Oncol. 17:211–222. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim TO, Park J, Kang MJ, Lee SH, Jee SR,
Ryu DY, Yang K and Yi JM: DNA hypermethylation of a selective gene
panel as a risk marker for colon cancer in patients with ulcerative
colitis. Int J Mol Med. 31:1255–1261. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hahn S and Hermeking H: ZNF281/ZBP-99: A
new player in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness, and
cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 92:571–581. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I,
Pinzani M and Bosch J: Angiogenesis in liver disease. J Hepatol.
50:604–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sampat KR and O'Neil B: Antiangiogenic
therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist.
18:430–438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|