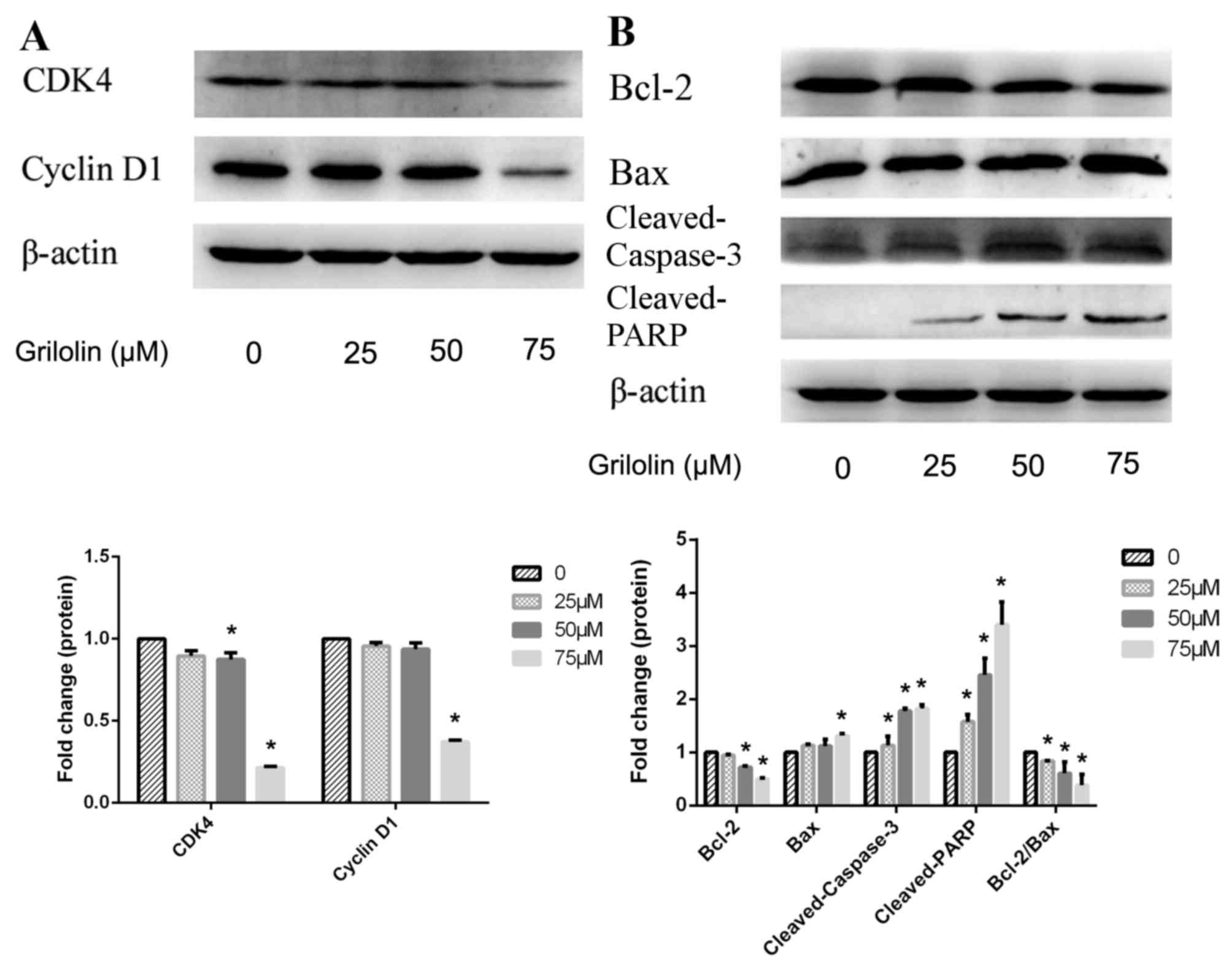
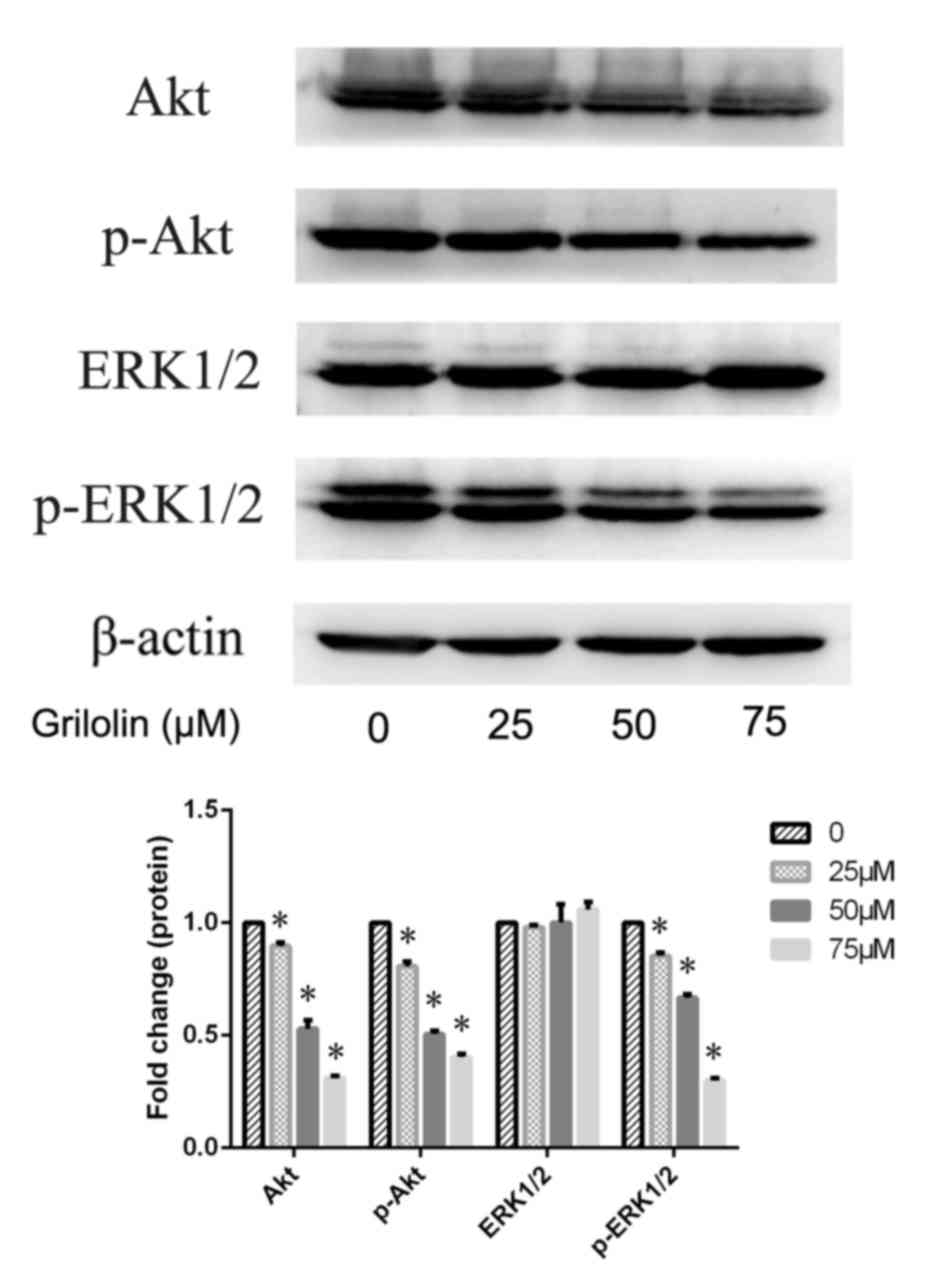
|
1
|
Gloss BS and Samimi G: Epigenetic
biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 342:257–263.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen C, Chang YC, Lan MS and Breslin M:
Leptin stimulates ovarian cancer cell growth and inhibits apoptosis
by increasing cyclin D1 and Mcl-1 expression via the activation of
the MEK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
42:1113–1119. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo X, Yu X, Liu S, Deng Q, Liu X, Peng S,
Li H, Liu J and Cao Y: The role of targeting kinase activity by
natural products in cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy
(review). Oncol Rep. 34:547–554. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ye M, Luo X, Li L, Shi Y, Tan M, Weng X,
Li W, Liu J and Cao Y: Grifolin, a potential antitumor natural
product from the mushroom Albatrellus confluens, induces cell-cycle
arrest in G1 phase via the ERK1/2 pathway. Cancer Lett.
258:199–207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin S, Pang RP, Shen JN, Huang G, Wang J
and Zhou JG: Grifolin induces apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/AKT
signalling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Apoptosis.
12:1317–1326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hilakivi-Clarke L, Wang C, Kalil M,
Riggins R and Pestell RG: Nutritional modulation of the cell cycle
and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 11:603–622. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hall M and Peters G: Genetic alterations
of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and Cdk inhibitors in human
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 68:67–108. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaukoniemi KM, Rauhala HE, Scaravilli M,
Latonen L, Annala M, Vessella RL, Nykter M, Tammela TL and
Visakorpi T: Epigenetically altered miR-193b targets cyclin D1 in
prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 4:1417–1425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Denault JB and Boatright K: Apoptosis in
biochemistry and structural biology. 3–8 February 2004, Keystone,
CO, USA. IDrugs. 7:315–317. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gupta S, Kass GE, Szegezdi E and Joseph B:
The mitochondrial death pathway: A promising therapeutic target in
diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1004–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA
Jr, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I and Flavell RA: Caspases 3 and 7:
Key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science.
311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Langelier MF and Pascal JM: PARP-1
mechanism for coupling DNA damage detection to poly(ADP-ribose)
synthesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 23:134–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sukhanova MV, Khodyreva SN and Lavrik OI:
Influence of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and its apoptotic 24-kD
fragment on repair of DNA duplexes in bovine testis nuclear
extract. Biochemistry (Mosc). 71:736–748. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Monian P and Jiang X: Clearing the final
hurdles to mitochondrial apoptosis: Regulation post cytochrome C
release. Exp Oncol. 34:185–191. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martinou JC and Youle RJ: Mitochondria in
apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev
Cell. 21:92–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cotter TG: Apoptosis and cancer: The
genesis of a research field. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:501–507. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Antonsson B: Bax and other pro-apoptotic
Bcl-2 family ‘killer-proteins’ and their victim the mitochondrion.
Cell Tissue Res. 306:347–361. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF and
Carnero A: PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis.
28:1379–1386. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fingar DC, Salama S, Tsou C, Harlow E and
Blenis J: Mammalian cell size is controlled by mTOR and its
downstream targets S6K1 and 4EBP1/elF4E. Genes Dev. 16:1472–1487.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Serrano ML, Sánchez-Gómez M, Bravo MM,
Yakar S and LeRoith D: Differential expression of IGF-I and insulin
receptor isoforms in HPV positive and negative human cervical
cancer cell lines. Horm Metab Res. 40:661–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Diab S, Kumarasiri M, Yu M, Teo T, Proud
C, Milne R and Wang S: MAP kinase-interacting kinases-emerging
targets against cancer. Chem Biol. 21:441–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|