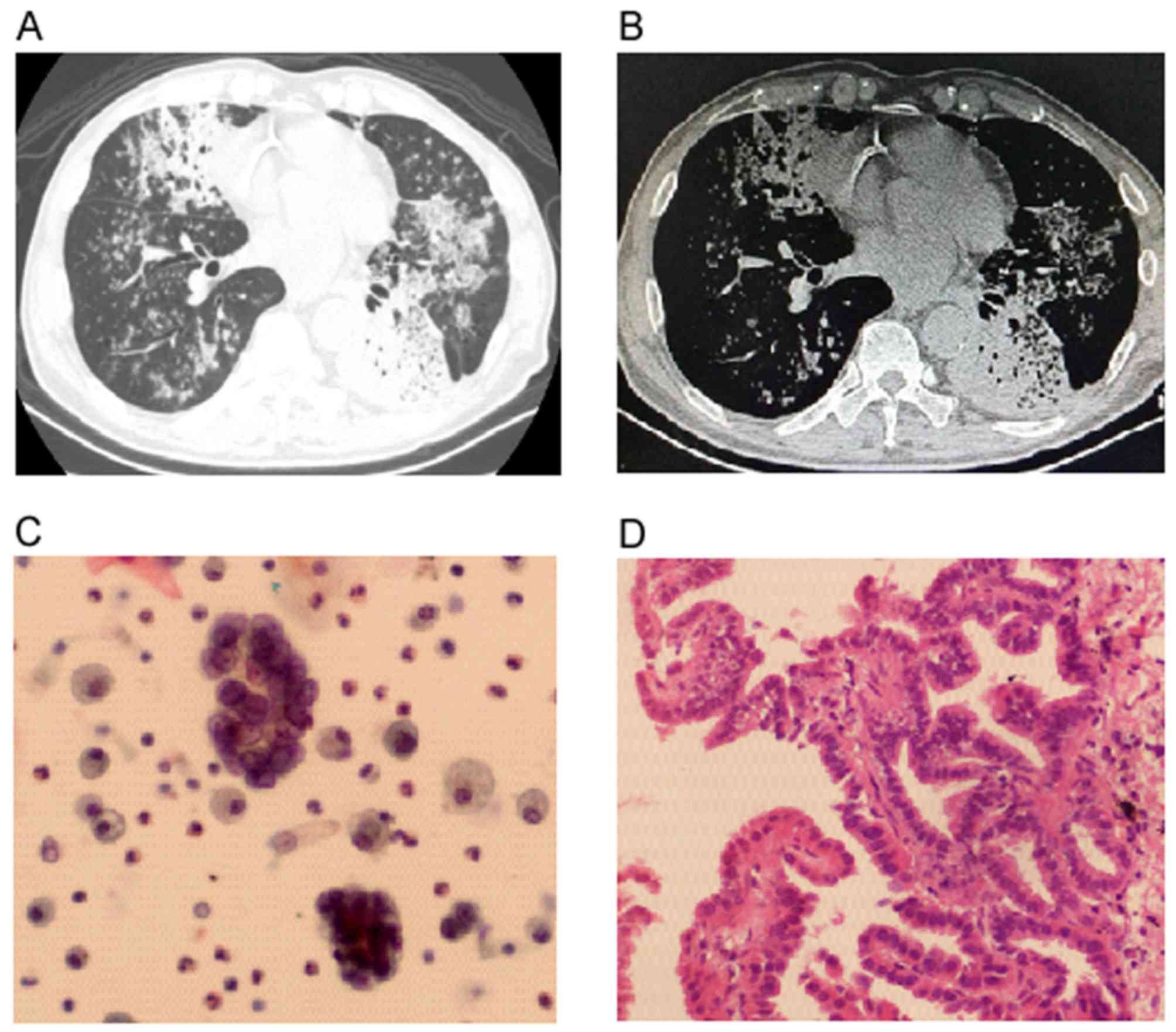
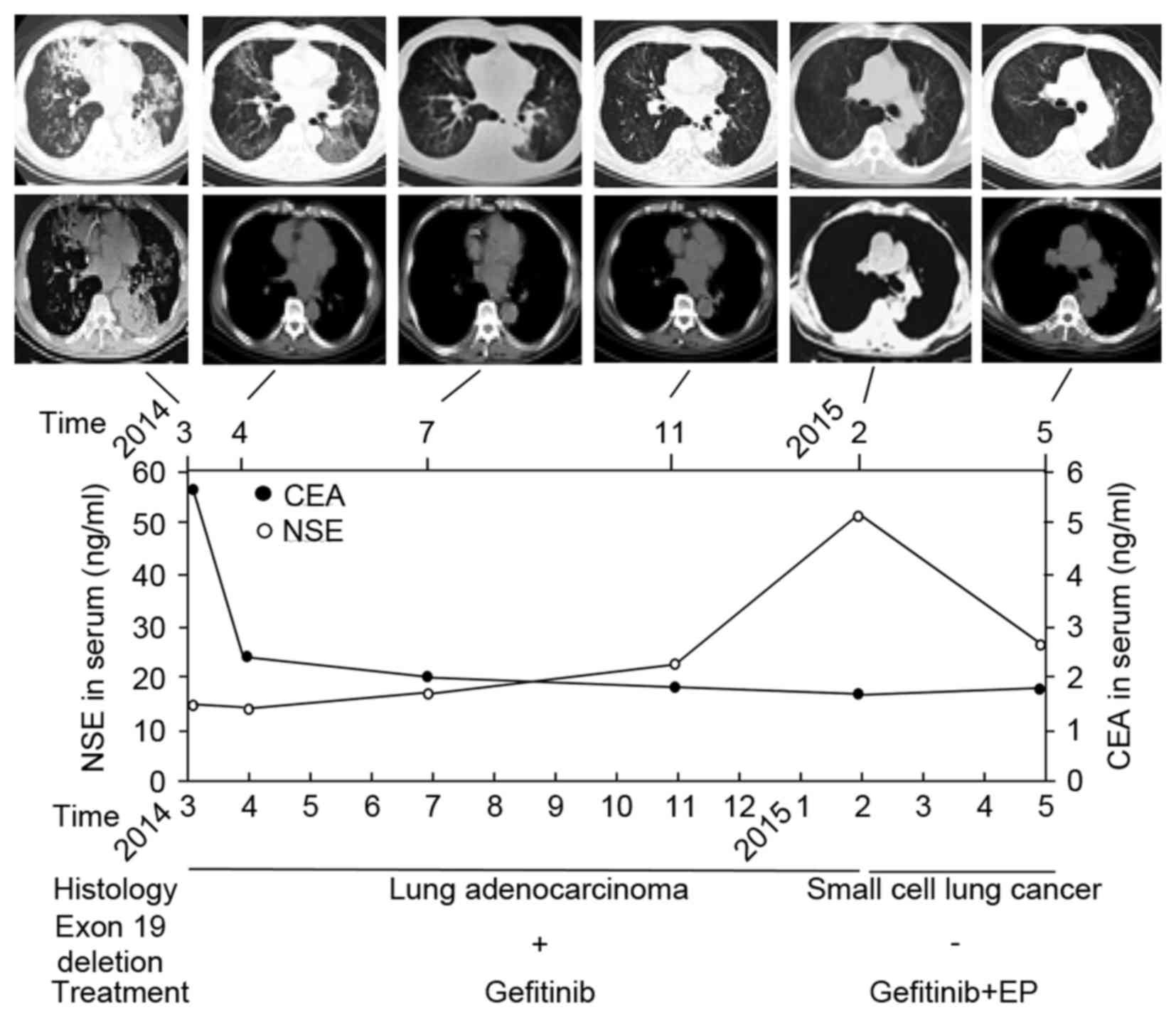
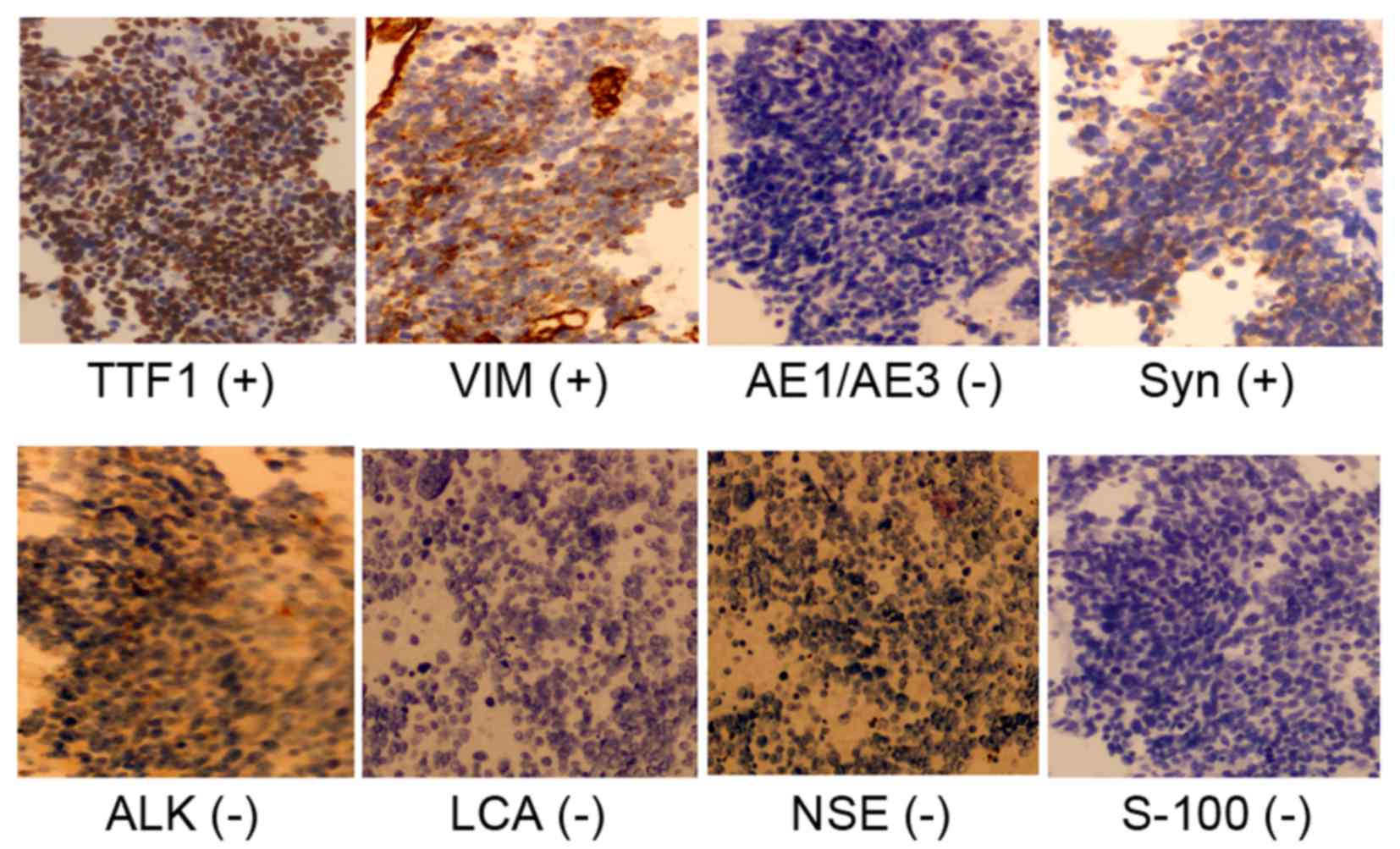
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wakelee H and Belani CP: Optimizing
first-line treatment options for patients with advanced NSCLC.
Oncologist. 10 Suppl 3:S1–S10. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu JY, Wu SG, Yang CH, Chang YL, Chang YC,
Hsu YC, Shih JY and Yang PC: Comparison of gefitinib and erlotinib
in advanced NSCLC and the effect of EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer.
72:205–212. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu M, Xie Y, Ni S and Liu H: The latest
therapeutic strategies after resistance to first generation
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR
TKIs) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann
Transl Med. 3:962015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Camidge DR, Pao W and Sequist LV: Acquired
resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: Learning from lung cancer. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 11:473–481. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li W, Ren S, Li J, Li A, Fan L, Li X, Zhao
C, He Y, Gao G, Chen X, et al: T790M mutation is associated with
better efficacy of treatment beyond progression with EGFR-TKI in
advanced NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer. 84:295–300. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brugger W and Thomas M: EGFR-TKI resistant
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): New developments and
implications for future treatment. Lung Cancer. 77:2–8. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cretella D, Saccani F, Quaini F, Frati C,
Lagrasta C, Bonelli M, Caffarra C, Cavazzoni A, Fumarola C, Galetti
M, et al: Trastuzumab emtansine is active on HER-2 overexpressing
NSCLC cell lines and overcomes gefitinib resistance. Mol Cancer.
13:1432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin Y, Wang X and Jin H: EGFR-TKI
resistance in NSCLC patients: Mechanisms and strategies. Am J
Cancer Res. 4:411–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Yang Z, Li W, Xu S, Wang T, Wang T,
Niu M, Zhang S, Jia L and Li S: TOPK promotes lung cancer
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors by phosphorylating
and activating c-Jun. Oncotarget. 7:6748–6764. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rudisch A, Dewhurst MR, Horga LG, Kramer
N, Harrer N, Dong M, van der Kuip H, Wernitznig A, Bernthaler A,
Dolznig H and Sommergruber W: High EMT signature score of invasive
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells correlates with NFκB
driven colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2/GM-CSF) secretion by
neighboring stromal fibroblasts. PLoS One. 10:e01242832015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang SY, Zhao J, Wang MZ, Huo Z, Zhang J,
Zhong W and Xu Y: Small-cell lung cancer transformation in patients
with pulmonary adenocarcinoma: A case report and review of
literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e27522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watanabe S, Sone T, Matsui T, Yamamura K,
Tani M, Okazaki A, Kurokawa K, Tambo Y, Takato H, Ohkura N, et al:
Transformation to small-cell lung cancer following treatment with
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a patient with lung
adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 82:370–372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oser MG, Niederst MJ, Sequist LV and
Engelman JA: Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to
small-cell lung cancer: Molecular drivers and cells of origin.
Lancet Oncol. 16:e165–e172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS,
Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M and Riely GJ:
Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to
EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:2240–2247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu SG, Liu YN, Tsai MF, Chang YL, Yu CJ,
Yang PC, Yang JC, Wen YF and Shih JY: The mechanism of acquired
resistance to irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-afatinib
in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 7:12404–12413.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
de Bruin EC, McGranahan N, Mitter R, Salm
M, Wedge DC, Yates L, Jamal-Hanjani M, Shafi S, Murugaesu N, Rowan
AJ, et al: Spatial and temporal diversity in genomic instability
processes defines lung cancer evolution. Science. 346:251–256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGranahan N, Favero F, De Bruin EC,
Birkbak NJ, Szallasi Z and Swanton C: Clonal status of actionable
driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer
evolution. Sci Transl Med. 7:283ra542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Fujimoto J, Zhang J, Wedge DC,
Song X, Zhang J, Seth S, Chow CW, Cao Y, Gumbs C, et al: Intratumor
heterogeneity in localized lung adenocarcinomas delineated by
multiregion sequencing. Science. 346:256–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uramoto H, Yamada S and Hanagiri T:
Clinicopathological characteristics of resected adenosquamous cell
carcinoma of the lung: Risk of coexistent double cancer. J
Cardiothorac Surg. 5:922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adelstein DJ, Tomashefski JF Jr, Snow NJ,
Horrigan TP and Hines JD: Mixed small cell and non-small cell lung
cancer. Chest. 89:699–704. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mangum MD, Greco FA, Hainsworth JD, Hande
KR and Johnson DH: Combined small-cell and non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 7:607–612. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim WJ, Kim S, Choi H, Chang J, Shin HJ,
Park CK, Oh IJ, Kim KS, Kim YC and Choi YD: Histological
transformation from non-small cell to small cell lung carcinoma
after treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine
kinase inhibitor. Thorac Cancer. 6:800–804. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Poirier JT,
Mermel CH, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, Katayama R, Costa C, Ross KN,
Moran T, et al: RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung
adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat
Commun. 6:63772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang Y, Kim SY, Choi YJ, So KS, Rho JK,
Kim WS, Lee JC, Chung JH and Choi CM: Neuroendocrine
differentiation in acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul).
75:95–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Li XY, Tang Y, Xu Y, Guo WH, Li
YC, Liu XK, Huang CY, Wang YS and Wei YQ: Rapid increase of serum
neuron specific enolase level and tachyphylaxis of EGFR-tyrosine
kinase inhibitor indicate small cell lung cancer transformation
from EGFR positive lung adenocarcinoma? Lung Cancer. 81:302–305.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hwang KE, Jung JW, Oh SJ, Park MJ, Shon
YJ, Choi KH, Jeong ET and Kim HR: Transformation to small cell lung
cancer as an acquired resistance mechanism in EGFR-mutant lung
adenocarcinoma: A case report of complete response to etoposide and
cisplatin. Tumori. 101:e96–e98. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Molenaar WM, Oosterhuis JW, Oosterhuis AM
and Ramaekers FC: Mesenchymal and muscle-specific intermediate
filaments (vimentin and desmin) in relation to differentiation in
childhood rhabdomyosarcomas. Hum Pathol. 16:838–843. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kidd ME, Shumaker DK and Ridge KM: The
role of vimentin intermediate filaments in the progression of lung
cancer. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:1–6. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Donnem T, Persson
M, Bremnes RM and Busund LT: The prognostic impact of NF-kappaB
p105, vimentin, E-cadherin and Par6 expression in epithelial and
stromal compartment in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer.
99:1476–1483. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tadokoro A, Kanaji N, Liu D, Yokomise H,
Haba R, Ishii T, Takagi T, Watanabe N, Kita N, Kadowaki N and
Bandoh S: Vimentin regulates invasiveness and is a poor prognostic
marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 36:1545–1551.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu CY, Lin HH, Tang MJ and Wang YK:
Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer
cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal
adhesion maturation. Oncotarget. 6:15966–15983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan Y and Li X, Duan J, Yuan L, Fan S, Fan
J, Xiaokaiti Y, Yang H, Wang Y and Li X: Enoxaparin sensitizes
human non-small-cell lung carcinomas to gefitinib by inhibiting
DOCK1 expression, vimentin phosphorylation and Akt activation. Mol
Pharmacol. 87:378–390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lahat G, Zhu QS, Huang KL, Wang S,
Bolshakov S, Liu J, Torres K, Langley RR, Lazar AJ, Hung MC and Lev
D: Vimentin is a novel anti-cancer therapeutic target; insights
from in vitro and in vivo mice xenograft studies. PLoS One.
5:e101052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Richardson F, Young GD, Sennello R, Wolf
J, Argast GM, Mercado P, Davies A, Epstein DM and Wacker B: The
evaluation of E-Cadherin and vimentin as biomarkers of clinical
outcomes among patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated
with erlotinib as second- or third-line therapy. Anticancer Res.
32:537–552. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|